A Geographical Exploration of Scandinavia: Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of Scandinavia: Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of Scandinavia: Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of Scandinavia: Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark
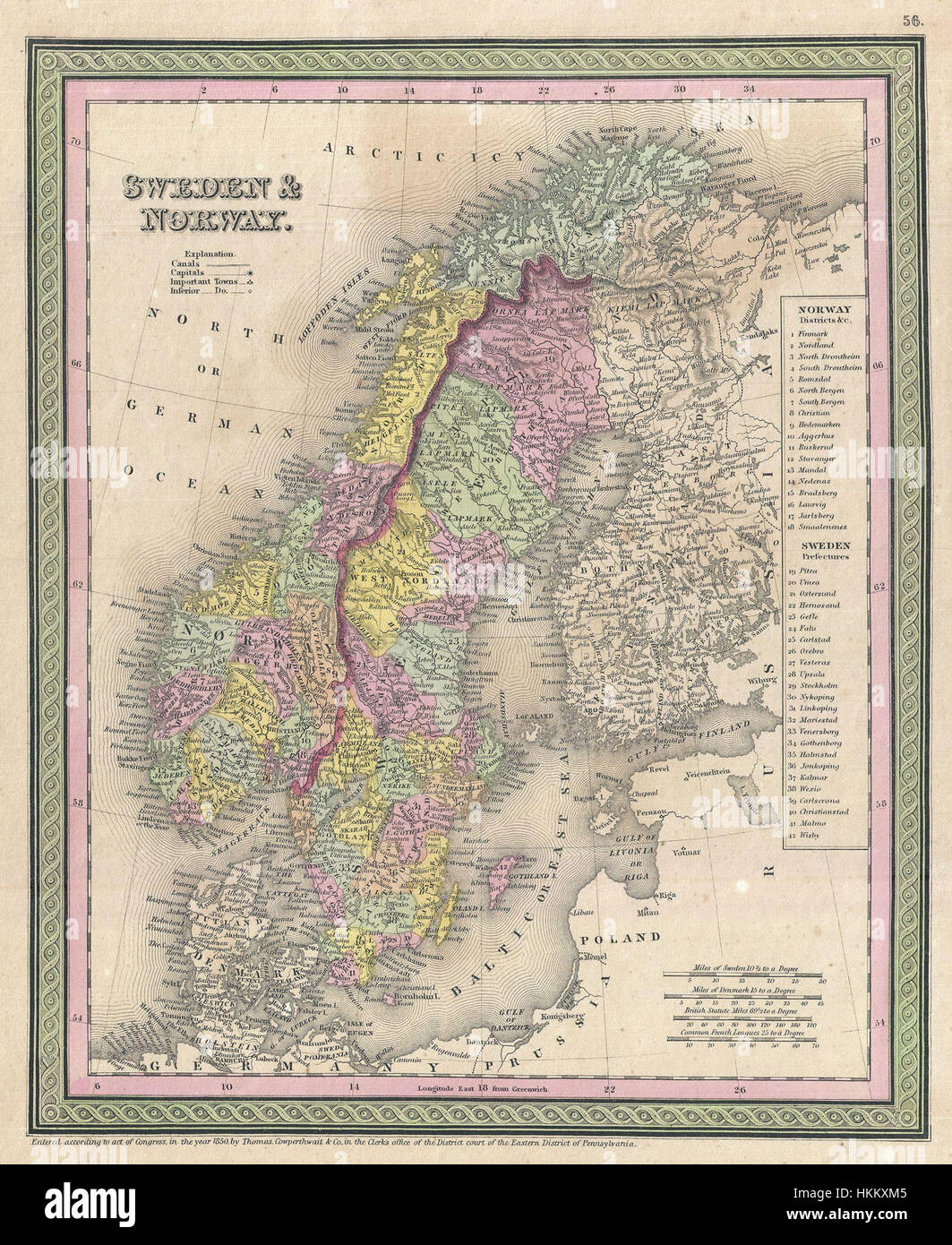
