A Border Shaped by History: Tracing the Franco-German Divide
Related Articles: A Border Shaped by History: Tracing the Franco-German Divide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Border Shaped by History: Tracing the Franco-German Divide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Border Shaped by History: Tracing the Franco-German Divide
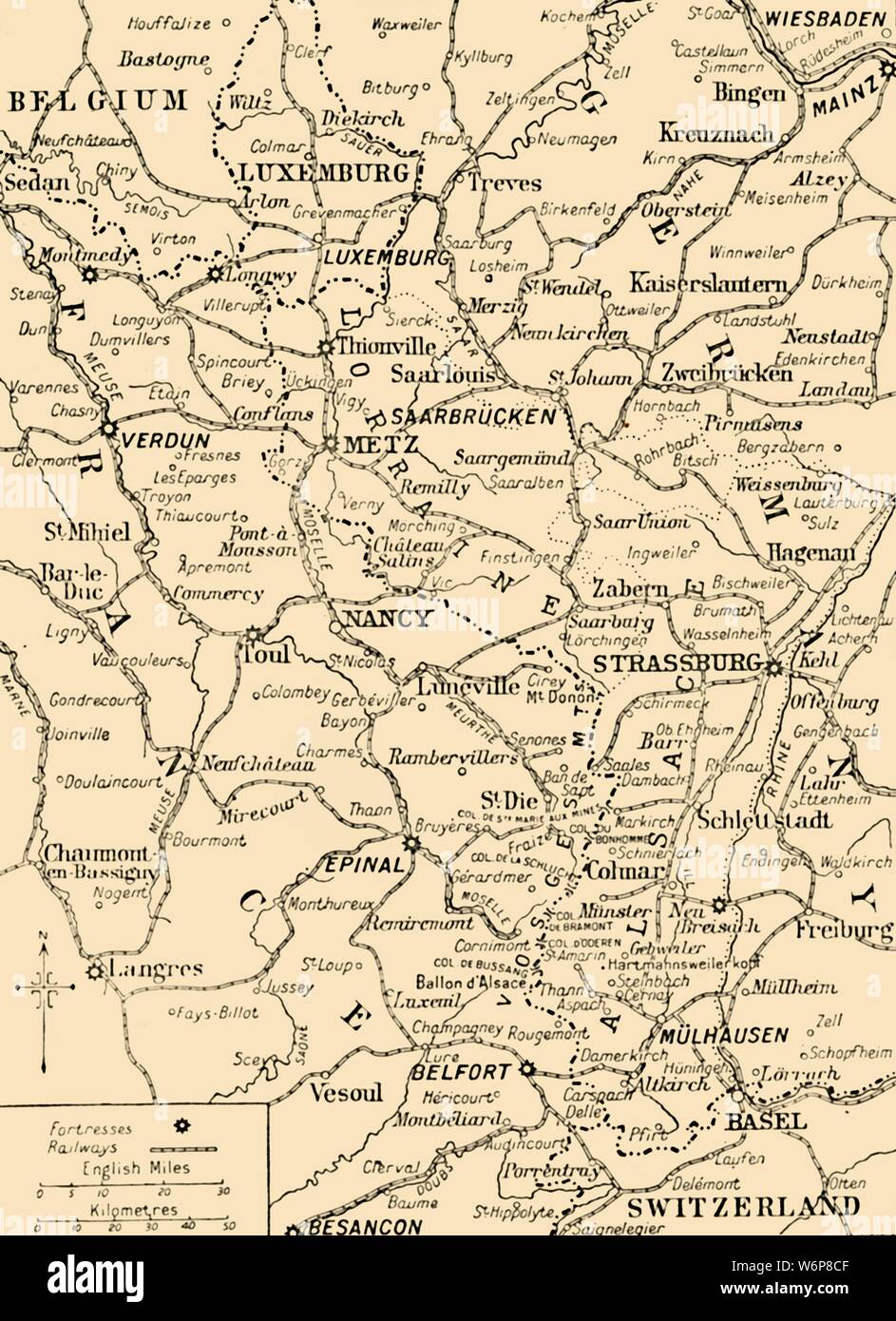
The border between France and Germany, a line etched across the landscape of Europe, is more than just a geographical boundary. It is a tapestry woven with threads of history, conflict, and cooperation, reflecting the complex relationship between these two powerful nations. Understanding this border’s evolution, its impact on the surrounding regions, and its significance in the broader European context is crucial for appreciating the multifaceted dynamics of the modern world.
A Shifting Landscape: From Ancient Times to the Treaty of Versailles
The Franco-German border has seen a dynamic evolution over centuries. Its origins can be traced back to the Roman Empire, with the Rhine River serving as a natural barrier between Gaul (present-day France) and Germania. The Frankish Empire, encompassing both territories, further blurred the lines during the Middle Ages. However, with the emergence of separate kingdoms, the border began to solidify, marked by constant skirmishes and territorial disputes.
