A Global Snapshot of Seismic Activity: Examining Earthquake Trends Over the Past Week
Related Articles: A Global Snapshot of Seismic Activity: Examining Earthquake Trends Over the Past Week
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Global Snapshot of Seismic Activity: Examining Earthquake Trends Over the Past Week. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Global Snapshot of Seismic Activity: Examining Earthquake Trends Over the Past Week

The Earth, a dynamic and ever-shifting planet, experiences constant movement beneath its surface. This movement, primarily driven by the interaction of tectonic plates, manifests itself in various ways, including volcanic eruptions and, most notably, earthquakes. Monitoring these seismic events is crucial for understanding the Earth’s inner workings, predicting potential hazards, and ensuring the safety of communities worldwide.
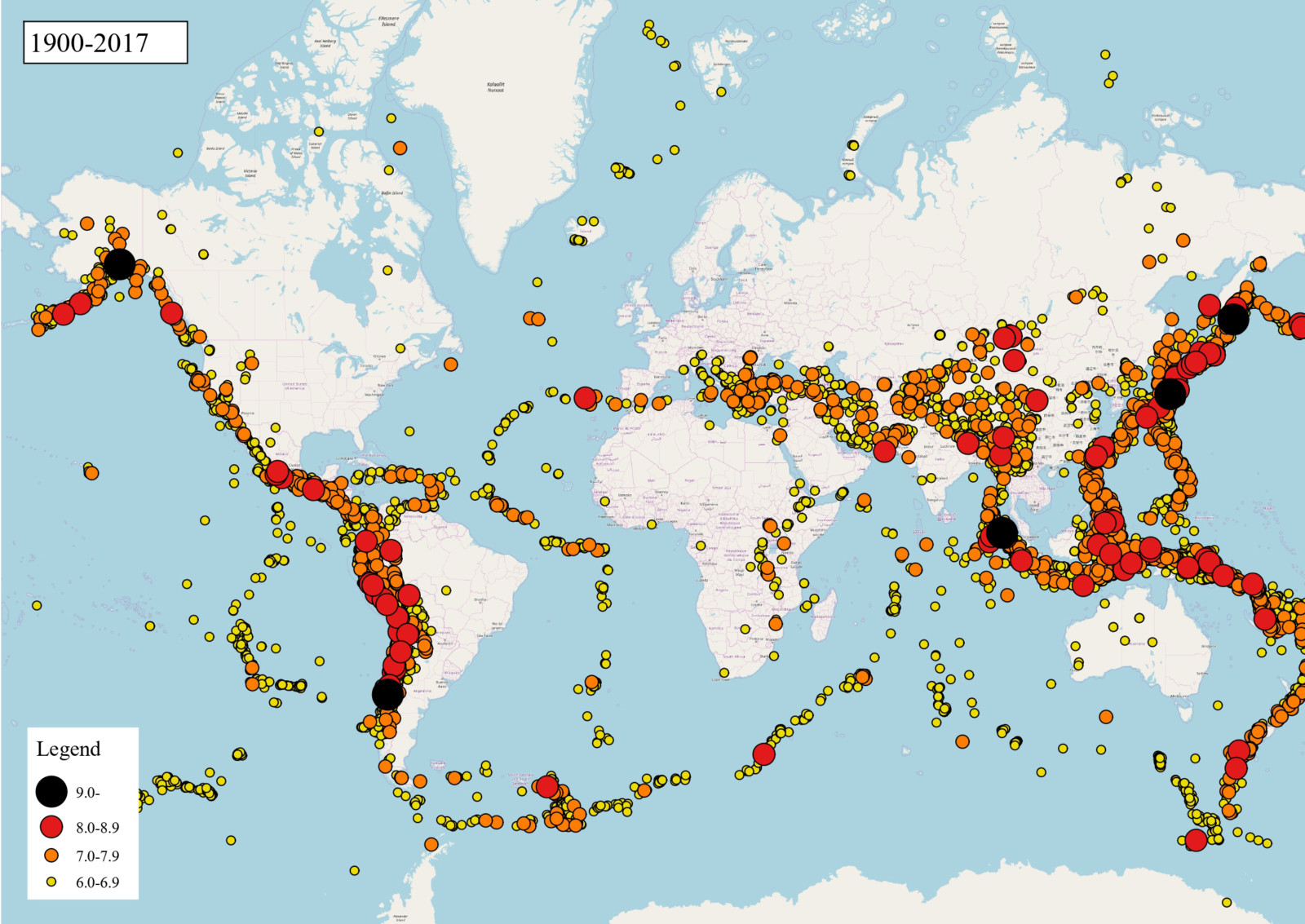
Understanding the Global Earthquake Map
A global earthquake map, updated regularly, provides a visual representation of recent seismic activity. It serves as a vital tool for scientists, disaster management agencies, and the public alike. The map typically displays the location, magnitude, and depth of earthquakes recorded over a specific timeframe, often a week or a month.
Interpreting the Data: Insights into Global Seismic Trends
Analyzing the data presented on a global earthquake map reveals valuable insights into the Earth’s dynamic nature. Several key observations emerge:
-
Concentration of Activity: Earthquakes are not randomly distributed across the globe. Instead, they tend to cluster along specific regions known as seismic zones. These zones coincide with the boundaries of tectonic plates, where the plates interact, creating friction and generating seismic waves.
