A Comprehensive Guide to Map Flag Names: Navigating the World of Visual Representation
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Flag Names: Navigating the World of Visual Representation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Map Flag Names: Navigating the World of Visual Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Map Flag Names: Navigating the World of Visual Representation

Maps, the quintessential tools for spatial understanding, are often adorned with flags, adding a vibrant layer of visual information. These flags, more formally known as map flags, serve a dual purpose: they identify specific locations and simultaneously convey cultural and political nuances. Understanding the nuances of map flag names is crucial for both mapmakers and map users, enabling a richer and more informed interpretation of geographic data.
The Anatomy of a Map Flag Name
Map flag names typically follow a specific structure, often incorporating the following elements:
- Country or Region: This is the primary identifier, specifying the geographic entity the flag represents. Examples include "United States," "France," or "European Union."
- Specific Entity: This element further refines the location, specifying a particular state, province, or city within the broader country or region. For instance, "California" within the United States or "Paris" within France.
- Flag Type: This element differentiates between various flag styles, such as the national flag, the state flag, or a specific historical flag. For instance, "United States National Flag," "California State Flag," or "French Royal Standard."
Beyond Simple Identification: The Deeper Significance of Map Flag Names
Map flags transcend their basic function as visual markers. They embody a multitude of historical, cultural, and political narratives.
- Historical Context: The evolution of flags often reflects significant historical events, revolutions, or political shifts. For example, the flags of former Soviet republics often incorporate elements of the Soviet Union’s flag, highlighting a shared past.
- Cultural Identity: Flags are powerful symbols of national pride and cultural identity. They often feature distinct colors, patterns, and symbols representing the heritage and values of a particular people.
- Political Landscape: Map flags can highlight political boundaries and affiliations. For instance, the use of different flags for different regions within a country can indicate varying degrees of autonomy or political divisions.
The Importance of Accuracy and Consistency
Using correct and consistent map flag names is essential for maintaining accuracy and clarity in map representation. Misleading or outdated flag names can lead to misinterpretations and confusion. For example, using the flag of the Soviet Union to represent Russia would be inaccurate and misleading.
Navigating the World of Map Flags: A Guide for Mapmakers and Users
For Mapmakers:
- Research Thoroughly: Before incorporating flags into a map, conduct thorough research to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the chosen flags. Consult reliable sources like official government websites, flag encyclopedias, and reputable academic journals.
- Consider Context: The choice of flags should be informed by the map’s purpose and target audience. For example, a historical map might feature flags from different periods, while a contemporary map would focus on current national flags.
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure consistent flag usage throughout the map, adhering to a standardized naming convention. This enhances clarity and avoids confusion.
- Use High-Quality Images: Employ high-resolution, accurate images of flags to ensure visual clarity and avoid pixelation or distortion.
For Map Users:
- Pay Attention to Detail: Observe the flag names carefully to understand the specific location and entity being represented.
- Recognize Historical Context: Be aware that flags can reflect historical changes and political shifts. This understanding enriches the interpretation of map data.
- Interpret Cultural Significance: Recognize that flags often symbolize cultural identity and values. This perspective adds a deeper layer of meaning to map interpretation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Map Flag Names
Q: What are the best resources for finding accurate and up-to-date information about map flags?
A: Reliable sources for accurate information on map flags include:
- Official Government Websites: National and regional government websites often provide accurate information on official flags.
- Flag Encyclopedias: Specialized books and online encyclopedias dedicated to flags offer comprehensive information on flag history, design, and symbolism.
- Reputable Academic Journals: Journals focusing on cartography, history, and cultural studies often publish articles on flag usage and symbolism.
Q: How can I differentiate between different types of flags, such as national flags, state flags, and historical flags?
A: Pay close attention to the flag name. It typically specifies the type of flag being represented. For instance, "United States National Flag" clearly indicates a national flag, while "California State Flag" identifies a state flag.
Q: Are there any standardized conventions for naming map flags?
A: While there are no universally accepted conventions, adhering to a consistent structure, such as "Country/Region – Specific Entity – Flag Type," can enhance clarity and avoid confusion.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using map flags?
A: Common mistakes include:
- Using outdated or inaccurate flags: Ensure that the flags used represent the current status of the entity.
- Misrepresenting the scale of the flag: Use flags that are appropriately sized for the map’s scale.
- Ignoring cultural sensitivity: Consider the cultural significance of flags and avoid using them in a disrespectful or insensitive manner.
Tips for Using Map Flag Names Effectively
- Prioritize Accuracy: Always strive for accuracy in flag names to avoid misinterpretations.
- Consider Context: Choose flags that are relevant to the map’s purpose and target audience.
- Maintain Consistency: Adhere to a consistent naming convention for flags throughout the map.
- Utilize High-Quality Images: Employ high-resolution, accurate images of flags for optimal visual clarity.
