A Tapestry of Territories: Understanding France’s Overseas Possessions
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Territories: Understanding France’s Overseas Possessions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Territories: Understanding France’s Overseas Possessions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Territories: Understanding France’s Overseas Possessions

France, a nation renowned for its continental history and cultural influence, also boasts a remarkable network of overseas territories scattered across the globe. These territories, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, cultures, and populations, represent a unique aspect of French identity and hold significant political, economic, and strategic importance. This article delves into the complexities of France’s overseas territories, examining their geographical distribution, historical evolution, and the multifaceted benefits they contribute to the nation.
A Geographic Tapestry:
France’s overseas territories are geographically dispersed, reflecting the nation’s historical involvement in exploration, colonization, and trade. These territories can be broadly categorized into five distinct regions:
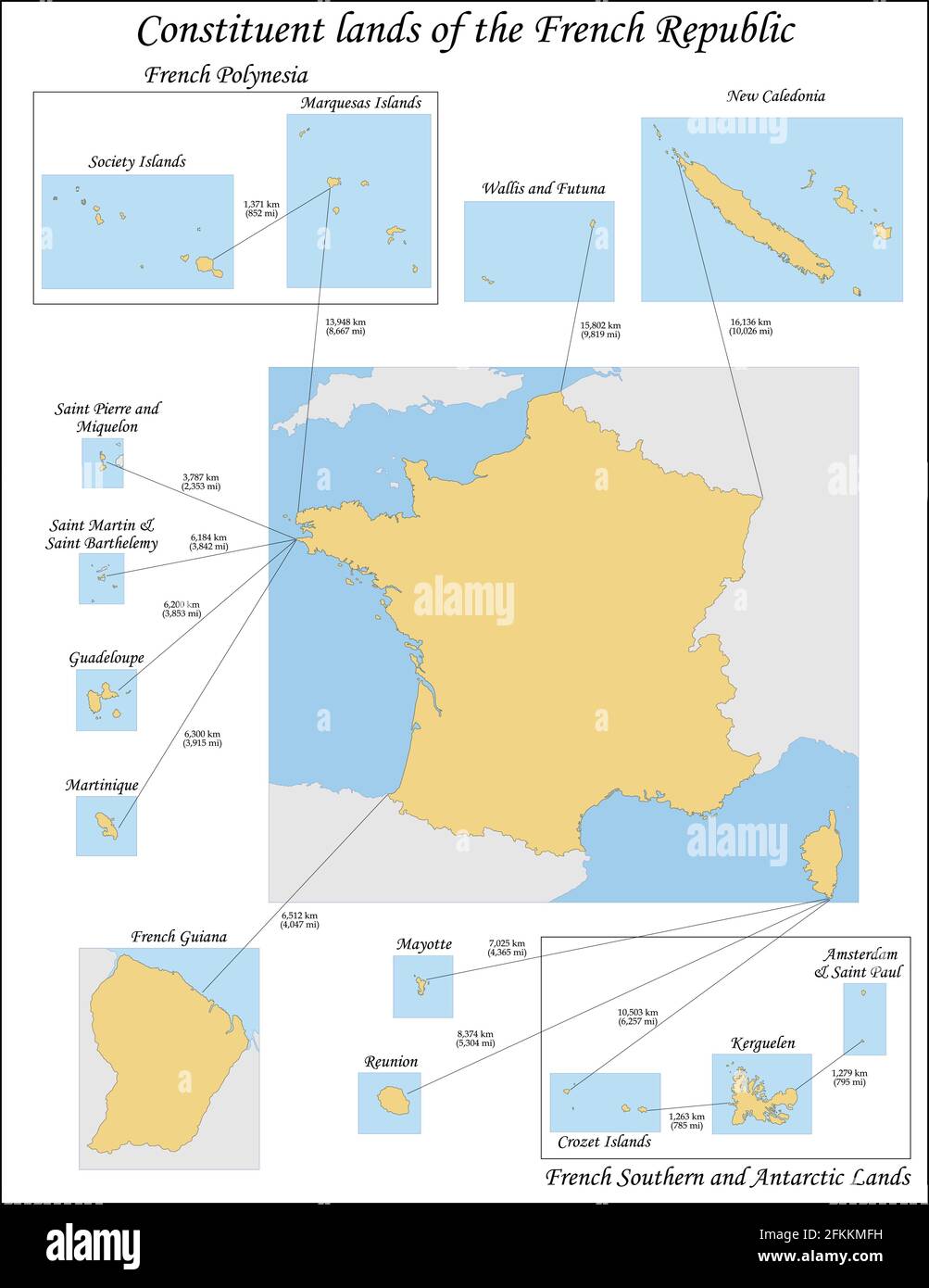
1. The Caribbean:
- Guadeloupe: A volcanic archipelago known for its lush landscapes, sugarcane plantations, and vibrant Creole culture.
- Martinique: Another volcanic island with scenic beaches, rum production, and a rich history intertwined with slavery and emancipation.
- Saint Barthélemy: A small island with luxury resorts, exclusive boutiques, and a relaxed Caribbean atmosphere.
- Saint Martin: Divided between France and the Netherlands, this island boasts diverse beaches, bustling markets, and a cosmopolitan vibe.