-
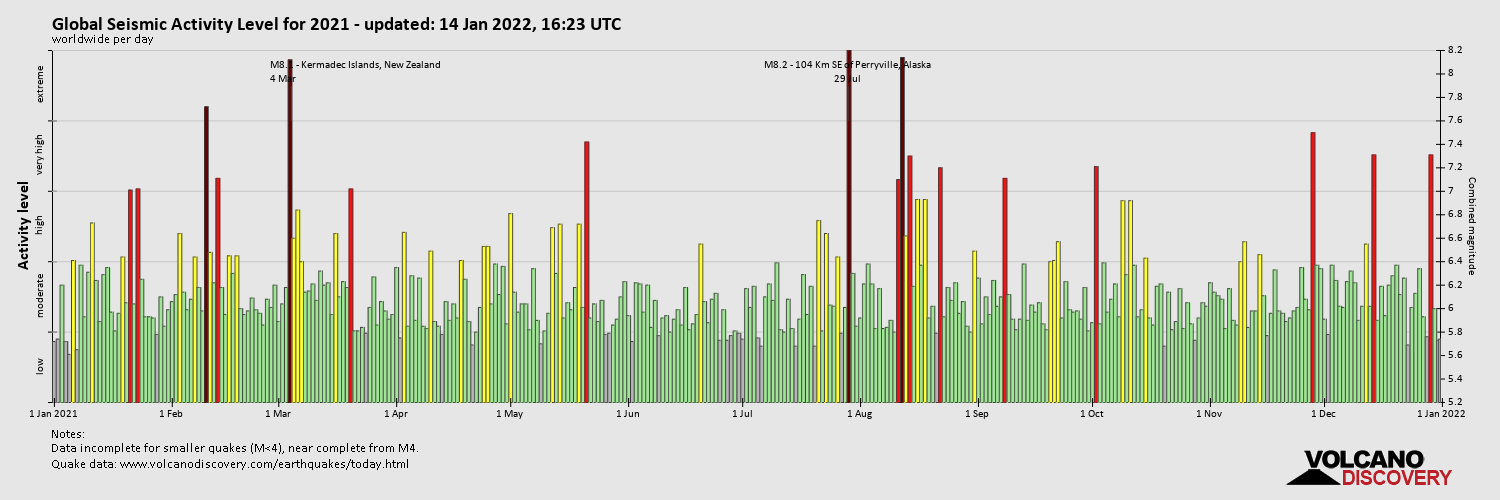
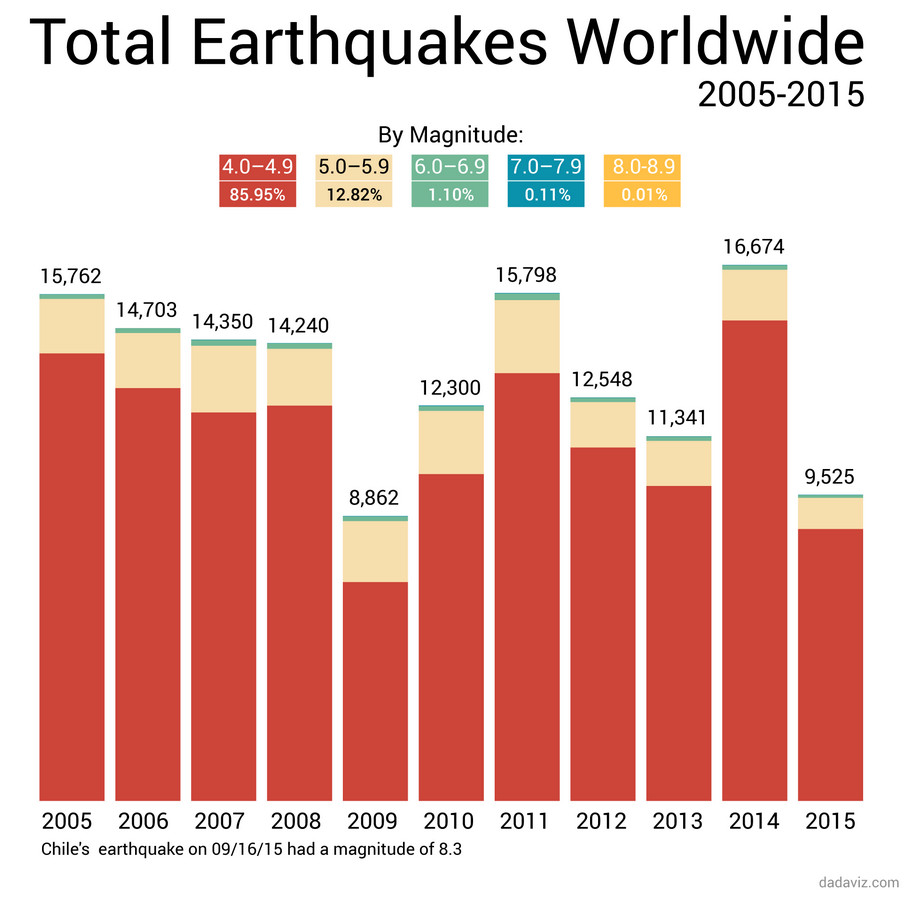
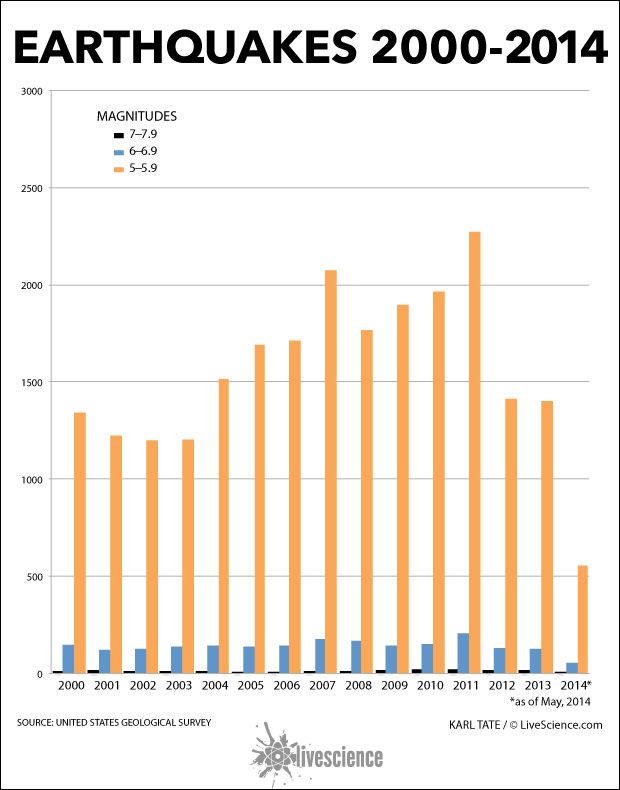
Magnitude Distribution: The map highlights the varying intensity of earthquakes. While numerous minor tremors occur daily, significant earthquakes, those with magnitudes exceeding 6.0 on the Richter scale, are less frequent but pose a greater threat.
-
Depth of Earthquakes: The map also indicates the depth at which earthquakes originate. Shallow earthquakes, occurring within the Earth’s crust, typically cause more damage than deep earthquakes, which originate in the mantle.
-
Timely Information: The map provides up-to-date information on recent seismic activity, enabling authorities to assess potential risks and respond swiftly to any emergency situations.
The Importance of Global Earthquake Mapping
The global earthquake map serves several critical purposes:
-
Scientific Research: Scientists use the map to study the Earth’s internal structure, plate tectonics, and the mechanisms behind earthquake generation. This data contributes to a deeper understanding of our planet’s dynamic processes.
-
Disaster Mitigation: The map provides valuable information for disaster management agencies. By monitoring earthquake activity, authorities can implement early warning systems, prepare for potential disasters, and guide evacuation efforts.
-
Public Awareness: The map raises public awareness about earthquake risks and encourages preparedness. Accessing the map allows individuals to understand the seismic activity in their region and take necessary precautions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Global Earthquake Mapping
Q: What is the difference between the epicenter and the hypocenter of an earthquake?
A: The epicenter refers to the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake’s origin, while the hypocenter, also known as the focus, represents the actual point where the earthquake originates beneath the surface.
Q: How is the magnitude of an earthquake measured?
