A Geographical Tapestry: Unveiling the Nordic Landscape of Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway
Related Articles: A Geographical Tapestry: Unveiling the Nordic Landscape of Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Tapestry: Unveiling the Nordic Landscape of Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Tapestry: Unveiling the Nordic Landscape of Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway

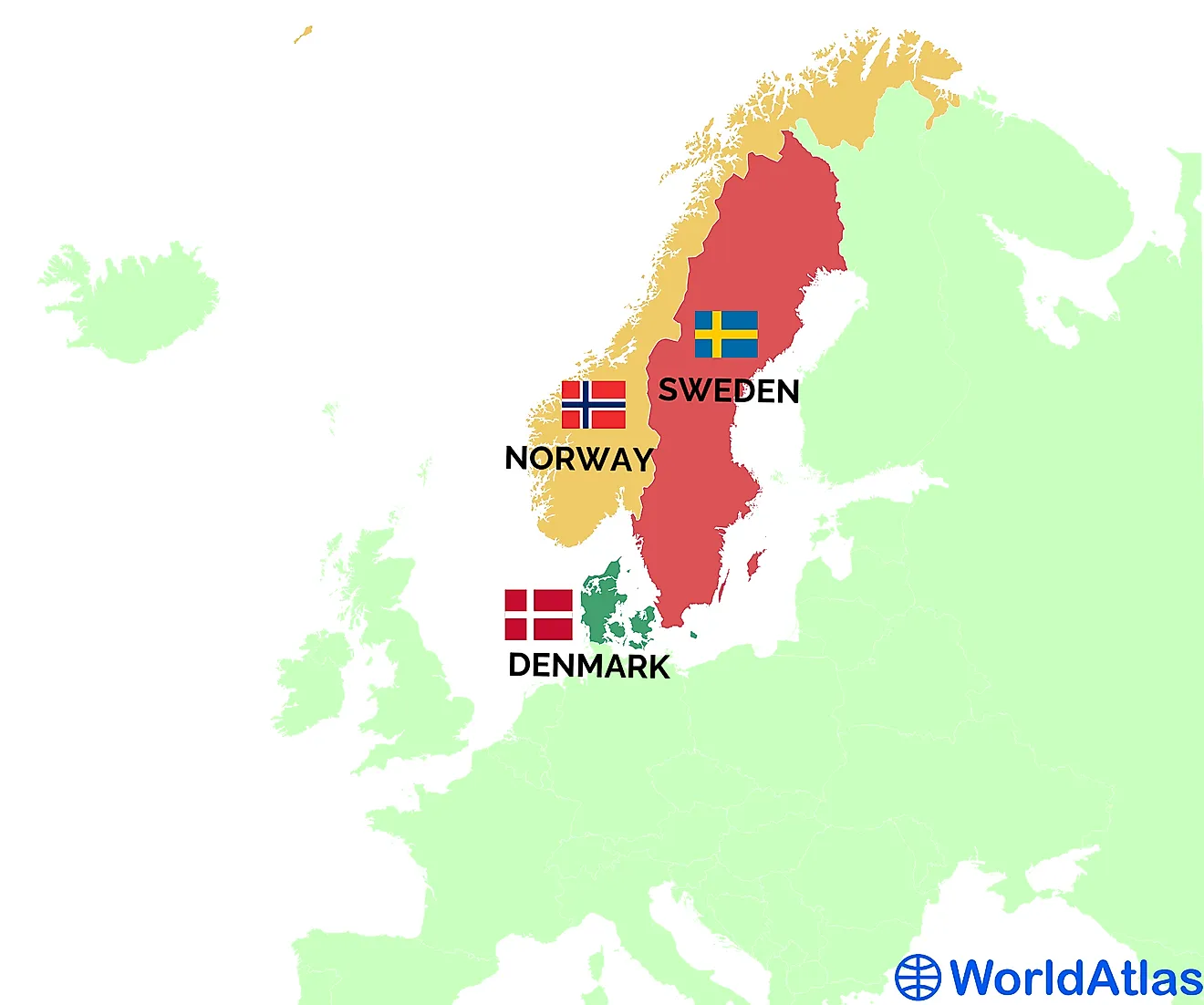
The Nordic region, a captivating tapestry of rugged landscapes, vibrant cultures, and rich histories, is home to four distinct nations: Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway. Understanding their geographical relationships, interwoven through the intricate web of land and water, provides crucial insight into their shared past, present, and future. This article delves into the unique characteristics of each nation, highlighting their geographical features, historical influences, and present-day connections.
Denmark: The Gateway to Scandinavia
Located in Northern Europe, Denmark occupies the Jutland Peninsula and 443 islands, with only 44 inhabited. Its strategic position on the North Sea, connecting the Baltic Sea to the Atlantic Ocean, has historically made Denmark a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange. The country’s flat terrain, punctuated by rolling hills and vast agricultural fields, contrasts sharply with its iconic coastline, characterized by dramatic cliffs and picturesque fjords.
