Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape
Related Articles: Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape
- 3.1 Origins and Evolution: A Response to Modern Agriculture
- 3.2 Structure and Function: A Collaborative Network
- 3.3 Benefits and Impact: A Multifaceted Approach
- 3.4 Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future
- 3.5 FAQs by Amap France
- 3.6 Tips by Amap France
- 3.7 Conclusion by Amap France
- 4 Closure
Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape
Amap France, an acronym for "Association pour le Maintien de l’Agriculture Paysanne" (Association for the Maintenance of Peasant Agriculture), represents a unique and vital movement in French agriculture. It stands as a testament to the growing demand for locally sourced, sustainable food and the desire to support small-scale, family-run farms. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of Amap France, exploring its origins, structure, benefits, challenges, and ongoing impact on the French food system.
Origins and Evolution: A Response to Modern Agriculture
Amap France emerged in the early 1990s as a direct response to the perceived shortcomings of industrial agriculture. Concerns about the environmental impact of intensive farming practices, the decline of rural communities, and the loss of agricultural biodiversity fueled the movement’s growth. The concept of "circuits courts" (short circuits) – emphasizing direct relationships between producers and consumers – became central to Amap’s philosophy.
The initial Amap groups were primarily driven by consumer activism, with individuals seeking to secure access to fresh, high-quality produce directly from local farmers. This direct connection fostered a sense of community and facilitated a deeper understanding of agricultural practices.
Over time, Amap France evolved into a more organized network, with regional and national associations coordinating efforts. This collaborative approach fostered shared resources, facilitated knowledge exchange, and strengthened the movement’s collective voice.
Structure and Function: A Collaborative Network
Amap France operates as a decentralized network of independent associations, each with its own unique structure and operating model. However, a common thread runs through all Amap groups: the commitment to establishing direct, sustainable relationships between farmers and consumers.
The core components of an Amap group typically include:
- Producers: Family-run farms committed to sustainable and ethical agricultural practices.
- Consumers: Individuals or families who subscribe to receive regular deliveries of fresh produce.
- Distribution Points: Designated locations where consumers collect their produce, often at community centers or farmers’ markets.
- Management Committee: A group of volunteers responsible for coordinating logistics, communication, and financial management.
The structure of Amap groups varies depending on factors such as size, geographical location, and the specific needs of producers and consumers. Some groups operate solely as a delivery system, while others engage in educational initiatives, community events, and advocacy work.
Benefits and Impact: A Multifaceted Approach
Amap France offers a multitude of benefits for both producers and consumers, contributing to a more sustainable and equitable food system.
Benefits for Producers:
- Guaranteed Income: Amap subscriptions provide producers with a stable income, reducing reliance on fluctuating market prices.
- Direct Connection with Consumers: Amap groups offer farmers a platform to connect directly with consumers, fostering relationships and building trust.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Direct delivery systems minimize transportation distances, reducing environmental impact and maximizing product freshness.
- Market Diversification: Amap groups provide an alternative market channel, expanding opportunities for small-scale farms.
Benefits for Consumers:
- Access to Fresh, Local Produce: Amap subscriptions guarantee access to high-quality, seasonal fruits and vegetables grown locally.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Consumers contribute to the preservation of traditional farming practices and environmental stewardship.
- Community Building: Amap groups foster a sense of community, bringing together individuals who share a commitment to local food systems.
- Increased Food Security: By supporting local agriculture, Amap groups contribute to the resilience of local food systems and reduce reliance on global supply chains.
Overall Impact:
- Preservation of Agricultural Biodiversity: Amap groups support the cultivation of diverse crops and traditional varieties, safeguarding agricultural heritage.
- Economic Revitalization of Rural Areas: By providing a stable market for local produce, Amap groups contribute to the economic vitality of rural communities.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Amap’s emphasis on local sourcing and sustainable practices minimizes food miles and associated carbon emissions.
- Increased Food Awareness: Amap groups educate consumers about the importance of food choices and the interconnectedness of food systems.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future
While Amap France has achieved significant success, it also faces challenges that require ongoing attention and adaptation.
- Scaling Up: Expanding Amap’s reach to new communities and regions requires overcoming logistical hurdles and attracting new participants.