A: The magnitude of an earthquake is measured using the Richter scale, a logarithmic scale that quantifies the amount of energy released during an earthquake. Each increase of one unit on the Richter scale represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of seismic waves and approximately a 32-fold increase in energy released.
Q: How does the depth of an earthquake affect its impact?
A: Shallow earthquakes, occurring within the Earth’s crust, tend to cause more damage than deep earthquakes. This is because the seismic waves from shallow earthquakes travel directly through the crust, resulting in stronger ground shaking.
Q: Can earthquakes be predicted?
A: While predicting the exact time and location of an earthquake remains a scientific challenge, advancements in seismology have enabled scientists to develop early warning systems. These systems monitor seismic activity and issue alerts when significant earthquakes are detected.
Tips for Staying Safe During an Earthquake
-
Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies, including food, water, first-aid materials, and a flashlight.
-
Secure Heavy Objects: Secure heavy objects that could fall and cause injury during an earthquake.
-
Know Your Exit Routes: Familiarize yourself with multiple escape routes from your home and workplace.
-
Practice Drop, Cover, and Hold On: During an earthquake, drop to the ground, cover your head and neck, and hold on to a sturdy object.
-
Stay Informed: Stay informed about earthquake safety procedures and follow the guidance of local authorities.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Global Earthquake Monitoring
The global earthquake map serves as a powerful tool for understanding and mitigating seismic risks. By providing a comprehensive overview of recent earthquake activity, it empowers scientists, disaster management agencies, and the public to respond effectively to seismic events. Through continued monitoring, research, and preparedness, we can minimize the impact of earthquakes and build more resilient communities.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Snapshot of Seismic Activity: Examining Earthquake Trends Over the Past Week. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!