A World Transformed: Mapping the Earth After Climate Change
Related Articles: A World Transformed: Mapping the Earth After Climate Change
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World Transformed: Mapping the Earth After Climate Change. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World Transformed: Mapping the Earth After Climate Change
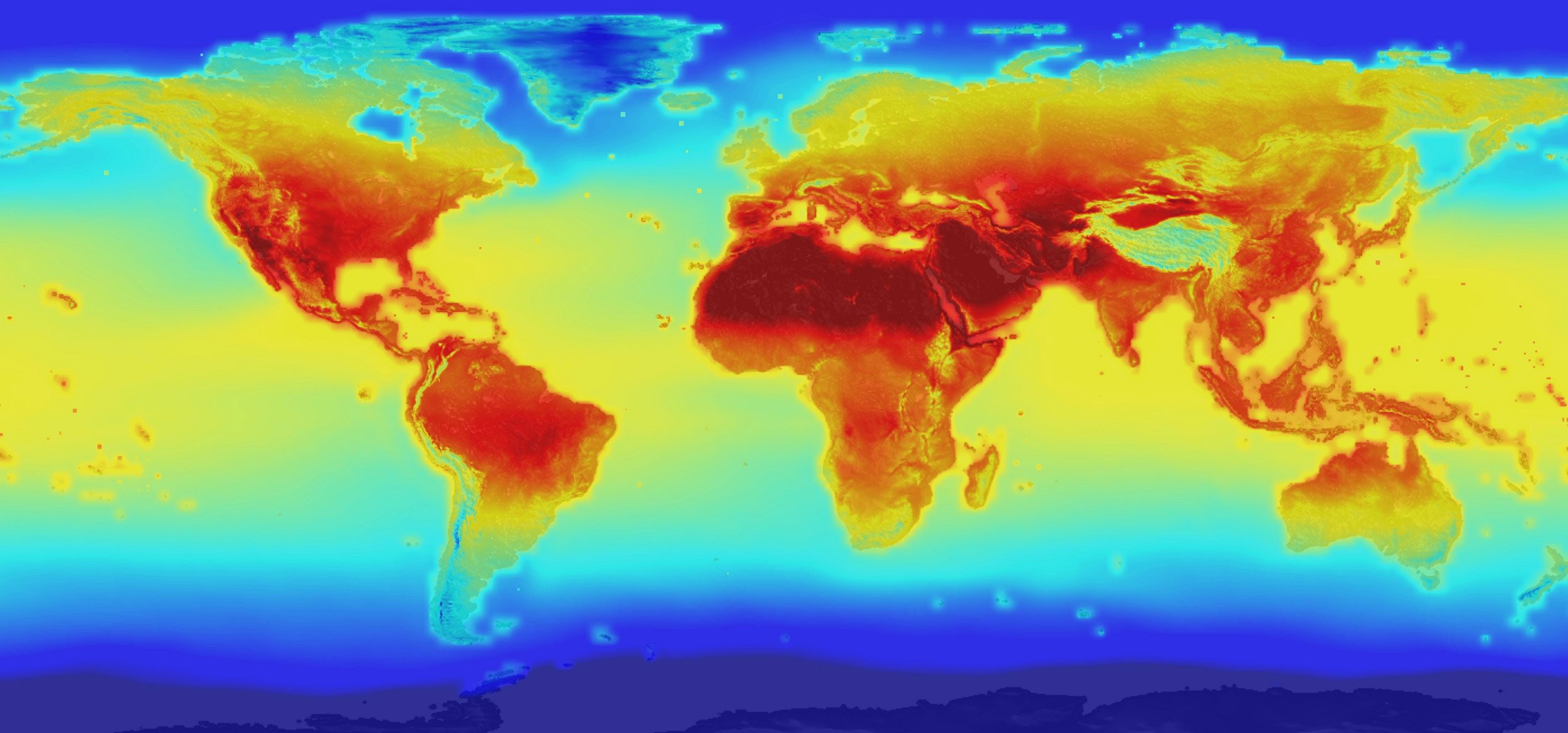
The Earth’s climate is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by human activities that have significantly increased greenhouse gas emissions. This change is not merely a matter of rising temperatures; it reshapes entire ecosystems, alters coastlines, and disrupts human societies. To understand the scale of this transformation, visualizing the Earth after climate change through maps becomes crucial.
