A Glimpse into Finland’s Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map
Related Articles: A Glimpse into Finland’s Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Glimpse into Finland’s Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Glimpse into Finland’s Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map
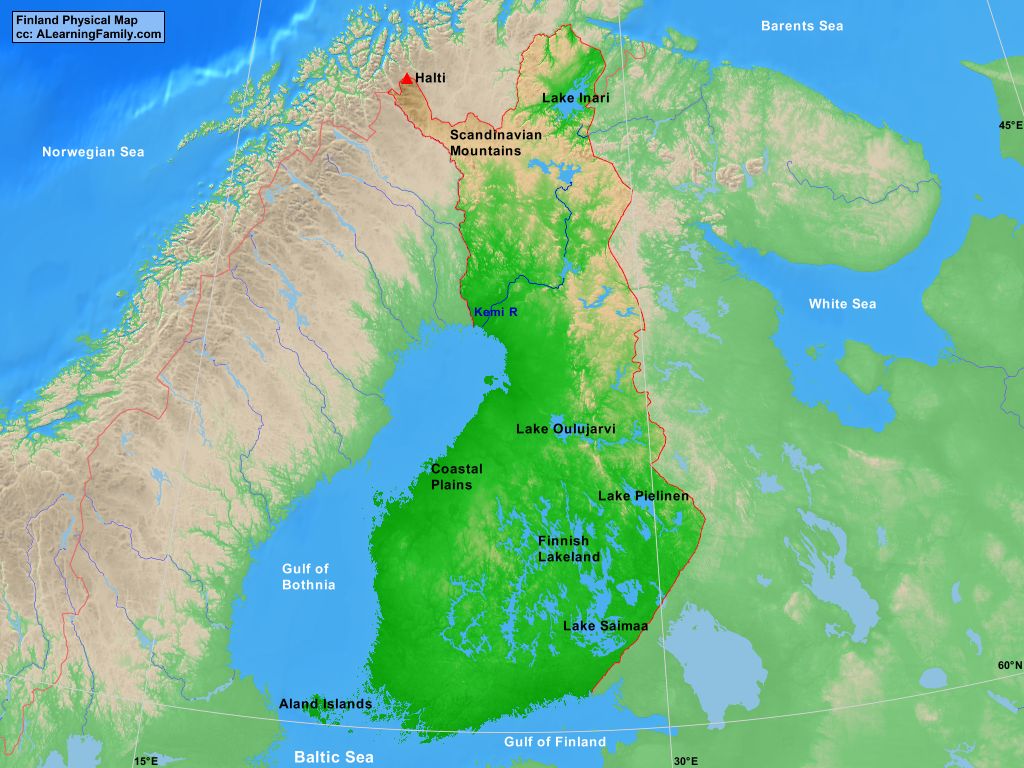
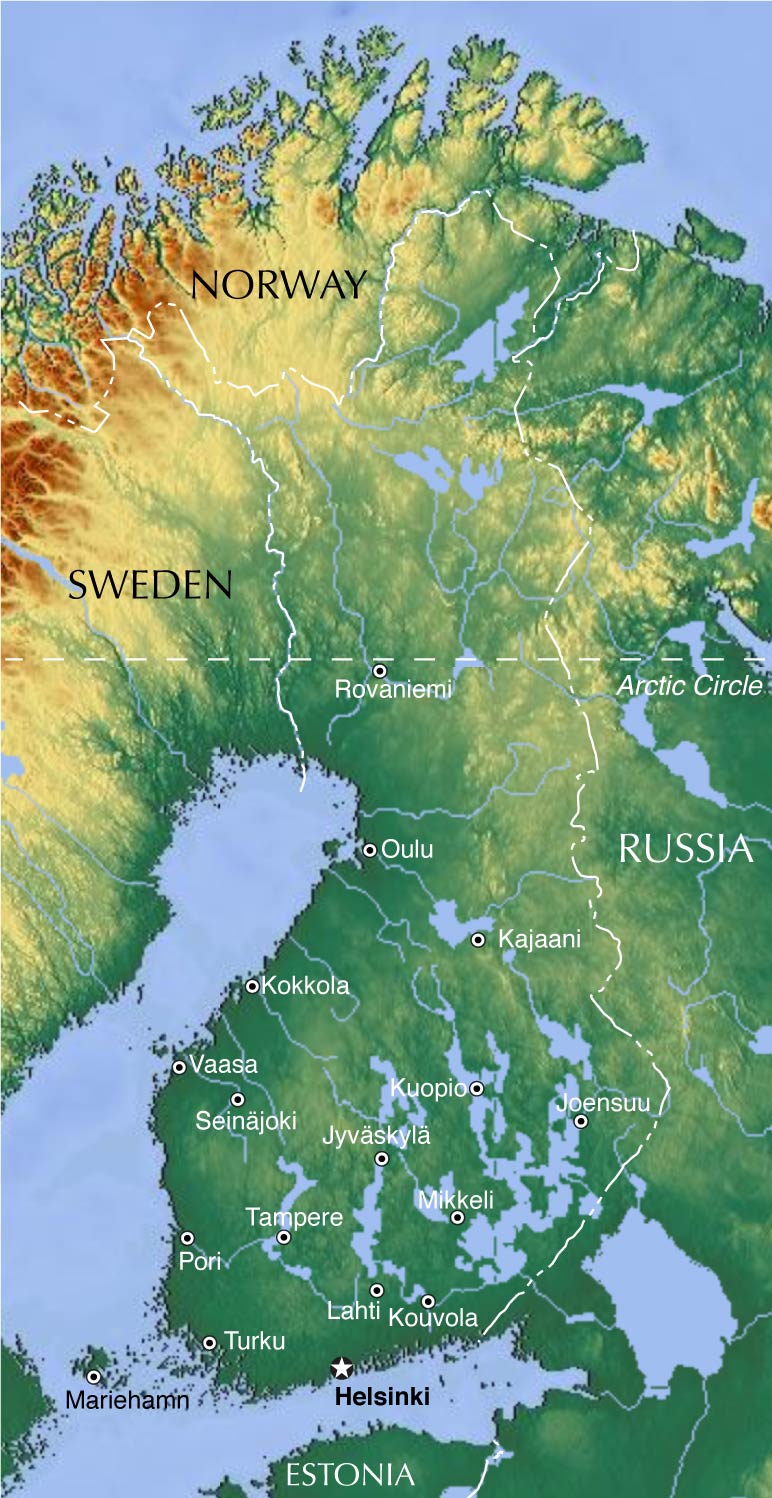
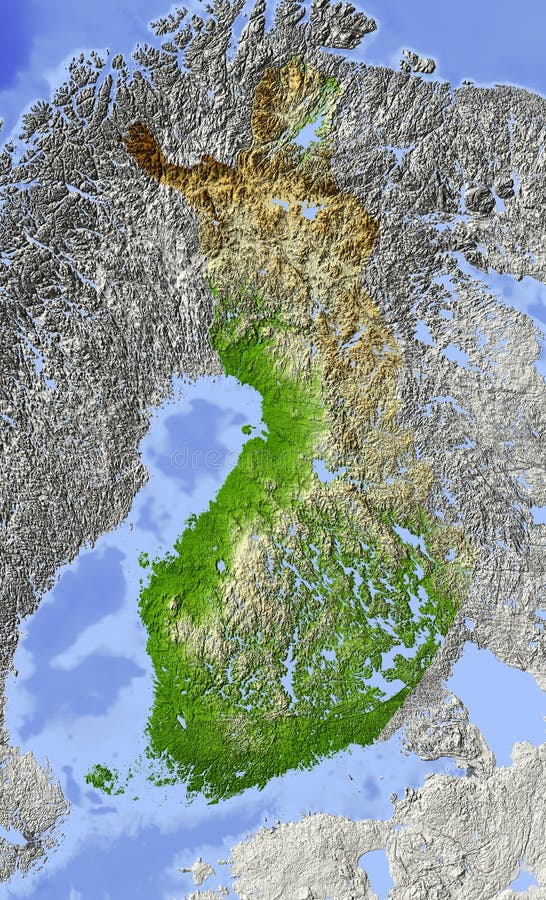
Finland, a Nordic nation renowned for its pristine lakes, vast forests, and unique cultural heritage, presents a fascinating tapestry of geographical features. Understanding the physical map of Finland is crucial for appreciating its natural beauty, comprehending its diverse ecosystems, and gaining insights into its history, culture, and economic activities. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Finland’s physical geography, delving into its major landforms, water bodies, climate, and ecological significance.
