A Window to Our Planet: The Power of Earth Observation Satellites
Related Articles: A Window to Our Planet: The Power of Earth Observation Satellites
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Window to Our Planet: The Power of Earth Observation Satellites. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Window to Our Planet: The Power of Earth Observation Satellites

The Earth, a vibrant tapestry of diverse ecosystems, swirling weather patterns, and human settlements, has always fascinated humanity. But our understanding of this intricate planet has been significantly enhanced by the advent of Earth observation satellites. These celestial sentinels, orbiting high above, provide us with a unique perspective, capturing detailed images and data that reveal the Earth’s dynamic processes and the impact of human activities.
The Evolution of Earth Observation:
The journey of Earth observation began with rudimentary aerial photography in the early 20th century. However, it was the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, in 1957, that truly ushered in a new era. This marked the beginning of our ability to observe the Earth from space, offering a global perspective previously unimaginable.
Early Earth observation satellites were primarily focused on military applications, such as reconnaissance and surveillance. However, the scientific and societal benefits of this technology quickly became apparent. As the technology advanced, the focus shifted towards environmental monitoring, resource management, disaster response, and various other applications that directly impact human lives.
A Multifaceted Perspective: The Capabilities of Earth Observation Satellites
Earth observation satellites are equipped with a diverse array of sensors, each designed to capture specific types of data. These sensors include:
-
Optical Sensors: These sensors capture images in various wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including visible light, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared. Optical imagery provides valuable information on land cover, vegetation health, water bodies, and urban development.
-
Radar Sensors: Radar sensors emit microwave radiation and measure the reflected signals, enabling them to penetrate clouds and observe the Earth’s surface in various weather conditions. This technology is particularly useful for mapping topography, monitoring land use changes, and detecting forest fires.
-
Infrared Sensors: Infrared sensors detect thermal radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface. They are used to monitor temperature changes, identify heat sources like volcanic eruptions and wildfires, and track the movement of ocean currents.
-
Microwave Sensors: Microwave sensors operate at longer wavelengths than radar sensors, allowing them to penetrate vegetation and even soil. This technology is crucial for monitoring soil moisture, measuring precipitation, and assessing agricultural productivity.
The Applications of Earth Observation Data:
The data collected by Earth observation satellites is used across a wide range of disciplines and applications, impacting our lives in numerous ways:
1. Environmental Monitoring and Resource Management:
-
Climate Change Monitoring: Satellites provide crucial data for monitoring global warming, sea-level rise, glacier retreat, and changes in vegetation patterns. This information helps scientists understand the complex dynamics of climate change and develop mitigation strategies.
-
Forest Management: Satellite imagery allows for monitoring deforestation rates, mapping forest cover, and identifying areas prone to fires. This information is vital for sustainable forest management, conservation efforts, and carbon sequestration strategies.
-
Water Resource Management: Satellites monitor water bodies, track water quality, and assess the impact of droughts and floods. This data is crucial for water resource management, irrigation planning, and disaster preparedness.
2. Disaster Response and Emergency Management:
-
Disaster Monitoring: Satellites provide near real-time imagery of natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, volcanic eruptions, and wildfires. This information enables rapid assessment of damage, identification of affected areas, and coordination of rescue efforts.
-
Search and Rescue: Satellite imagery and communication systems are used to locate survivors and coordinate rescue operations in remote areas or during natural disasters.
-
Emergency Response Planning: Satellite data helps in developing disaster preparedness plans, identifying potential risk areas, and allocating resources effectively.
3. Agriculture and Food Security:
-
Crop Monitoring: Satellites track crop health, monitor irrigation needs, and detect pest infestations. This information enables farmers to optimize crop yields, manage resources effectively, and ensure food security.
-
Precision Agriculture: Satellite data supports precision agriculture practices, allowing farmers to apply fertilizers, pesticides, and water precisely where needed, reducing waste and maximizing productivity.
