A Seismic Story: Understanding Earthquake Risk in California
Related Articles: A Seismic Story: Understanding Earthquake Risk in California
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Seismic Story: Understanding Earthquake Risk in California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Seismic Story: Understanding Earthquake Risk in California
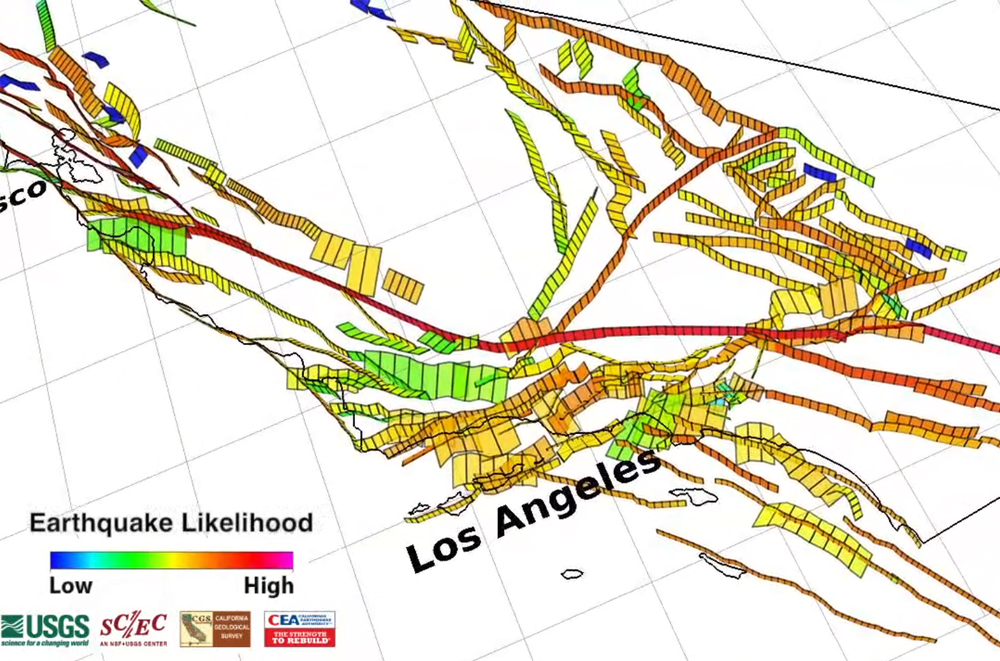
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and vibrant culture, also sits atop a complex and active geological fault system. This reality makes the state susceptible to earthquakes, a constant reminder of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. Understanding the distribution and frequency of these seismic events is crucial for mitigating risk and ensuring the safety of California’s residents and infrastructure.
The San Andreas Fault: A Major Player in California’s Seismic Activity
The San Andreas Fault, a transform plate boundary running for over 800 miles along the coast of California, is the most prominent feature in the state’s seismic landscape. This fault marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, where the two plates slide horizontally past each other. This movement is not smooth; it occurs in sudden, jerky bursts, releasing immense amounts of energy in the form of earthquakes.