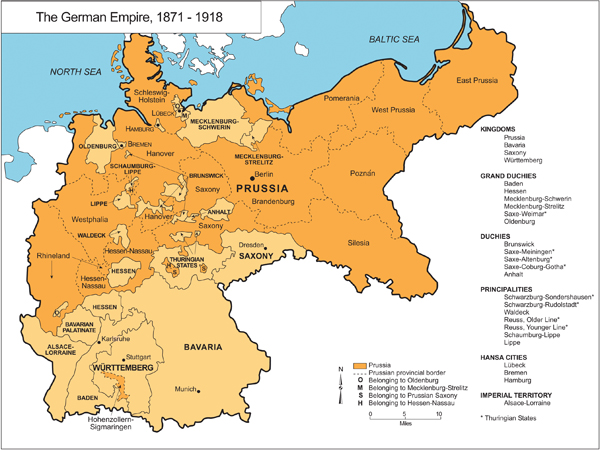
The Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453) witnessed a fierce struggle for control of French territories, solidifying the border’s importance. The subsequent centuries saw further territorial adjustments, with France expanding eastward during the reign of Louis XIV and Germany consolidating its power under Prussia. The Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71 marked a turning point, resulting in the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine by Germany, a region that would become a focal point of future conflicts.
The Treaty of Versailles, signed after World War I, aimed to redraw the border and punish Germany for its aggression. Alsace-Lorraine was returned to France, and Germany was forced to cede territory in the west, creating a new border that was seen as a guarantee of French security. However, this punitive approach sowed the seeds of resentment in Germany, ultimately contributing to the rise of Nazi Germany and the outbreak of World War II.
Post-War Reconciliation and European Integration
The aftermath of World War II witnessed a dramatic shift in the Franco-German relationship. The creation of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) in 1951, followed by the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1957, marked a new era of cooperation and economic integration. This process, driven by the desire for peace and prosperity, facilitated the gradual dismantling of border barriers and fostered a sense of shared destiny.
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the subsequent reunification of Germany in 1990 further reshaped the geopolitical landscape. The Franco-German border lost its military significance, evolving into a symbol of cooperation and reconciliation. The creation of the Eurozone in 1999 and the expansion of the European Union have further reinforced the interconnectedness between the two nations.
A Border of Interdependence: Economic and Cultural Exchange
The Franco-German border is no longer defined by conflict but by a thriving network of economic and cultural exchange. The region is home to numerous industrial centers, research institutions, and cultural hubs, fostering collaboration across national boundaries. The border itself has become a catalyst for innovation and economic growth, with businesses leveraging their proximity to tap into each other’s markets and expertise.
The border region also boasts a rich cultural heritage, with shared traditions, languages, and historical narratives. This cultural intermingling is evident in the numerous cross-border events, festivals, and artistic collaborations, fostering a sense of shared identity and mutual understanding.
A Border of Challenges: Regional Disparities and Environmental Concerns
Despite the progress made in fostering cooperation, the Franco-German border still faces challenges. Regional disparities persist, with pockets of economic hardship and unemployment in both countries. The border region, often characterized by rural areas and agricultural communities, can be particularly susceptible to economic downturns and the changing dynamics of global markets.
Environmental concerns also play a significant role in shaping the border’s future. Issues like air pollution, water management, and biodiversity preservation require coordinated efforts from both countries. The shared challenges posed by climate change further necessitate close collaboration and joint action.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the Franco-German Border
Q: What are the main cities located on the Franco-German border?
A: Some of the key cities located on the Franco-German border include Strasbourg, Mulhouse, Freiburg im Breisgau, and Saarbrücken. These cities serve as centers of economic activity, cultural exchange, and cross-border cooperation.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in the border region?
A: The dominant languages spoken in the border region are French and German. However, regional dialects and minority languages, such as Alsatian and Lorraine Franconian, are also prevalent, reflecting the linguistic diversity of the area.
Q: What are the major industries and economic activities in the border region?
A: The border region is home to a diverse range of industries, including automotive manufacturing, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and tourism. The presence of research institutions and universities also contributes to the region’s economic dynamism.
Q: What are the main environmental challenges facing the border region?
A: The border region faces environmental challenges such as air pollution from industrial activity, water pollution from agricultural runoff, and the loss of biodiversity. Climate change poses a growing threat, requiring coordinated efforts to mitigate its impact.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating the Franco-German Border:
- Travel to the border region: Experience the unique cultural blend and historical sites firsthand.
- Learn about the region’s history: Delve into the stories of conflict, cooperation, and cultural exchange.
- Engage with local communities: Connect with people on both sides of the border to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives.
- Follow the work of cross-border organizations: Stay informed about initiatives promoting cooperation and addressing shared challenges.
