A Comparative Geography of Finland and Sweden: Exploring the Shared and Distinct Landscapes of the Nordic Region
Related Articles: A Comparative Geography of Finland and Sweden: Exploring the Shared and Distinct Landscapes of the Nordic Region
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Geography of Finland and Sweden: Exploring the Shared and Distinct Landscapes of the Nordic Region. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Geography of Finland and Sweden: Exploring the Shared and Distinct Landscapes of the Nordic Region
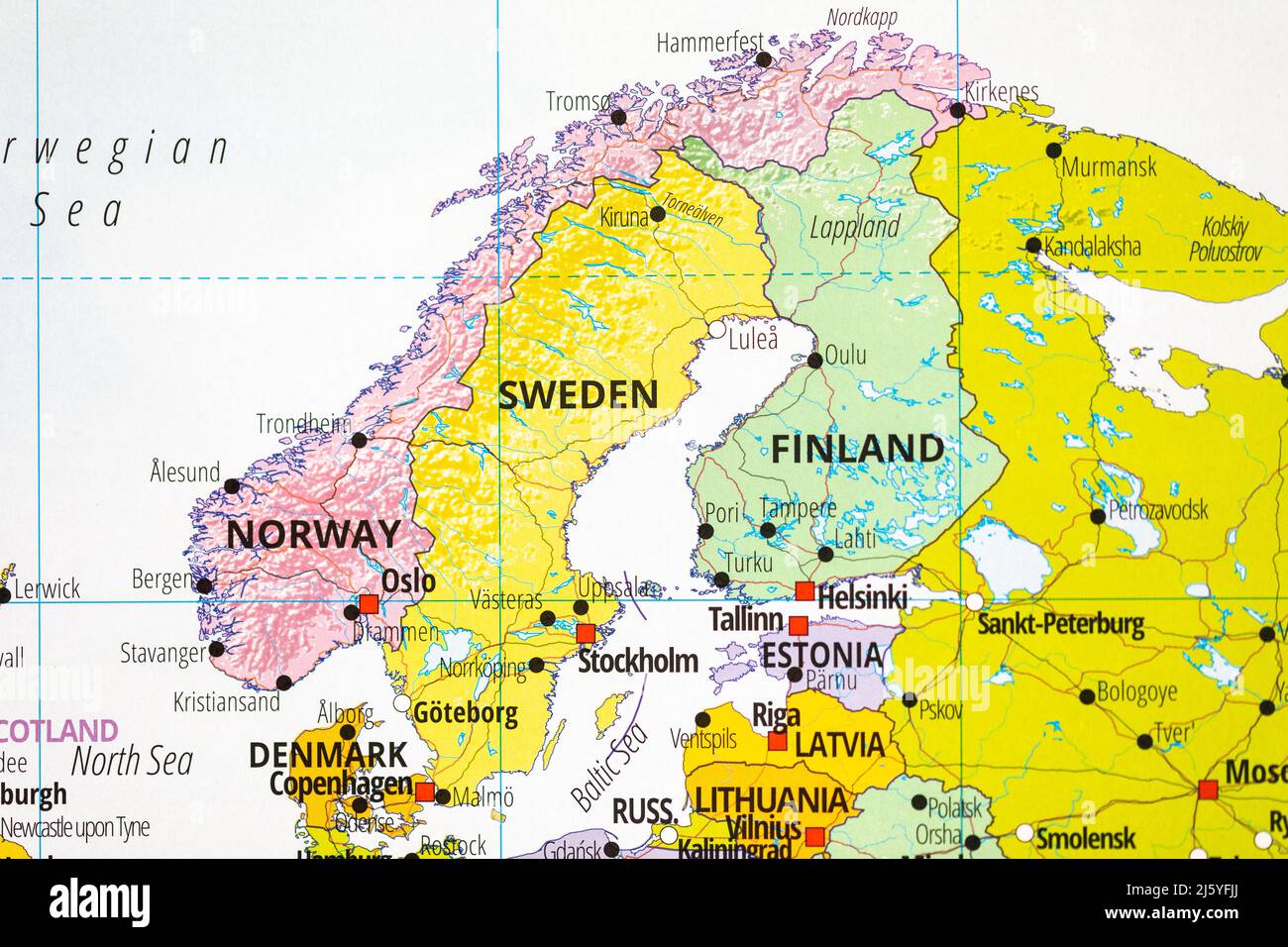
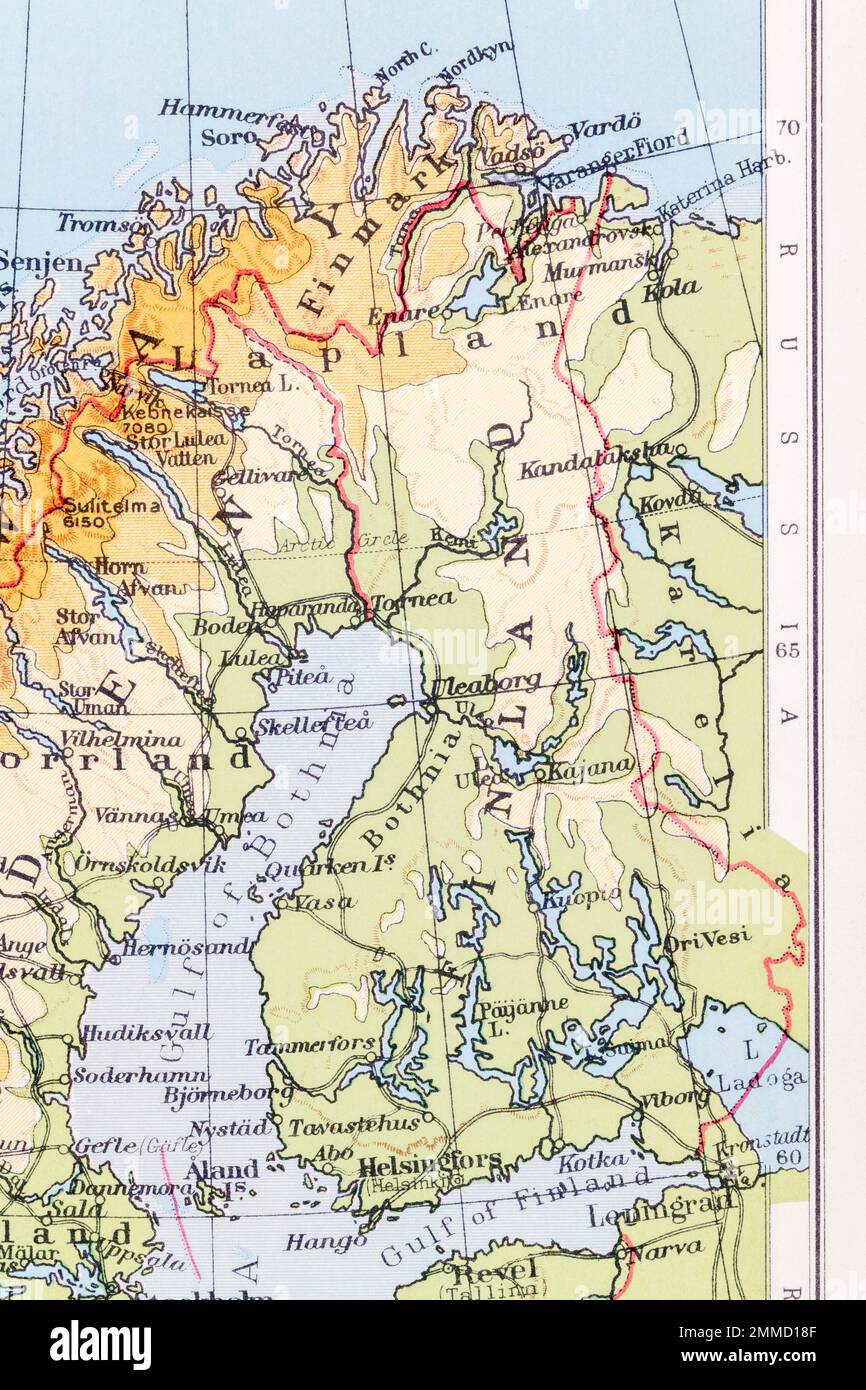
The Scandinavian Peninsula, a rugged and captivating landmass stretching across northern Europe, houses two prominent nations: Finland and Sweden. While sharing a common historical and cultural heritage, these countries exhibit unique geographical features and landscapes that contribute to their distinct identities. This exploration delves into the complexities of their geography, examining the similarities and differences that shape their respective environments, economies, and societies.
