A Seismic Portrait of the United States: Understanding the Earthquake Map
Related Articles: A Seismic Portrait of the United States: Understanding the Earthquake Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Seismic Portrait of the United States: Understanding the Earthquake Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Seismic Portrait of the United States: Understanding the Earthquake Map

The United States, with its vast and diverse landscape, is not immune to the powerful forces that shape our planet. Earthquakes, a testament to the dynamic nature of Earth’s crust, are a constant reality for many regions within the country. Understanding the distribution and frequency of these seismic events is crucial for mitigating their potential impacts and ensuring public safety. A comprehensive earthquake map serves as a vital tool for achieving this goal.
The Seismic Landscape of the United States
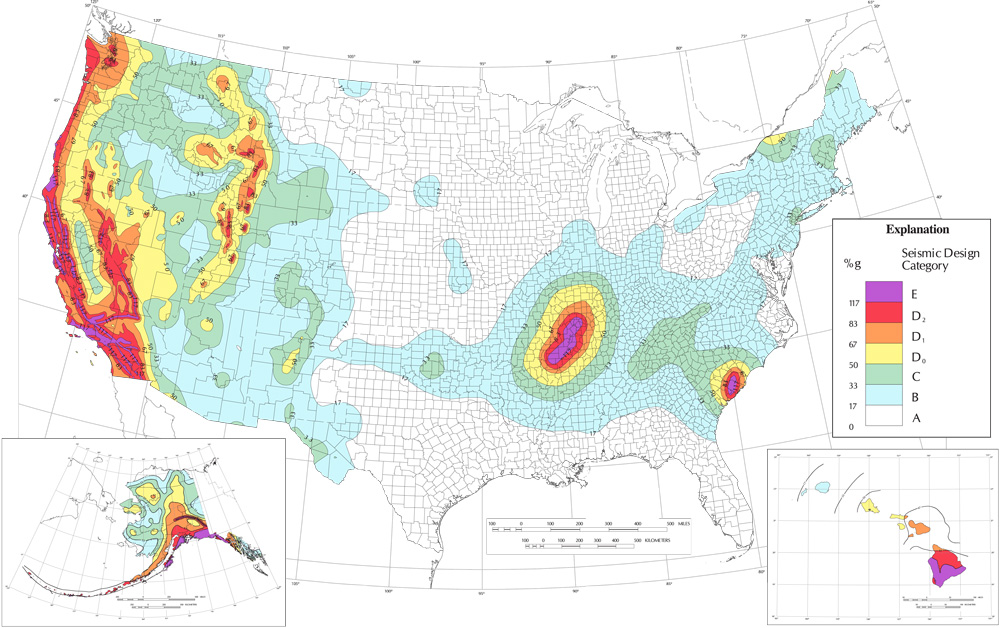
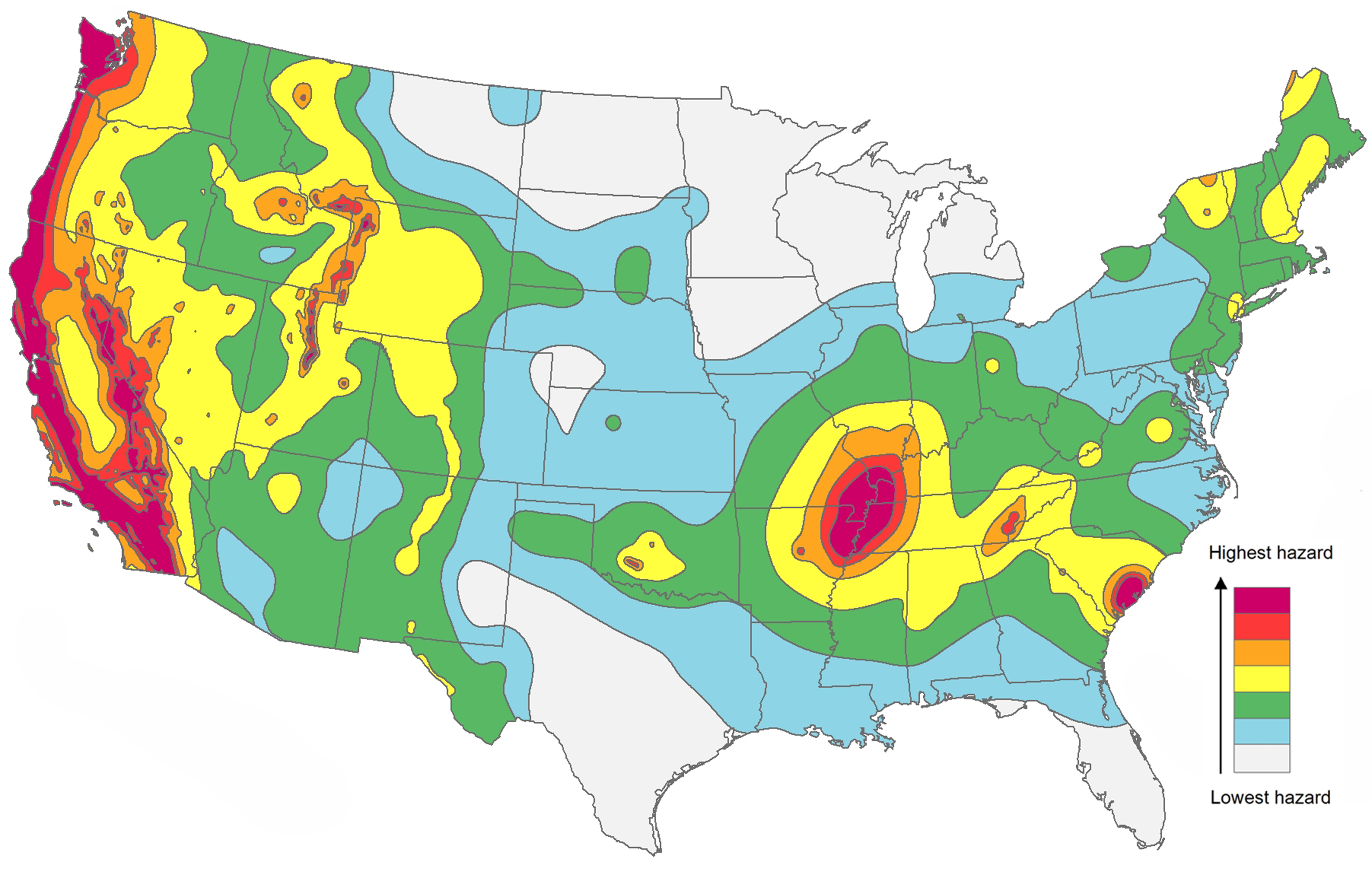
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) maintains a detailed earthquake map, a visual representation of seismic activity across the nation. This map, updated regularly with data from seismographic networks, reveals the intricate tapestry of earthquake zones that define the country’s seismic landscape.
The map highlights several key features:
- The Pacific Coast: A Zone of High Activity: The westernmost edge of the United States, bordering the Pacific Ocean, is characterized by intense seismic activity. This region, known as the "Ring of Fire," is a horseshoe-shaped zone of tectonic plate boundaries where the Pacific Plate interacts with other plates. This interaction results in frequent earthquakes, ranging from minor tremors to devastating events. California, in particular, is renowned for its seismic history, with major earthquakes such as the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1994 Northridge earthquake serving as stark reminders of the region’s vulnerability.
- The New Madrid Seismic Zone: A Hidden Threat: The central United States, far from the Pacific coast, also harbors significant seismic potential. The New Madrid Seismic Zone, located in the Mississippi River Valley, is an area of ancient fault lines. Despite being relatively inactive in recent history, this zone is capable of producing powerful earthquakes. The New Madrid earthquakes of 1811-1812, which were among the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded in North America, demonstrate the region’s capacity for devastation.
