Australia’s Gas Pipeline Network: A Vital Backbone for Energy Security and Economic Growth
Related Articles: Australia’s Gas Pipeline Network: A Vital Backbone for Energy Security and Economic Growth
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Australia’s Gas Pipeline Network: A Vital Backbone for Energy Security and Economic Growth. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Australia’s Gas Pipeline Network: A Vital Backbone for Energy Security and Economic Growth

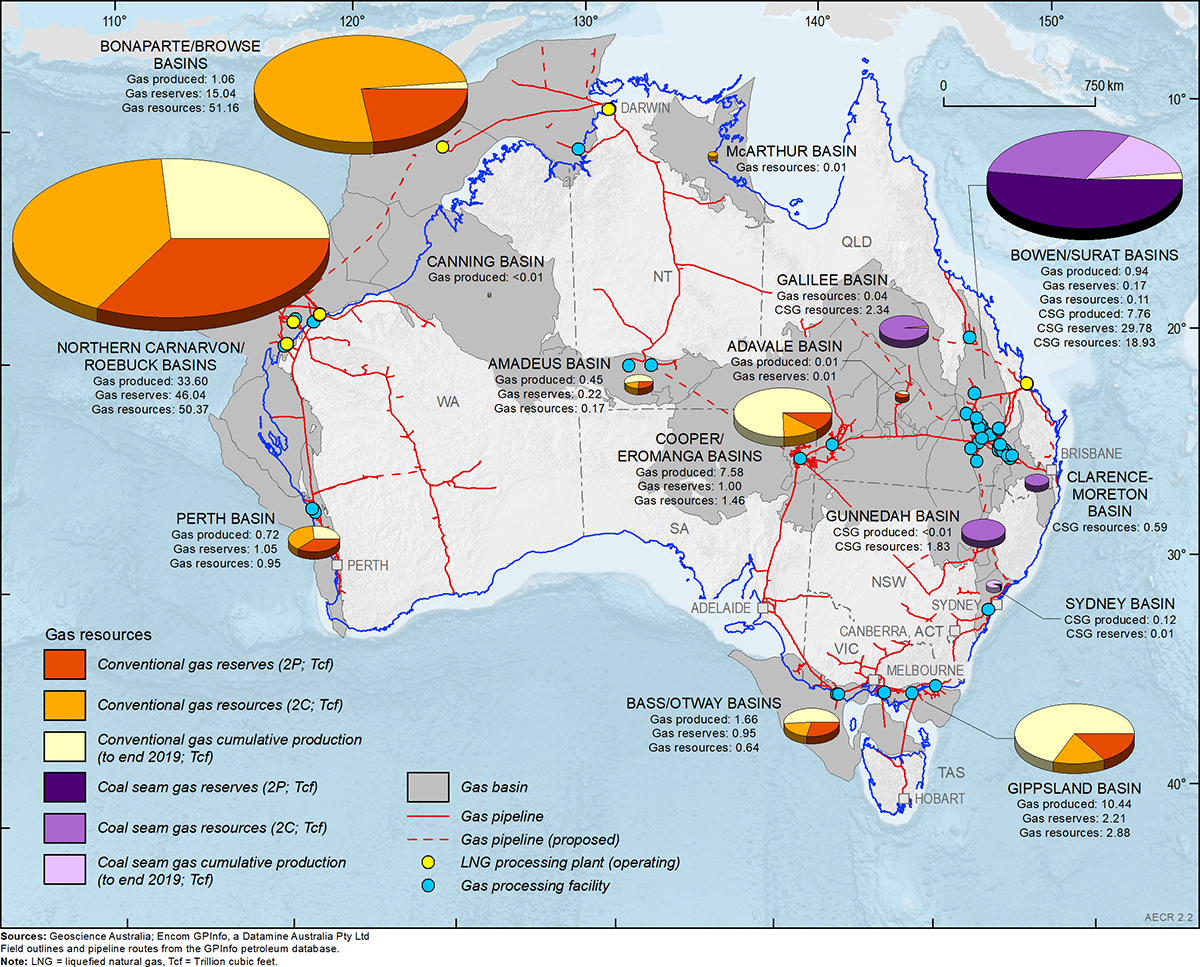
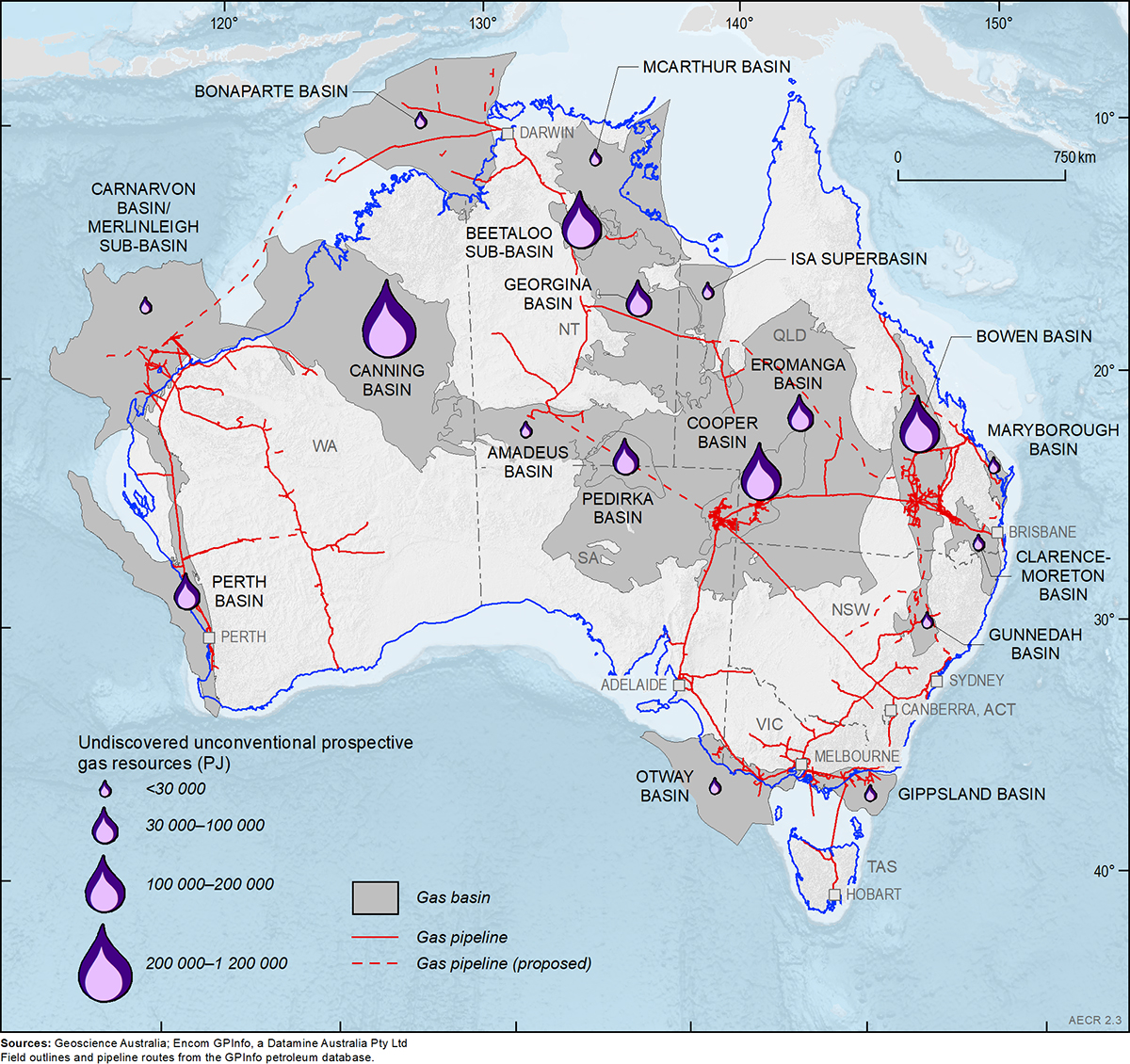
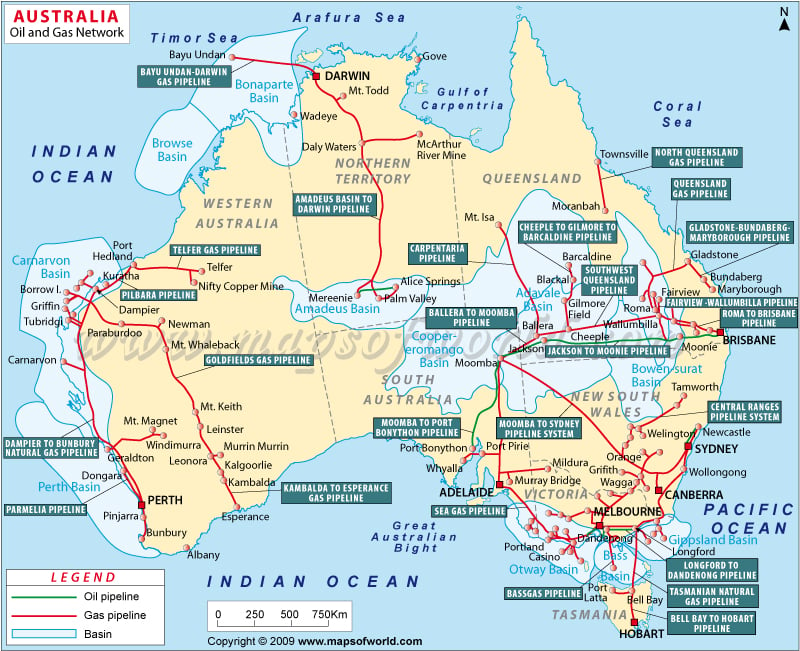
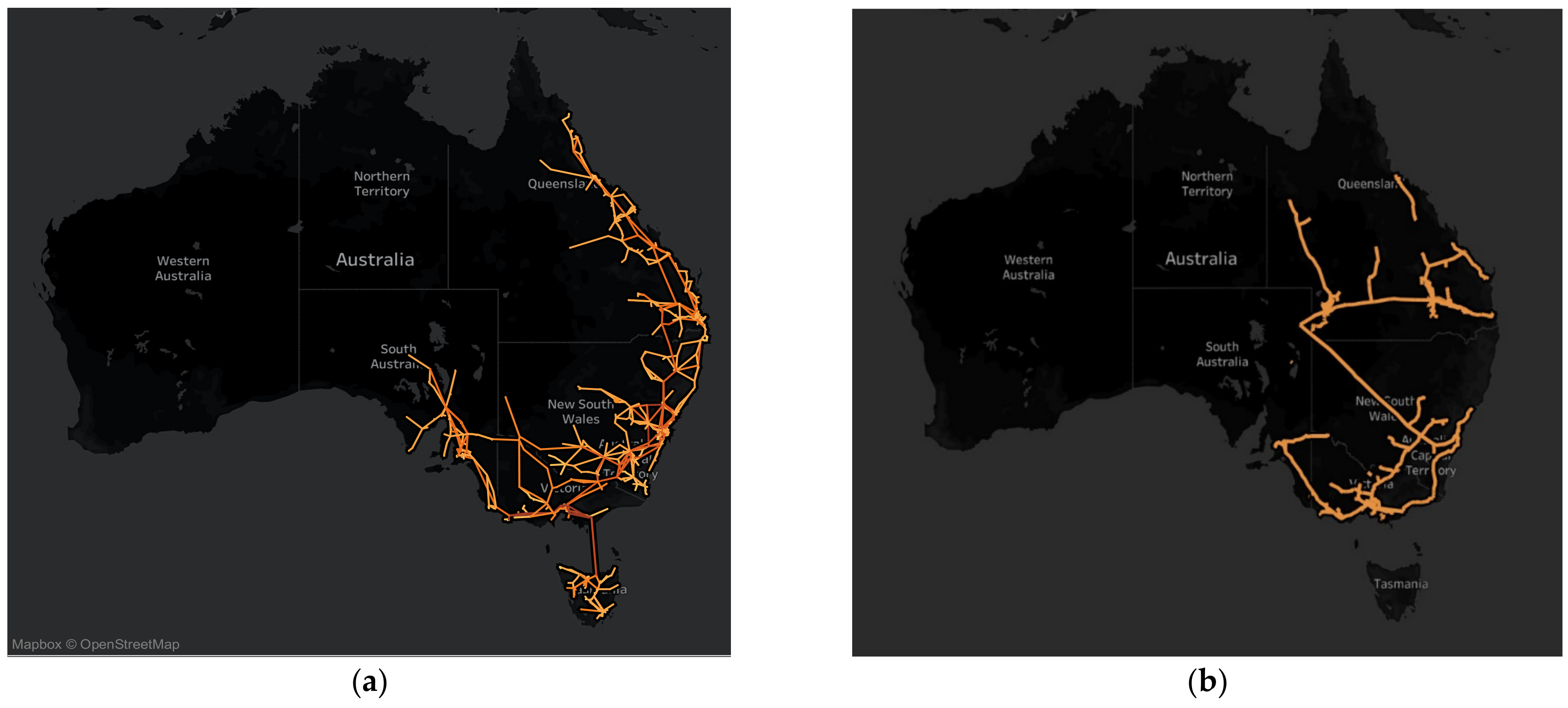
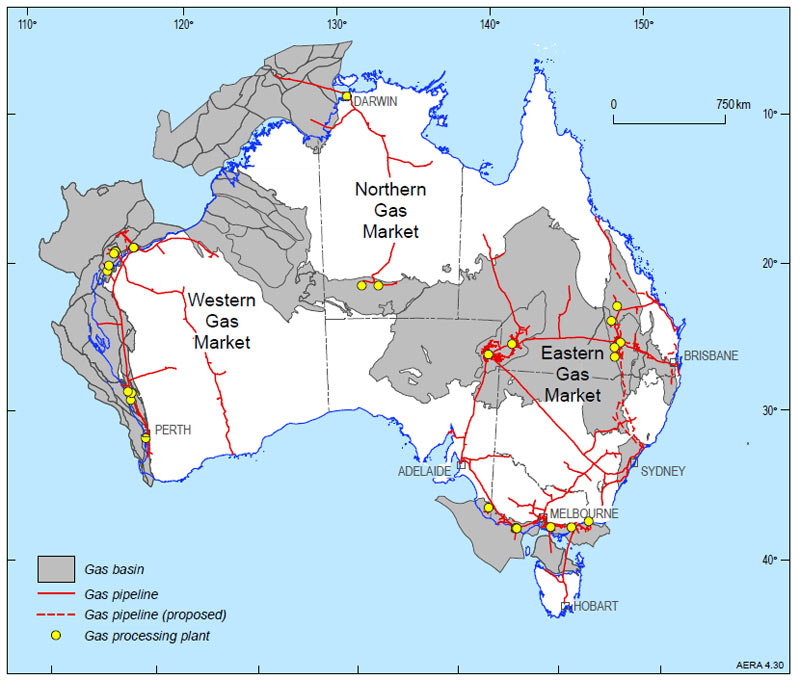