Similarities in Landscape:
Both Finland and Sweden are characterized by a predominantly northern latitude, resulting in a shared climate dominated by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The presence of vast, boreal forests, known as taiga, dominates both landscapes, providing a significant source of timber and natural beauty. Additionally, both countries boast extensive coastlines along the Baltic Sea, offering access to maritime trade and recreational activities.
Distinct Geographical Features:
Despite these similarities, Finland and Sweden exhibit notable differences in their terrain and geographical features.
Finland:
-
Lake District: Finland is renowned for its extensive lake district, encompassing thousands of interconnected lakes that cover approximately 10% of the country’s landmass. This unique feature, shaped by glacial activity, creates a distinctive landscape dotted with islands, peninsulas, and vast waterways. The largest lake, Lake Saimaa, is the fourth largest in Europe and is home to the Saimaa ringed seal, an endangered species.
-
Low-Lying Terrain: Finland’s terrain is generally low-lying, with an average elevation of only 87 meters above sea level. This low altitude contributes to a relatively flat landscape, punctuated by rolling hills and forested areas.
-
Archipelago: Finland’s coastline is characterized by a vast archipelago of over 40,000 islands, particularly in the southwest. This archipelago offers scenic beauty and provides opportunities for fishing, boating, and tourism.
Sweden:
-
Mountain Ranges: In contrast to Finland, Sweden boasts a more mountainous landscape, with the Scandinavian Mountains running along its western border. These mountains, reaching heights of over 2,000 meters, provide stunning vistas and opportunities for skiing, hiking, and other outdoor activities.
-
Diverse Topography: Sweden’s topography is more diverse, featuring not only mountains but also vast plains, rolling hills, and coastal lowlands. The country’s southern region is relatively flat, while the north is dominated by the vast, sparsely populated Lapland region.
-
Coastal Diversity: Sweden’s coastline is more varied than Finland’s, with long stretches of sandy beaches, rocky shores, and numerous inlets and bays. The country’s western coast is known for its dramatic fjords, deep, narrow inlets carved by glaciers.
The Importance of Geography:
The geographical features of Finland and Sweden have profoundly shaped their histories, economies, and cultures.
Economic Impact:
-
Forestry and Natural Resources: Both countries heavily rely on their abundant forests for timber production, a key economic driver. The vast forests also provide a source of pulp and paper, contributing significantly to their respective economies.
-
Hydropower: The abundance of rivers and lakes in both countries has facilitated the development of hydropower, providing a sustainable source of energy.
-
Tourism: The unique landscapes, from the Finnish lake district to the Swedish mountains, attract tourists from around the world, generating revenue and supporting local economies.
Cultural Influence:
-
Nature-Oriented Culture: The prevalence of forests, lakes, and mountains has instilled a deep appreciation for nature in both cultures. This connection to the natural world is reflected in their art, literature, and way of life.
-
Outdoor Recreation: The abundance of natural resources has fostered a strong tradition of outdoor recreation, with activities such as fishing, hiking, skiing, and camping deeply embedded in their cultural identity.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While geography has offered numerous benefits, it also presents challenges:
-
Climate Change: Both countries are experiencing the effects of climate change, with rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased risk of forest fires.
-
Population Distribution: Both countries face challenges related to population distribution, with a high concentration of people in urban areas and sparsely populated rural regions.