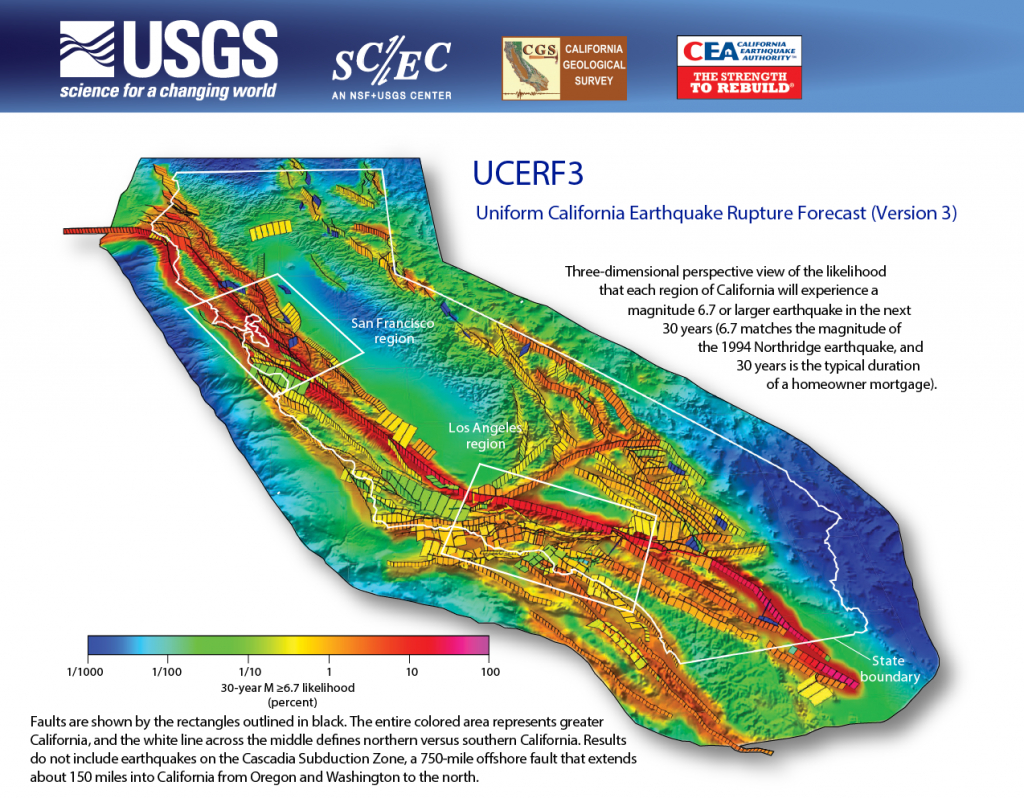
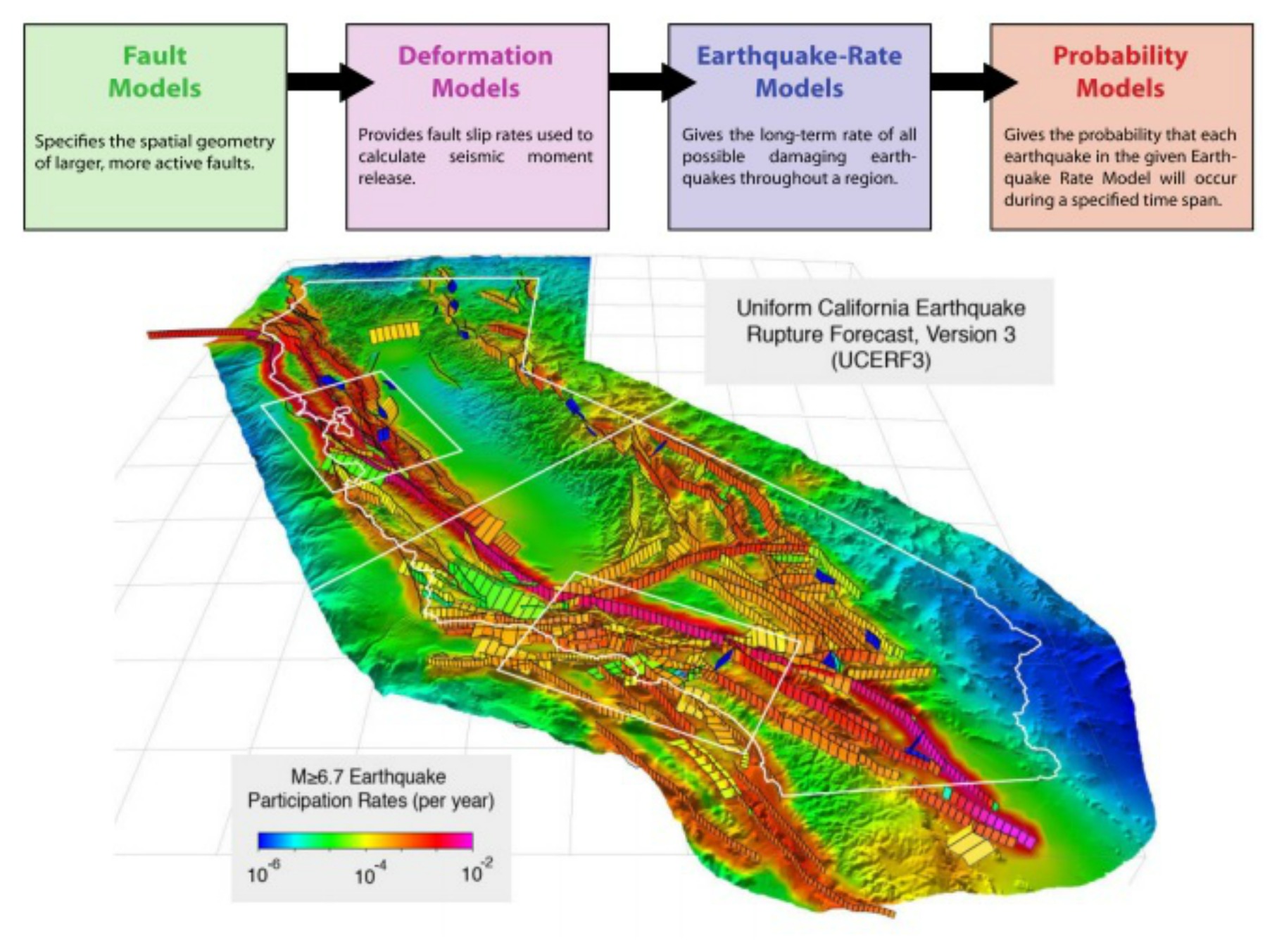
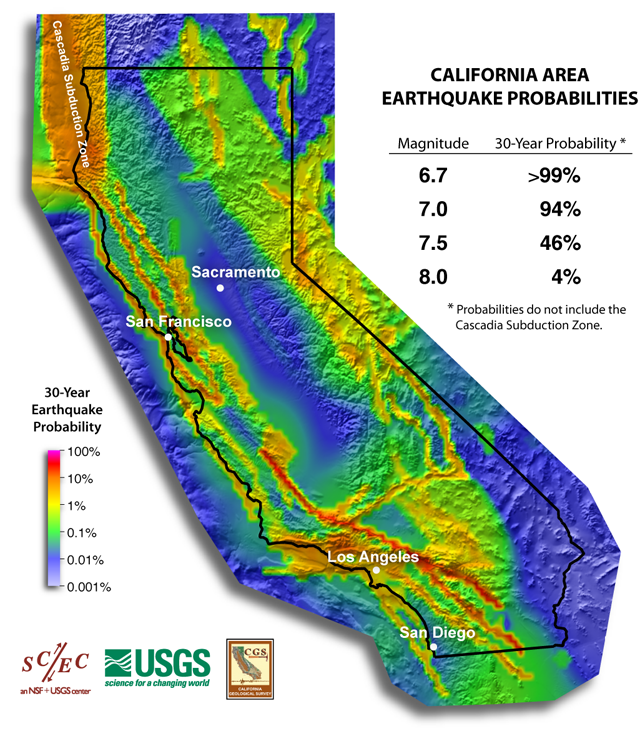
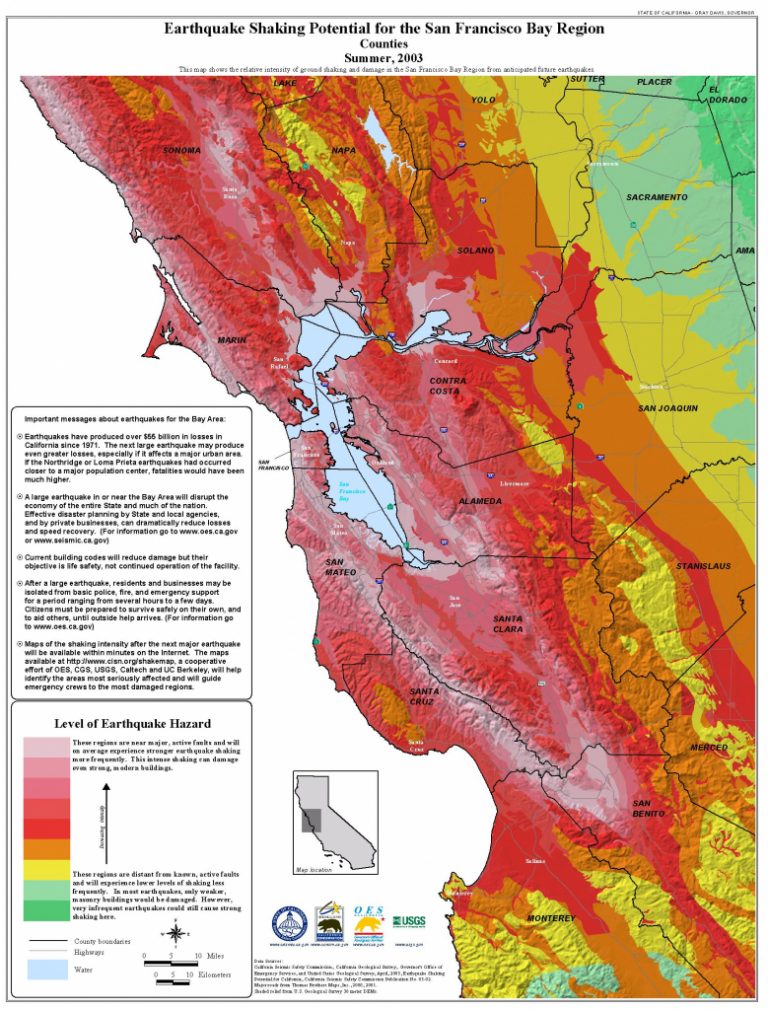
Mapping Earthquake Risk: A Visual Guide to Seismic Hazards
Seismic maps, tools that visually represent earthquake risk, are indispensable for understanding the potential impact of earthquakes in California. These maps are created by analyzing historical earthquake data, geological formations, and the movement of tectonic plates. They provide a comprehensive overview of earthquake risk across the state, highlighting areas with high seismic activity and potential for significant ground shaking.
Key Elements of California Earthquake Maps:
- Fault Zones: Maps clearly delineate major fault lines, like the San Andreas Fault, indicating areas prone to seismic activity.
- Seismic Hazard Zones: These zones are classified based on the probability of experiencing ground shaking of a certain intensity during a specific timeframe.
- Ground Shaking Intensity: Maps often use color scales to represent the intensity of ground shaking, measured in Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) scale, which provides a qualitative measure of the earthquake’s effects on the ground and structures.
- Liquefaction Zones: These zones identify areas where loose, saturated soils can turn into a fluid-like consistency during an earthquake, causing structural damage and ground failures.
