A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)

Introduction
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing how we understand, analyze, and interact with the world around us. This powerful toolset allows us to capture, store, analyze, manage, and visualize geographically referenced data, providing invaluable insights across various fields. GIS has become an indispensable tool for diverse applications, ranging from environmental monitoring and urban planning to resource management and disaster response.
Understanding the Foundations of GIS
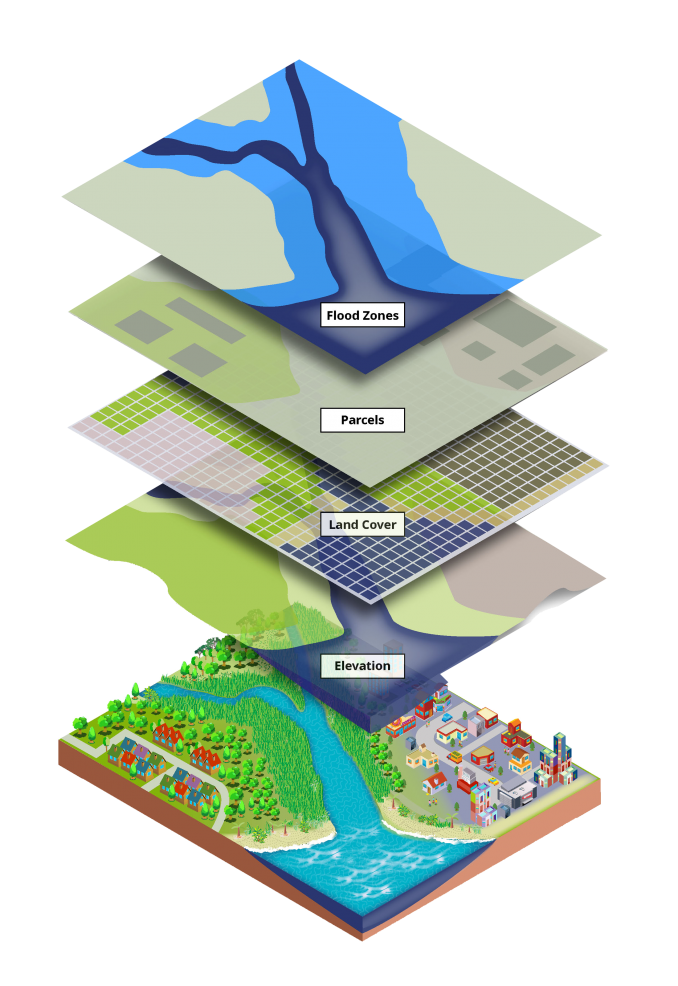
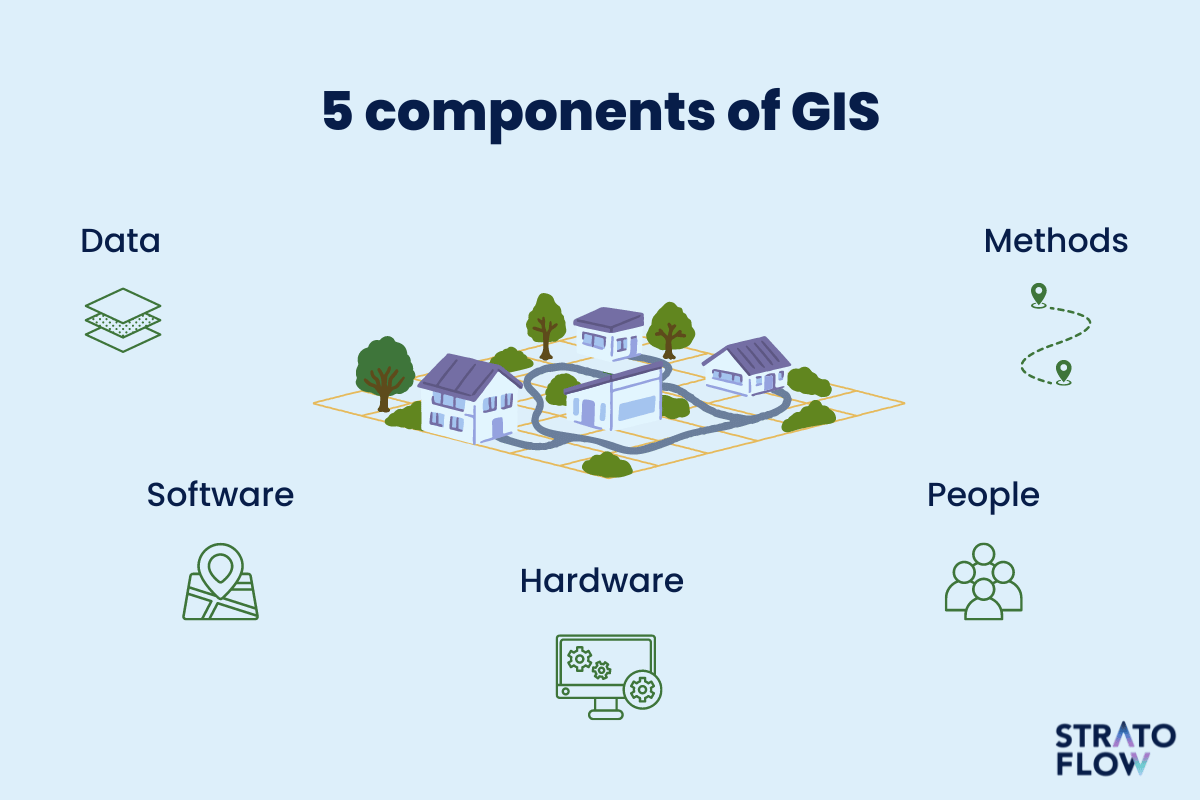
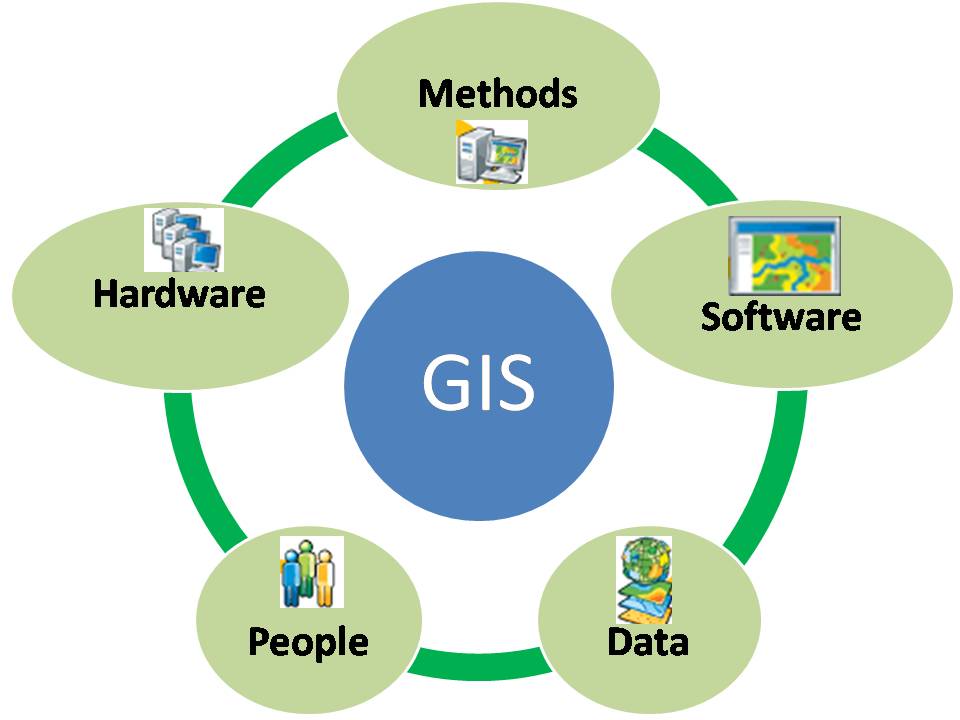
At its core, GIS integrates spatial data with non-spatial attributes, creating a comprehensive understanding of geographic phenomena. This integration is achieved through the use of various components, including:
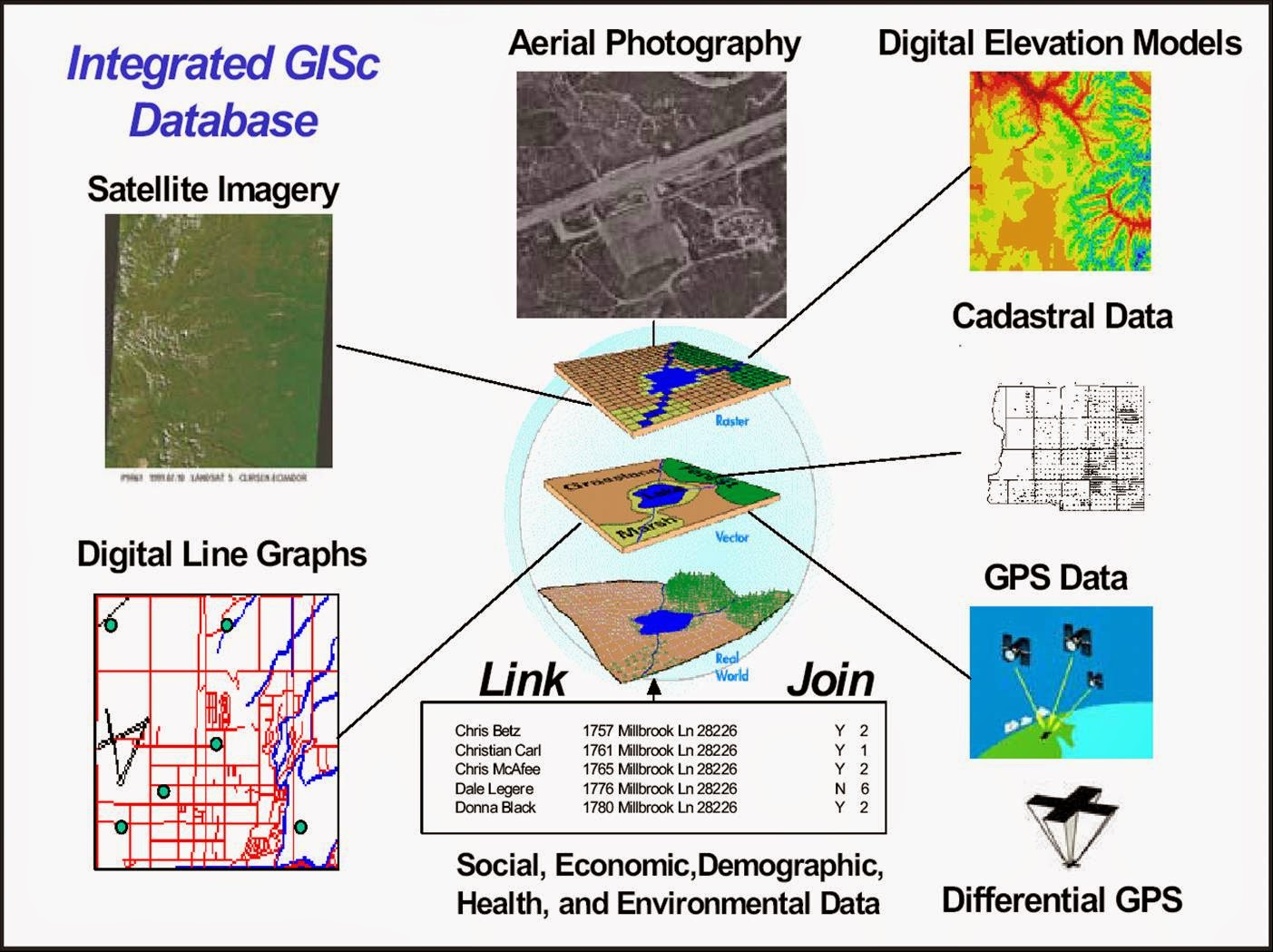
- Data Acquisition: GIS utilizes a multitude of sources to gather spatial data, including aerial photographs, satellite imagery, GPS data, and sensor networks.
