A Geographic Exploration of the Nordic and Baltic Regions: Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of the Nordic and Baltic Regions: Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of the Nordic and Baltic Regions: Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of the Nordic and Baltic Regions: Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland
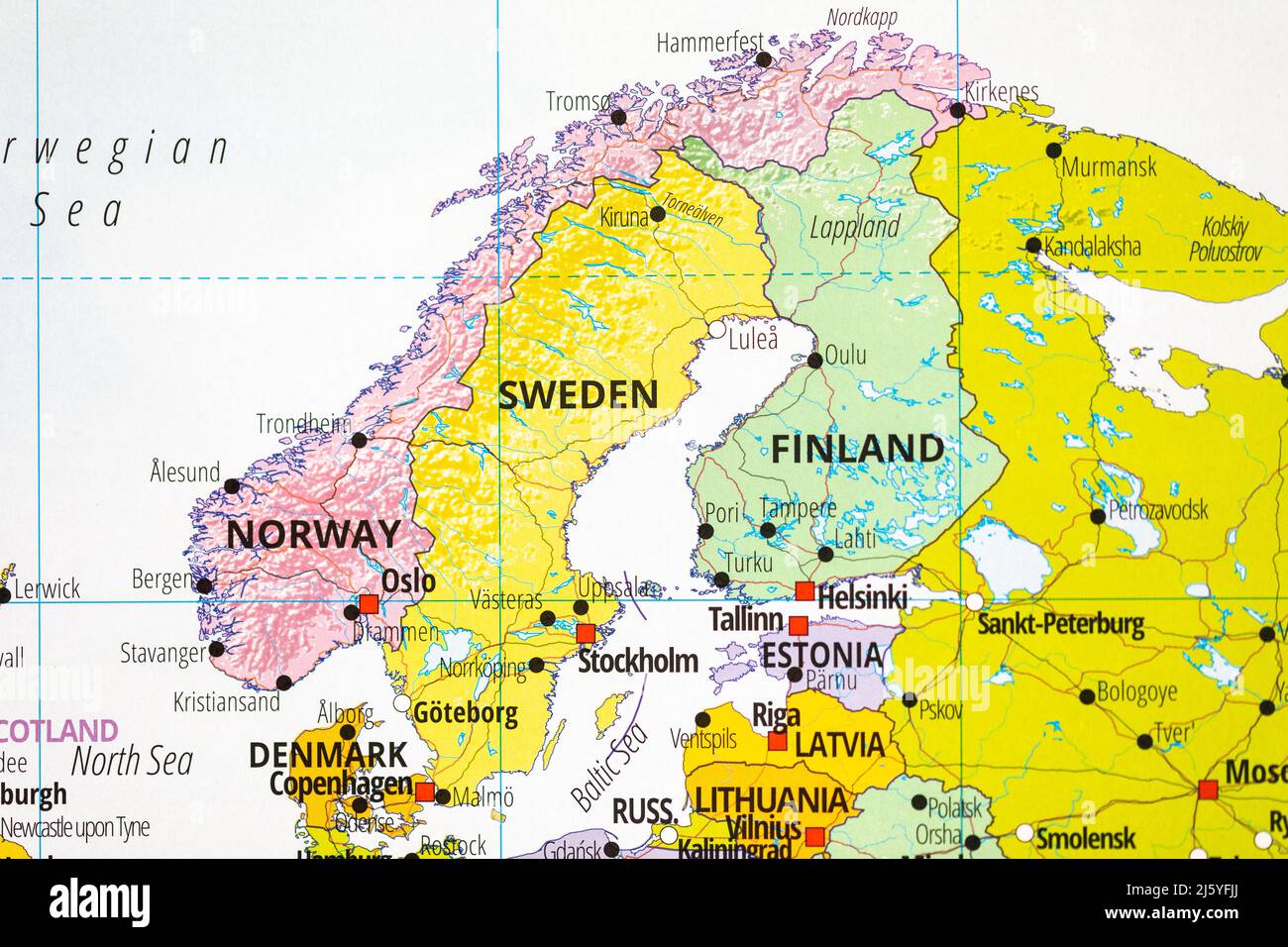
The Nordic and Baltic regions, encompassing Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland, constitute a diverse and fascinating geographical landscape. These countries, sharing a common history and cultural heritage, offer a unique blend of rugged natural beauty, vibrant cities, and rich cultural traditions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the geography, history, culture, and economy of each nation, highlighting their individual characteristics and collective significance.