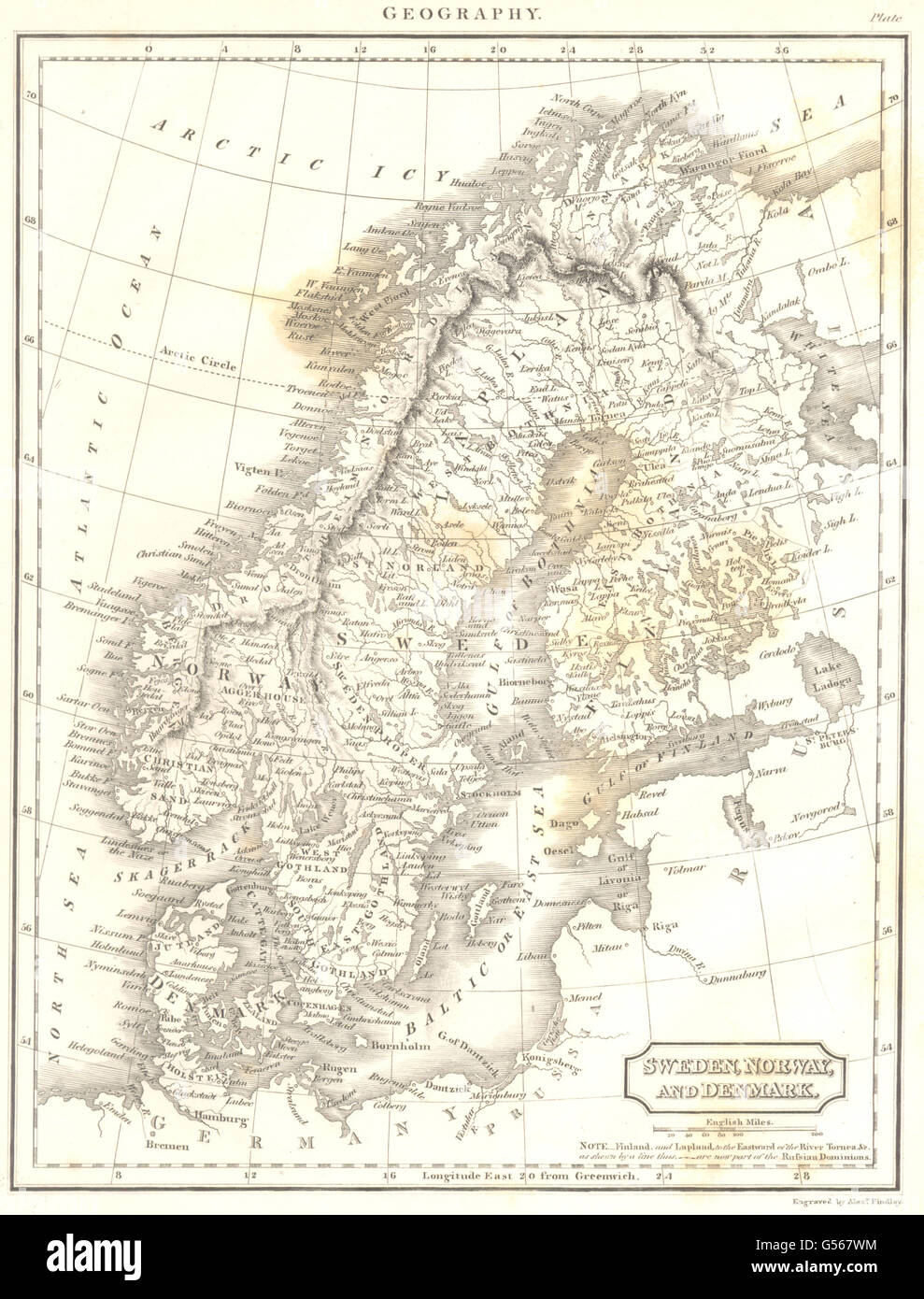
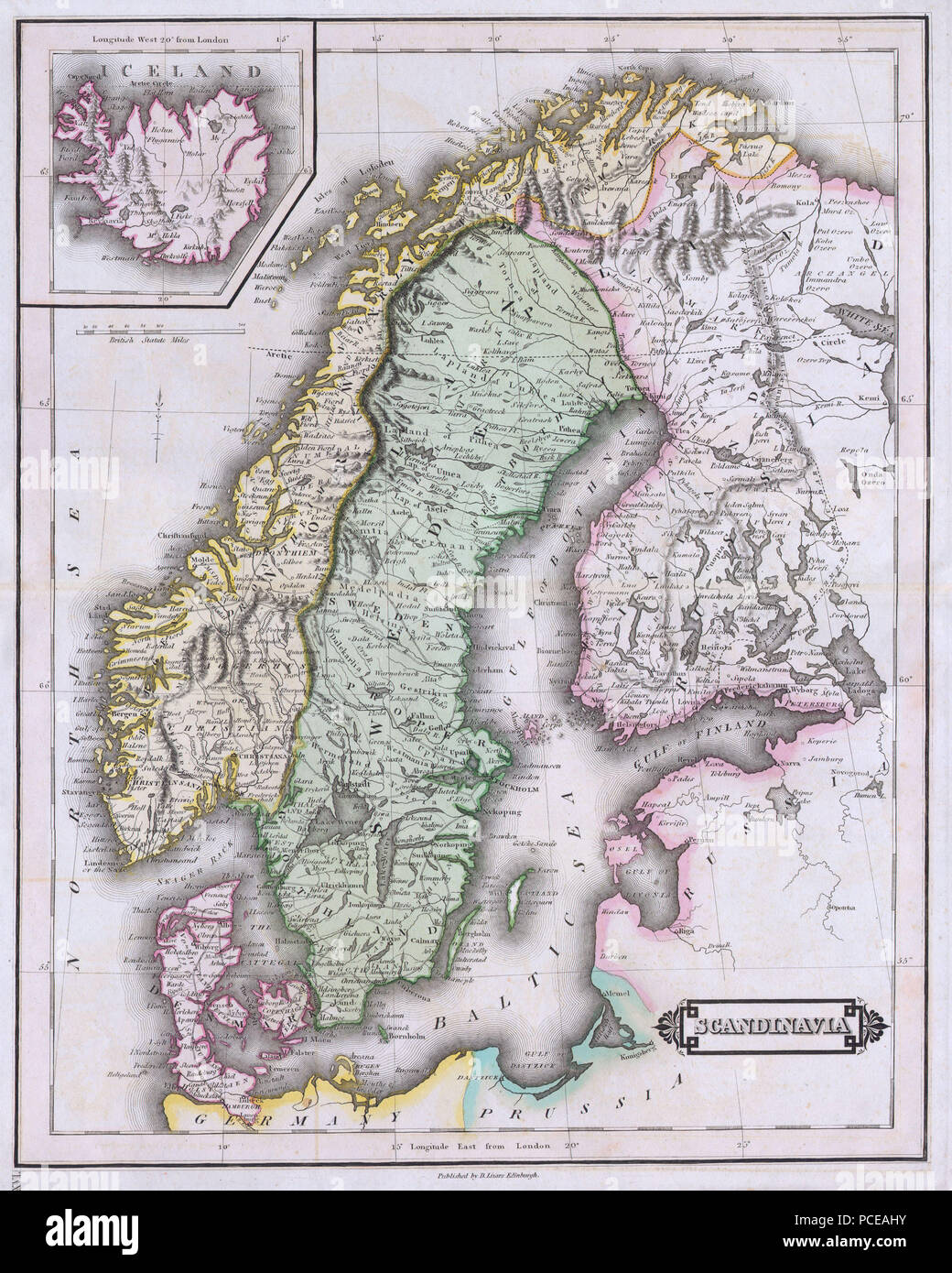
The region known as Scandinavia, often encompassing Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark, holds a unique place in the world’s geography and history. While the term "Scandinavia" historically referred solely to Sweden, Norway, and Denmark, its modern usage often includes Finland, acknowledging the shared cultural and linguistic ties that bind these Nordic nations. Understanding the geographical features and relationships of these countries requires a detailed examination of their individual landscapes, their shared history, and the interconnectedness they possess.
