Alsace-Lorraine: A Shifting Landscape on the Map of Europe
Related Articles: Alsace-Lorraine: A Shifting Landscape on the Map of Europe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Alsace-Lorraine: A Shifting Landscape on the Map of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Alsace-Lorraine: A Shifting Landscape on the Map of Europe
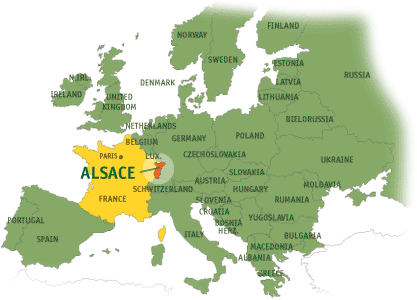
The region of Alsace-Lorraine, nestled in the heart of Europe, has a history as intricate and dynamic as the borders that have defined it. Its position on the map has been a source of both prosperity and conflict, reflecting the complex interplay of power, culture, and identity that has shaped its destiny. This article will delve into the historical evolution of Alsace-Lorraine, focusing on its cartographic representation in 1820, and exploring the factors that contributed to its shifting borders and the enduring impact on the region’s cultural and political landscape.
A Tapestry of Shifting Borders:
The story of Alsace-Lorraine is inextricably linked to the ever-changing map of Europe. This region, situated at the confluence of German, French, and Swiss influences, has been a crossroads of cultures and empires for centuries.
Prior to the French Revolution, Alsace-Lorraine was divided between the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of France. Alsace, predominantly German-speaking, was under Habsburg rule, while Lorraine, with a French majority, was a duchy independent of the French crown. The French Revolution, however, ushered in a new era of territorial change. In 1792, France annexed both Alsace and Lorraine, incorporating them into its national territory.
This annexation, however, was not without controversy. The region’s population, divided by language and cultural affinity, experienced a period of political and cultural upheaval. The French government sought to integrate the region, promoting French language and culture, while simultaneously facing resistance from those who felt their traditions and identities were threatened.
The Map in 1820: A Period of Relative Stability
The year 1820 marks a period of relative stability in the map of Alsace-Lorraine. After the turbulent Napoleonic Wars, the region remained firmly within French territory. The map of 1820 reflects this status quo, showing Alsace and Lorraine as integral parts of France, with their borders established and recognized by the international community.
This period witnessed a gradual integration of Alsace-Lorraine into French society. The French language gained prominence, and the region’s economy experienced growth under French administration. However, cultural tensions persisted, particularly in Alsace, where German language and traditions continued to hold sway.
The Franco-Prussian War and the Birth of a Contested Territory
The relative stability of Alsace-Lorraine in the 1820s was shattered by the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. This conflict, fueled by growing nationalistic ambitions and competing claims over the region, ended with a decisive Prussian victory. The Treaty of Frankfurt in 1871, a bitter consequence of French defeat, resulted in the annexation of Alsace and most of Lorraine by the newly formed German Empire.
This annexation, known as the "Lost Territories," sparked a wave of outrage and resentment in France. It also triggered a period of cultural and political upheaval in Alsace-Lorraine. The region, once again divided by its identity, found itself caught between two competing nationalisms. German authorities sought to integrate the region into the German Empire, promoting German language and culture, while French sentiment remained strong, particularly among the population of Lorraine.
The Shifting Sands of Identity:
The period between 1871 and 1918, marked by German rule, witnessed a complex interplay of cultural and political forces in Alsace-Lorraine. While German authorities sought to assert their dominance, French identity and culture remained resilient. The region’s population, caught between two national narratives, developed a unique cultural identity, characterized by a blend of German and French influences.
The outbreak of World War I, fueled by the unresolved tensions between France and Germany, further complicated the situation. Alsace-Lorraine became a battleground, its population caught in the crossfire of a conflict that had its roots in the region’s contested history.
Return to France and the Legacy of Alsace-Lorraine:
The end of World War I saw the return of Alsace-Lorraine to France, a victory celebrated by the French population. However, the region’s return did not erase the scars of its tumultuous past. The period of German rule had left its mark on the region’s cultural landscape, fostering a complex and nuanced identity that was both French and German.
The period following World War I witnessed a renewed effort to integrate Alsace-Lorraine into French society. The French government implemented policies aimed at promoting French language and culture, while acknowledging the region’s unique cultural heritage.
