A Comparative Study of Finland and Norway: Exploring Geography, Culture, and Economy
Related Articles: A Comparative Study of Finland and Norway: Exploring Geography, Culture, and Economy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Study of Finland and Norway: Exploring Geography, Culture, and Economy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Study of Finland and Norway: Exploring Geography, Culture, and Economy
Finland and Norway, two Scandinavian nations sharing a common Nordic heritage, occupy distinct geographical spaces and possess unique cultural and economic identities. A comparative examination of these two countries reveals fascinating contrasts and intriguing similarities, offering a deeper understanding of their individual strengths and the forces that shape their respective destinies.
Geography: A Tale of Two Landscapes
The landscapes of Finland and Norway are sculpted by the forces of nature, each exhibiting a distinct character. Finland, known as the "Land of a Thousand Lakes," boasts a vast network of inland waterways, dotted with countless islands and forests. Its terrain is primarily characterized by low-lying plains and rolling hills, with a few higher elevations in the north, including the Saana fell in Lapland. In contrast, Norway, with its dramatic coastline and towering mountains, presents a more rugged and mountainous landscape. The country’s iconic fjords, carved by glaciers over millennia, are a testament to the powerful forces of nature that have shaped its geography.
Climate: From Temperate to Arctic
Both Finland and Norway experience a predominantly temperate climate, influenced by the North Atlantic Current. However, the geographical differences between the two countries lead to variations in their climate. Finland, being situated further inland, experiences a more continental climate with warmer summers and colder winters. Norway, on the other hand, enjoys a milder climate due to the moderating influence of the North Atlantic Current. The western coast of Norway, exposed to the open sea, experiences relatively mild winters, while the eastern parts of the country are subject to harsher conditions.
Demographics: A Population Divide
Despite their relatively small populations, Finland and Norway exhibit a significant demographic disparity. Finland, with a population of approximately 5.5 million, is considerably more populous than Norway, which has a population of around 5.4 million. This difference is largely attributed to the historical development of each country. Finland, having been part of the Russian Empire for centuries, experienced a larger population growth than Norway, which enjoyed a more independent status.
Culture: A Blend of Tradition and Modernity
Both Finland and Norway are renowned for their rich cultural heritage, blending traditional values with modern influences. Finnish culture is deeply rooted in nature, with a strong emphasis on outdoor activities, such as skiing, fishing, and hiking. The country is also known for its vibrant music scene, with a distinctive folk tradition and a growing contemporary music industry. Norwegian culture is characterized by a strong sense of community and a deep appreciation for its natural beauty. The country is renowned for its literature, with authors like Henrik Ibsen and Sigrid Undset achieving international acclaim.
Economy: Diversification and Dependence
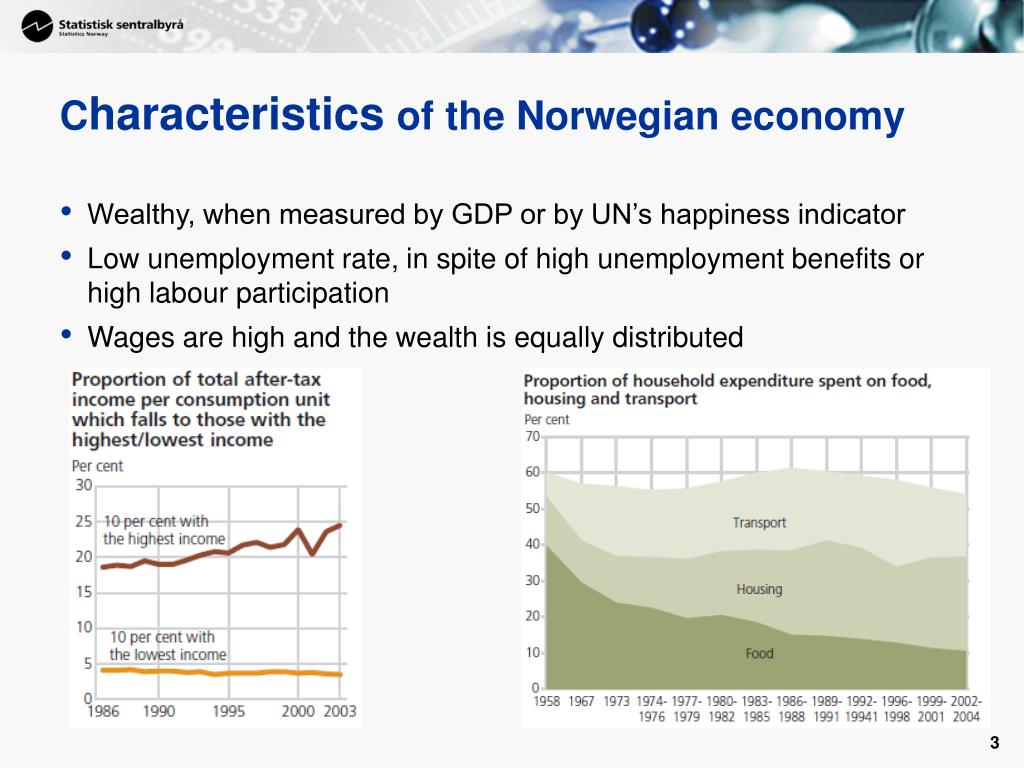
Finland and Norway have developed distinct economic profiles, reflecting their respective strengths and challenges. Finland, with its robust manufacturing sector, is a leading exporter of technology, machinery, and paper products. The country’s economy has also been increasingly diversified in recent years, with the growth of sectors such as information technology and renewable energy. Norway, on the other hand, is heavily reliant on its natural resources, particularly oil and gas. The country has vast reserves of these commodities, which have fueled its economic prosperity. However, this dependence has also raised concerns about the sustainability of its economic model.