-
Environmental Sustainability: The need to balance economic growth with environmental protection is a constant concern, particularly in managing forest resources and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion:
The geographical landscapes of Finland and Sweden, while sharing some similarities, exhibit distinct features that have shaped their unique identities. The vast forests, lakes, and mountains have provided resources, opportunities, and inspiration, contributing to their economic prosperity, cultural heritage, and way of life. Understanding the geographical nuances of these two Nordic nations provides valuable insights into their history, present-day challenges, and future prospects.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main geographical differences between Finland and Sweden?
A: While both countries share a northern latitude and boreal forests, Finland is characterized by its extensive lake district and low-lying terrain, while Sweden features mountainous landscapes, diverse topography, and a more varied coastline.
Q: How has geography impacted the economies of Finland and Sweden?
A: Both countries rely heavily on their forests for timber production and have developed hydropower as a major source of energy. Their unique landscapes also attract tourists, contributing to their economies.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing Finland and Sweden?
A: Climate change is a major concern, with rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased risk of forest fires. Both countries also face challenges in managing their forest resources and ensuring environmental sustainability.
Q: What are some of the cultural influences of geography in Finland and Sweden?
A: The prevalence of natural landscapes has instilled a strong appreciation for nature in both cultures. This connection to the natural world is reflected in their art, literature, and way of life, fostering a strong tradition of outdoor recreation.
Tips:
-
When exploring the geography of Finland and Sweden, consider visiting their national parks and protected areas to experience their diverse landscapes firsthand.
-
Research the history of the glacial activity that shaped their terrain and the impact of these events on their ecosystems and cultural development.
-
Engage with local communities to learn about their traditional practices and how they have adapted to their unique geographical environments.
-
Explore the art, literature, and music of both countries, which often draw inspiration from their natural landscapes and cultural heritage.
-
Consider the role of climate change and sustainable development in shaping the future of these Nordic nations.
Conclusion:
The geography of Finland and Sweden is a testament to the power of nature to shape landscapes, economies, and cultures. By understanding the intricate relationships between their geographical features and their societies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique character of these two Nordic nations and their place in the wider world.

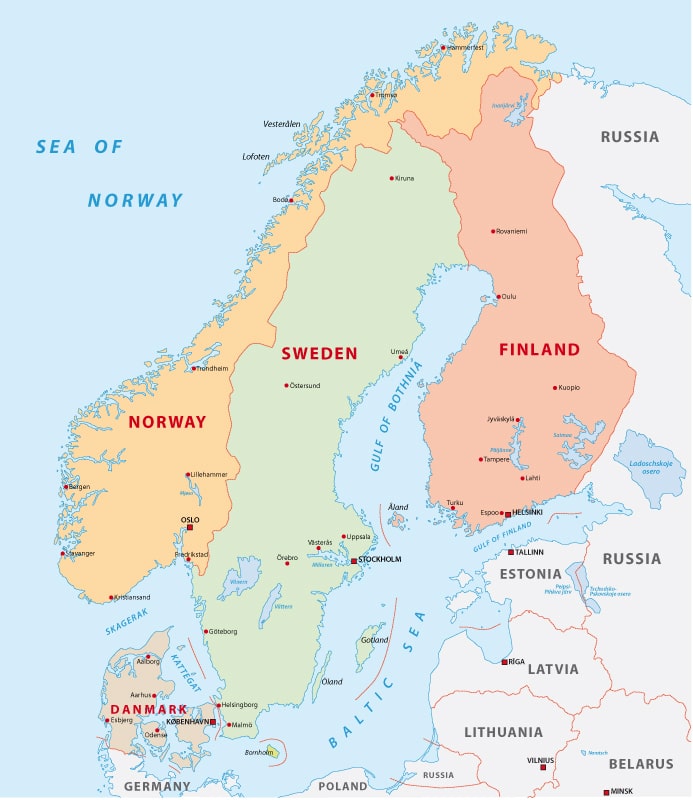



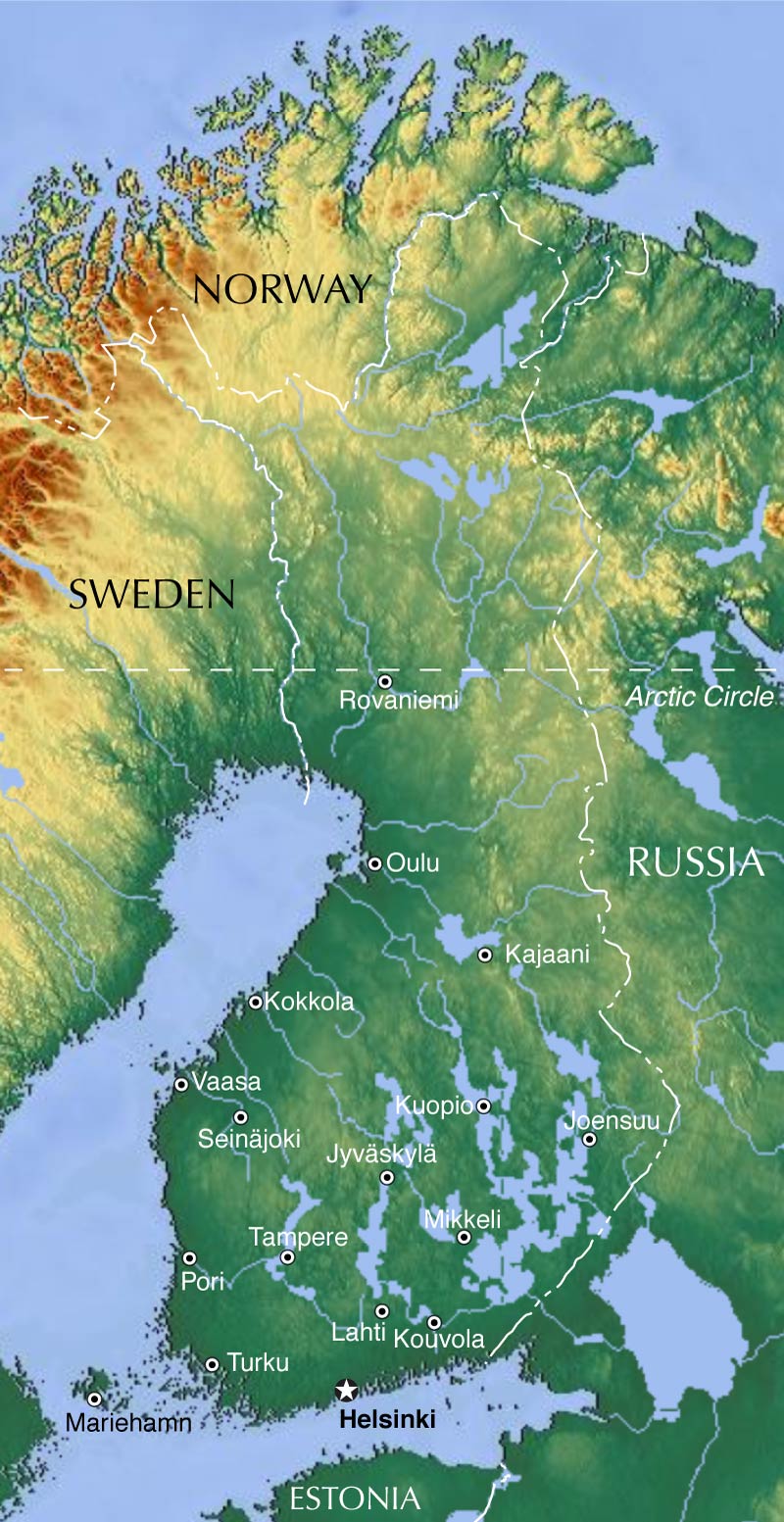
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Geography of Finland and Sweden: Exploring the Shared and Distinct Landscapes of the Nordic Region. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!