Denmark’s proximity to its Scandinavian neighbors, particularly Sweden, has profoundly shaped its history and culture. The two nations share a long and complex relationship, marked by both conflict and cooperation. The Øresund Bridge, connecting Copenhagen to Malmö, Sweden, serves as a tangible symbol of their interconnectedness, facilitating trade, tourism, and cultural exchange.
Finland: Land of a Thousand Lakes
Finland, nestled between Sweden and Russia, is a land of vast forests, sparkling lakes, and rugged terrain. Its landscape is defined by its numerous lakes, covering over 10% of the country’s area, and its vast boreal forests, stretching across the north. The country’s terrain is characterized by rolling hills and low-lying mountains, with the highest peak, Halti, rising to over 1,300 meters.
Finland’s history is intricately linked to its geographic location. Its proximity to Russia has shaped its political and cultural development, leading to periods of both conflict and collaboration. The country’s unique language, Finnish, is a Finno-Ugric language, distinct from the Germanic languages spoken in its Scandinavian neighbors.
Sweden: The Land of the Vikings
Sweden, the largest of the Nordic countries, boasts a diverse landscape, ranging from the flat plains of the south to the majestic mountains of the north. Its western coast is characterized by a jagged coastline dotted with numerous islands, while the interior is dominated by vast forests and numerous lakes. The country’s highest peak, Kebnekaise, reaches over 2,100 meters, making it a popular destination for hikers and skiers.
Sweden’s history is deeply intertwined with its geographical features. Its long coastline, rich in resources, enabled the Vikings to establish a vast trading network across Europe. The country’s vast forests provided timber for shipbuilding, while its mineral resources fueled its industrial development.
Norway: The Land of the Fjords
Norway, a country of breathtaking natural beauty, is known for its dramatic coastline, characterized by deep fjords, towering mountains, and vast glaciers. The country’s rugged terrain, with its numerous fjords and mountains, has shaped its history and culture. Its long and narrow coastline, stretching for over 25,000 kilometers, offers stunning views and diverse ecosystems.
Norway’s geographical isolation has played a significant role in its development. The country’s mountainous terrain and challenging climate have presented obstacles to transportation and communication, contributing to the development of a strong sense of national identity.
Interconnectedness and Collaboration
While each Nordic nation possesses distinct characteristics, their geographical proximity and shared history have fostered strong connections and collaboration. The region has a long history of cultural exchange, with shared traditions, languages, and values.
The Nordic Council, established in 1952, serves as a platform for cooperation between the Nordic countries, promoting collaboration in areas such as trade, research, and education. The region also boasts a strong sense of solidarity, working together on issues such as environmental protection, sustainable development, and social welfare.
The Importance of Understanding the Nordic Landscape
Understanding the geographical relationships between Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway is crucial for comprehending their historical development, cultural identities, and present-day challenges.
The region’s shared history, shaped by its unique geography, has fostered a sense of unity and cooperation. Their interconnectedness, evident in their shared resources, cultural exchanges, and political collaboration, underscores the importance of understanding the Nordic landscape as a dynamic and interconnected entity.
FAQs
Q: What are the main geographical features of the Nordic region?
A: The Nordic region is characterized by diverse landscapes, including rugged mountains, vast forests, numerous lakes, and dramatic coastlines. Each country possesses unique geographical features: Denmark’s flat terrain and numerous islands, Finland’s thousands of lakes and vast forests, Sweden’s diverse landscape ranging from flat plains to majestic mountains, and Norway’s dramatic coastline with deep fjords and towering mountains.
Q: What are the historical connections between the Nordic countries?
A: The Nordic countries share a long and complex history, marked by both conflict and cooperation. Their proximity and shared resources have fostered cultural exchange and trade. The Vikings, originating from Scandinavia, established a vast trading network across Europe. The region’s history also includes periods of conflict, particularly between Denmark and Sweden.
Q: How do the Nordic countries cooperate today?
A: The Nordic countries cooperate through various platforms, including the Nordic Council, which promotes collaboration in areas such as trade, research, and education. The region also shares a strong sense of solidarity, working together on issues like environmental protection, sustainable development, and social welfare.
Q: What are the challenges facing the Nordic region?
A: The Nordic region faces challenges such as climate change, economic inequality, and immigration. The region is committed to addressing these challenges through collaboration and sustainable development.
Tips
- Travel to the Nordic region: Experience the diverse landscapes and rich cultures of Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway firsthand.
- Learn about Nordic history and culture: Explore the region’s fascinating past and its unique cultural traditions.
- Engage with Nordic literature and film: Immerse yourself in the region’s rich literary and cinematic heritage.
- Support Nordic businesses and organizations: Contribute to the region’s economic growth and social progress.
Conclusion
The Nordic landscape, encompassing Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway, is a testament to the power of geography to shape history, culture, and identity. The region’s shared past, present, and future are intertwined through its intricate web of land and water, fostering a sense of unity and collaboration. Understanding the unique characteristics of each nation and their interconnectedness provides valuable insight into the region’s dynamic and evolving landscape. As the Nordic region continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its geographical tapestry will continue to shape its destiny.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Tapestry: Unveiling the Nordic Landscape of Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!