4. Urban Planning and Development:
-
Urban Growth Monitoring: Satellites track urban sprawl, monitor population density, and assess the impact of urbanization on the environment. This information is essential for sustainable urban planning and development.
-
Infrastructure Management: Satellites monitor the condition of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure, helping to identify areas requiring maintenance or repair.
-
Traffic Management: Satellite data can be used to track traffic flow, identify congestion points, and optimize traffic management systems.
5. Navigation and Positioning:
-
Global Positioning System (GPS): Satellites provide the basis for GPS systems, enabling accurate navigation and location tracking.
-
Navigation and Mapping: Satellite data is used to create detailed maps, update navigation systems, and support various applications requiring precise location information.
The Benefits of Earth Observation:
The benefits of Earth observation are far-reaching, impacting various aspects of our lives:
-
Enhanced Understanding of Earth Systems: Earth observation provides a comprehensive view of the planet, enabling scientists to study complex interactions between different Earth systems, such as the atmosphere, oceans, land, and biosphere.
-
Improved Decision-Making: Satellite data provides valuable information for informed decision-making in various fields, including environmental management, disaster response, agriculture, and urban planning.
-
Sustainable Development: Earth observation supports sustainable development practices by providing data for monitoring resource consumption, environmental impacts, and progress towards sustainability goals.
-
Improved Public Safety: Satellite data helps in early warning systems for natural disasters, improving public safety and reducing the impact of disasters.
-
Scientific Advancement: Earth observation data drives scientific research and innovation in various fields, leading to new discoveries and advancements in our understanding of the planet.
FAQs about Earth Observation Satellites:
1. How accurate is the data collected by Earth observation satellites?
The accuracy of Earth observation data depends on several factors, including the type of sensor used, the resolution of the imagery, and the processing techniques applied. Modern satellites can achieve resolutions of less than a meter, providing highly detailed information.
2. How often are Earth observation satellites able to capture data?
The revisit frequency of Earth observation satellites varies depending on their orbit and mission objectives. Some satellites have daily revisit capabilities, while others may revisit specific areas every few days or weeks.
3. What are the limitations of Earth observation satellites?
Despite their immense capabilities, Earth observation satellites have some limitations. These include:
-
Cloud Cover: Cloud cover can obstruct the view of the Earth’s surface, limiting the effectiveness of optical sensors.
-
Atmospheric Interference: Atmospheric conditions can distort the signals received by sensors, impacting data accuracy.
-
Data Processing and Analysis: Processing and analyzing large volumes of satellite data can be challenging and time-consuming.
4. How is Earth observation data accessed and used?
Earth observation data is typically made available through government agencies, commercial companies, and research institutions. The data can be accessed through online portals, data archives, or direct partnerships.
5. What is the future of Earth observation?
The future of Earth observation is promising, with advancements in technology leading to higher resolution sensors, improved data processing capabilities, and more sophisticated applications. Emerging technologies like hyperspectral imaging, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), and lidar are expected to revolutionize Earth observation, providing even more detailed and insightful information about our planet.
Tips for Using Earth Observation Data:
-
Identify the Specific Data Needs: Clearly define the objectives and specific data requirements for the intended application.
-
Choose the Right Data Source: Select the appropriate Earth observation satellite and sensor based on the required resolution, spectral range, and revisit frequency.
-
Utilize Data Processing Tools: Utilize specialized software and tools for processing and analyzing satellite data, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
-
Collaborate with Experts: Seek guidance from experts in Earth observation, data analysis, and specific application areas.
-
Disseminate Findings: Communicate findings and insights derived from Earth observation data to relevant stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making.
Conclusion:
Earth observation satellites have revolutionized our understanding of the Earth, providing a unique and invaluable perspective on our planet’s dynamic processes. From monitoring climate change and managing resources to responding to disasters and supporting sustainable development, these celestial sentinels play a vital role in shaping our future. As technology continues to advance, Earth observation is poised to become even more powerful, providing us with unprecedented insights into our planet and enabling us to make informed decisions for a more sustainable future.