- Competition: Amap groups face competition from conventional supermarkets and online grocery platforms, requiring innovative strategies to attract and retain consumers.
- Labor Shortages: The aging population in rural areas poses challenges for recruitment and retention of agricultural workers, impacting production capacity.
- Climate Change: Climate change poses significant risks to agricultural production, necessitating adaptation strategies and support for farmers.
Despite these challenges, Amap France presents significant opportunities for further growth and development.
- Technological Innovation: Utilizing digital platforms and online tools can enhance communication, streamline logistics, and expand reach.
- Policy Support: Government policies promoting local food systems, sustainable agriculture, and rural development can create a more favorable environment for Amap groups.
- Consumer Education: Raising awareness about the benefits of Amap and promoting the value of local food systems can drive consumer engagement.
- Collaboration: Building stronger partnerships between Amap groups, farmers’ organizations, and other stakeholders can enhance collective impact.
FAQs by Amap France
Q: How do I join an Amap group?
A: To join an Amap group, you can visit the website of the national association (Amap France) or search for local Amap groups in your area. Most groups have a website or social media presence where you can find information about membership, subscription options, and contact details.
Q: What types of produce are available through Amap groups?
A: Amap groups typically offer a variety of fresh, seasonal produce, including fruits, vegetables, eggs, dairy products, and sometimes meat and other agricultural products depending on the specific group.
Q: How much does it cost to subscribe to an Amap group?
A: Subscription fees vary depending on the size and location of the group, the types of produce offered, and the frequency of deliveries. You can find this information on the website or by contacting the group directly.
Q: What are the benefits of joining an Amap group?
A: Joining an Amap group offers numerous benefits, including access to fresh, local produce, support for sustainable agriculture, community building, and increased food security.
Q: How can I get involved in Amap France beyond being a consumer?
A: You can get involved in Amap France by volunteering your time, participating in events, advocating for policies that support local food systems, or starting your own Amap group.
Tips by Amap France
- Choose a group that aligns with your values and needs. Consider factors such as geographical location, produce availability, subscription options, and community involvement.
- Communicate with your farmer. Ask questions about their farming practices, the types of produce they grow, and any seasonal variations.
- Be flexible and understanding. Amap groups are based on the natural rhythms of agriculture, so there may be occasional variations in the availability of certain products.
- Share your experience with others. Encourage friends and family to join Amap groups and contribute to the movement’s growth.
- Advocate for policies that support local food systems. Contact your elected officials and support initiatives that promote sustainable agriculture and rural development.
Conclusion by Amap France
Amap France represents a powerful movement that redefines the relationship between consumers and producers, fostering a more sustainable and equitable food system. By supporting local agriculture, promoting direct connections, and prioritizing environmental stewardship, Amap groups contribute to a brighter future for both people and the planet. As the movement continues to evolve, its commitment to sustainable food practices and community building will continue to shape the landscape of French agriculture for years to come.