Visualizing the Impacts:
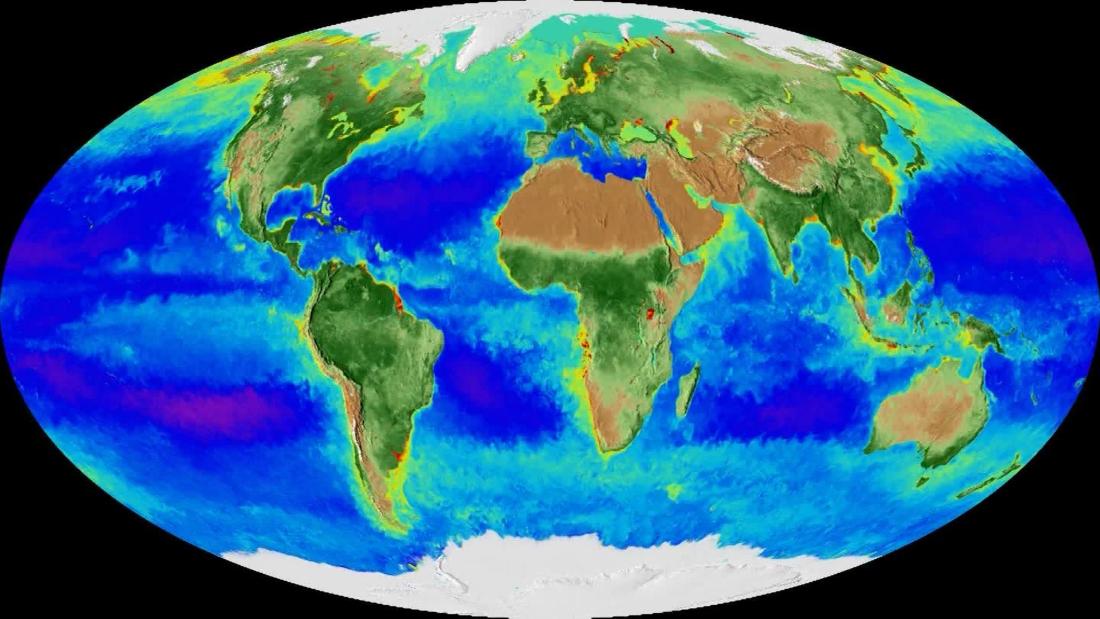
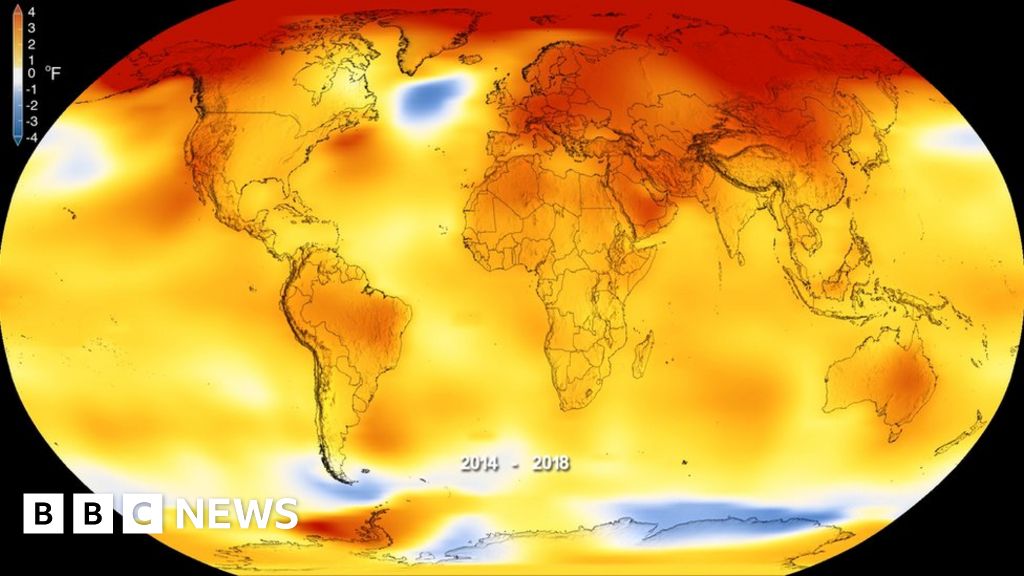
Maps provide a powerful tool for comprehending the multifaceted effects of climate change. They offer a visual representation of the changes occurring across diverse geographical regions, facilitating a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of environmental systems.
