A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Transformation of France in 987
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Transformation of France in 987
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Transformation of France in 987. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Transformation of France in 987
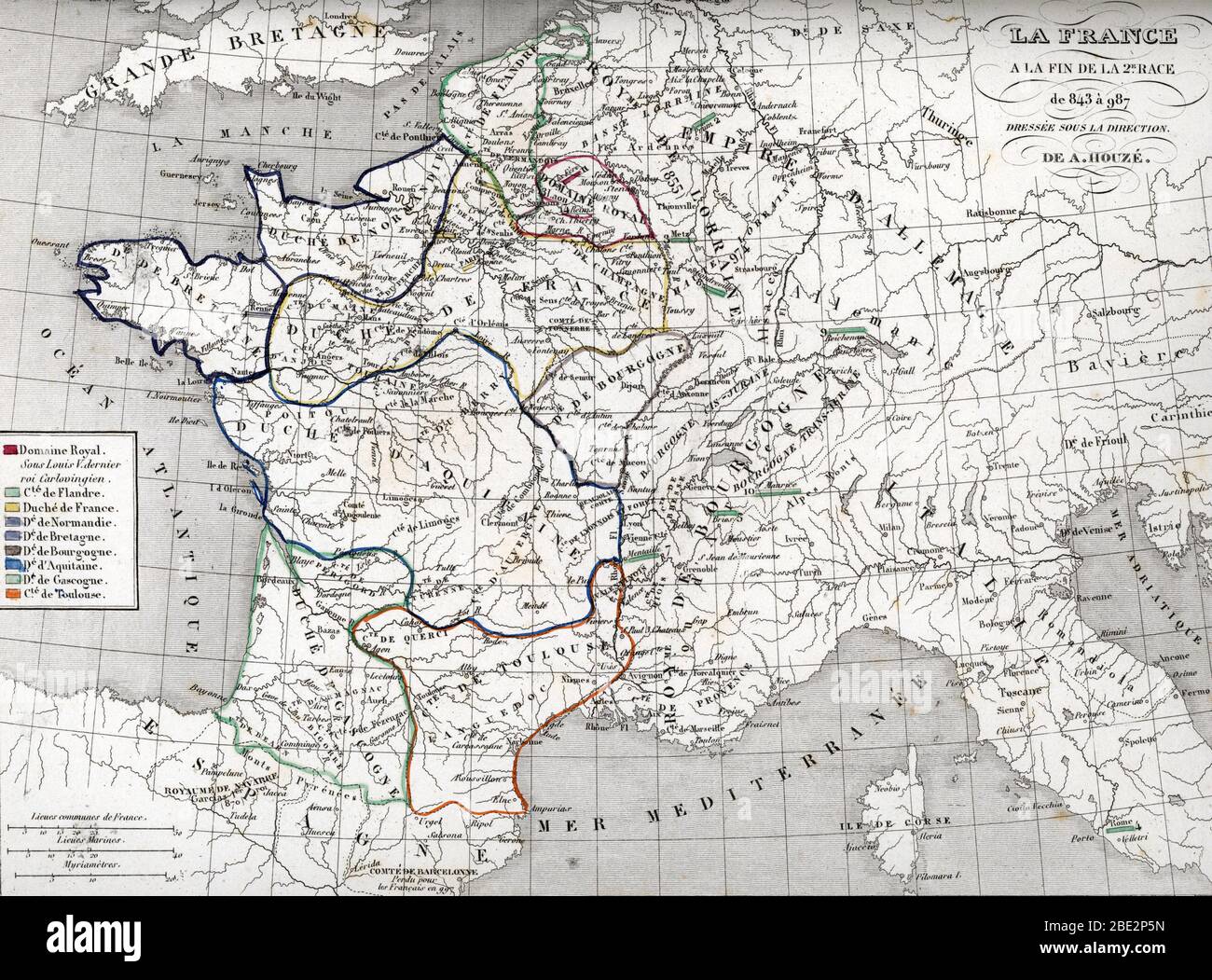
The year 987 marks a pivotal moment in French history. It is the year Hugh Capet, Count of Paris, ascended to the throne, effectively ending the Carolingian dynasty and ushering in the Capetian era. This transition, marked by a change in ruling families, was not merely a political shift; it also had profound implications for the territorial landscape of France, shaping its future trajectory.
To understand the significance of this transition, it is crucial to examine the map of France in 987. This map reveals a fragmented kingdom, a tapestry woven with diverse and often competing powers.