Conclusion
Map flags are more than just visual markers; they are powerful symbols that encapsulate history, culture, and political realities. Understanding the nuances of map flag names enables a richer and more informed interpretation of geographic data. By prioritizing accuracy, consistency, and context, mapmakers and users can leverage the power of map flags to navigate the world with greater clarity and understanding.
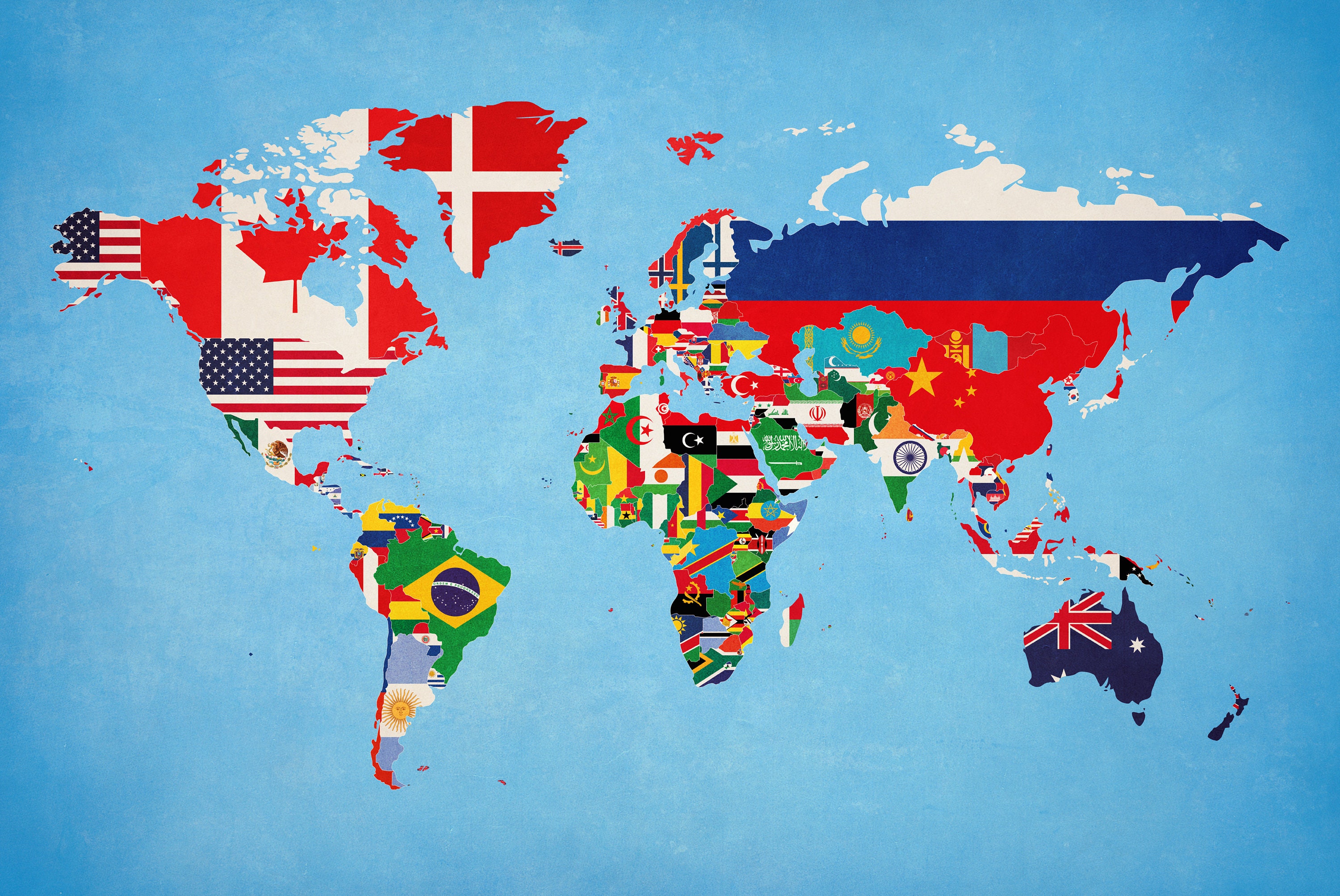
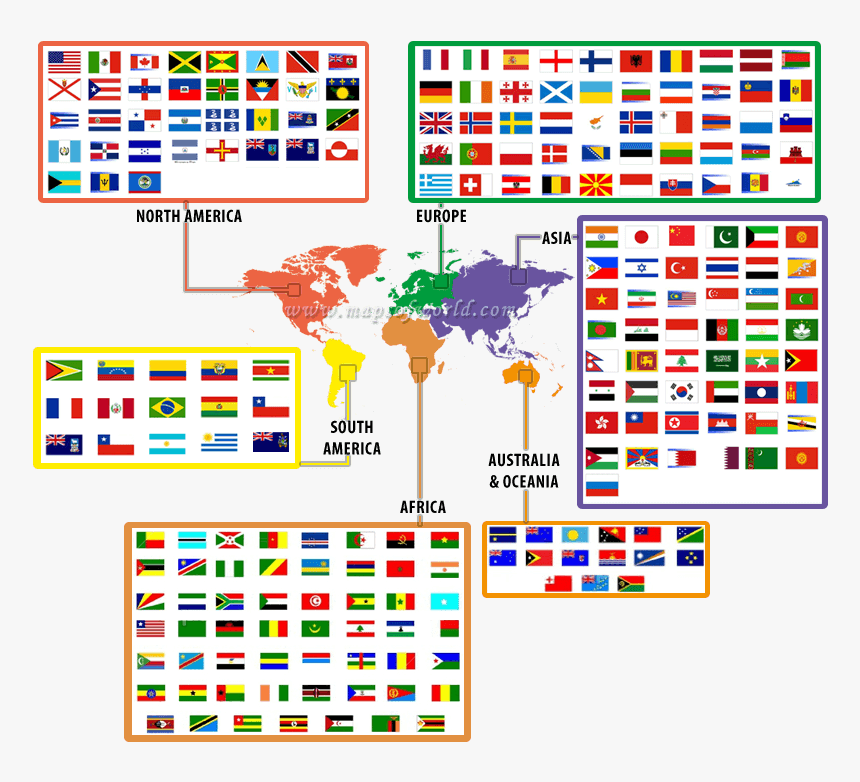