Shifting Coastlines:
One of the most significant impacts of climate change is rising sea levels. As glaciers melt and ocean water expands due to rising temperatures, coastal regions face inundation and erosion. Maps depicting projected sea level rise highlight the vulnerability of coastal cities, densely populated areas, and low-lying islands. The disappearance of islands and coastal regions will have profound consequences for human populations, ecosystems, and infrastructure.
Changing Landscapes:
Climate change alters landscapes in various ways. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns lead to changes in vegetation, with some regions experiencing desertification while others witness the spread of forests. Maps showcasing these shifts in vegetation cover reveal the vulnerability of ecosystems and the potential for biodiversity loss.
Migration and Displacement:
Climate change acts as a driver of human migration. As extreme weather events become more frequent and intense, people are forced to relocate from areas affected by floods, droughts, and rising sea levels. Maps illustrating migration patterns under climate change scenarios reveal the potential for large-scale displacement and the challenges of managing refugee populations.
Resource Availability:
Climate change impacts the availability of essential resources like water and food. Altered precipitation patterns can lead to water scarcity in some regions, while increased temperatures affect agricultural yields. Maps depicting these changes in resource availability highlight the potential for conflict and instability as competition for scarce resources intensifies.
The Importance of Mapping:
Visualizing the Earth after climate change through maps serves several critical purposes:
- Raising Awareness: Maps provide a powerful tool for communicating the complex impacts of climate change to the public, policymakers, and stakeholders.
- Informing Decision-Making: Maps inform decision-making by providing data on vulnerable areas, potential risks, and adaptation strategies.
- Facilitating Adaptation: Maps support the development of adaptation plans by identifying areas requiring immediate attention and prioritizing resource allocation.
- Promoting Collaboration: Maps foster collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and communities by providing a common platform for understanding the challenges of climate change.
FAQs:
Q: What are the most vulnerable regions to climate change?
A: Coastal areas, low-lying islands, arid regions, and regions heavily dependent on agriculture are particularly vulnerable to climate change.
Q: How are maps used to predict future impacts?
A: Maps incorporate climate models and projections to simulate future scenarios, allowing for the visualization of potential impacts under different levels of warming.
Q: What are the limitations of climate change maps?
A: Maps rely on data and models that are constantly evolving. Uncertainty remains regarding the exact magnitude and timing of climate change impacts.
Tips for Understanding Climate Change Maps:
- Pay attention to the scale: Maps should be interpreted in relation to the spatial scale they represent.
- Consider the data source: The reliability of maps depends on the quality and accuracy of the data used.
- Understand the projections: Maps often present future scenarios based on different emission pathways.
- Engage with the context: Maps should be interpreted within the broader context of social, economic, and environmental factors.
Conclusion:
Visualizing the Earth after climate change through maps is essential for understanding the complex and multifaceted nature of this global challenge. These maps serve as powerful tools for raising awareness, informing decision-making, facilitating adaptation, and promoting collaboration. By understanding the potential impacts and taking necessary actions, we can strive to mitigate the worst effects of climate change and build a more resilient future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World Transformed: Mapping the Earth After Climate Change. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!