Demystifying the Power of DMAP GIS: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Demystifying the Power of DMAP GIS: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Power of DMAP GIS: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the Power of DMAP GIS: A Comprehensive Guide
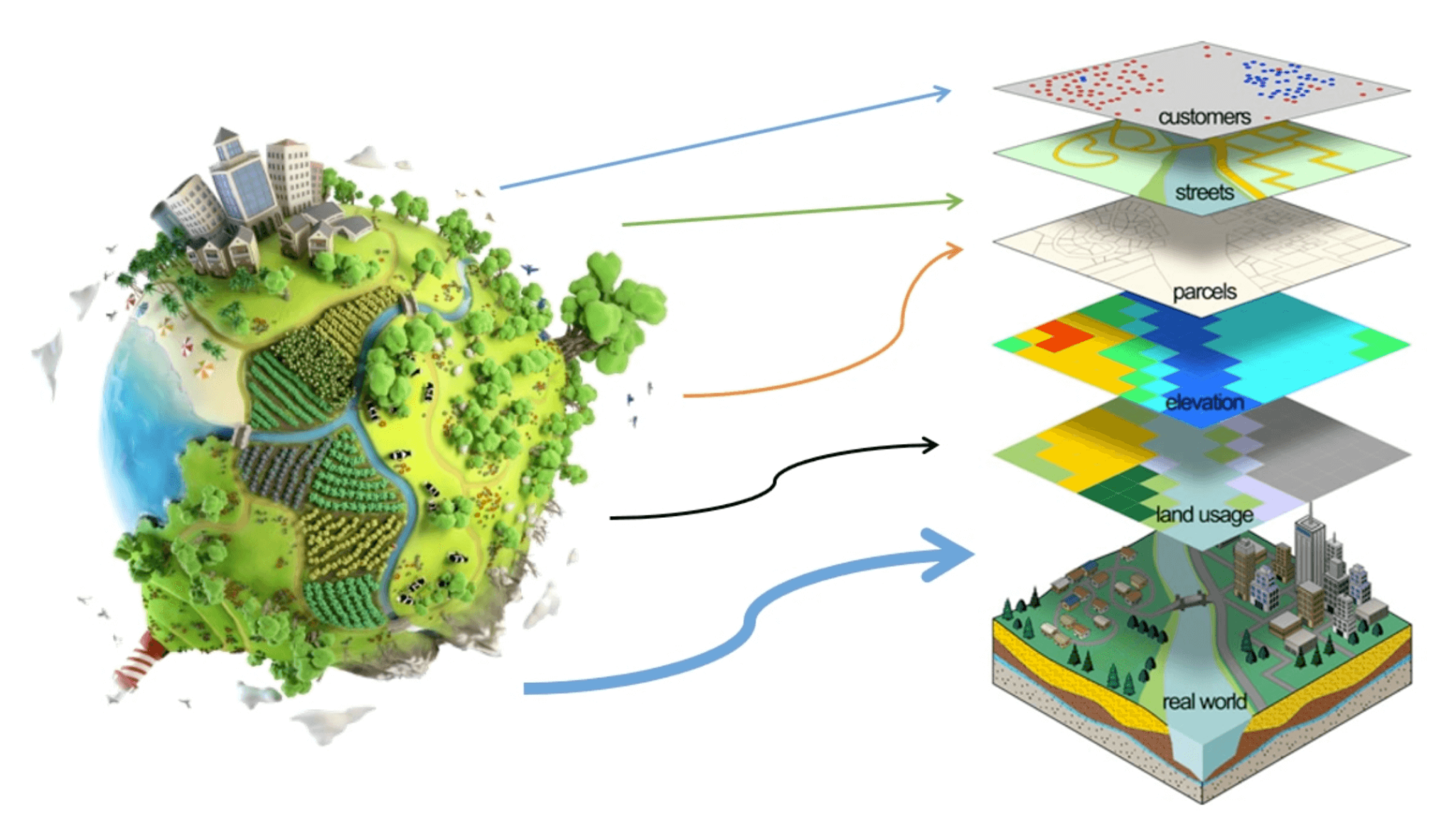
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized the way we understand and interact with our world. From mapping urban sprawl to tracking wildlife migration, GIS technology has become an indispensable tool across diverse fields. Within this landscape, a powerful and versatile tool known as DMAP GIS stands out, offering a unique approach to spatial data management and analysis.