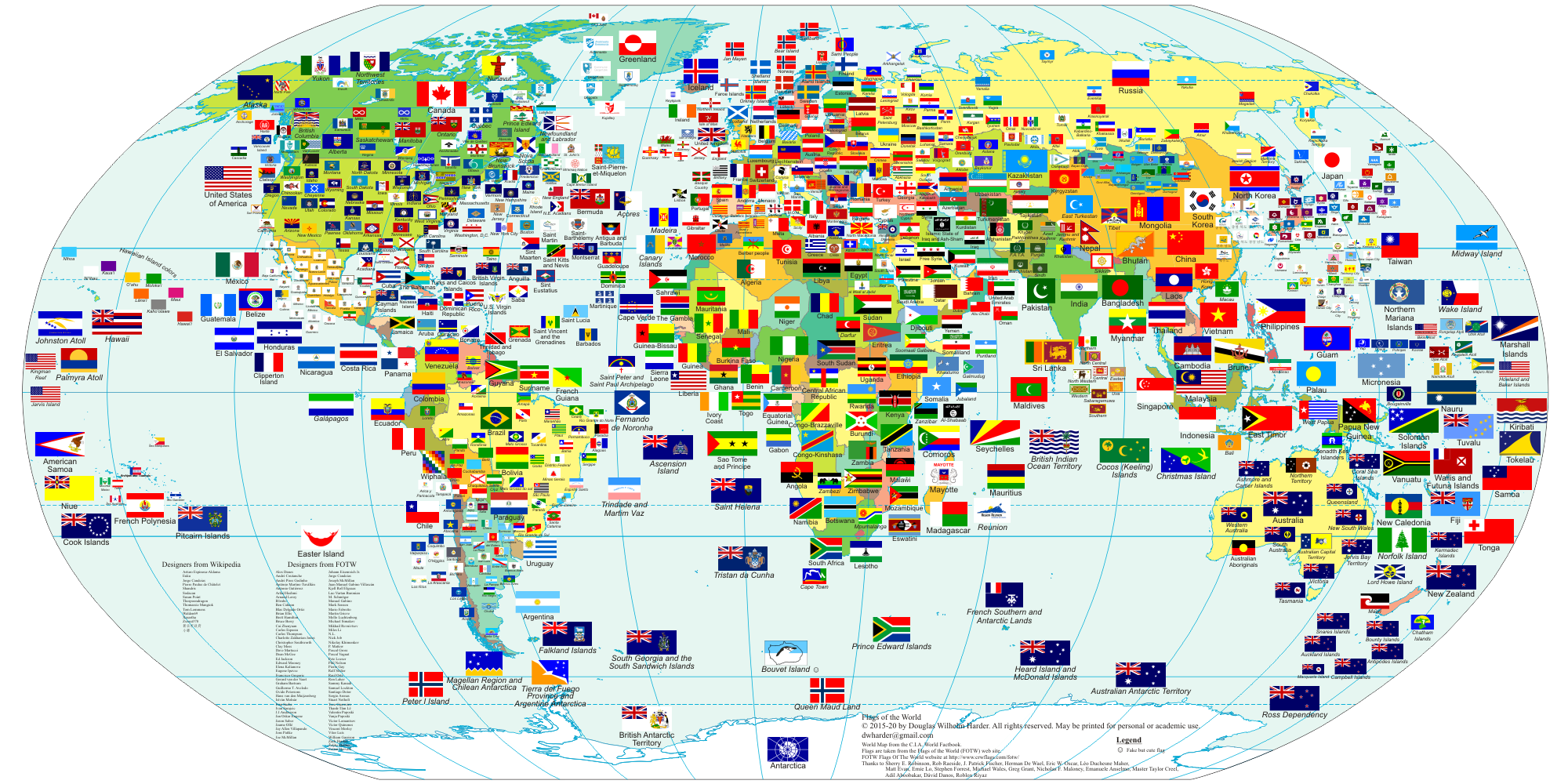
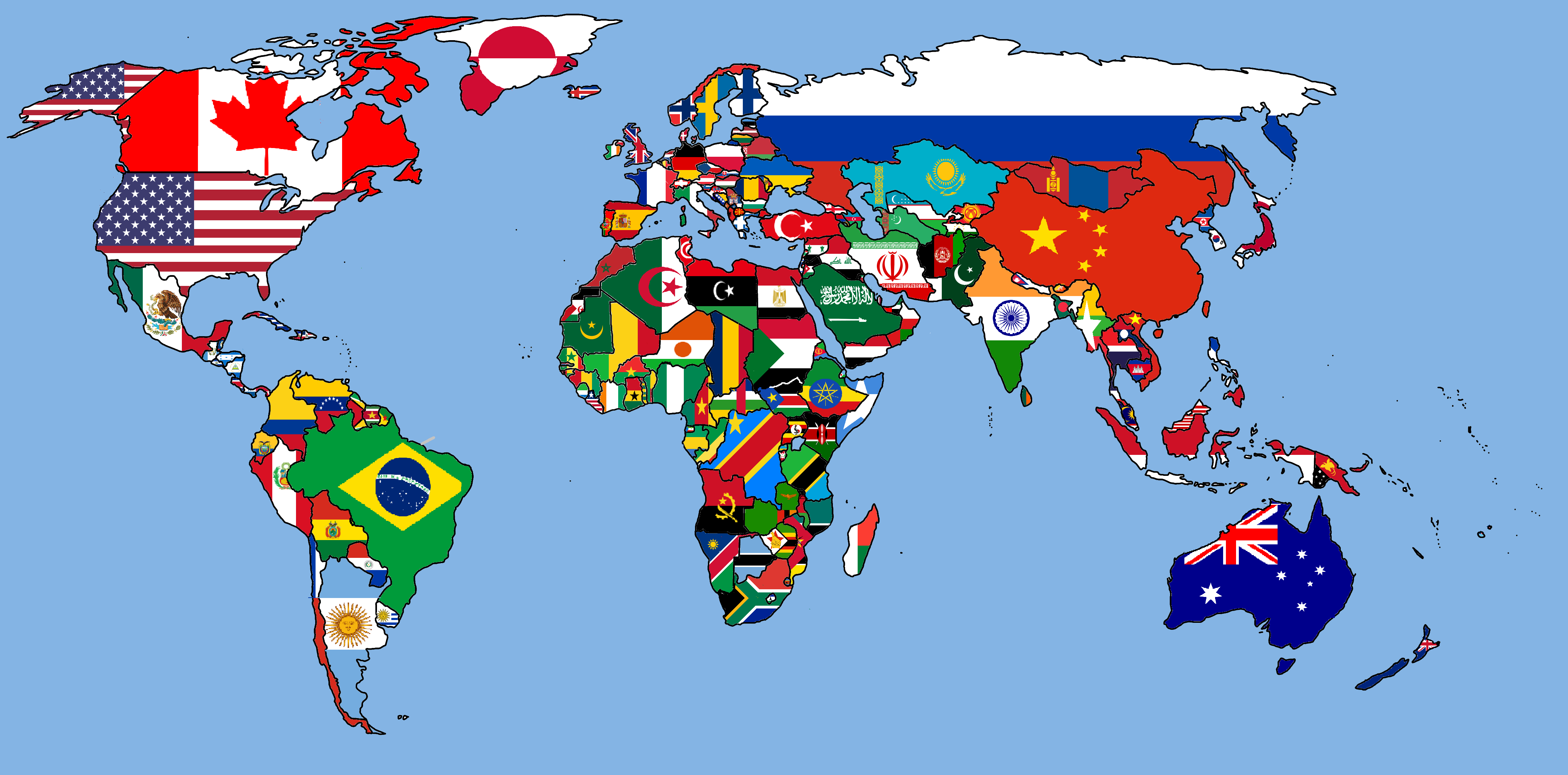


![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Map Flag Names: Navigating the World of Visual Representation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!