- Tsunami Zones: Coastal areas susceptible to tsunami waves, triggered by earthquakes, are highlighted, providing crucial information for evacuation planning.
Understanding the Importance of Earthquake Maps:
- Building Codes and Regulations: Earthquake maps inform building codes and regulations, ensuring structures are designed to withstand potential seismic events.
- Infrastructure Planning: Maps help engineers and planners design and construct resilient infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and power grids, that can withstand the forces of earthquakes.
- Emergency Response: Maps guide emergency responders, helping them prioritize resources and deploy personnel to areas most affected by earthquakes.
- Public Awareness: Maps educate the public about earthquake risks, encouraging preparedness and promoting safety measures.
FAQs about Earthquake Maps in California:
Q: How often are earthquake maps updated?
A: Earthquake maps are regularly updated as new data becomes available, including data from recent earthquakes, geological studies, and advancements in seismic hazard modeling.
Q: Are earthquake maps always accurate?
A: While earthquake maps are based on the best available scientific data, they are not infallible. The complex nature of earthquake prediction makes it impossible to predict the exact location, timing, and magnitude of future earthquakes.
Q: What should I do if my home is located in a high-risk seismic zone?
A: Consult with a qualified structural engineer to assess your home’s earthquake resistance. Consider retrofitting your home to improve its seismic resilience.
Tips for Using Earthquake Maps:
- Locate your home or workplace on the map. This will provide a clear understanding of your local earthquake risk.
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend. Understand the different symbols, colors, and classifications used to represent earthquake hazards.
- Develop an emergency plan. Plan evacuation routes and gather essential supplies in case of an earthquake.
- Participate in earthquake preparedness drills. Regular drills will help you and your family respond effectively in an emergency.
Conclusion: A Constant Reminder of Nature’s Power
Earthquake maps are not just visual representations of risk; they serve as a critical tool for understanding and mitigating the impacts of earthquakes in California. By providing a clear picture of seismic hazards, these maps empower individuals, communities, and authorities to make informed decisions, build resilient infrastructure, and prepare for the inevitable occurrence of earthquakes. California’s history of seismic activity underscores the importance of preparedness and the ongoing need to invest in research, infrastructure, and public education to ensure the safety and well-being of its residents.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Seismic Story: Understanding Earthquake Risk in California. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!