The Foundation of Finland’s Landscape: The Fennoscandian Shield
The bedrock of Finland’s physical map lies in the ancient Fennoscandian Shield, a vast expanse of Precambrian bedrock that stretches across northern Europe. This shield, formed billions of years ago, is characterized by its resistance to erosion, resulting in a landscape dominated by low-lying hills, undulating plains, and numerous lakes. The shield’s composition, primarily granite and gneiss, contributes to the country’s distinctive terrain and mineral resources.
A Land of Lakes and Forests: The Defining Features of Finland’s Landscape
Finland is often referred to as the "Land of a Thousand Lakes," a moniker aptly reflecting its extensive network of water bodies. Over 188,000 lakes dot the Finnish landscape, a testament to the country’s glacial history. These lakes, ranging from small ponds to vast expanses like Lake Saimaa, are interconnected by a complex system of rivers and canals, shaping the nation’s transportation routes and influencing its biodiversity.
Forests, covering approximately 75% of Finland’s land area, are another defining feature of its physical map. These forests, primarily composed of coniferous species like pine and spruce, provide a vital habitat for numerous animal and plant species, contribute significantly to the country’s economy through timber production, and play a crucial role in regulating the global carbon cycle.
The Influence of Glaciation: Shaping Finland’s Physical Geography
The Pleistocene glaciations, which covered Finland for thousands of years, profoundly shaped the country’s physical map. As the glaciers retreated, they left behind a legacy of distinctive landforms, including:
- Ås: Long, narrow ridges formed by glacial erosion.
- Esker: Winding, narrow ridges of gravel and sand deposited by meltwater flowing beneath the glaciers.
- Drumlin: Elongated hills formed by glacial deposition.
- Outwash plain: Flat, sandy plains created by meltwater flowing from glaciers.
These glacial features, visible throughout the country, contribute to the variety and beauty of Finland’s landscape, influencing the distribution of water bodies, soil types, and plant communities.
Climate: A Temperate Transition
Finland’s climate is classified as humid continental, transitioning from a subarctic climate in the north to a temperate climate in the south. The country experiences long, cold winters with significant snowfall, followed by short, cool summers. The Gulf Stream, a warm ocean current, moderates Finland’s climate, preventing it from being as harsh as other countries at similar latitudes.
Ecological Significance: A Haven for Biodiversity
The unique combination of landforms, water bodies, and climate has fostered a rich and diverse ecosystem in Finland. The country is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, including:
- Boreal Forests: These forests, dominated by coniferous trees, provide habitat for a diverse range of species, including bears, wolves, lynx, and numerous bird species.
- Lakes and Wetlands: These ecosystems support a rich diversity of fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds.
- Coastal Areas: Finland’s extensive coastline, dotted with islands and archipelagos, provides a haven for marine life, including seals, seabirds, and a variety of fish species.
The Importance of Understanding the Physical Map
Understanding the physical map of Finland is crucial for:
- Sustainable Resource Management: Knowing the distribution of forests, lakes, and mineral resources allows for effective resource management, ensuring their long-term sustainability.
- Infrastructure Development: The physical landscape influences transportation networks, energy production, and urban planning, requiring careful consideration of geographical features.
- Conservation and Biodiversity Protection: Recognizing the importance of Finland’s unique ecosystems, including its forests, lakes, and coastal areas, is essential for protecting biodiversity and ensuring the long-term health of the environment.
- Cultural Heritage: Finland’s physical landscape has deeply influenced its culture, folklore, and traditions, shaping its identity and providing inspiration for its arts and literature.
FAQs
Q: What are the highest and lowest points in Finland?
A: The highest point in Finland is Halti, a mountain located on the border with Norway, reaching a height of 1,324 meters. The lowest point is the Gulf of Finland, which is at sea level.
Q: What are the major rivers in Finland?
