A Crossroads of History and Geography: Exploring the Map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia
Related Articles: A Crossroads of History and Geography: Exploring the Map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Crossroads of History and Geography: Exploring the Map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Crossroads of History and Geography: Exploring the Map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia
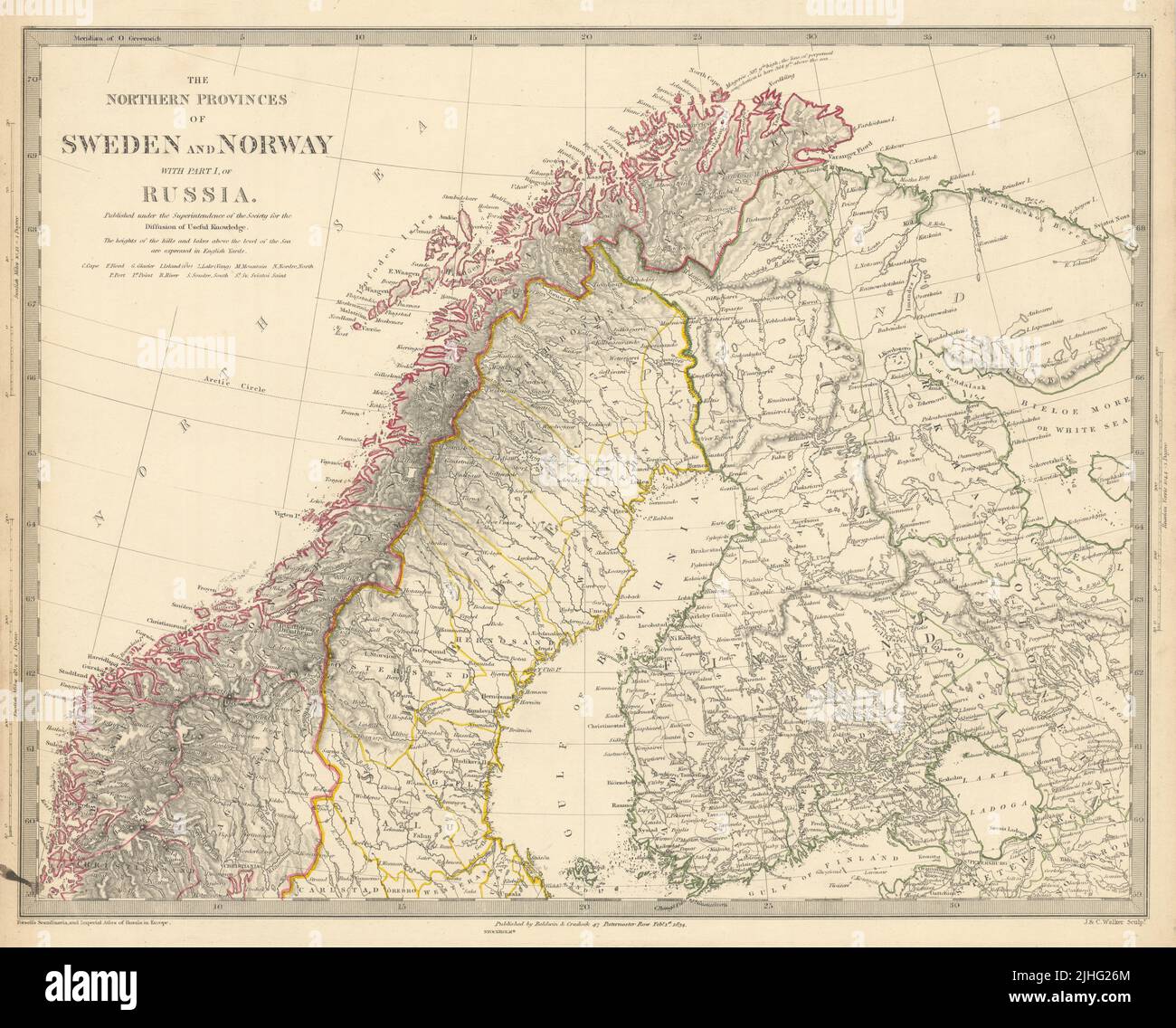
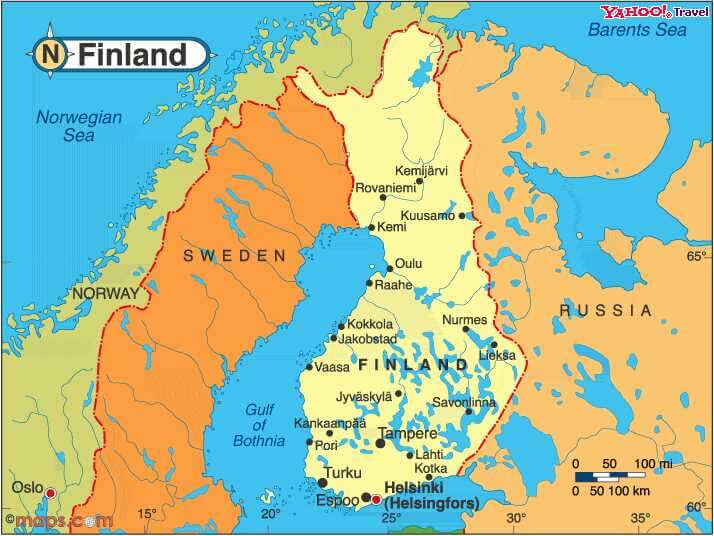
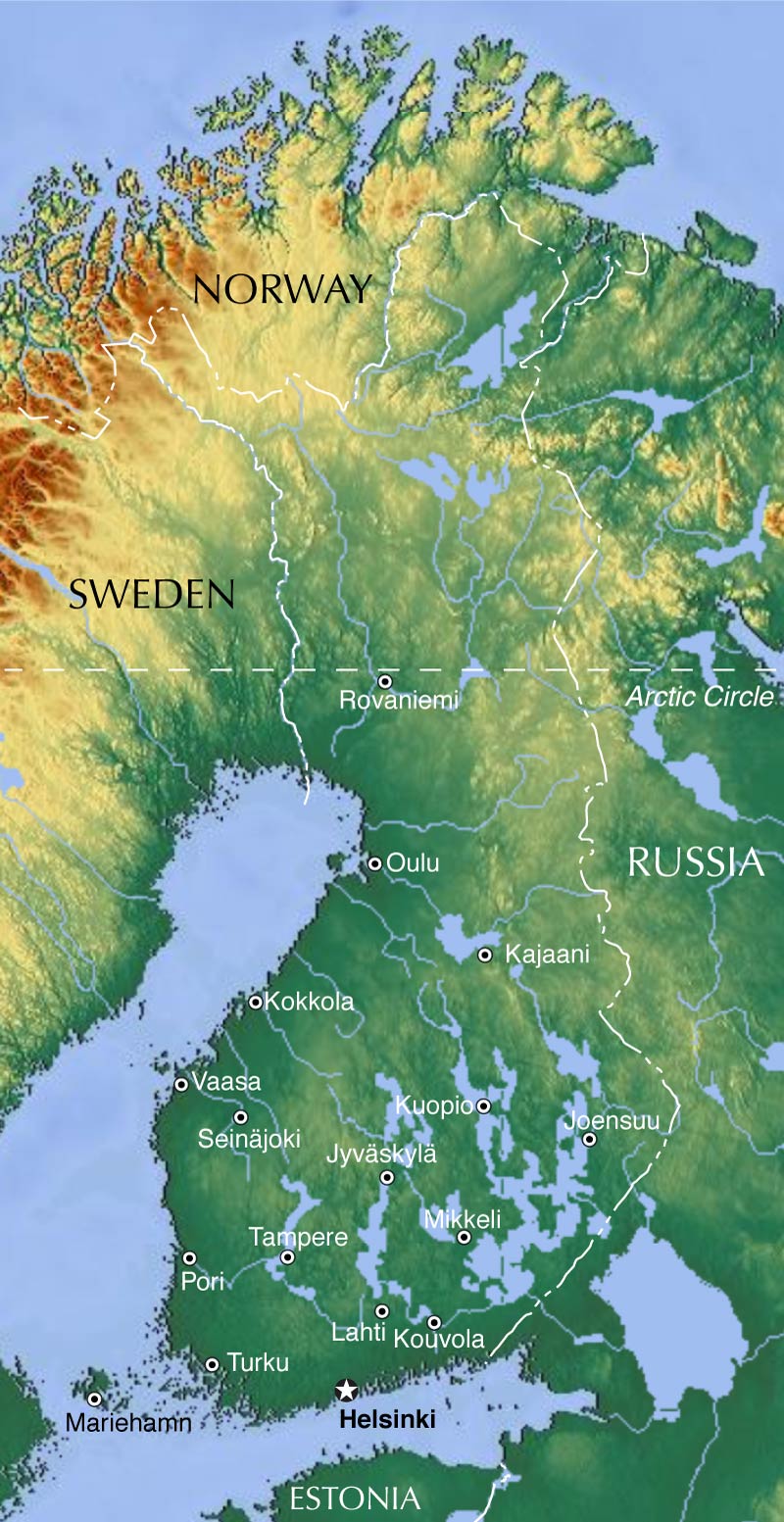
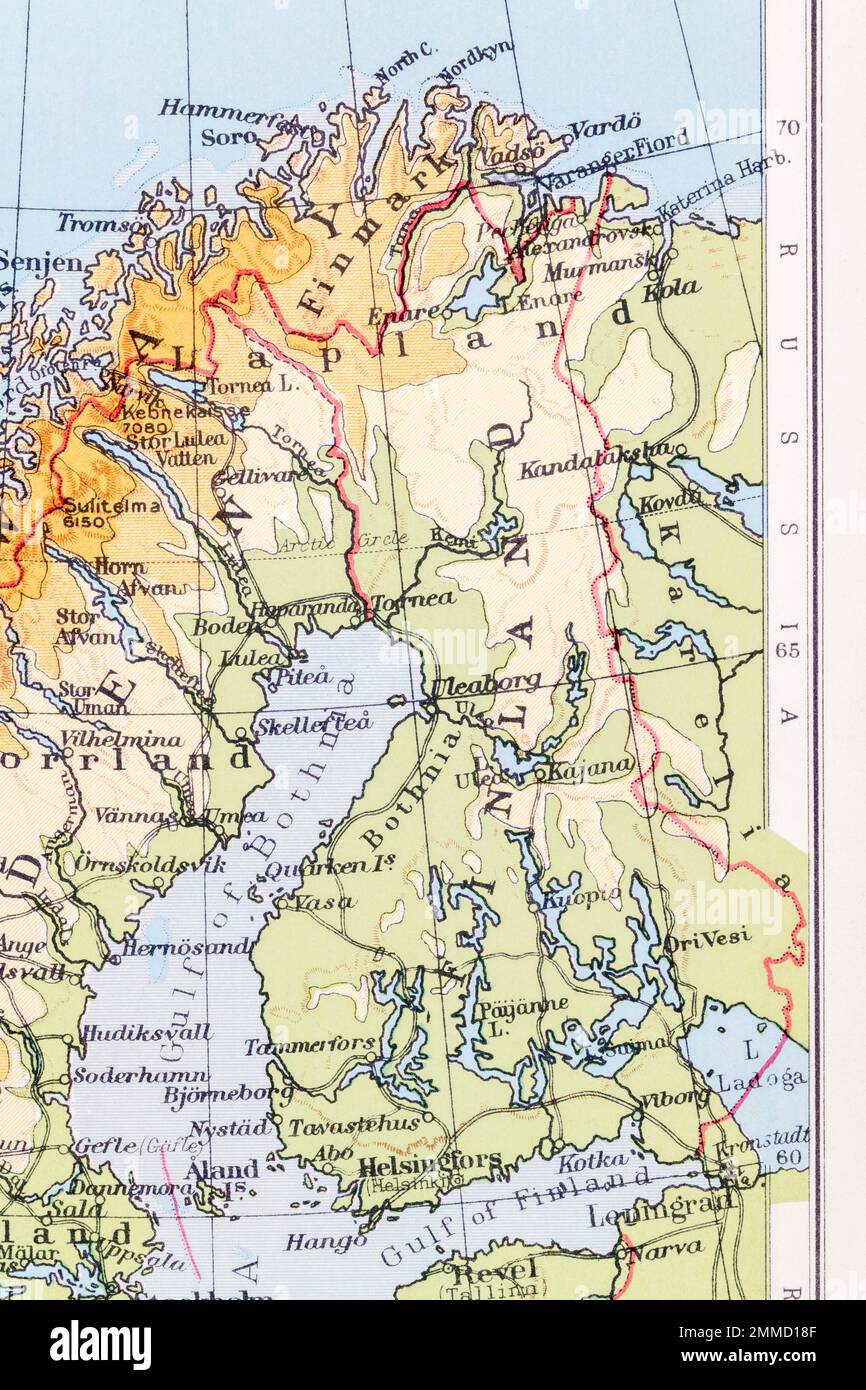
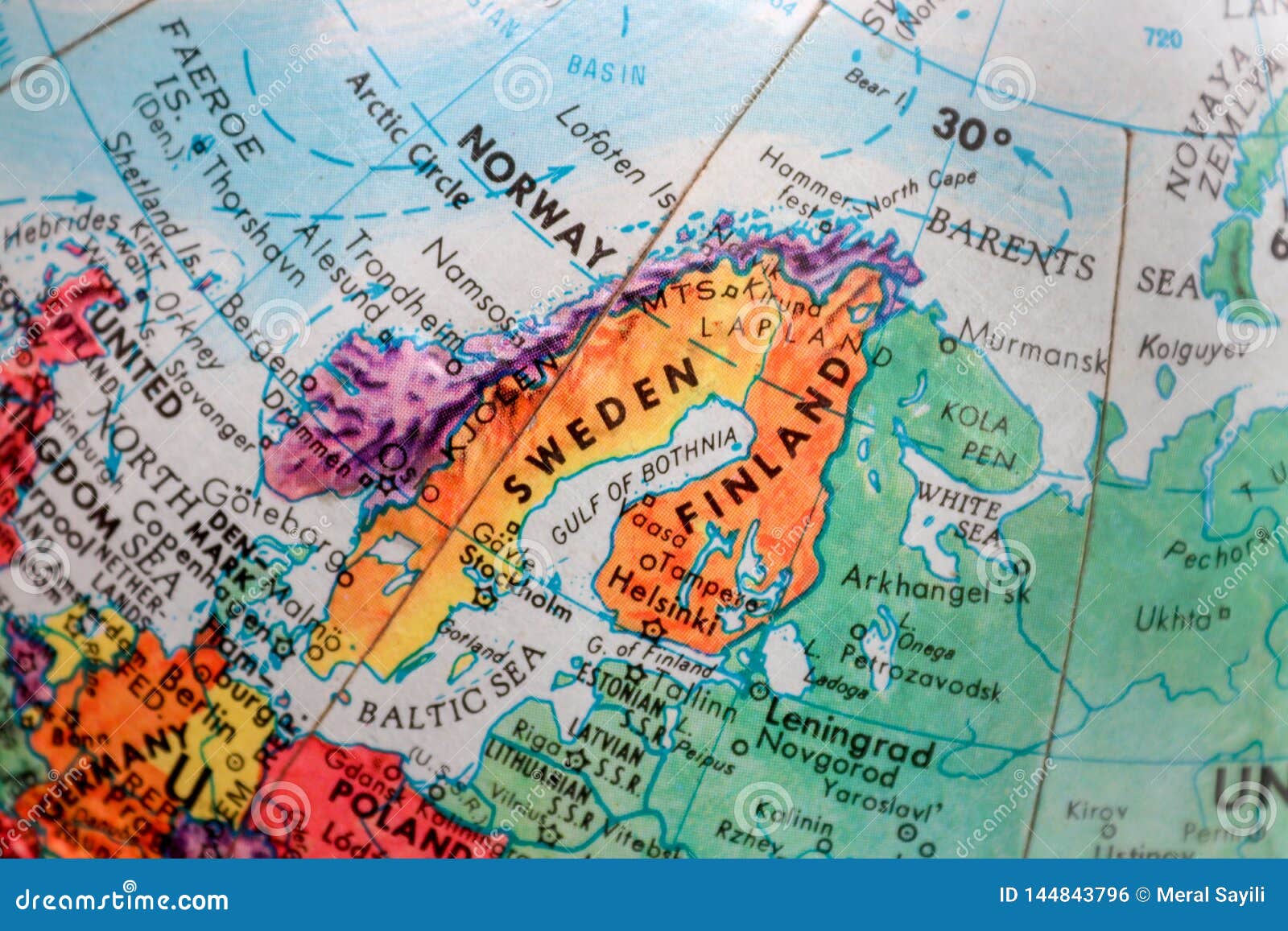
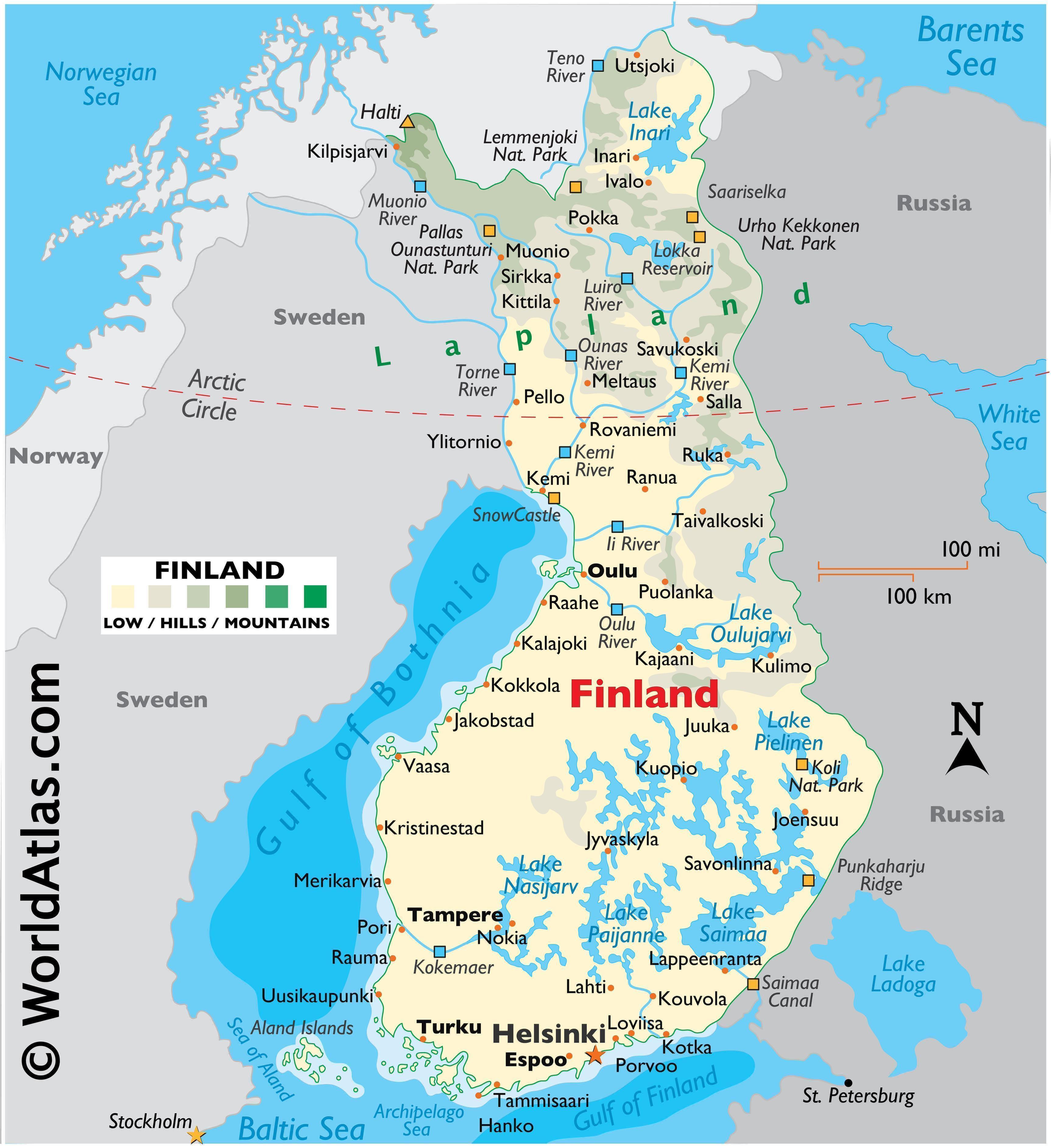
The map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia reveals a complex tapestry of historical interactions, cultural exchanges, and geopolitical dynamics. Situated in Northern Europe, this region has witnessed centuries of shifting borders, evolving identities, and enduring connections. Understanding the geographical and historical context of this triangular relationship is crucial for appreciating the present and envisioning the future of these nations.
The Geography of Shared Borders:
The map highlights a shared border between Finland and Russia, stretching over 1,300 kilometers along the eastern boundary of Finland. This border, formed in 1944 after the Winter War and Continuation War, is a legacy of historical conflict and political tension. Sweden, located to the west of Finland, shares a maritime border with Finland and a land border with Russia in the Kola Peninsula. This geographical proximity has fostered trade, cultural exchange, and, at times, political friction throughout history.
Historical Crossroads:
The region’s history is characterized by periods of conflict and cooperation. Finland, historically part of the Kingdom of Sweden, became an autonomous Grand Duchy within the Russian Empire in 1809. This period witnessed significant cultural and linguistic influences from Russia, shaping Finnish identity and language. Sweden, a historical power in the Baltic Sea, maintained close ties with Finland and influenced its political and cultural development.
