A Comparative Study: Mapping the Landscapes of France and the United Kingdom
Related Articles: A Comparative Study: Mapping the Landscapes of France and the United Kingdom
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Study: Mapping the Landscapes of France and the United Kingdom. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Study: Mapping the Landscapes of France and the United Kingdom

Introduction:
The geographic proximity of France and the United Kingdom, separated only by the English Channel, has fostered a rich history of interaction and exchange. Yet, despite their closeness, these two nations boast distinct landscapes, climates, and cultural identities, each shaping their respective histories and development. This article aims to provide a comparative analysis of France and the United Kingdom, exploring their unique geographical features and highlighting the impact of their physical environments on their societies.
I. Topography and Geology:
A. France:
France exhibits a diverse topography, ranging from the towering peaks of the Alps and Pyrenees to the vast plains of the Paris Basin and the rolling hills of the Massif Central. The country’s geological history is marked by the collision of tectonic plates, resulting in the formation of its prominent mountain ranges. The Alps, in particular, have played a significant role in shaping the country’s climate, influencing rainfall patterns and creating fertile valleys.
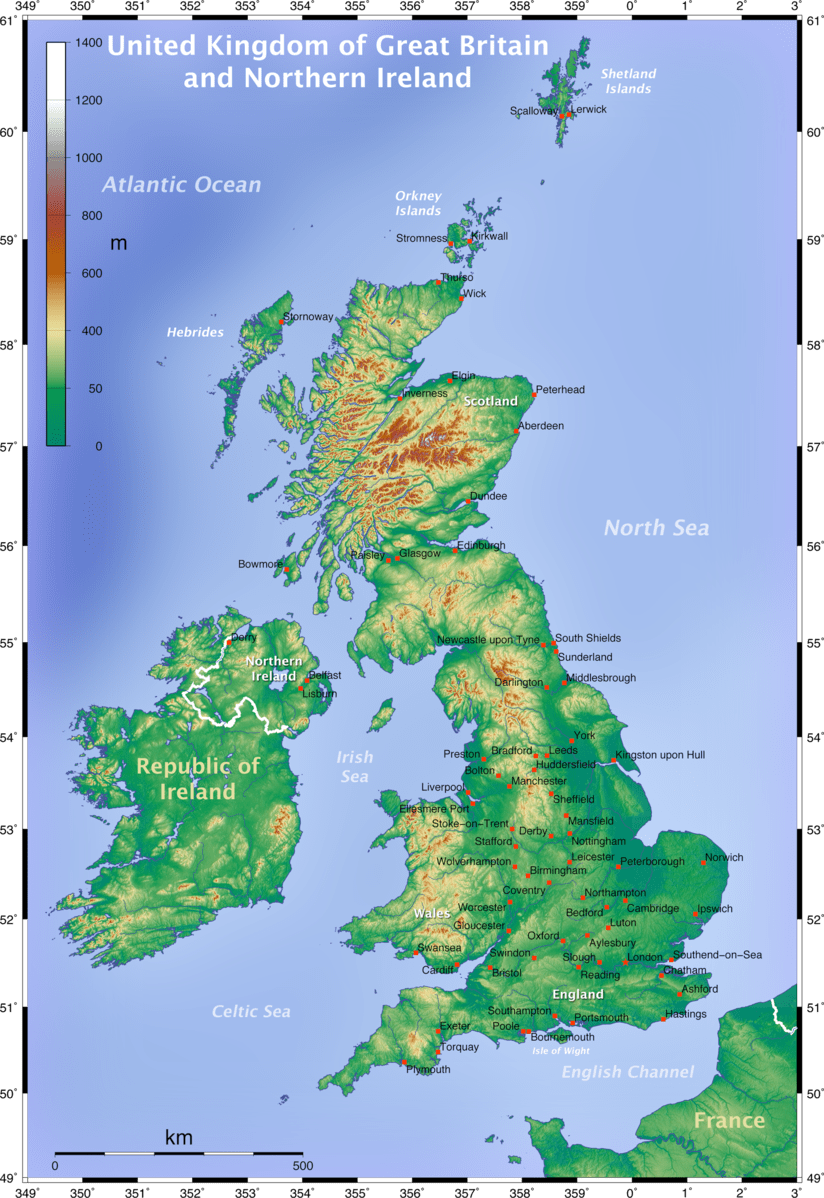
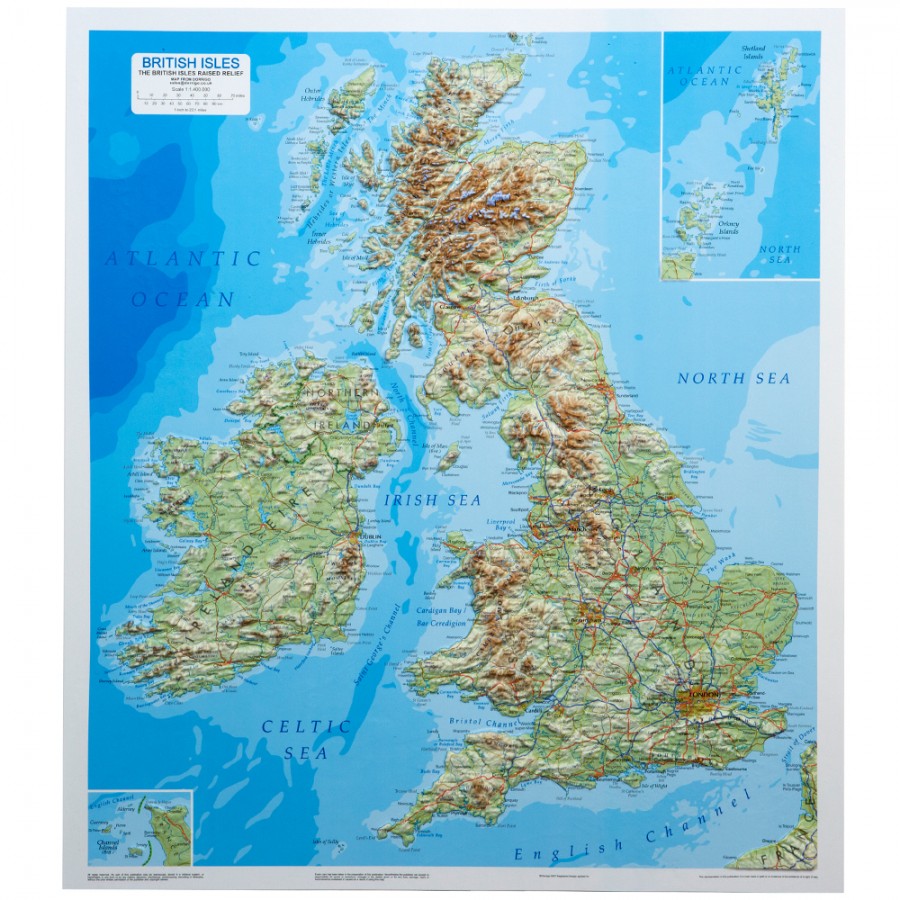
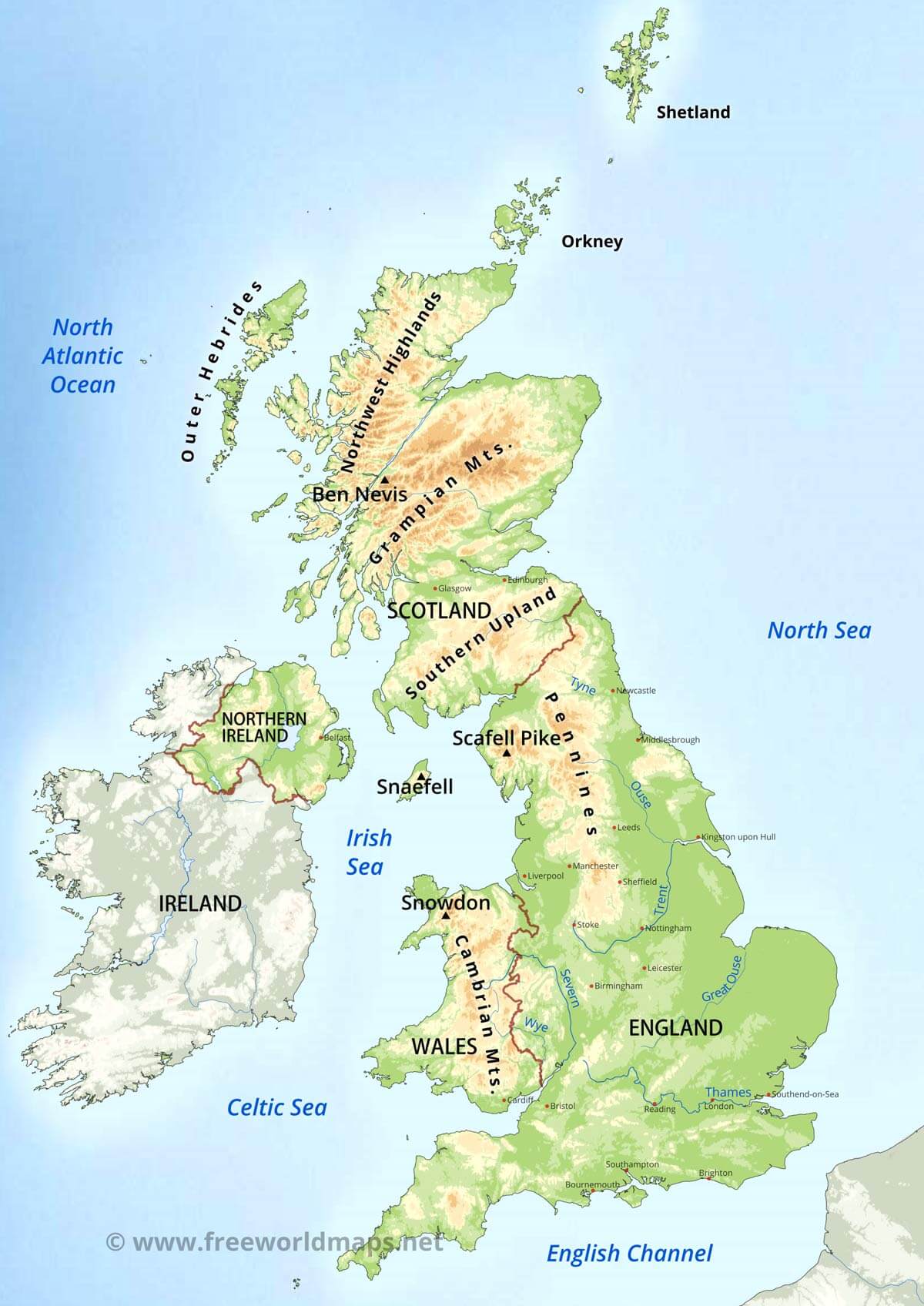
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom, in contrast, is characterized by a more subdued topography, with its highest peaks found in the Scottish Highlands. The country’s geological history is dominated by a series of ice ages, which sculpted the landmass, leaving behind glacial valleys, lakes, and distinctive coastline formations. The lowlands of England, formed by sedimentary deposits, provide fertile agricultural land, while the rugged terrain of Wales and Scotland presents a stark contrast.
II. Climate and Weather Patterns:
A. France:
France experiences a temperate climate, with distinct regional variations. The Mediterranean coast enjoys warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, while the Atlantic coast experiences a more moderate climate with abundant rainfall. The interior of the country is subject to continental influences, with hot summers and cold winters.
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom also enjoys a temperate climate, influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean. The country experiences a relatively mild climate with abundant rainfall, particularly in the west. The north of the country, including Scotland, is subject to colder temperatures and more frequent precipitation.
III. Natural Resources and Agriculture:
A. France:
France is endowed with a wealth of natural resources, including fertile agricultural land, forests, and mineral deposits. The country is a leading producer of wine, cheese, and agricultural products, with its diverse terrain supporting a wide range of crops and livestock.
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom also possesses a range of natural resources, including coal, oil, and natural gas. However, its agricultural sector is less prominent than France’s, with a smaller land area devoted to farming. Nevertheless, the country remains a significant producer of livestock, dairy products, and grains.
IV. Population Distribution and Urbanization:
A. France:
France exhibits a relatively even population distribution, with a significant portion of its population residing in urban areas. The country’s major cities, such as Paris, Lyon, and Marseille, serve as important economic and cultural centers.