Australia’s vast and diverse landscape is crisscrossed by a complex network of natural gas pipelines, forming a vital artery for the nation’s energy supply. This intricate infrastructure, spanning thousands of kilometers, connects gas fields with major cities, industrial centers, and export terminals, ensuring a reliable and efficient flow of natural gas to meet the energy needs of households, businesses, and industries across the country.
Understanding the Network’s Complexity
The Australian gas pipeline network is a multifaceted system, encompassing various pipeline types and ownership structures. It can be broadly categorized into:
- Transmission Pipelines: These large-diameter pipelines, often exceeding 1 meter in diameter, carry natural gas over long distances, connecting major gas fields to key consumption centers. They are typically operated by independent pipeline companies and play a crucial role in facilitating long-distance gas transportation.
- Distribution Pipelines: These smaller-diameter pipelines branch out from transmission pipelines, delivering gas to local communities, industrial sites, and commercial buildings. Distribution pipelines are usually owned and operated by gas retailers or local distribution companies.
- Gathering Pipelines: These pipelines connect individual gas wells within a field to a central processing facility, where the gas is treated and prepared for transport. Gathering pipelines are typically owned and operated by gas producers.
Key Pipeline Systems and their Significance:
Several major pipeline systems contribute to the network’s overall strength and functionality:
- The Moomba-Sydney Pipeline: This iconic pipeline, stretching over 1,400 kilometers, links the vast Moomba gas field in South Australia to Sydney, supplying gas to millions of homes and businesses in New South Wales.
- The Dampier-Perth Natural Gas Pipeline: This 1,400-kilometer pipeline carries gas from the North West Shelf gas fields in Western Australia to Perth, powering the state’s industrial heartland and providing gas for residential use.
- The Queensland Gas Pipeline: This extensive network, spanning over 1,500 kilometers, connects gas fields in Queensland to major cities like Brisbane, Sydney, and Melbourne, supplying gas to both domestic and industrial consumers.