2. The Indian Ocean:
- Réunion: A volcanic island with diverse landscapes, from active volcanoes to lush rainforests, renowned for its unique Creole cuisine and culture.
- Mayotte: A volcanic island with a rich history, known for its coral reefs, diverse wildlife, and traditional music.
3. The South Pacific:
- French Polynesia: A collection of islands and atolls, known for its breathtaking lagoons, coral reefs, and Polynesian culture.
- New Caledonia: An archipelago with diverse landscapes, including mountains, rainforests, and beaches, known for its nickel mining and indigenous Kanak culture.
- Wallis and Futuna: Two small volcanic islands with a unique Polynesian culture, renowned for their traditional dances and crafts.
4. The North Atlantic:
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon: A small archipelago located near Newfoundland, Canada, known for its fishing industry and historical significance.
5. The Americas:
- French Guiana: A territory on the northern coast of South America, known for its dense rainforest, spaceport, and gold mining.
Historical Evolution:
The origins of France’s overseas territories can be traced back to the Age of Exploration and the subsequent period of colonization. The establishment of trading posts, settlements, and colonies across the globe led to the acquisition of vast territories, shaping France’s global influence and contributing to its economic prosperity.
However, the process of decolonization, beginning in the mid-20th century, led to the independence of many former French colonies. Despite this, several territories remained under French administration, evolving into overseas departments, collectivities, or territories.
The Importance of Overseas Territories:
France’s overseas territories hold significant importance for the nation, contributing to its economic, political, and cultural landscape:
1. Economic Contributions:
- Natural Resources: Many territories possess valuable natural resources, including nickel, gold, phosphates, and seafood, contributing to France’s overall economic output.
- Tourism: Stunning landscapes, diverse cultures, and unique experiences attract tourists, generating revenue and supporting local economies.
- Strategic Value: Some territories, particularly those in the Indian Ocean and the Pacific, hold strategic importance for France’s military presence and maritime security.
2. Political and Strategic Significance:
- International Influence: Overseas territories provide France with a global presence, strengthening its diplomatic relations and international influence.
- Defense and Security: Territories contribute to France’s defense capabilities, providing strategic locations for military bases and operations.
3. Cultural Diversity and Identity:
- Cultural Exchange: Overseas territories contribute to the richness and diversity of French culture, fostering cultural exchange and understanding.
- Representation: Territories are represented in the French Parliament, ensuring their voices are heard in national decision-making.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the benefits, France’s overseas territories face numerous challenges, including:
- Economic Disparities: Economic development varies significantly across territories, leading to disparities in living standards and opportunities.
- Environmental Concerns: Fragile ecosystems, including coral reefs and rainforests, face threats from pollution, climate change, and unsustainable practices.
- Political Autonomy: Some territories seek greater autonomy or even independence, leading to political tensions and debates.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach, involving both the French government and local authorities. This includes promoting sustainable development, investing in infrastructure, and empowering local communities to participate in decision-making processes.
Conclusion:
France’s overseas territories are a testament to the nation’s historical legacy and its enduring global presence. These territories, with their diverse landscapes, cultures, and populations, contribute significantly to France’s economic prosperity, political influence, and cultural richness. While challenges remain, addressing them through collaborative efforts will ensure a sustainable and prosperous future for these territories and their inhabitants, further solidifying France’s role as a global power.
FAQs:
1. What is the legal status of France’s overseas territories?
France’s overseas territories have varying legal statuses, ranging from overseas departments (DOM) with the same legal status as mainland France, to overseas collectivities (COM) with greater autonomy, and overseas territories (TOM) with a more decentralized administration.
2. Do residents of overseas territories have French citizenship?
Yes, residents of all overseas territories have French citizenship and enjoy the same rights and responsibilities as citizens residing in mainland France.
3. How are overseas territories represented in French politics?
Overseas territories are represented in the French Parliament through elected deputies and senators. They also have local elected assemblies responsible for managing their internal affairs.
4. What are the main economic activities in overseas territories?
Economic activities vary depending on the territory but often include fishing, agriculture, tourism, mining, and other industries related to their natural resources.
5. What are the environmental challenges facing overseas territories?
Overseas territories face various environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, deforestation, and overfishing, which threaten their fragile ecosystems and biodiversity.
Tips:
- Explore the cultural richness: Each territory offers unique cultural experiences, from traditional dances and music to local cuisine and crafts.
- Engage in responsible tourism: Respect local customs, minimize your environmental impact, and support sustainable tourism initiatives.
- Learn about the history: Understanding the historical context of each territory provides valuable insights into their present-day realities.
- Support local communities: Patronize local businesses, engage with local residents, and contribute to community projects.
- Stay informed: Follow news and developments related to overseas territories to stay updated on their challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion:
France’s overseas territories are a fascinating tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and histories. Understanding their unique characteristics and contributions is crucial for appreciating the complexity and diversity of France’s global presence. By recognizing their importance and addressing their challenges, France can foster a sustainable and prosperous future for these territories, further strengthening its role as a nation with global reach and influence.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Territories: Understanding France’s Overseas Possessions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!