Conclusion: A Border of Hope and Opportunity
The Franco-German border, once a symbol of division and conflict, has evolved into a testament to the power of reconciliation and cooperation. The shared history, cultural heritage, and economic interdependence between France and Germany have created a dynamic and complex landscape, offering both challenges and opportunities. As the two nations continue to work together within the framework of the European Union, the border serves as a reminder of the enduring importance of dialogue, understanding, and shared responsibility in building a peaceful and prosperous future for Europe.

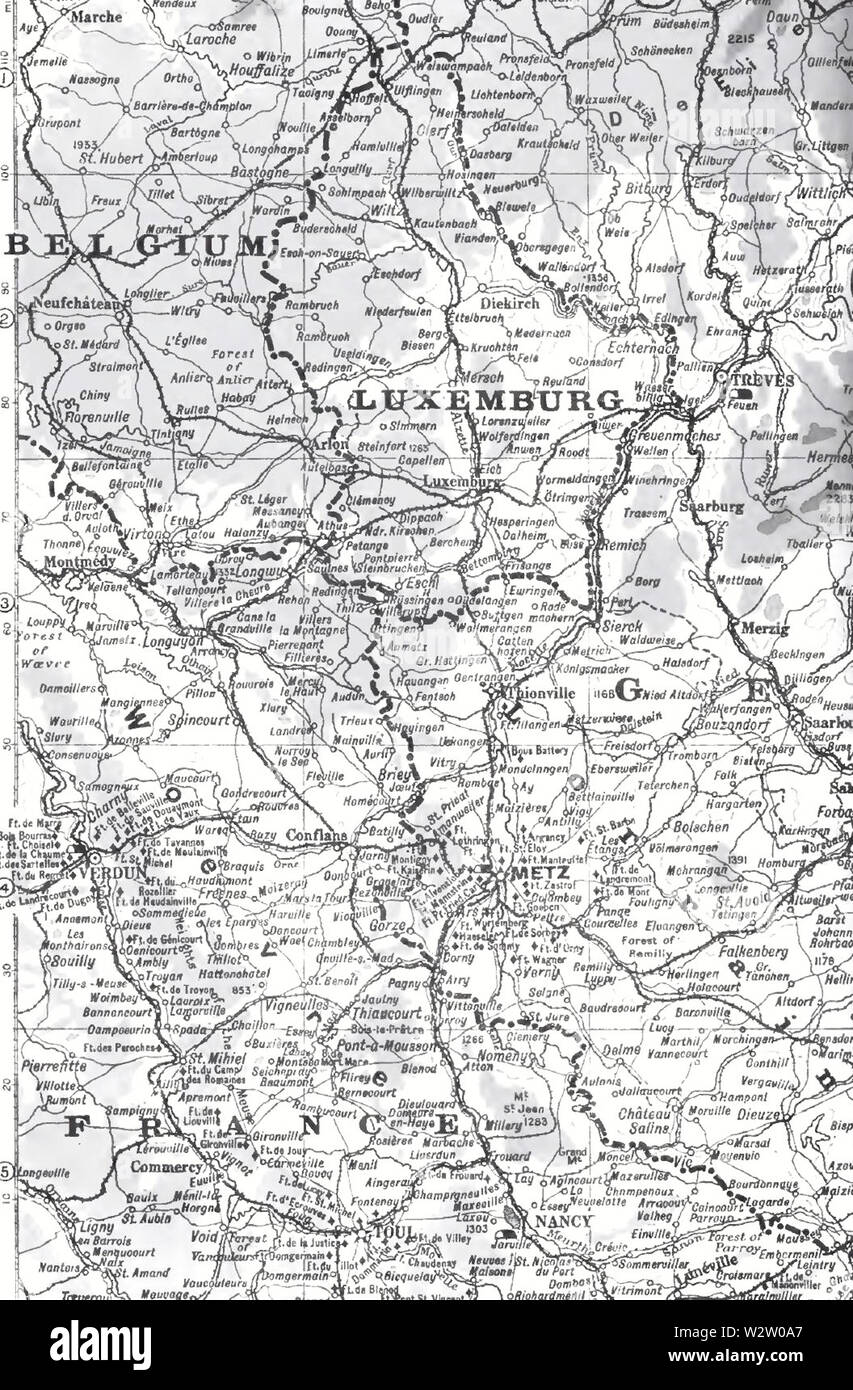
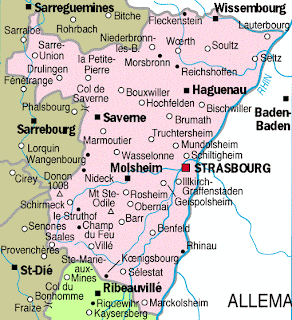

![Franco-German border (circa 1900) [what if France won the Franco-Prussian war] this is my first](https://preview.redd.it/empt449tbwl71.png?auto=webpu0026s=8673878d9b37be2de3d4b4b27d125dd84fdde135)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Border Shaped by History: Tracing the Franco-German Divide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!