Norway: The Land of Fjords and Mountains
Norway, situated on the westernmost edge of the Scandinavian Peninsula, is renowned for its dramatic coastline, towering mountains, and vast glaciers. The country’s geography is dominated by the Norwegian Sea, which has carved out countless fjords – deep, narrow inlets surrounded by steep cliffs – that offer breathtaking views and opportunities for exploration. The rugged terrain also features the Scandinavian Mountains, which stretch across the country’s interior, providing ample opportunities for hiking, skiing, and other outdoor activities.
Norway’s history is intricately intertwined with its geography. Its long coastline facilitated trade with other European nations, while its mountainous terrain fostered a sense of independence and self-sufficiency. The country’s rich Viking heritage is evident in its archaeological sites, historical narratives, and cultural traditions.
Today, Norway is a modern, developed nation with a strong economy based on oil and gas production, fishing, and hydropower. Its social welfare system is highly regarded, and the country boasts a high standard of living. Norway’s commitment to environmental sustainability is evident in its renewable energy sources and its focus on conservation.
Sweden: The Land of Lakes and Forests
Sweden, occupying the eastern half of the Scandinavian Peninsula, is characterized by its vast forests, numerous lakes, and rolling plains. The country’s geography is shaped by the Baltic Sea, which provides access to international trade routes, and the Scandinavian Mountains, which create a natural barrier to the west. Sweden’s numerous lakes, including Lake Vänern, the largest in Scandinavia, contribute to its diverse ecosystem and provide opportunities for recreation.
Sweden’s history is marked by periods of war and peace, with its strategic location making it a frequent battleground. The country’s rich cultural heritage includes a strong tradition of literature, music, and design.
Modern Sweden is known for its innovative technology sector, its high standard of living, and its commitment to social equality. The country is a leader in renewable energy, and its environmental policies have earned international recognition.
Denmark: The Land of Islands and Canals
Denmark, situated on the Jutland Peninsula and a collection of islands in the Baltic Sea, offers a unique blend of mainland and island landscapes. The country’s geography is characterized by flat plains, fertile farmland, and a long coastline. The Jutland Peninsula, connected to the rest of Europe, is a major agricultural hub, while the islands, including Zealand, Funen, and Bornholm, provide picturesque scenery and historical significance.
Denmark’s history is rich in Viking lore, with the country playing a significant role in the Viking Age. Its strategic location has also made it a focal point for trade and cultural exchange.
Today, Denmark is a prosperous and highly developed nation with a strong economy based on manufacturing, agriculture, and services. The country is known for its high standard of living, its social welfare system, and its focus on environmental sustainability.
Finland: The Land of Forests and Lakes
Finland, situated in Northern Europe, is characterized by its vast forests, numerous lakes, and unique geographical features, including the Arctic Circle. The country’s geography is shaped by the Baltic Sea, which provides access to international trade routes, and the Scandinavian Mountains, which create a natural barrier to the west. Finland’s numerous lakes, including Lake Saimaa, the largest in Finland, contribute to its diverse ecosystem and provide opportunities for recreation.
Finland’s history is marked by its close ties with Sweden and Russia, with the country experiencing periods of both autonomy and foreign rule. The country’s rich cultural heritage includes a strong tradition of music, literature, and design.
Modern Finland is a technologically advanced nation with a strong economy based on forestry, telecommunications, and technology. The country is known for its high standard of living, its social welfare system, and its commitment to environmental sustainability.
Iceland: The Land of Fire and Ice
Iceland, situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, is a land of dramatic contrasts, with glaciers, volcanoes, hot springs, and geothermal activity shaping its unique landscape. The island’s geography is dominated by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a geological fault line that runs through the island, causing volcanic eruptions and geothermal activity. The country’s glaciers, including Vatnajökull, the largest in Europe, contribute to its breathtaking scenery and offer opportunities for adventure tourism.
Iceland’s history is shaped by its isolation and its volcanic activity, with the country’s early settlers adapting to its challenging environment. The country’s rich cultural heritage includes a strong tradition of folklore, literature, and music.
Modern Iceland is a developed nation with a strong economy based on fishing, tourism, and renewable energy. The country is known for its high standard of living, its commitment to environmental sustainability, and its unique cultural identity.