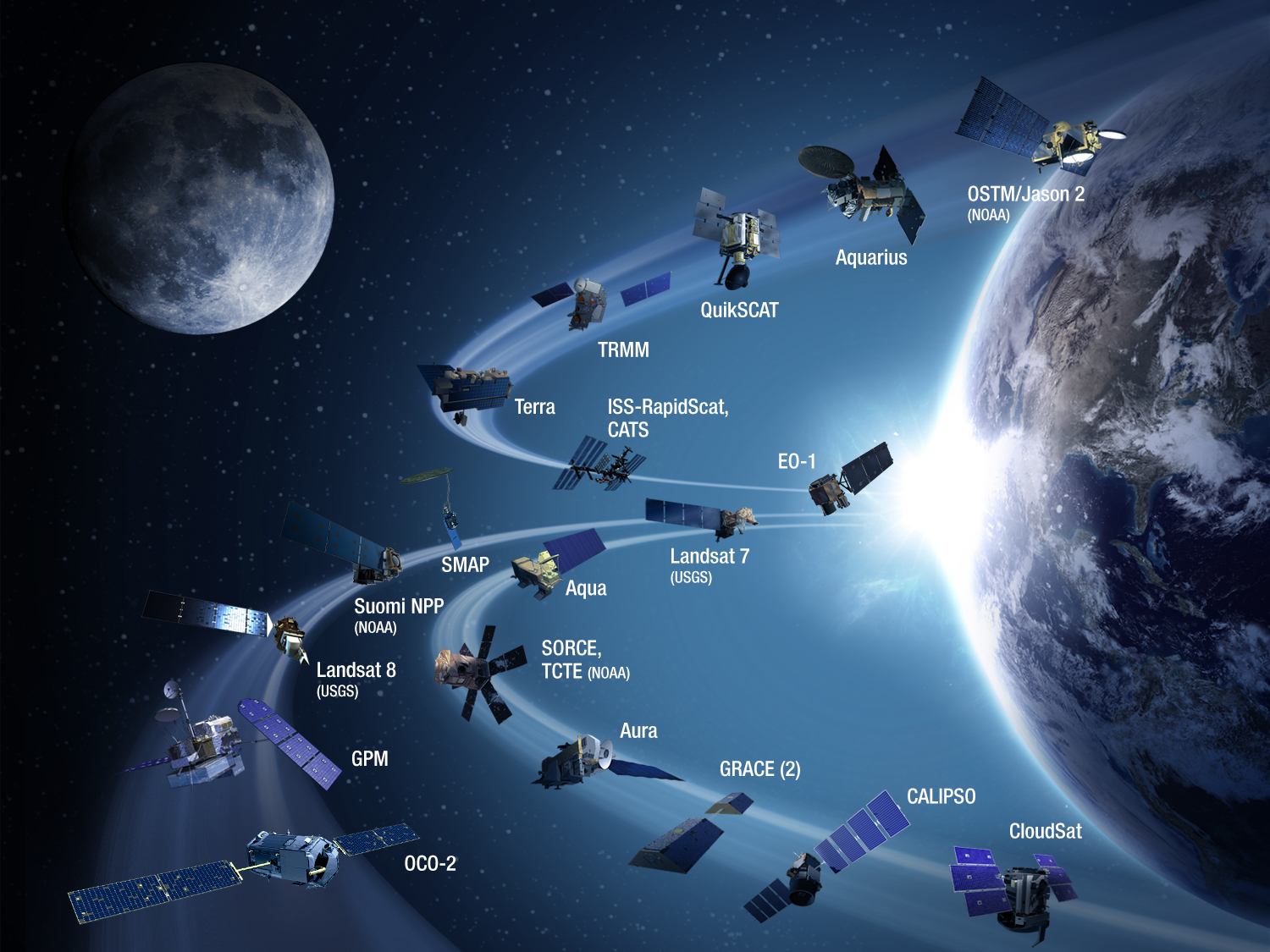







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Window to Our Planet: The Power of Earth Observation Satellites. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!