- The Eastern United States: A Zone of Moderate Activity: While the eastern United States experiences far fewer earthquakes than the west coast, it is not immune to seismic events. The Appalachian Mountains and the Eastern Tennessee Seismic Zone are areas with a history of moderate earthquakes. While these events are generally less frequent and less intense than those on the Pacific coast, they can still cause significant damage.
Beyond Location: Understanding Earthquake Magnitude and Frequency
The earthquake map is not merely a static representation of earthquake locations. It provides critical information about the magnitude and frequency of seismic events. The map employs a color scale to depict the intensity of earthquakes, with darker shades representing higher magnitudes. This allows scientists and the public to quickly assess the potential impact of an earthquake based on its location and magnitude.
Furthermore, the map incorporates historical data on earthquake frequency, providing insights into the likelihood of future events. This information is crucial for seismic hazard assessments, which evaluate the potential risks associated with earthquakes in specific areas.
The Importance of the Earthquake Map: A Tool for Safety and Resilience
The earthquake map serves as a vital tool for:
- Public Awareness: The map raises awareness about the potential for earthquakes in different parts of the United States. This knowledge empowers individuals, communities, and policymakers to take proactive measures to prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with seismic events.
- Building Codes and Infrastructure Design: The map informs the development of building codes and infrastructure design standards that are specifically tailored to the seismic hazards of different regions. By incorporating earthquake-resistant design principles, structures can be made more resilient to seismic forces.
- Emergency Response Planning: The map aids in the development of effective emergency response plans. By understanding the potential impact of earthquakes in different areas, emergency responders can better anticipate the needs of affected communities and deploy resources strategically.
- Scientific Research: The earthquake map provides a valuable dataset for scientists studying earthquake processes, seismic hazard assessment, and earthquake forecasting. By analyzing the distribution and characteristics of earthquakes over time, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the forces that drive seismic activity and improve their ability to predict future events.
FAQs about the Earthquake Map
Q: How often is the earthquake map updated?
A: The earthquake map is constantly updated by the USGS, incorporating real-time data from seismographic networks. This ensures that the map reflects the latest seismic activity and provides the most accurate information available.
Q: What is the difference between an earthquake’s epicenter and its focus?
A: The epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus, which is the point of origin of the earthquake within the Earth’s crust.
Q: What is the difference between magnitude and intensity?
A: Magnitude refers to the energy released by an earthquake, measured on the Richter scale. Intensity, on the other hand, describes the effects of an earthquake on the Earth’s surface and on human structures, measured on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale.
Q: Can earthquakes be predicted?
A: While scientists have made significant progress in understanding earthquake processes, predicting the exact time, location, and magnitude of an earthquake remains a significant challenge. However, ongoing research and advancements in technology are constantly improving our ability to assess seismic hazards and develop early warning systems.
Tips for Using the Earthquake Map
- Familiarize Yourself with the Map: Take time to explore the earthquake map and understand the distribution of seismic activity across the United States.
- Identify Your Location: Locate your home or workplace on the map and assess the potential seismic hazards in your area.
- Prepare for Earthquakes: Develop an earthquake preparedness plan that includes securing heavy objects, creating an emergency kit, and practicing earthquake drills.
- Stay Informed: Monitor the USGS website and other reliable sources for updates on earthquake activity and alerts.
Conclusion
The earthquake map is a powerful tool that provides a crucial window into the seismic forces that shape our planet. By understanding the distribution, magnitude, and frequency of earthquakes, we can better prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with these natural hazards. The map serves as a constant reminder of the dynamic nature of the Earth and the importance of preparedness in facing the challenges posed by seismic activity. Its use empowers individuals, communities, and policymakers to make informed decisions and build a more resilient future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Seismic Portrait of the United States: Understanding the Earthquake Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!