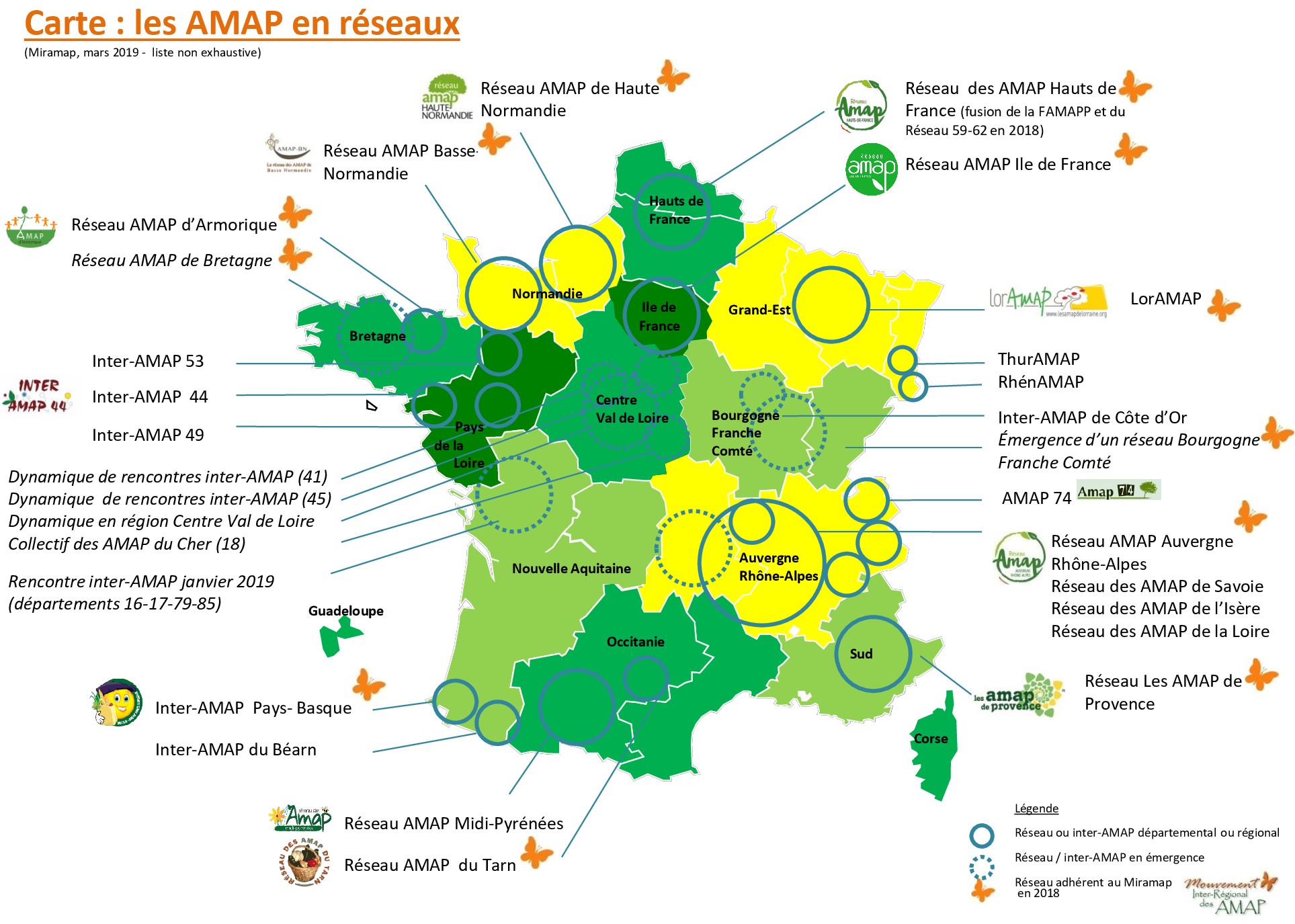

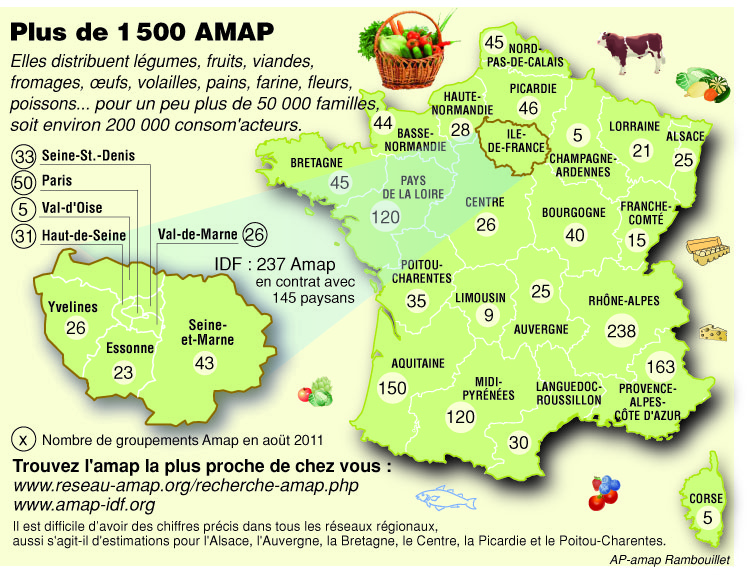

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Amap France: Navigating the French Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