- The Bass Strait Pipeline: This subsea pipeline, stretching over 350 kilometers, connects gas fields in the Bass Strait to Victoria and Tasmania, supplying gas to the island state and contributing to Victoria’s energy mix.
The Network’s Benefits: Fueling Growth and Security
The Australian gas pipeline network plays a pivotal role in supporting the nation’s economic prosperity and energy security. Its key benefits include:
- Reliable and Secure Energy Supply: The network ensures a consistent and reliable flow of natural gas, meeting the diverse energy needs of Australian households, businesses, and industries. This reliability is crucial for maintaining economic activity and ensuring the smooth functioning of essential services.
- Economic Growth and Development: Natural gas is a versatile fuel source used in various industries, including power generation, manufacturing, and transportation. The pipeline network facilitates the delivery of this valuable resource, supporting economic growth and job creation across different sectors.
- Environmental Benefits: Natural gas is a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal, emitting lower levels of greenhouse gases. The network’s role in facilitating the use of natural gas contributes to reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Regional Development and Connectivity: The network’s reach extends to remote and regional areas, providing access to affordable and reliable energy, supporting economic development and improving quality of life in these regions.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the Australian gas pipeline network has been a vital asset for the country, it also faces challenges:
- Aging Infrastructure: Some sections of the network are aging, requiring maintenance and upgrades to ensure continued safe and efficient operation.
- Environmental Concerns: The extraction and transportation of natural gas can have environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and potential risks to ecosystems.
- Competition from Renewables: The growing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is creating competition for natural gas in the energy market.
- Regulation and Policy: The regulatory environment surrounding the gas industry is constantly evolving, with changes impacting pipeline investment and operations.
To address these challenges and ensure the network’s long-term viability, several initiatives are underway:
- Infrastructure Investment: Ongoing investments are being made to upgrade and expand the network, ensuring its capacity to meet future energy demands.
- Environmental Sustainability: Industry players are implementing measures to minimize the environmental impacts of gas extraction and transportation, including carbon capture and storage technologies.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies are being explored to enhance pipeline efficiency, safety, and environmental performance.
- Policy and Regulatory Framework: The government is working to create a supportive regulatory environment that encourages investment in the gas industry and ensures the network’s long-term sustainability.
FAQs about Australia’s Gas Pipeline Network:
Q: What are the main sources of natural gas for the Australian pipeline network?
A: The majority of natural gas in the Australian pipeline network originates from onshore and offshore gas fields located in various states, including Queensland, Western Australia, South Australia, and Victoria.
Q: How does the pipeline network contribute to Australia’s energy security?
A: The network ensures a reliable and consistent supply of natural gas, meeting the energy needs of households, businesses, and industries across the country. This reliability is crucial for maintaining economic activity and ensuring the smooth functioning of essential services.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of the gas pipeline network?
A: The extraction and transportation of natural gas can have environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, potential risks to ecosystems, and land disturbance. However, the industry is implementing measures to mitigate these impacts and promote environmental sustainability.
Q: What are the future prospects for the Australian gas pipeline network?
A: The network is expected to continue playing a significant role in Australia’s energy mix, with ongoing investments in upgrades and expansions. However, the network will need to adapt to the changing energy landscape, including the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with the Australian Gas Pipeline Network:
- Research and Information: Access reliable sources of information about the network, including government websites, industry reports, and academic research.
- Community Engagement: Participate in community discussions and consultations related to gas pipeline projects, ensuring your voice is heard.
- Environmental Awareness: Stay informed about the environmental impacts of gas extraction and transportation and advocate for responsible practices.
- Policy and Regulation: Follow developments in government policies and regulations related to the gas industry, understanding their potential impact on the network.
Conclusion:
Australia’s gas pipeline network is a vital infrastructure asset, playing a crucial role in the nation’s energy security and economic growth. The network’s complexity and vast reach ensure a reliable and efficient flow of natural gas to meet the diverse energy needs of households, businesses, and industries across the country. While facing challenges related to aging infrastructure, environmental concerns, and competition from renewables, the network is undergoing continuous adaptation and modernization to meet future energy demands and contribute to a sustainable and prosperous future for Australia.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Australia’s Gas Pipeline Network: A Vital Backbone for Energy Security and Economic Growth. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!