The Collective Significance of the Nordic and Baltic Regions
The Nordic and Baltic regions, while distinct in their individual characteristics, share a common history, culture, and set of values. They are united by their strong commitment to democracy, social welfare, and environmental sustainability. These nations have consistently ranked high in global indices of human development, happiness, and quality of life.
The region’s collective significance extends beyond its internal strengths. The Nordic and Baltic countries are actively engaged in international cooperation, contributing to global initiatives in areas such as climate change, human rights, and sustainable development. Their shared values and commitment to international collaboration serve as a model for other nations seeking to build a more peaceful and prosperous world.
FAQs about the Nordic and Baltic Regions
Q1: What are the official languages of the Nordic and Baltic countries?
A: Each country has its own official language:
- Norway: Norwegian (Bokmål and Nynorsk)
- Sweden: Swedish
- Denmark: Danish
- Finland: Finnish and Swedish
- Iceland: Icelandic
Q2: What are the major religions practiced in the Nordic and Baltic countries?
A: The majority of the population in these countries adheres to Christianity, primarily Lutheranism. However, there are also significant minorities of other faiths, including Islam, Buddhism, and Hinduism.
Q3: What are the major industries in the Nordic and Baltic countries?
A: The major industries vary by country, but common sectors include:
- Norway: Oil and gas production, fishing, hydropower
- Sweden: Manufacturing, technology, forestry
- Denmark: Manufacturing, agriculture, services
- Finland: Forestry, telecommunications, technology
- Iceland: Fishing, tourism, renewable energy
Q4: What are the key challenges facing the Nordic and Baltic countries?
A: The Nordic and Baltic countries face a range of challenges, including:
- Climate change: The region is experiencing the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and more extreme weather events.
- Economic inequality: Despite high standards of living, there is growing economic inequality within some of these countries.
- Immigration and integration: The region is facing challenges related to immigration and the integration of immigrants into society.
- Aging populations: The Nordic and Baltic countries are experiencing aging populations, which presents challenges for healthcare, social services, and economic growth.
Tips for Traveling to the Nordic and Baltic Regions
- Plan your trip in advance: These countries are popular tourist destinations, so it is advisable to book flights, accommodations, and tours well in advance, especially during peak season.
- Pack for all weather conditions: The weather in the Nordic and Baltic regions can be unpredictable, so it is essential to pack for all seasons, even during the summer months.
- Learn a few basic phrases in the local language: While English is widely spoken, learning a few basic phrases in the local language will enhance your travel experience and show respect for the local culture.
- Embrace the outdoors: The Nordic and Baltic regions offer a wide range of outdoor activities, from hiking and skiing to kayaking and fishing.
- Enjoy the local cuisine: The Nordic and Baltic regions have unique culinary traditions, so be sure to try some of the local dishes.
Conclusion
The Nordic and Baltic regions, comprising Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland, offer a unique and rewarding travel experience. These countries, with their stunning landscapes, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage, provide ample opportunities for exploration, adventure, and cultural immersion. Their shared values of democracy, social welfare, and environmental sustainability serve as a model for other nations seeking to build a more peaceful and prosperous world. Understanding the geography, history, culture, and economy of these nations provides a deeper appreciation for their individual characteristics and collective significance in the global landscape.

