A Portrait of Finland: Unveiling Population Distribution and Its Implications
Related Articles: A Portrait of Finland: Unveiling Population Distribution and Its Implications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Portrait of Finland: Unveiling Population Distribution and Its Implications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Portrait of Finland: Unveiling Population Distribution and Its Implications
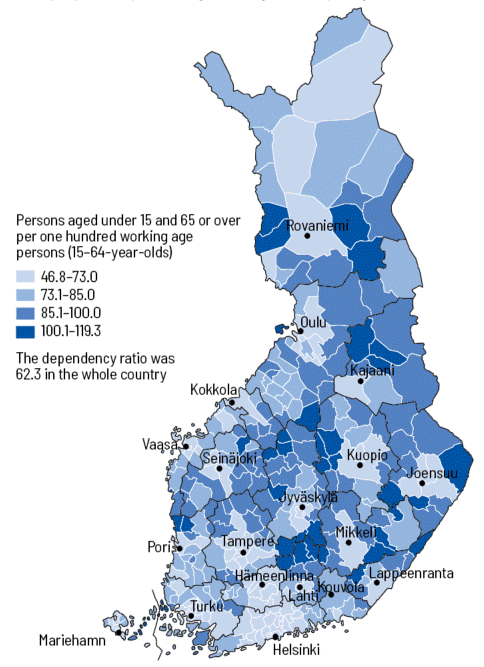
Finland, a Nordic nation known for its breathtaking landscapes, robust economy, and high standard of living, boasts a population of approximately 5.5 million. Understanding the distribution of this population across the vast Finnish terrain provides crucial insights into the country’s social, economic, and cultural fabric. This article delves into the complexities of the Finnish population map, exploring its historical evolution, key demographic trends, and the ramifications of these patterns on various facets of Finnish life.
A Historical Perspective: From Sparse Settlements to Urban Concentration
Finland’s population distribution has undergone a significant transformation over the centuries. Historically, the country’s sparsely populated landscape was characterized by small, rural communities scattered across the vast expanse of forests and lakes. This pattern was shaped by factors such as the challenging terrain, harsh climate, and limited agricultural opportunities.
The 19th century witnessed a gradual shift towards urbanization, spurred by industrialization and the emergence of new economic centers. This trend accelerated in the 20th century, fueled by rapid economic growth and societal modernization. As a result, Finland’s population map began to reflect a growing concentration of people in urban areas, particularly in the southern and southwestern regions.
The Modern Landscape: Population Density and Key Trends
Today, Finland’s population map reveals a stark contrast between its densely populated urban centers and sparsely populated rural areas. The majority of the population resides in the southern and southwestern regions, with the capital city of Helsinki serving as the epicenter of population density.
Several key trends are shaping Finland’s population distribution:
- Urbanization: The ongoing trend of urbanization continues to draw people towards urban centers, driven by factors such as employment opportunities, access to services, and cultural amenities. This trend is evident in the growth of major cities like Helsinki, Tampere, and Turku, while rural areas experience a gradual decline in population.
- Aging Population: Finland, like many developed countries, is facing an aging population, with a declining birth rate and increasing life expectancy. This demographic shift has significant implications for social security systems, healthcare, and the labor market.
- Internal Migration: The movement of people within Finland, from rural areas to urban centers, is another notable trend. This internal migration is driven by economic opportunities, educational prospects, and lifestyle preferences.
- Immigration: While historically a country with limited immigration, Finland is increasingly experiencing a rise in the number of immigrants. This influx of new residents is contributing to a more diverse population and enriching the cultural landscape.
Implications of Population Distribution: A Multifaceted Impact
The distribution of Finland’s population has profound implications for various aspects of the country’s development:
- Economic Development: The concentration of population in urban centers fosters economic activity, driving innovation, entrepreneurship, and employment opportunities. However, this can also lead to disparities in economic development between urban and rural areas, requiring targeted policies to address regional inequalities.
- Infrastructure and Services: The distribution of population necessitates strategic planning for infrastructure development and service provision. Densely populated areas require robust transportation networks, healthcare facilities, and educational institutions, while rural communities face challenges in accessing these resources.
- Social Cohesion: Population distribution can impact social cohesion and community engagement. Urban areas often experience challenges related to social isolation and integration, while rural communities may face challenges in maintaining a vibrant social fabric.
- Environmental Sustainability: Population density can exert pressure on natural resources and the environment. Urban areas often face challenges related to pollution, waste management, and resource consumption, while rural areas may experience pressure on forests and water resources.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the most densely populated areas in Finland?