A Region Defined by Its Diversity:
The map of Alsace-Lorraine, a testament to the region’s complex history, continues to evolve. The region’s unique cultural identity, shaped by centuries of influence from both France and Germany, remains a source of both pride and complexity. The region’s history serves as a reminder of the enduring power of cultural exchange and the challenges of reconciling competing national narratives.
FAQs about Alsace-Lorraine in 1820:
-
What were the main reasons for the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine by France in 1792? The French Revolution, fueled by a desire for national unity and expansion, led to the annexation of Alsace and Lorraine. The region’s strategic location and its economic resources also played a role in the French government’s decision.
-
What was the cultural and linguistic landscape of Alsace-Lorraine in 1820? The region was linguistically and culturally diverse in 1820. Alsace, with a predominantly German-speaking population, retained strong ties to its German heritage. Lorraine, with a majority French-speaking population, had a more integrated relationship with France.
-
What were the main challenges faced by the French government in integrating Alsace-Lorraine after 1792? The French government faced resistance from those who felt their cultural identity was threatened by the imposition of French language and culture. The region’s diverse population also posed challenges in terms of political and social integration.
-
How did the map of Alsace-Lorraine in 1820 differ from its previous cartographic representations? The map of 1820 showed Alsace and Lorraine as integral parts of France, reflecting their annexation during the French Revolution. Prior to this, Alsace had been part of the Holy Roman Empire, and Lorraine was an independent duchy.
-
What were the main economic activities in Alsace-Lorraine in 1820? The region’s economy was diverse in 1820, with agriculture, textile production, and mining playing significant roles. The region’s location at the crossroads of trade routes also contributed to its economic vitality.