A: Some of the major rivers in Finland include the Kemijoki, Oulujoki, Kymijoki, and Vuoksi. These rivers are important for transportation, hydropower production, and recreation.
Q: How does Finland’s climate affect its agriculture?
A: Finland’s climate, characterized by long, cold winters and short summers, limits the types of crops that can be grown. The country primarily produces grains, potatoes, and berries.
Q: How does Finland’s physical geography influence its population distribution?
A: Finland’s population is concentrated in the southern and southwestern regions, where the climate is more temperate and the terrain is more suitable for agriculture and urban development. The sparsely populated northern regions are characterized by vast forests and lakes.
Tips for Understanding Finland’s Physical Map
- Utilize online maps and resources: Websites like Google Maps and ArcGIS provide detailed physical maps of Finland, allowing you to explore its features in depth.
- Consult geographical textbooks and articles: Academic resources can provide valuable information about Finland’s physical geography, including its geological history, climate, and ecosystems.
- Travel to Finland: Experiencing Finland’s landscape firsthand is the best way to appreciate its unique features. Visiting national parks, hiking trails, and lakeside towns can provide a deeper understanding of the country’s physical geography.
Conclusion
The physical map of Finland is a testament to the country’s rich geological history, unique landscapes, and diverse ecosystems. From its ancient bedrock to its vast network of lakes and forests, Finland’s physical geography has shaped its culture, economy, and way of life. Understanding these features is crucial for appreciating the country’s natural beauty, promoting sustainable resource management, and ensuring the long-term health of its environment.
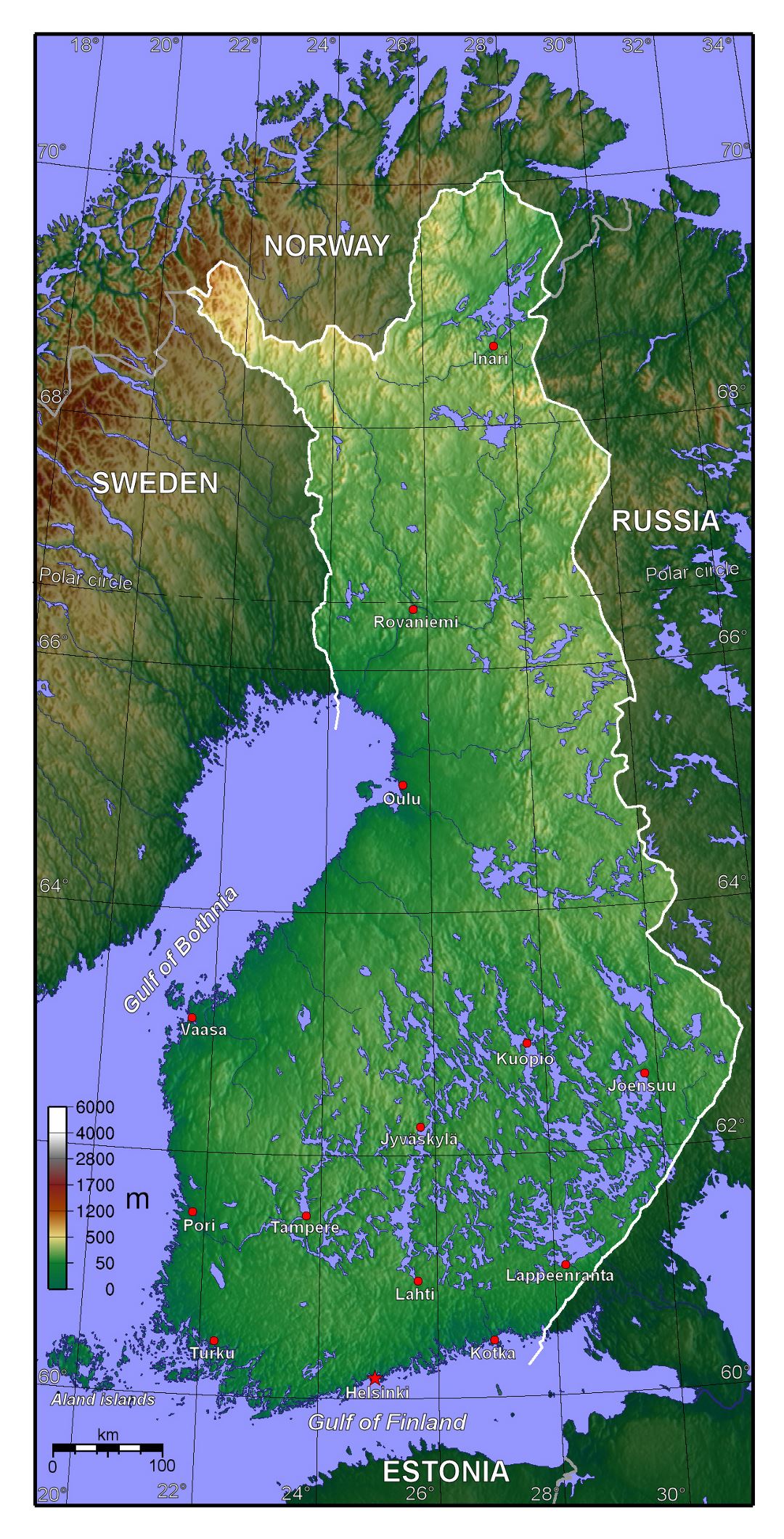
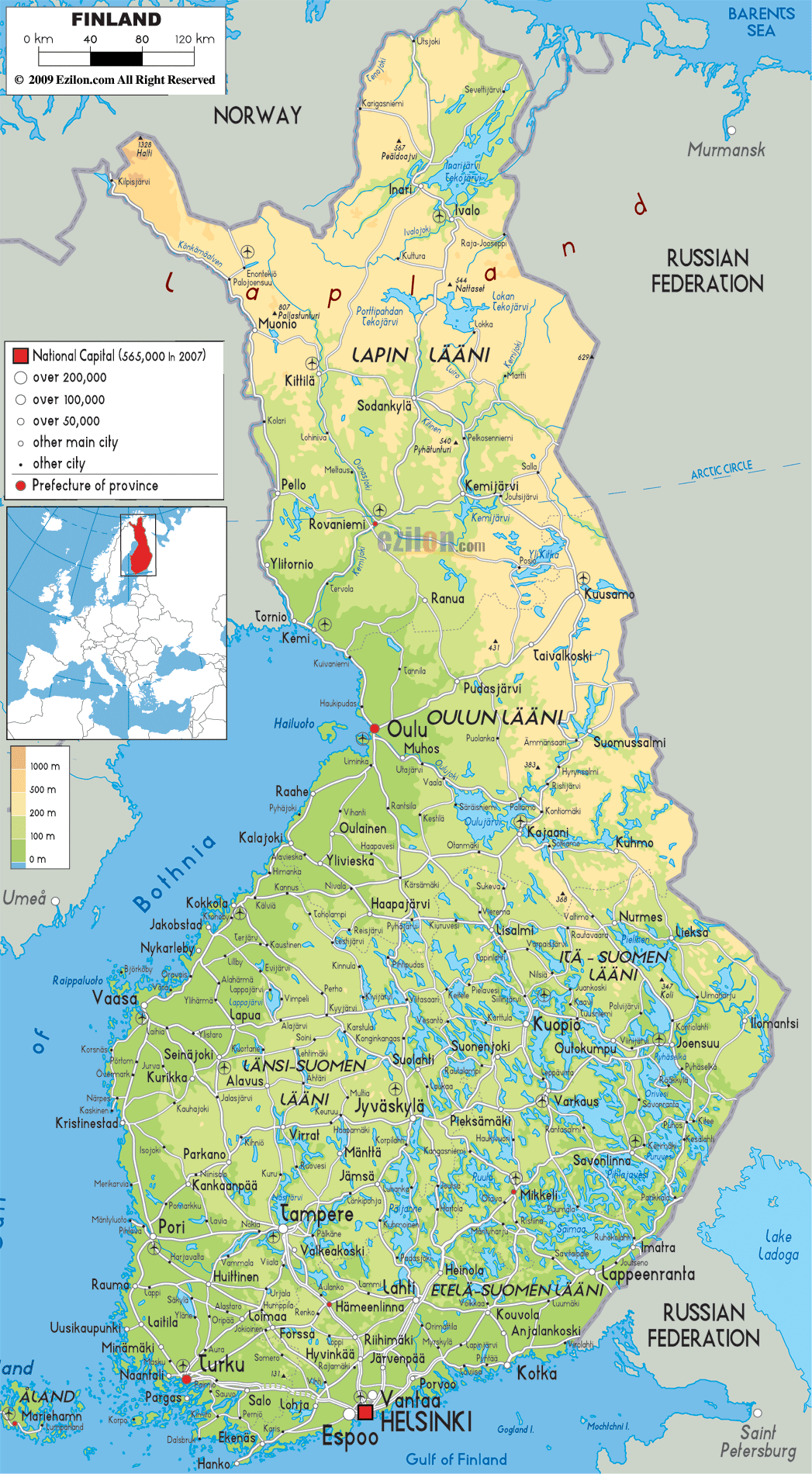
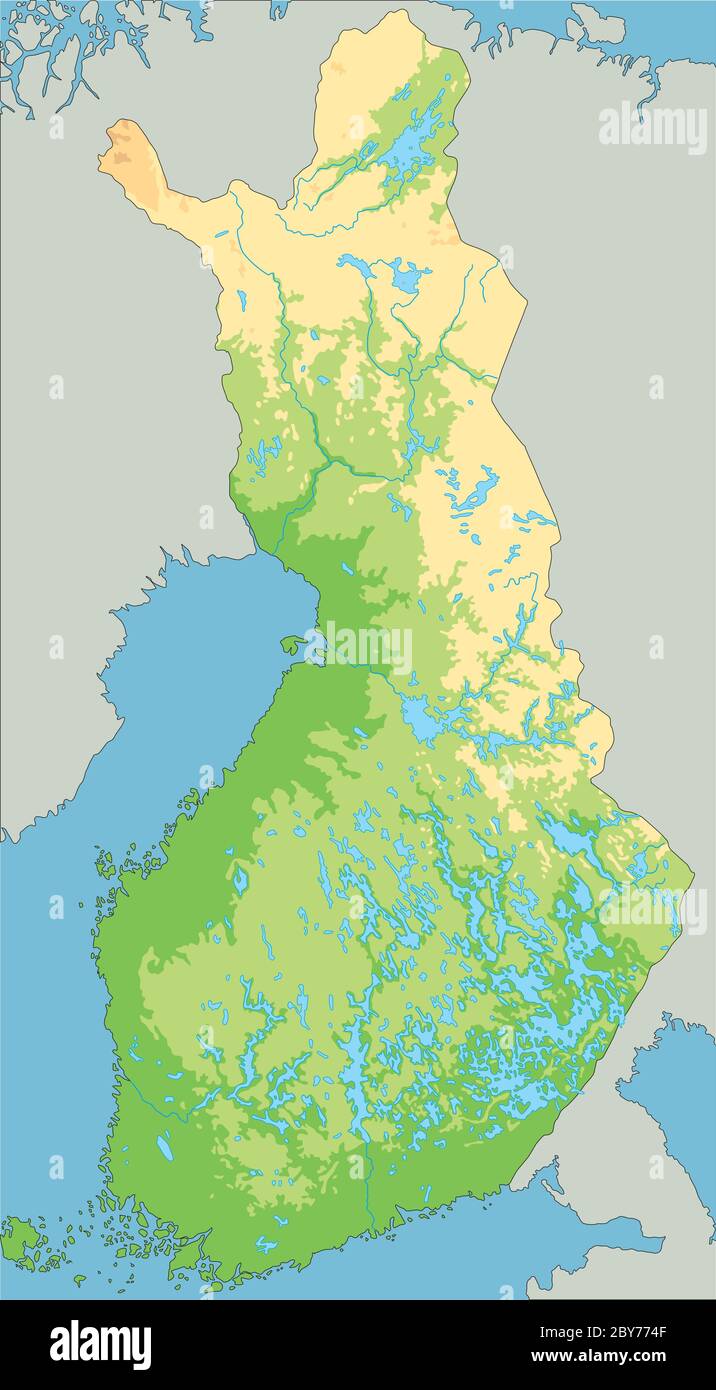



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Glimpse into Finland’s Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!