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom’s population is more concentrated in its urban areas, with London serving as the country’s largest metropolis. The country’s historical industrial development has led to a high concentration of population in urban centers, particularly in England.
V. Transportation and Infrastructure:
A. France:
France possesses a well-developed transportation infrastructure, with an extensive network of roads, railways, and airports. The country’s high-speed rail network, the TGV, connects major cities, facilitating efficient travel and trade.
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom also has a well-developed transportation infrastructure, with a dense network of roads and railways. However, its rail network is less extensive than France’s, and its reliance on road transport contributes to traffic congestion in major cities.
VI. Cultural and Historical Influences:
A. France:
France’s cultural landscape is deeply intertwined with its geography. The country’s diverse terrain has fostered regional identities, with each region developing its own unique traditions, cuisine, and language. France’s history is marked by periods of conquest and innovation, shaping its cultural identity and artistic expression.
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom’s cultural landscape is also shaped by its geography. Its island location has fostered a sense of national identity, while its diverse regions have developed distinct cultural traditions. The country’s history is characterized by its maritime prowess and its role as a global power, influencing its cultural development and artistic expression.
VII. Environmental Challenges:
A. France:
France faces a range of environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss. The country’s agricultural practices and industrial development have contributed to environmental degradation, necessitating sustainable solutions.
B. The United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom also faces environmental challenges, including climate change, air pollution, and water scarcity. The country’s dense population and industrial activity have placed significant pressure on its natural resources, requiring sustainable management practices.
VIII. Conclusion:
The comparative study of France and the United Kingdom reveals the profound impact of geography on their respective societies. Their unique landscapes, climates, and resources have shaped their histories, cultures, and economies. While both nations share similarities, their distinct geographical characteristics have led to different patterns of development and cultural expression. Understanding the interplay between geography and society is crucial for appreciating the complexities of these two nations and their enduring relationship.
FAQs:
Q1: What are the major differences in the topography of France and the United Kingdom?
A: France boasts a more diverse topography, with towering mountain ranges like the Alps and Pyrenees, while the United Kingdom is characterized by a more subdued landscape, with its highest peaks found in the Scottish Highlands.
Q2: How do the climates of France and the United Kingdom differ?
A: Both countries experience temperate climates, but France has a wider range of regional variations, from the Mediterranean coast’s warm, dry summers to the Atlantic coast’s moderate climate. The United Kingdom’s climate is more consistent, with abundant rainfall throughout the year.
Q3: What are the key differences in the agricultural sectors of France and the United Kingdom?
A: France has a larger and more diverse agricultural sector, with a greater emphasis on wine, cheese, and agricultural products. The United Kingdom’s agricultural sector is less prominent, with a smaller land area devoted to farming.
Q4: How do the transportation infrastructures of France and the United Kingdom compare?
A: France has a more extensive and developed transportation infrastructure, particularly its high-speed rail network. The United Kingdom’s rail network is less extensive, and its reliance on road transport contributes to traffic congestion.
Q5: What are the main environmental challenges faced by France and the United Kingdom?
A: Both countries face environmental challenges related to climate change, pollution, and resource management. France’s agricultural practices and industrial development have contributed to environmental degradation, while the United Kingdom’s dense population and industrial activity have placed significant pressure on its natural resources.
Tips:
- Utilize maps: Refer to maps of France and the United Kingdom to visualize their geographical features, including mountain ranges, rivers, and cities.
- Explore regional differences: Delve into the distinct cultural and geographical characteristics of different regions within each country.
- Consider historical context: Examine how historical events and developments have shaped the landscapes and societies of France and the United Kingdom.
- Analyze environmental data: Explore data on climate change, pollution, and resource consumption to understand the environmental challenges faced by both nations.
- Engage in comparative analysis: Compare and contrast the geographical features, cultural landscapes, and societal structures of France and the United Kingdom to gain a deeper understanding of their unique characteristics.
Conclusion:
The geographical landscapes of France and the United Kingdom are intricately intertwined with their histories, cultures, and economies. By examining their distinctive topographies, climates, resources, and societal structures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the multifaceted nature of these two nations. Their unique characteristics and enduring relationship continue to shape the political, economic, and cultural landscape of Europe and beyond.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Study: Mapping the Landscapes of France and the United Kingdom. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!