The most densely populated areas in Finland are located in the southern and southwestern regions, particularly around the capital city of Helsinki and other major urban centers like Tampere and Turku.
2. How has Finland’s population distribution changed over time?
Finland’s population distribution has shifted from a primarily rural pattern to a more urbanized landscape, with a growing concentration of people in cities and a decline in rural populations.
3. What are the challenges associated with Finland’s aging population?
The aging population poses challenges for Finland’s social security system, healthcare, and labor market, requiring adjustments to ensure sustainable development and social well-being.
4. How does Finland’s population distribution impact its economic development?
The concentration of population in urban centers fosters economic activity, but also presents challenges in addressing regional inequalities and ensuring equitable development across the country.
5. What measures are being taken to address the challenges associated with population distribution?
Finland is implementing various policies to address the challenges of population distribution, including regional development initiatives, investments in infrastructure, and programs to promote social cohesion and integration.
Tips for Understanding Finland’s Population Map
- Visualize the data: Utilize online maps and resources to visualize population density, distribution, and key demographic trends.
- Explore historical context: Understand the historical factors that have shaped Finland’s population distribution.
- Consider the implications: Analyze the impact of population distribution on various aspects of Finnish life, such as economic development, infrastructure, and social cohesion.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of current population trends and demographic changes in Finland.
- Engage in discussion: Participate in discussions and debates on population distribution and its implications for the future of Finland.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Landscape
Finland’s population map is a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by historical forces, ongoing trends, and the aspirations of its people. Understanding the nuances of population distribution is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and citizens alike, as it provides insights into the country’s social, economic, and environmental challenges and opportunities. By embracing a holistic perspective, acknowledging the complexities of population distribution, and implementing effective policies, Finland can navigate the challenges and harness the potential of its evolving population landscape to build a sustainable and prosperous future.


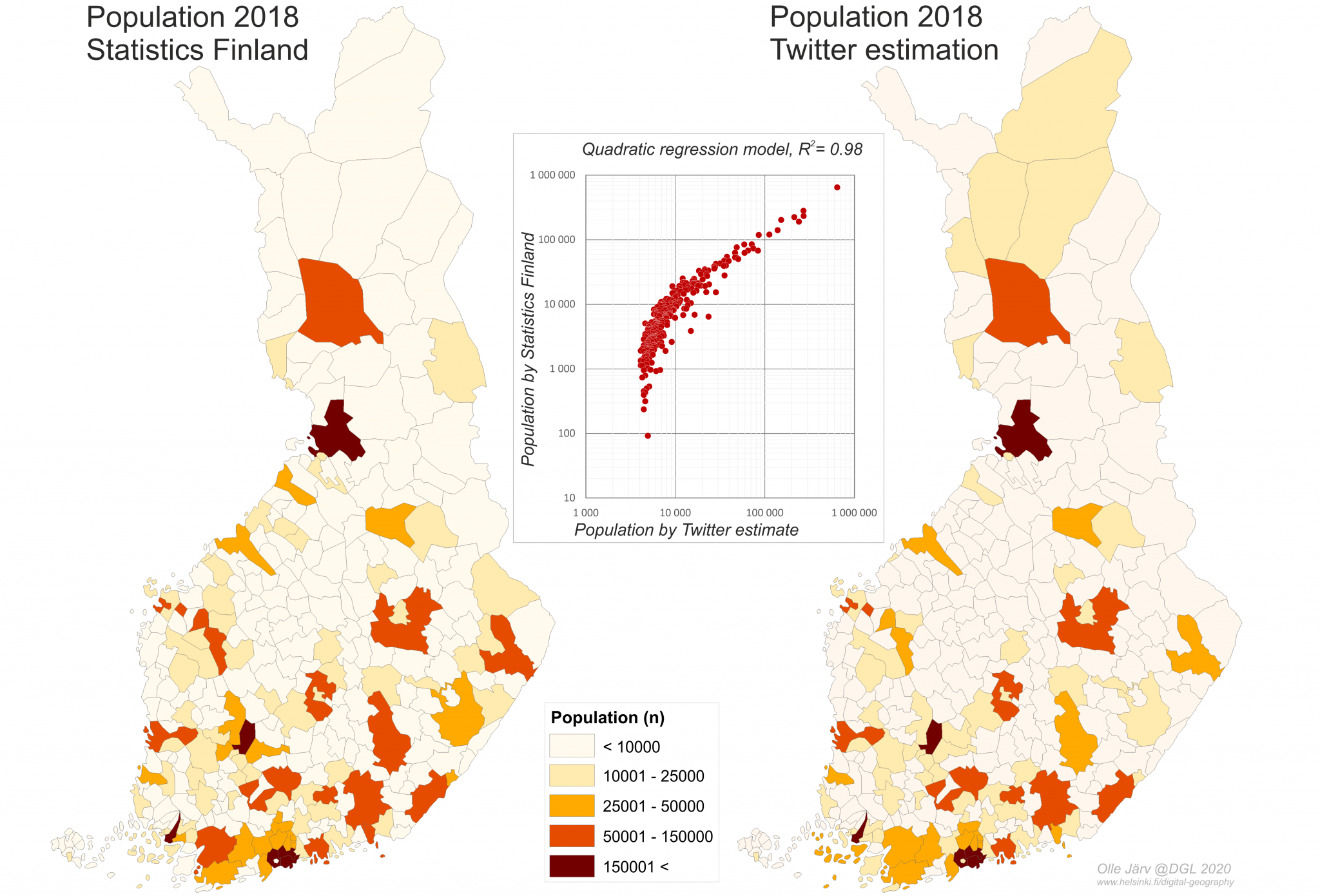
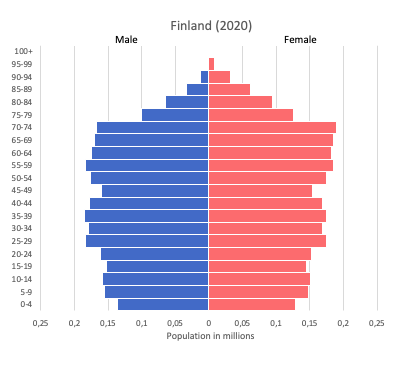

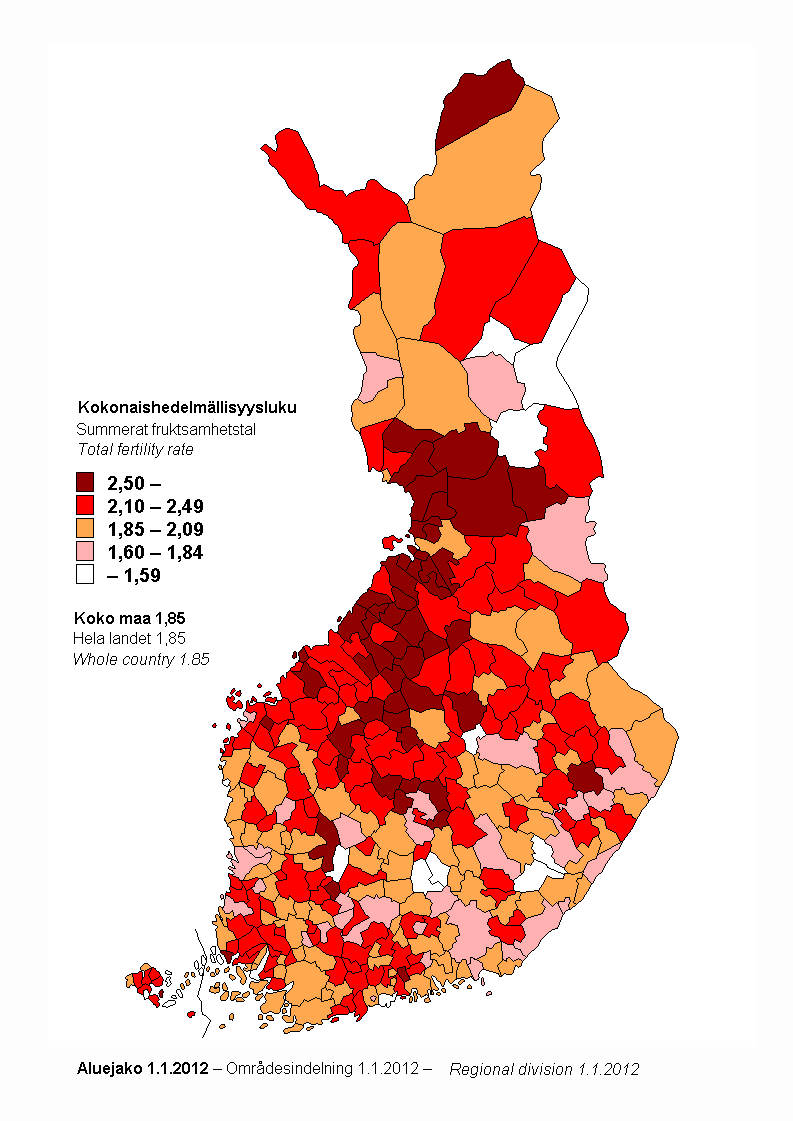


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Portrait of Finland: Unveiling Population Distribution and Its Implications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!