A Mosaic of Power: France in 987
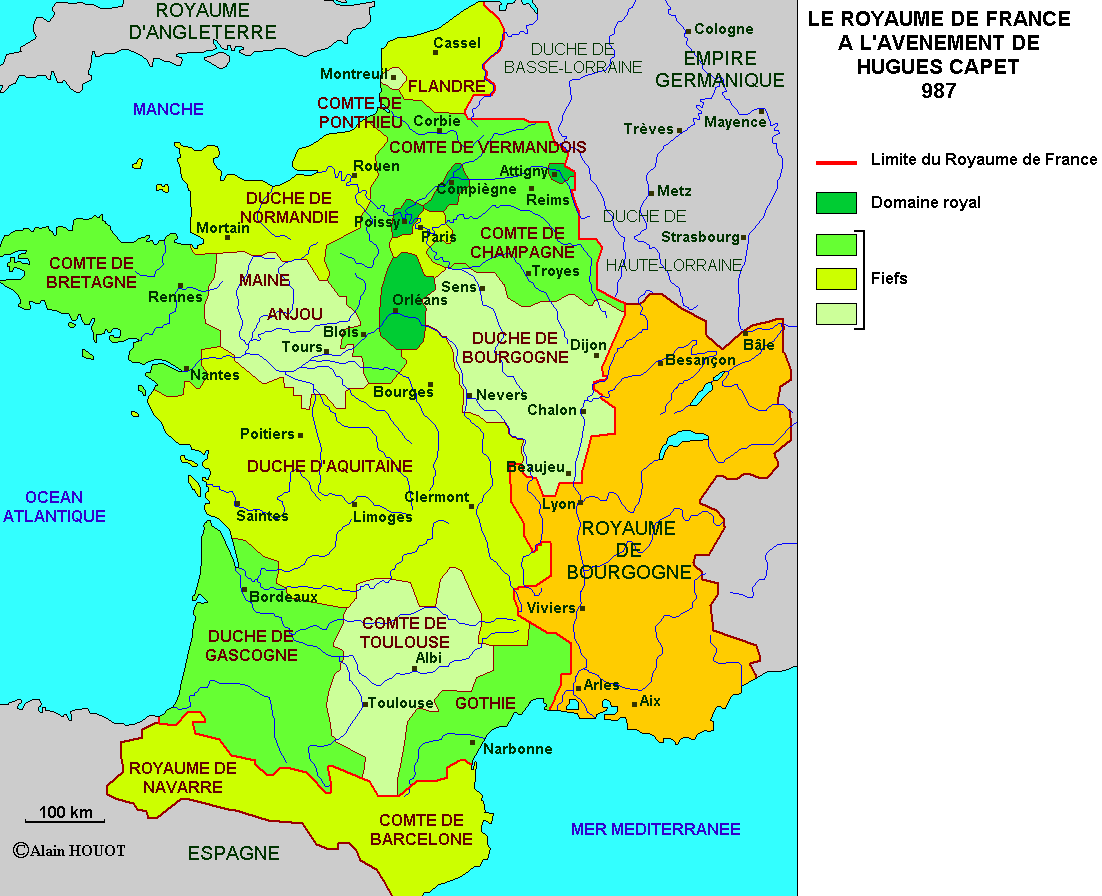
The map of France in 987 is a far cry from the unified nation-state we know today. The kingdom was a patchwork of territories, each with its own ruler, customs, and ambitions.
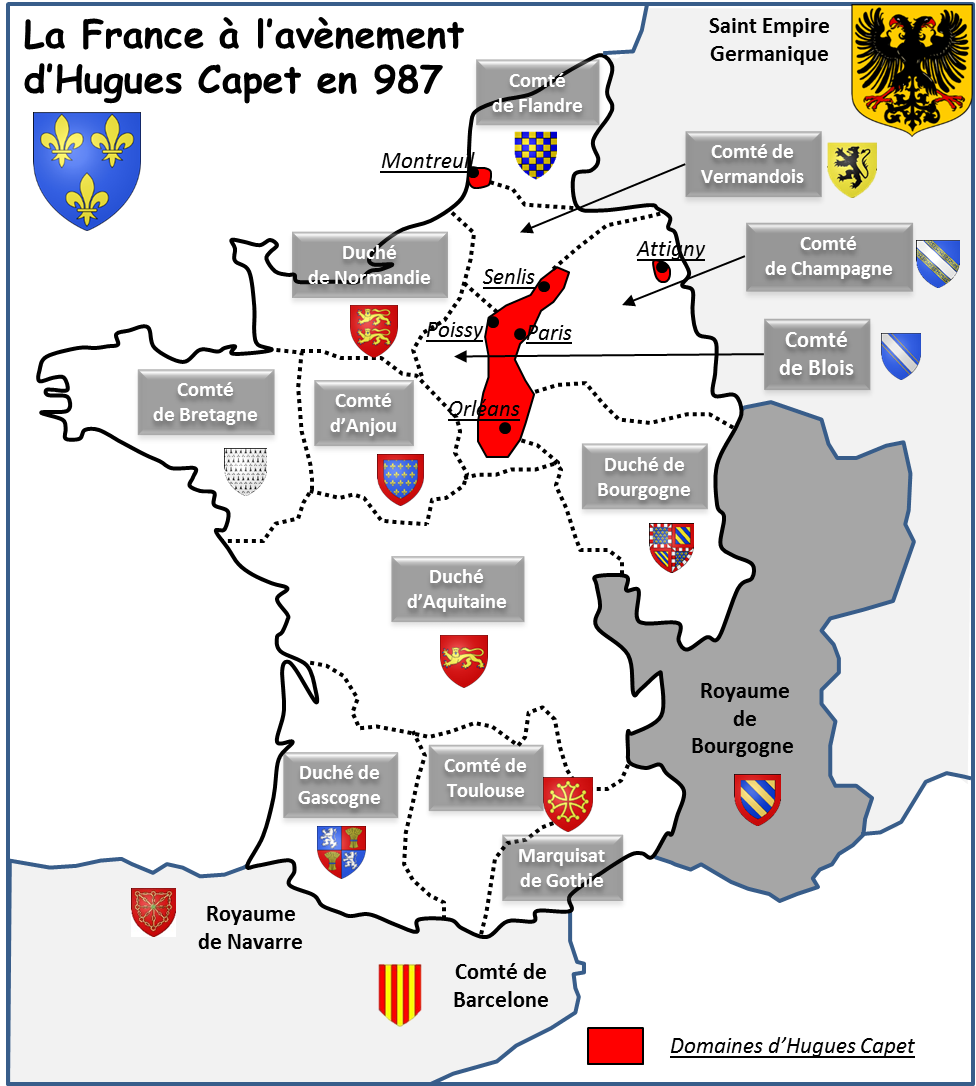
- The Crown’s Domain: The king’s direct control was limited to a small region around Paris, known as the Île-de-France. This area, while strategically important, lacked the vast resources and manpower of other powerful entities.
- The Duchy of Normandy: In the north, the Duchy of Normandy, established by Viking settlers, was a formidable power. The Dukes of Normandy, known for their ambition and military prowess, posed a constant threat to the king’s authority.
- The County of Flanders: To the north-east, the County of Flanders, another powerful entity, controlled vital trade routes and held sway over a wealthy and influential region.
- The Duchy of Aquitaine: In the southwest, the Duchy of Aquitaine, a vast and strategically important territory, was ruled by a powerful duke who often challenged the king’s authority.
- The County of Toulouse: Further south, the County of Toulouse, a powerful and independent entity, controlled a significant portion of the Languedoc region.
The Rise of the Capetians: Consolidating Power
Hugh Capet’s ascension to the throne marked the beginning of a long and complex process of consolidating royal power. The Capetian kings, through a combination of astute political maneuvering, strategic marriages, and military campaigns, gradually expanded their control over the kingdom.
- Strategic Marriages: The Capetians understood the importance of strategic marriages in securing alliances and expanding their influence. They married into powerful families, forging connections that helped them gain control over key territories.
- Military Campaigns: The Capetians also engaged in numerous military campaigns to subdue rebellious nobles and expand their territory. These campaigns were often long and arduous, but they proved crucial in establishing the king’s authority.
- The Rise of the French Monarchy: Over the centuries, the Capetians gradually transformed the fragmented kingdom into a unified nation-state. They established a strong central administration, developed a system of royal justice, and fostered a sense of national identity.