The 20th century brought significant changes. Finland declared independence in 1917, embarking on a path of neutrality, while Sweden remained neutral throughout the World Wars. However, the Winter War (1939-1940) and Continuation War (1941-1944) between Finland and the Soviet Union left a lasting impact on the region. These conflicts resulted in territorial losses for Finland and a heightened sense of security concerns.
The Post-Cold War Era:
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 ushered in a new era of political and economic transformation for the region. Finland joined the European Union in 1995, strengthening its economic ties with Western Europe. Sweden followed suit in 1995, further integrating the region into the European Union framework.
Despite these changes, the historical relationship between Finland and Russia remains complex. Finland maintains a policy of neutrality while navigating its economic and security interests with Russia. Sweden, while maintaining its neutrality, has actively participated in international security cooperation, particularly within the framework of the European Union.
Cultural Connections and Shared Heritage:
The map reveals more than just geographical boundaries; it showcases deep cultural connections and shared heritage. The Baltic Sea, a vital waterway connecting the three countries, has served as a conduit for trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Linguistic ties, particularly between Finland and Sweden, are evident in shared vocabulary and historical influences. The region boasts a rich cultural landscape, including traditional music, literature, and art, demonstrating shared artistic expressions and historical narratives.
Geopolitical Significance:
The strategic location of Finland, Sweden, and Russia makes the region a significant geopolitical player. Finland’s position between Russia and the European Union makes it a key mediator and bridge between these two power blocs. Sweden’s membership in the European Union and its active role in international security organizations further underscores its importance in regional and global affairs.
Russia, with its vast resources and historical influence, continues to exert a significant presence in the region. Its strategic interests in the Baltic Sea and its relationship with Finland and Sweden remain a key factor in regional security dynamics.
Conclusion:
The map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia is more than a geographical representation; it is a testament to a complex and dynamic history, a tapestry woven with threads of conflict and cooperation, cultural exchange and political tension. Understanding this triangular relationship is crucial for grasping the region’s present and anticipating its future. As these nations navigate the complexities of the 21st century, their shared past and geographical proximity will continue to shape their destinies.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the border between Finland and Russia?
A: The border between Finland and Russia is a result of historical conflicts and political tensions. It represents a legacy of the Winter War and Continuation War, which led to territorial losses for Finland. The border remains a sensitive issue, as it is a reminder of past conflicts and a focal point for current security concerns.
Q: How has Sweden’s relationship with Finland and Russia evolved over time?
A: Sweden has historically maintained close ties with Finland, both culturally and politically. However, its relationship with Russia has been more complex, marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. Since the end of the Cold War, Sweden has sought to strengthen its ties with Finland and other European nations, while maintaining a neutral stance in international affairs.
Q: What are the main cultural connections between Finland, Sweden, and Russia?
A: The region shares a rich cultural heritage, influenced by historical interactions and geographical proximity. Linguistic ties, particularly between Finland and Sweden, are evident in shared vocabulary and historical influences. The Baltic Sea has served as a conduit for trade and cultural exchange, leading to shared traditions in music, literature, and art.
Q: What are the key geopolitical issues in the region?
A: The region faces significant geopolitical challenges, including Russia’s military build-up and its assertive foreign policy. Finland’s strategic location between Russia and the European Union makes it a key mediator and bridge between these two power blocs. Sweden’s active role in international security organizations, particularly within the framework of the European Union, further complicates the geopolitical landscape.
Tips
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps can provide valuable insights into the shifting borders and evolving relationships between Finland, Sweden, and Russia.
- Explore cultural connections: Delving into the shared cultural heritage of the region, including music, literature, and art, can reveal deeper connections and shared narratives.
- Follow current events: Keeping abreast of current events in the region, particularly those related to security and political developments, is essential for understanding the present and anticipating the future.
Conclusion:
The map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia is a powerful tool for understanding the complex history, cultural connections, and geopolitical dynamics of this vital region. It serves as a reminder of the enduring connections between these nations, the challenges they face, and the potential for future cooperation. As the region continues to navigate the challenges of the 21st century, understanding this triangular relationship will be crucial for promoting stability, cooperation, and shared prosperity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Crossroads of History and Geography: Exploring the Map of Finland, Sweden, and Russia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!