Environmental Concerns: Navigating Sustainability
Both Finland and Norway are committed to environmental sustainability, recognizing the importance of preserving their natural resources and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Finland has established ambitious goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy sources. The country is also known for its innovative approach to sustainable forestry practices. Norway, with its vast forests and pristine fjords, is equally committed to environmental protection. The country has been a pioneer in carbon capture and storage technologies and has implemented policies to promote sustainable energy and transportation.
Comparative Analysis: Key Differences and Similarities
A comparative analysis of Finland and Norway reveals a number of key differences and similarities:
Differences:
- Geography: Finland’s landscape is predominantly characterized by lakes and forests, while Norway boasts a more rugged terrain with towering mountains and fjords.
- Climate: Finland experiences a more continental climate with warmer summers and colder winters, while Norway enjoys a milder climate due to the North Atlantic Current.
- Demographics: Finland has a larger population than Norway, reflecting its historical development.
- Economy: Finland’s economy is more diversified, with a strong manufacturing sector, while Norway is heavily reliant on its oil and gas resources.
Similarities:
- Culture: Both countries share a Nordic heritage, with a strong emphasis on nature, community, and tradition.
- Social Welfare: Finland and Norway both have robust social welfare systems, providing universal healthcare, education, and social security benefits.
- Environmental Concerns: Both countries are committed to environmental sustainability and have implemented policies to address climate change and promote renewable energy.
Conclusion: A Tale of Two Successes
Finland and Norway, despite their differences, have achieved remarkable success in various aspects of their national development. Finland’s commitment to education and innovation has propelled its economy to the forefront of the global technological landscape. Norway’s vast natural resources have fueled its economic prosperity, allowing it to invest in social welfare and environmental protection. Both countries serve as examples of how effective governance, a strong social safety net, and a commitment to sustainability can contribute to the well-being of their citizens.
FAQs
- What are the main differences between Finland and Norway?
Finland and Norway differ in their geography, climate, demographics, and economic structures. Finland has a more continental climate, a larger population, and a diversified economy, while Norway has a rugged mountain landscape, a smaller population, and an economy heavily reliant on oil and gas.
- What are the similarities between Finland and Norway?
Both countries share a Nordic heritage, a strong emphasis on nature and community, robust social welfare systems, and a commitment to environmental sustainability.
- What are the main industries in Finland and Norway?
Finland’s main industries include technology, machinery, paper products, and renewable energy. Norway’s economy is heavily reliant on oil and gas, but it also has a growing sector in renewable energy, tourism, and maritime industries.
- What are the main challenges facing Finland and Norway?
Finland faces challenges related to maintaining its economic competitiveness in a rapidly changing global landscape. Norway faces challenges related to managing its oil and gas resources sustainably and adapting to a post-fossil fuel future.
- What are the future prospects for Finland and Norway?
Both countries are well-positioned for future success, with their strong social welfare systems, commitment to innovation, and focus on environmental sustainability. Finland’s technological prowess and Norway’s renewable energy potential offer promising prospects for future growth.
Tips
- Visit both countries to experience their unique landscapes and cultures.
- Learn about their history, literature, and music to gain a deeper understanding of their cultural identities.
- Consider the environmental impact of your travels and choose sustainable options.
- Engage with local communities to gain insights into their perspectives and experiences.
Conclusion
Finland and Norway, two distinct yet interconnected Scandinavian nations, offer a compelling case study in the interplay of geography, culture, and economy. Their contrasting landscapes, diverse economic profiles, and shared Nordic heritage provide a rich tapestry of human experience, showcasing the resilience, innovation, and social responsibility that define the Nordic model. As they navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, their stories continue to inspire and inform, highlighting the importance of preserving cultural heritage, promoting sustainable development, and fostering a sense of community and social well-being.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Study of Finland and Norway: Exploring Geography, Culture, and Economy. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!