Delving into the Geography
A map of Scandinavia reveals a tapestry of diverse landscapes, from the dramatic fjords of Norway to the vast, forested expanse of Sweden and Finland. The region’s location at the northern edge of Europe contributes to its unique climate, with long, cold winters and short, cool summers.
Sweden:
- The largest of the four nations, Sweden stretches across the Scandinavian Peninsula, encompassing a mix of forests, mountains, and lakes.
- Its coastline boasts numerous islands and archipelagos, particularly in the south and east.
- The country’s interior is dominated by the Scandinavian Mountains, which rise to over 2,000 meters in elevation.
- Sweden’s landscape is characterized by its vast forests, which cover nearly two-thirds of the country, and its numerous lakes, making it a haven for nature enthusiasts.
Finland:
- Situated on the eastern side of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Finland shares a long border with Sweden.
- The country’s landscape is dominated by forests and lakes, with a vast network of waterways.
- Finland is known for its numerous islands, particularly in the southwestern archipelago.
- The country’s northern regions feature the Lapland region, known for its stunning wilderness and the Northern Lights.
Norway:
- Situated on the western side of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Norway boasts a dramatic and rugged coastline.
- Its landscape is characterized by towering mountains, deep fjords, and glaciers.
- Norway’s coastline is one of the longest in the world, with numerous islands and archipelagos.
- The country’s mountains are home to some of the largest glaciers in Europe, including the Jostedalsbreen glacier.
Denmark:
- While not geographically located on the Scandinavian Peninsula, Denmark is considered a part of Scandinavia due to its historical, cultural, and linguistic connections.
- It is a low-lying country, with most of its landmass situated on a peninsula.
- Denmark’s landscape is characterized by rolling hills, fertile plains, and numerous islands.
- The country’s coastline is dotted with beaches, harbors, and inlets.
The Intertwined History
The historical ties between these countries run deep, shaping their identities and influencing their present-day relationships. The Viking Age, a period of expansion and exploration from the 8th to the 11th centuries, saw these nations play a pivotal role in shaping the history of Europe. The Vikings, originating primarily from Scandinavia, established trade routes, raided settlements, and colonized territories across the continent.
The shared history of these countries also includes periods of conflict and cooperation. While they have engaged in wars with each other, they have also collaborated on various ventures, including trade, diplomacy, and defense. The development of the Nordic Council in 1952, an intergovernmental organization promoting cooperation between the Nordic countries, further cemented their shared interests and goals.
The Benefits of Collaboration
The close geographic proximity and interconnected history of these countries have fostered a strong sense of regional cooperation. The Nordic Council serves as a platform for collaboration on issues of common concern, including economic development, environmental protection, and social welfare. The Nordic countries have a long history of social welfare programs, ensuring high standards of living and social mobility for their citizens.
Furthermore, their shared cultural heritage and values have fostered a strong sense of community and understanding among the Nordic people. This cultural exchange is evident in their shared traditions, languages, and artistic expressions.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the difference between Scandinavia and the Nordic countries?
- A: While the terms are often used interchangeably, Scandinavia historically refers to Sweden, Norway, and Denmark. The Nordic countries include these three nations, along with Finland and Iceland.
-
Q: What is the most populated country in Scandinavia?
- A: Sweden is the most populous country in Scandinavia.
-
Q: What are the official languages of the Scandinavian countries?
- A: Sweden, Norway, and Denmark have official languages based on the Scandinavian branch of the North Germanic languages. Finland’s official languages are Finnish and Swedish.
-
Q: What are the main industries in the Scandinavian countries?
- A: The Scandinavian countries have diverse economies, with significant contributions from industries such as forestry, fishing, manufacturing, tourism, and technology.
Tips for Travelers
- Embrace the outdoors: Scandinavia offers a wealth of outdoor activities, from hiking and skiing to kayaking and fishing.
- Learn a few phrases: While English is widely spoken, learning a few basic phrases in the local language will enhance your travel experience.
- Respect the environment: The Scandinavian countries are renowned for their commitment to environmental sustainability. Be mindful of your impact on the environment during your travels.