- Data Management: The acquired data is stored and organized within a geospatial database, enabling efficient retrieval and analysis.
- Data Analysis: Powerful tools within GIS allow users to perform spatial analysis, such as proximity analysis, overlay analysis, and network analysis, to extract meaningful insights from the data.
- Data Visualization: GIS excels at presenting complex spatial data in visually compelling ways, using maps, charts, and 3D models to communicate information effectively.
The Applications of GIS: A Multifaceted Landscape
GIS finds applications in a wide array of fields, demonstrating its versatility and impact on various aspects of our lives:
-
Environmental Management: GIS plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing natural resources, assessing environmental impacts, and developing sustainable solutions. Applications include:
- Habitat mapping and conservation: Identifying and protecting critical habitats for endangered species.
- Pollution monitoring and control: Tracking air and water pollution sources and implementing mitigation strategies.
- Climate change adaptation: Analyzing climate change impacts and planning for adaptation measures.
-
Urban Planning and Development: GIS empowers urban planners to make informed decisions regarding land use, infrastructure development, and transportation planning. Key applications include:
- Urban growth modeling: Simulating future growth patterns and identifying potential development challenges.
- Infrastructure planning: Optimizing the location and design of utilities, transportation networks, and public facilities.
- Disaster risk management: Assessing vulnerability to natural disasters and developing emergency response plans.
-
Resource Management: GIS aids in efficient resource management, ensuring sustainable use of natural resources and optimizing resource allocation. Examples include:
- Forest management: Monitoring forest health, managing timber harvesting, and preventing wildfires.
- Water resource management: Assessing water availability, managing irrigation systems, and mitigating water scarcity.
- Agriculture and land use: Optimizing crop yields, managing soil health, and monitoring agricultural practices.