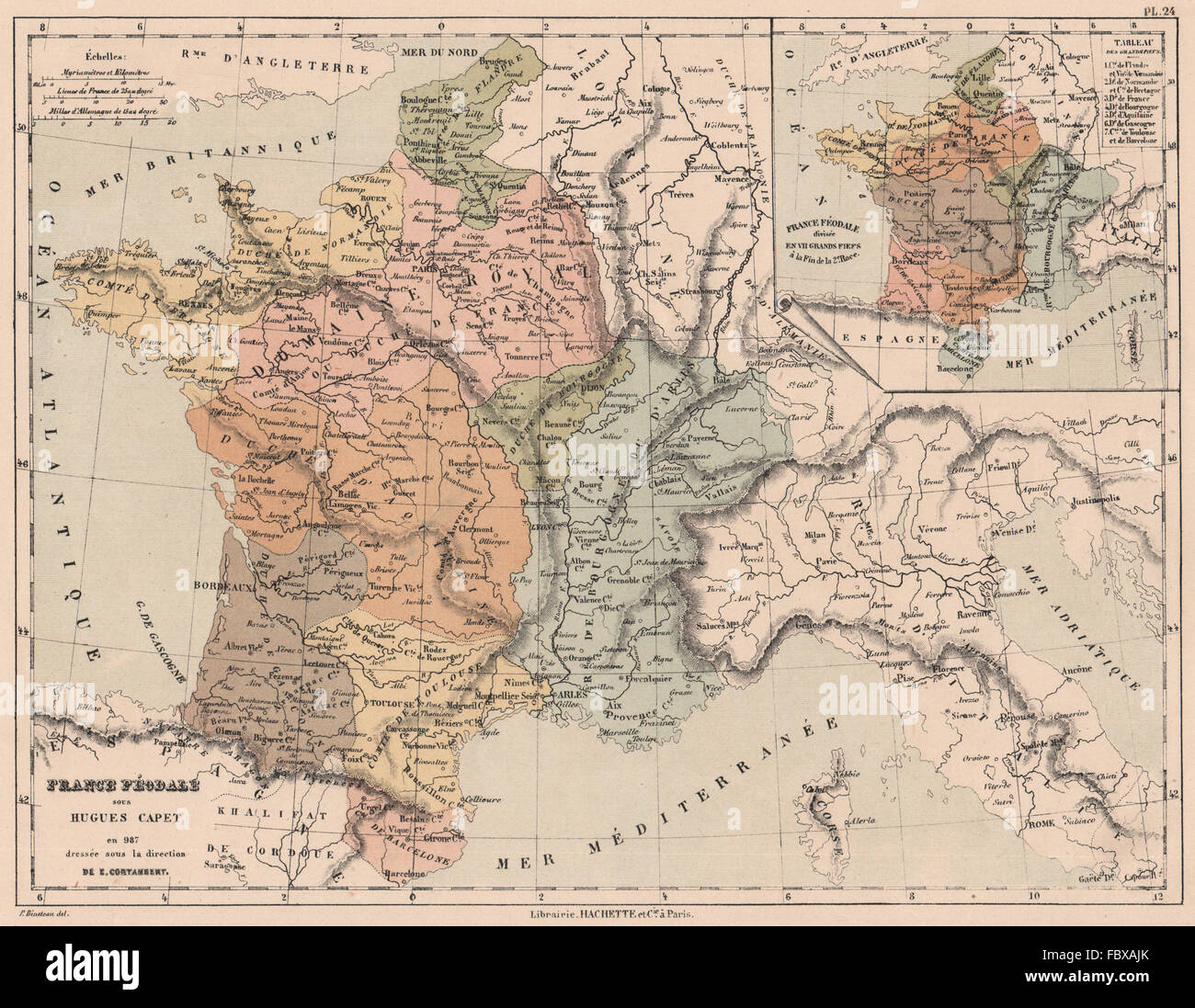
The Map of France in 987: A Foundation for the Future
The map of France in 987, despite its fragmentation, provides a crucial window into the early history of the French nation. It reveals the complex tapestry of power that existed in the 10th century, the challenges faced by the early Capetian kings, and the foundation upon which they built their kingdom.
FAQs
Q: Why was the map of France in 987 so fragmented?
A: The fragmentation of France in 987 was a legacy of the Carolingian era. The Carolingian kings, while powerful, faced constant challenges from rebellious nobles and Viking raids. This led to the emergence of powerful regional entities, each with its own ruler and ambitions.
Q: How did the Capetians manage to consolidate their power?
A: The Capetians used a combination of strategic marriages, military campaigns, and astute political maneuvering to gradually expand their control over the kingdom. They forged alliances with powerful families, subdued rebellious nobles, and established a strong central administration.
Q: What were the long-term implications of the Capetian era?
A: The Capetian era was a transformative period in French history. The Capetian kings laid the foundation for a strong and unified French monarchy, which would play a pivotal role in shaping the destiny of France for centuries to come.
Tips
- Use historical maps to visualize the changes in the French landscape. Maps provide a powerful tool for understanding the political and territorial dynamics of the period.
- Explore the biographies of key figures like Hugh Capet and his successors. Their actions and decisions had a profound impact on the trajectory of French history.
- Examine the development of institutions like the royal court and the French monarchy. These institutions played a crucial role in consolidating royal power and shaping the French nation.
Conclusion
The map of France in 987 is a powerful reminder of the fluid and dynamic nature of history. It reveals the challenges and opportunities faced by the early Capetian kings, and the foundations upon which they built a unified and powerful French nation. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex forces that shaped the French landscape and the enduring legacy of the Capetian era.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Transformation of France in 987. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!