- Try the local cuisine: From Swedish meatballs to Norwegian salmon, the Scandinavian countries offer a unique and delicious culinary experience.
Conclusion
The Scandinavian region, encompassing Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark, is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes, rich history, and strong cultural ties. Its geographical features, shared heritage, and collaborative spirit have shaped the region’s identity and fostered a sense of community among its inhabitants. Whether exploring the breathtaking fjords of Norway, the vast forests of Sweden and Finland, or the charming cities of Denmark, Scandinavia offers a unique and enriching travel experience. Understanding the region’s geography and history provides a deeper appreciation for its remarkable diversity and enduring legacy.
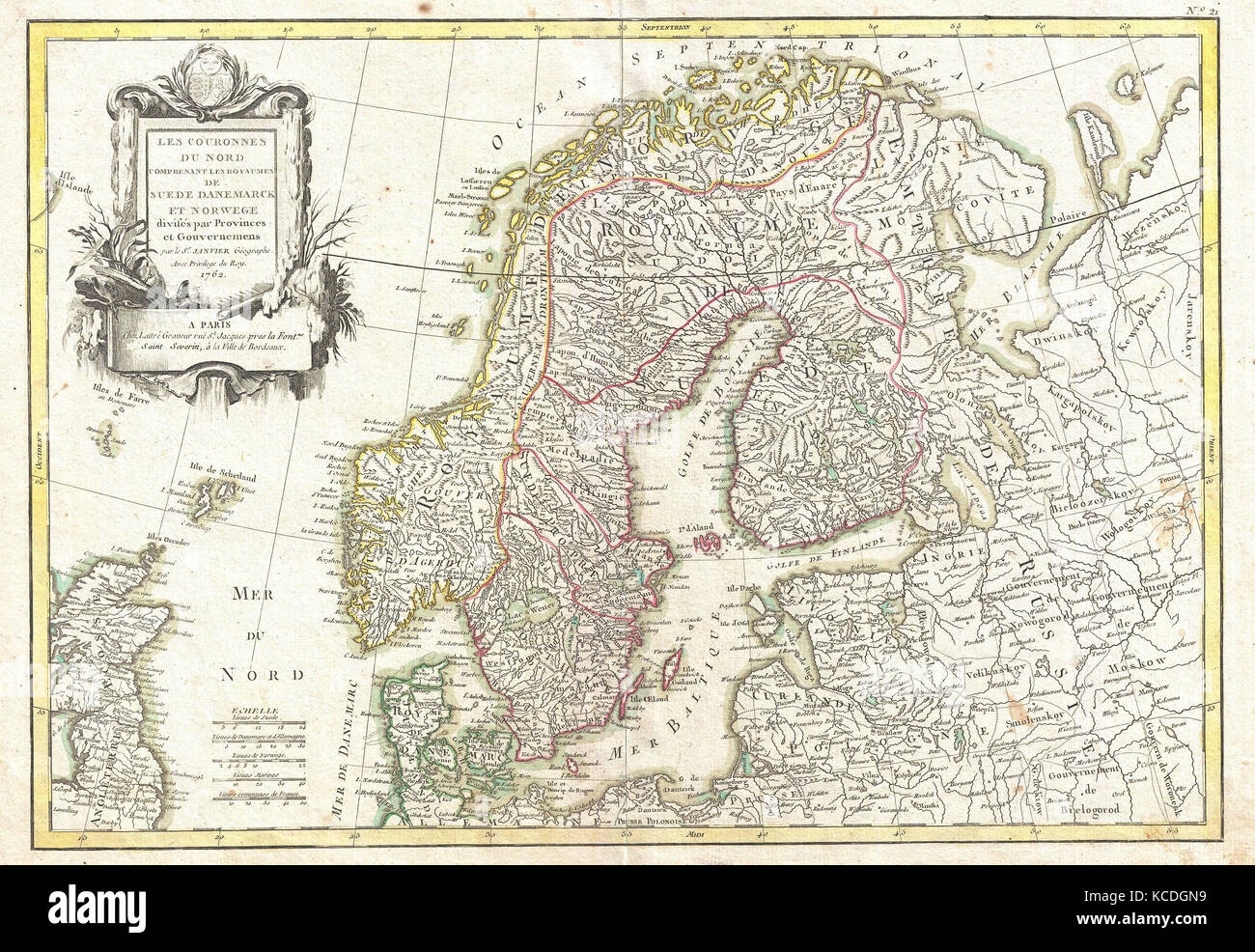
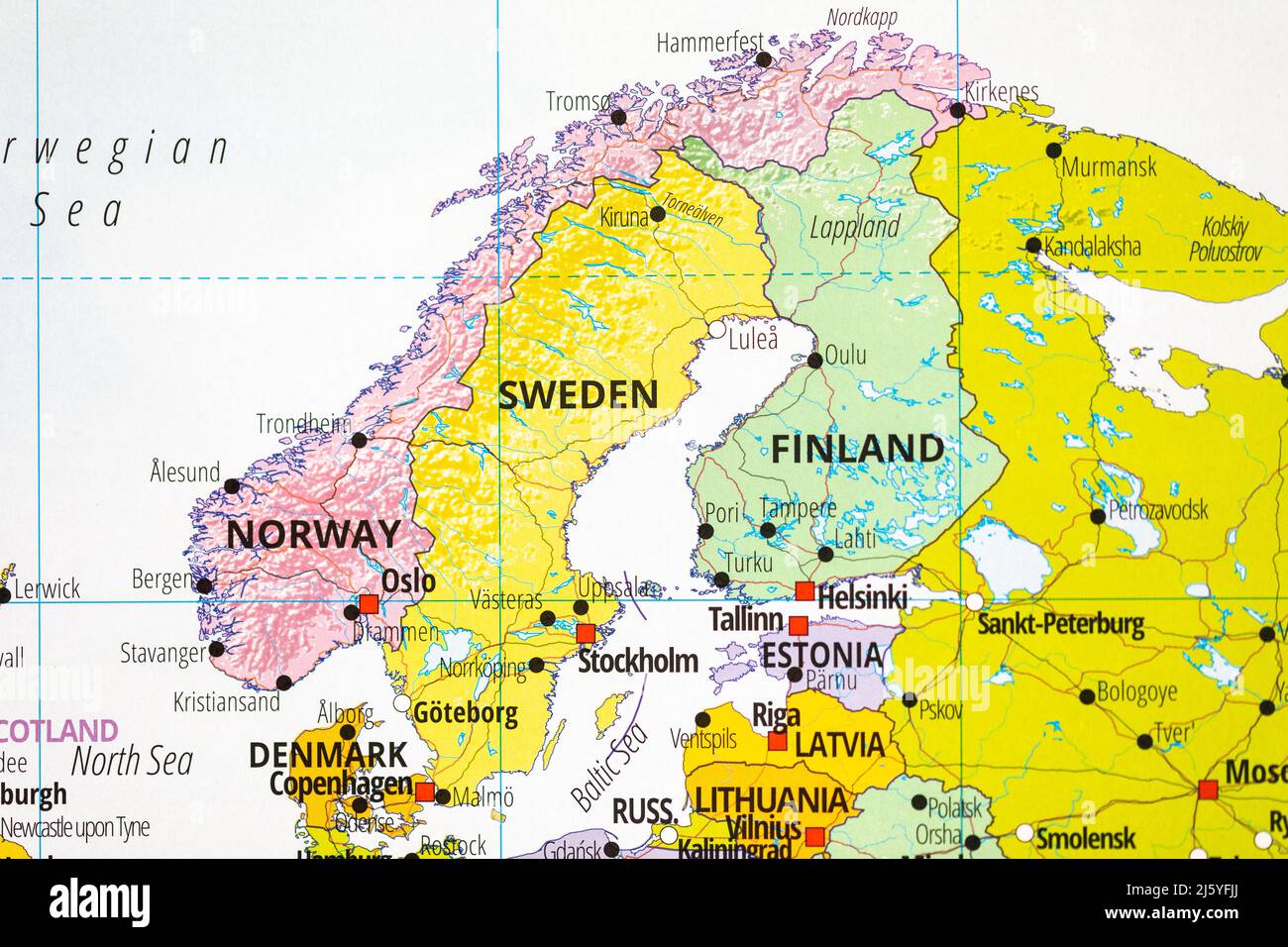
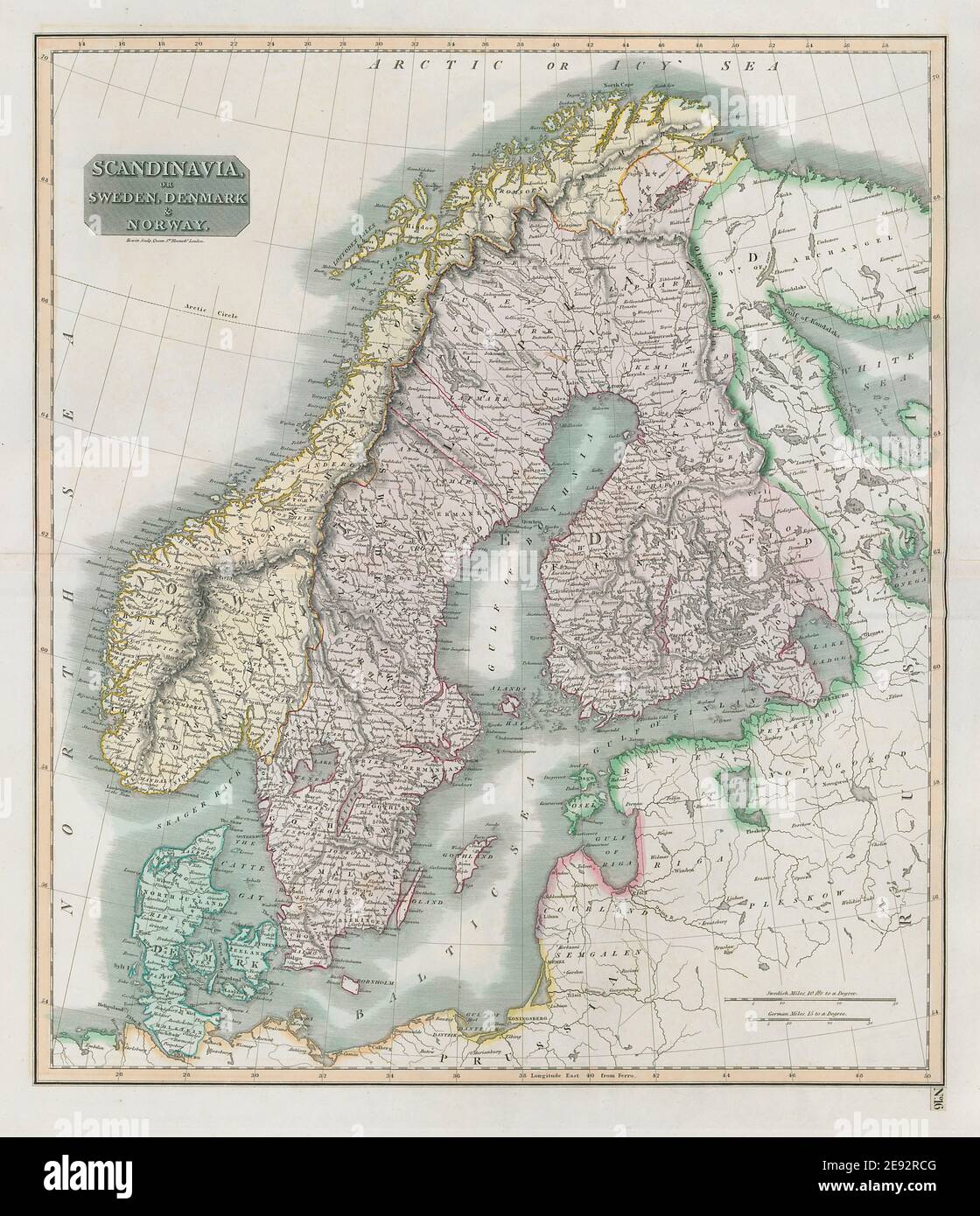



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of Scandinavia: Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!