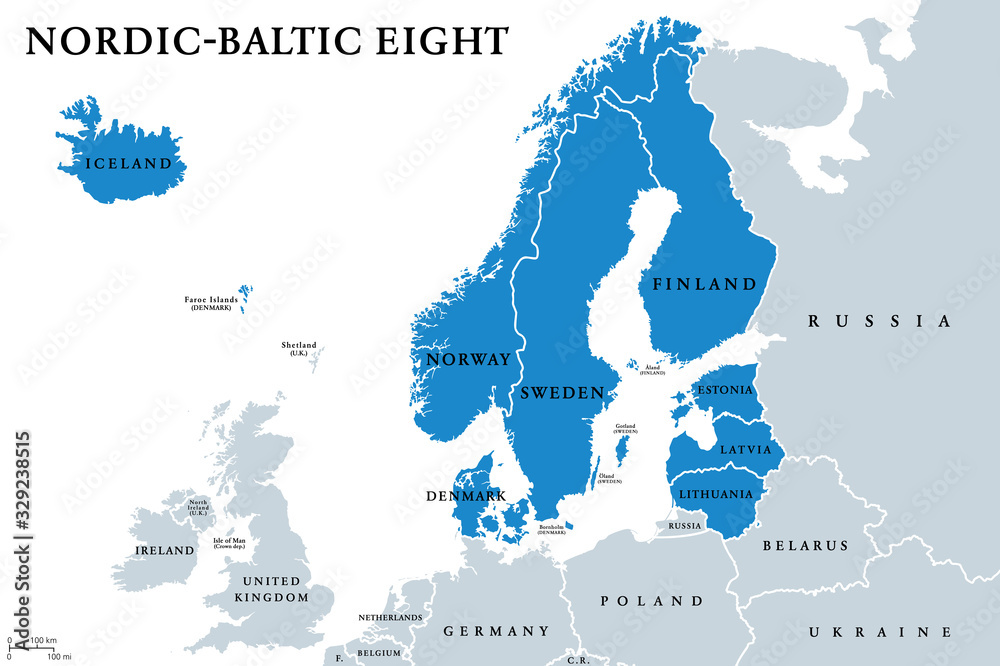

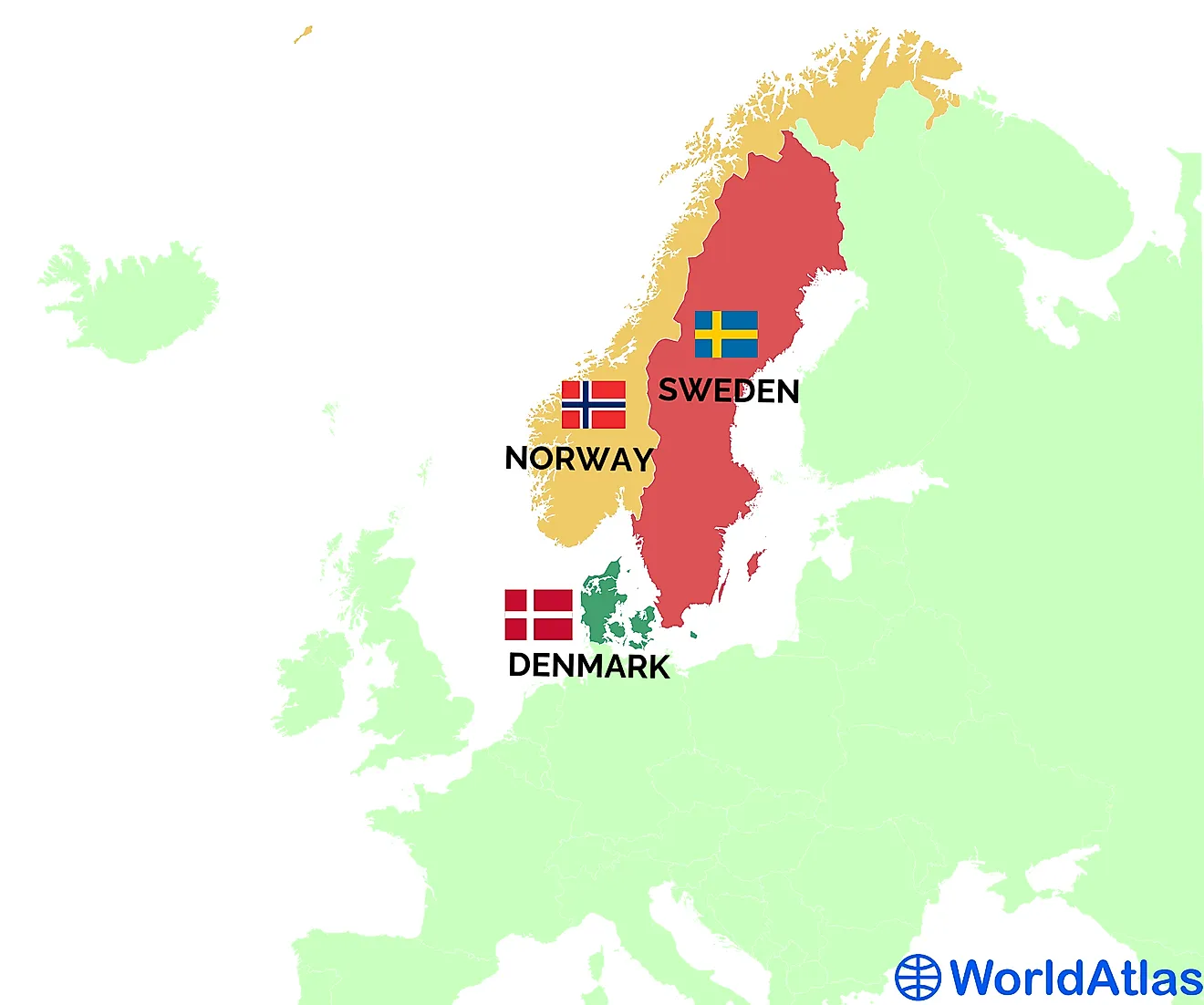


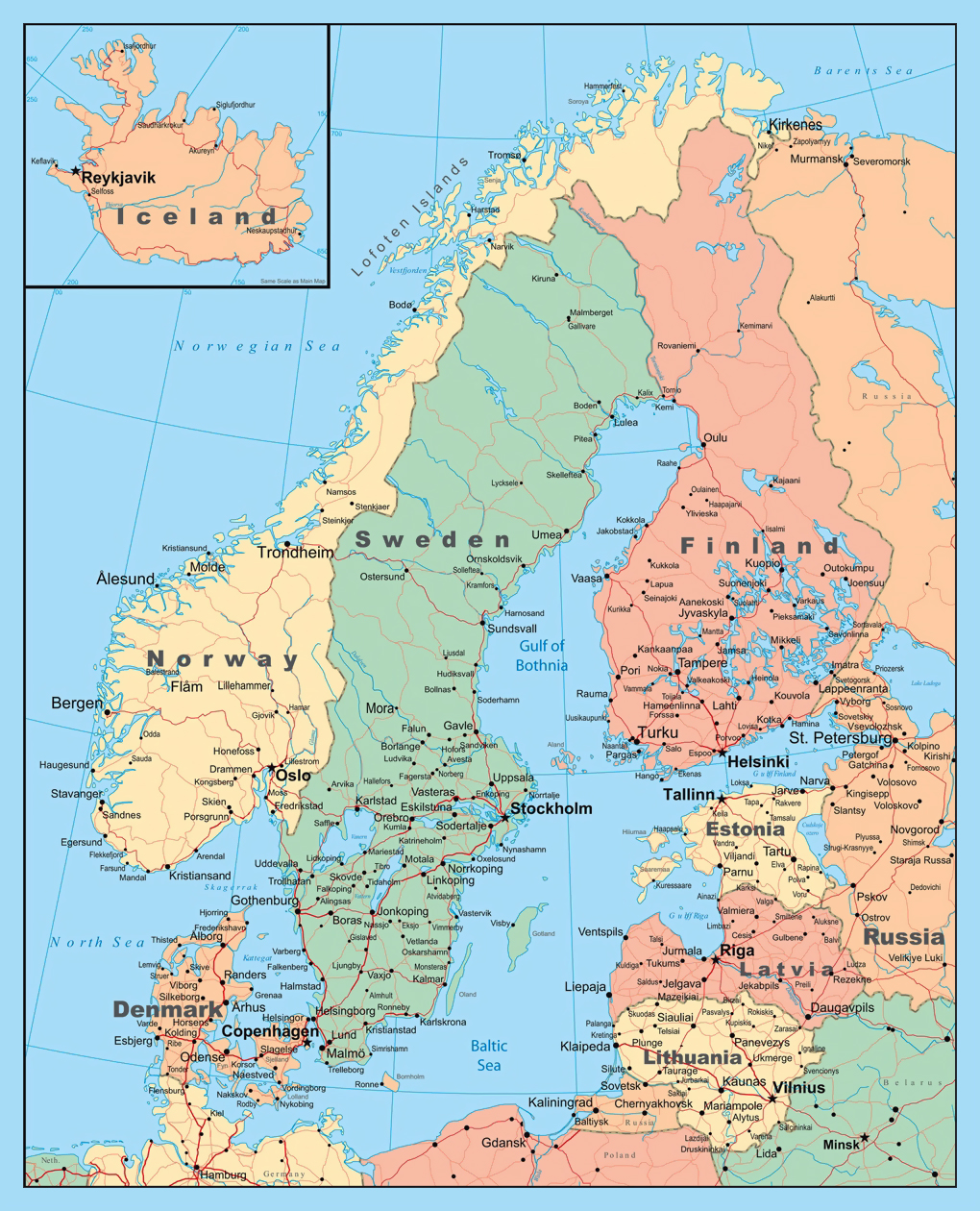

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of the Nordic and Baltic Regions: Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!