-
Public Safety and Emergency Response: GIS plays a vital role in enhancing public safety and improving emergency response capabilities. Applications include:
- Crime mapping and analysis: Identifying crime hotspots and deploying resources effectively.
- Emergency response planning: Optimizing routes for emergency vehicles and coordinating response efforts.
- Natural disaster management: Assessing disaster impacts, coordinating rescue operations, and providing relief assistance.
-
Transportation and Logistics: GIS supports efficient transportation planning, logistics optimization, and route planning. Key applications include:
- Traffic flow analysis: Identifying traffic bottlenecks and optimizing traffic management strategies.
- Route planning and optimization: Developing efficient routes for delivery vehicles and public transportation.
- Fleet management: Tracking vehicle locations, optimizing fuel consumption, and improving fleet efficiency.
-
Business and Marketing: GIS provides valuable insights for businesses, enabling targeted marketing campaigns, optimized location selection, and improved customer service. Examples include:
- Market analysis and segmentation: Identifying customer demographics and preferences for targeted marketing.
- Site selection and location analysis: Finding optimal locations for new businesses and facilities.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Using location data to personalize customer interactions and enhance service quality.
The Benefits of GIS: A Transformative Impact
The adoption of GIS brings numerous benefits across various sectors, leading to improved efficiency, better decision-making, and enhanced outcomes:
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships and patterns, GIS enables informed decision-making based on data-driven insights.
- Enhanced Efficiency: GIS streamlines processes, automates tasks, and optimizes resource allocation, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Better Communication: GIS facilitates effective communication of complex spatial information through visually compelling maps, charts, and 3D models.
- Increased Collaboration: GIS fosters collaboration by providing a shared platform for data access, analysis, and visualization, enabling stakeholders to work together effectively.
- Sustainable Development: GIS plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable development by enabling informed decisions regarding resource management, environmental protection, and urban planning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about GIS
1. What are the different types of GIS software available?
There are numerous GIS software packages available, each with its own strengths and features. Some popular options include:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS platform developed by Esri, offering a wide range of tools and capabilities.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS software package, known for its flexibility and user-friendliness.
- GRASS GIS: Another open-source GIS software, particularly popular for geospatial modeling and analysis.
- MapInfo Pro: A commercial GIS software package, known for its user-friendly interface and powerful analysis tools.
2. What are the key skills required for GIS professionals?
GIS professionals typically possess a combination of technical and analytical skills, including:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software Proficiency: Expertise in using GIS software packages like ArcGIS, QGIS, or GRASS GIS.
- Data Management and Analysis: Skills in data acquisition, processing, analysis, and visualization.
- Spatial Analysis Techniques: Understanding and applying various spatial analysis methods, such as proximity analysis, overlay analysis, and network analysis.
- Remote Sensing and Image Processing: Knowledge of remote sensing principles and techniques for interpreting satellite imagery and aerial photographs.
- Cartography and Visualization: Proficiency in creating effective maps, charts, and other visualizations to communicate spatial information.
3. What are the career opportunities in GIS?
GIS offers a wide range of career opportunities across various industries, including:
- Environmental Consulting: Environmental consultants use GIS to assess environmental impacts, develop mitigation strategies, and manage natural resources.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners utilize GIS for land use planning, infrastructure development, and transportation management.
- Resource Management: Resource managers employ GIS to monitor and manage natural resources, such as forests, water, and land.
- Public Safety: GIS plays a vital role in public safety, enabling crime mapping, emergency response planning, and disaster management.
- Transportation and Logistics: GIS is used for route planning, fleet management, and traffic analysis in the transportation and logistics sector.
- Business and Marketing: GIS helps businesses with market analysis, site selection, and customer relationship management.
Tips for Getting Started with GIS
- Start with the Basics: Begin by understanding the fundamental concepts of GIS, including spatial data, coordinate systems, and geospatial analysis.
- Explore Free Resources: Utilize online resources, such as tutorials, courses, and open-source software, to gain practical experience.
- Choose the Right Software: Select a GIS software package that suits your needs and budget, considering factors like features, user-friendliness, and cost.
- Practice and Experiment: Regularly practice using GIS software and explore different applications to develop your skills.
- Network with Other GIS Professionals: Join online forums, attend conferences, and connect with other GIS professionals to learn from their experiences.
Conclusion
GIS has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing how we understand, analyze, and interact with the world around us. Its applications span across various fields, from environmental management and urban planning to resource management and disaster response. By integrating spatial data with non-spatial attributes, GIS provides invaluable insights, empowers informed decision-making, and enhances efficiency across diverse sectors. As technology continues to evolve, GIS is poised to play an increasingly important role in addressing global challenges and shaping a more sustainable future.



![[Book] Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) – Long's blog](https://dothanhlong.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/gis.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!