Tips for understanding Alsace-Lorraine’s history:
-
Explore the region’s diverse cultural heritage: Immerse yourself in the region’s unique cultural traditions, from its architecture to its cuisine and its language.
-
Visit historical sites and museums: Explore the region’s rich history by visiting castles, churches, and museums that showcase its cultural heritage.
-
Engage with the local community: Interact with the region’s residents to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives on its history and identity.
-
Learn about the region’s linguistic diversity: Explore the region’s linguistic landscape, including French, German, and Alsatian, to appreciate the complexity of its cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
The map of Alsace-Lorraine in 1820, while representing a period of relative stability, provides a glimpse into the region’s dynamic and often turbulent history. Its shifting borders, reflecting the interplay of power and national ambition, have shaped its cultural identity and political landscape. The region’s story serves as a reminder of the complex interplay of language, culture, and identity that defines the human experience, and the enduring impact of historical events on the present.
Understanding the historical evolution of Alsace-Lorraine, through the lens of its cartographic representations, offers valuable insights into the forces that have shaped the region and its people. It is a story that continues to resonate in the present, reminding us of the enduring power of history and the challenges of navigating cultural and political identities in a complex and interconnected world.

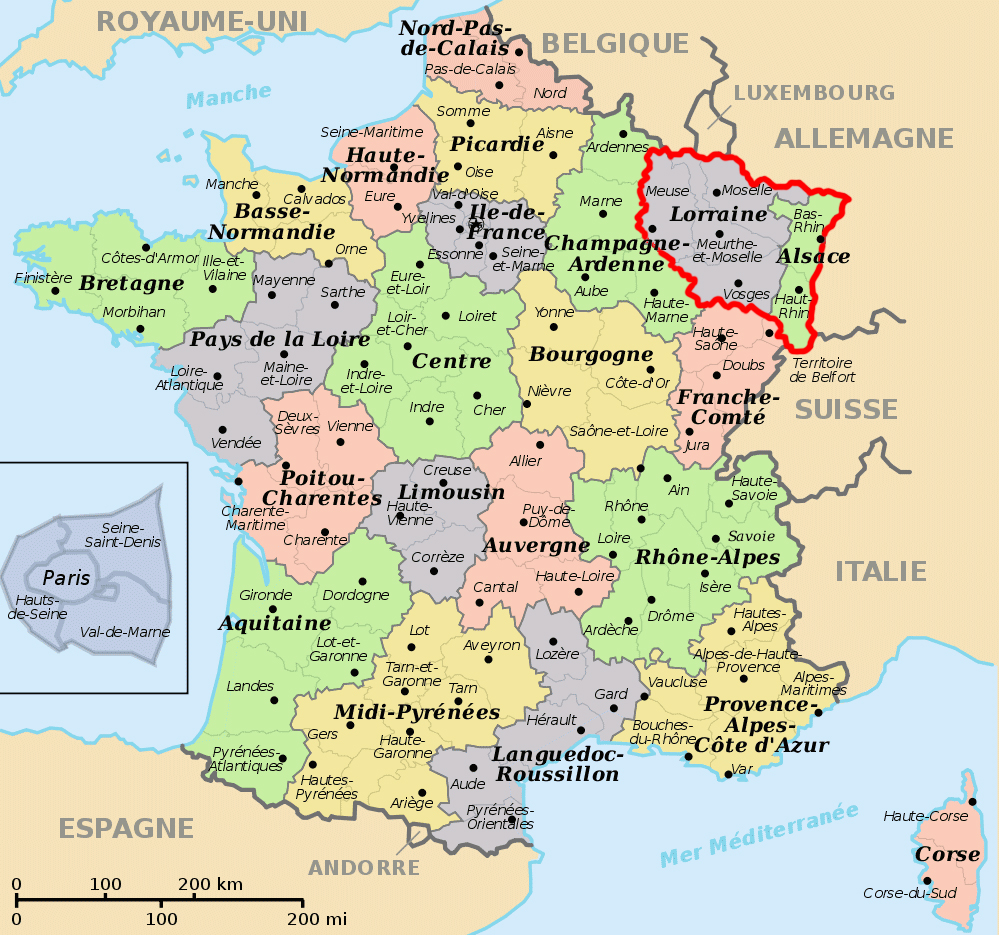




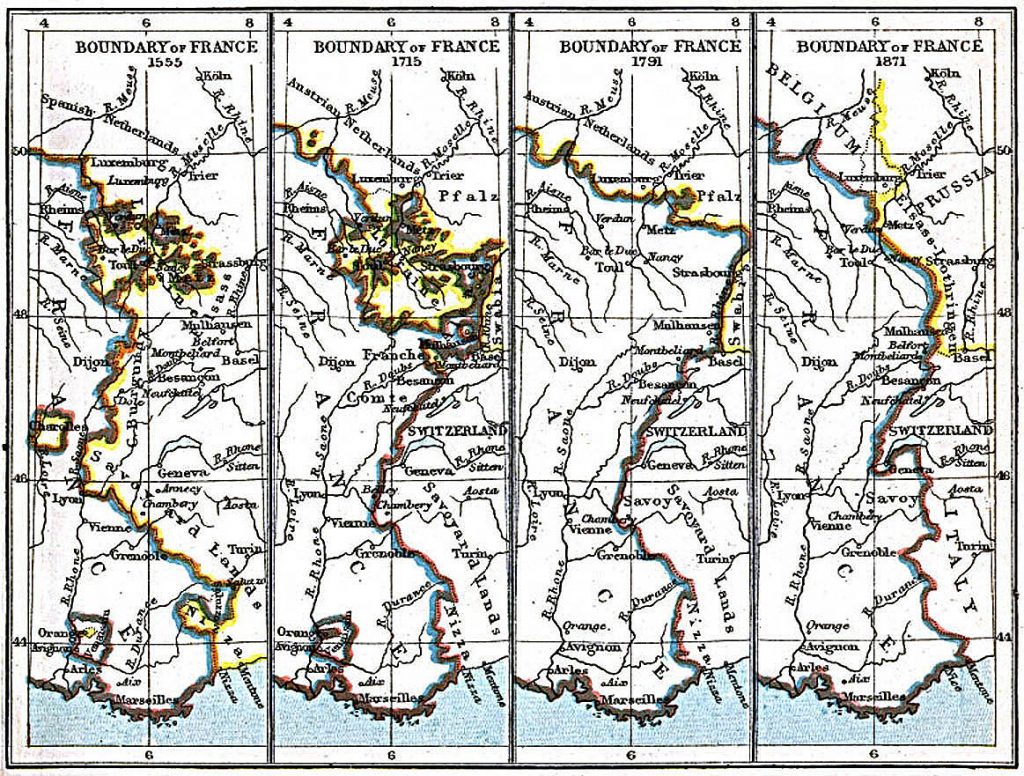
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Alsace-Lorraine: A Shifting Landscape on the Map of Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!