Understanding DMAP GIS: A Foundation for Spatial Analysis
DMAP GIS, an acronym for Data Management and Analysis Platform, is a sophisticated software suite designed to manage, analyze, and visualize vast amounts of geospatial data. It goes beyond traditional GIS functionalities by providing a comprehensive framework for data integration, manipulation, and interpretation. This comprehensive approach makes DMAP GIS a powerful tool for various applications, from environmental monitoring to urban planning and disaster management.
Key Features and Benefits of DMAP GIS
DMAP GIS distinguishes itself through its unique blend of features and benefits, making it a compelling choice for organizations seeking to leverage geospatial data effectively.
-
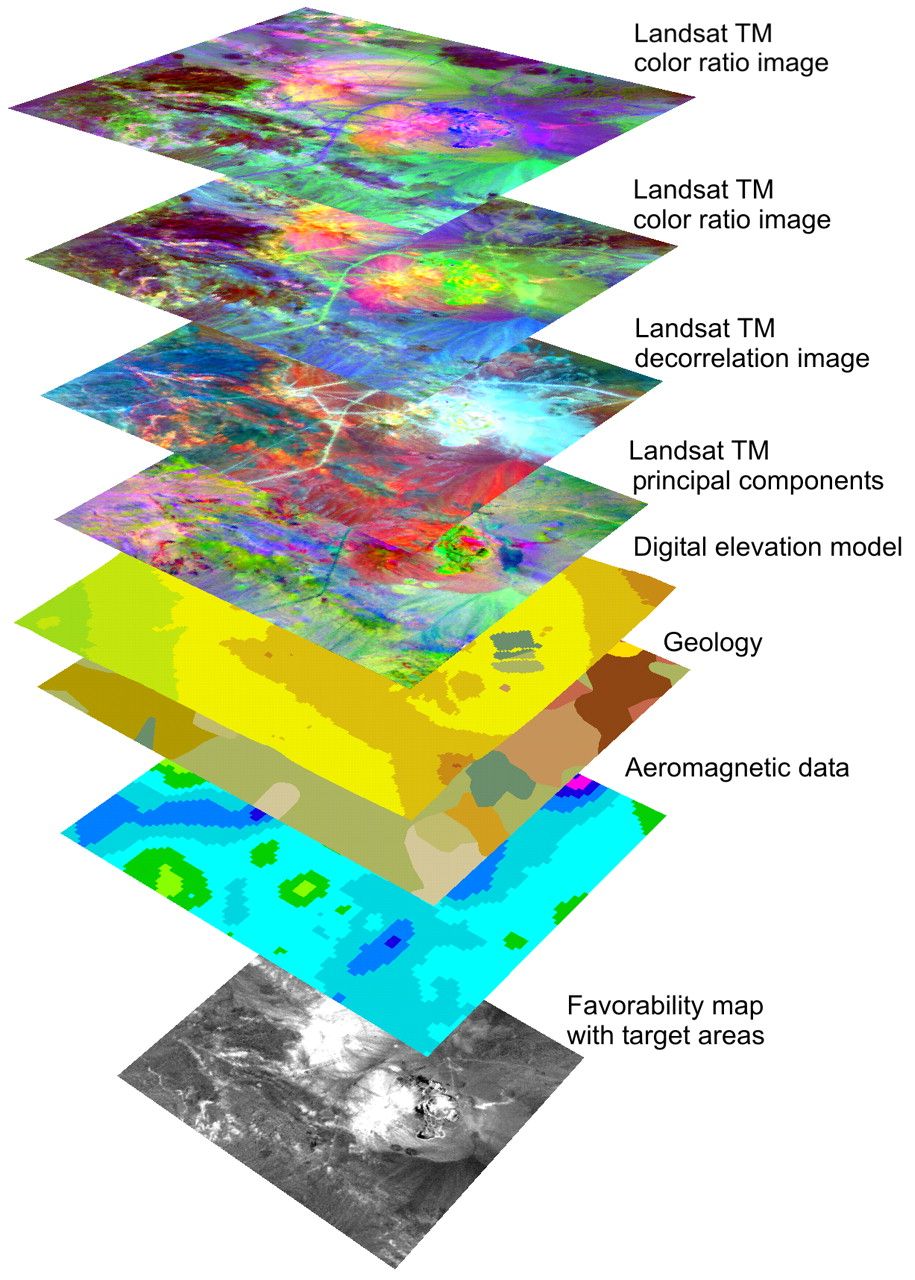
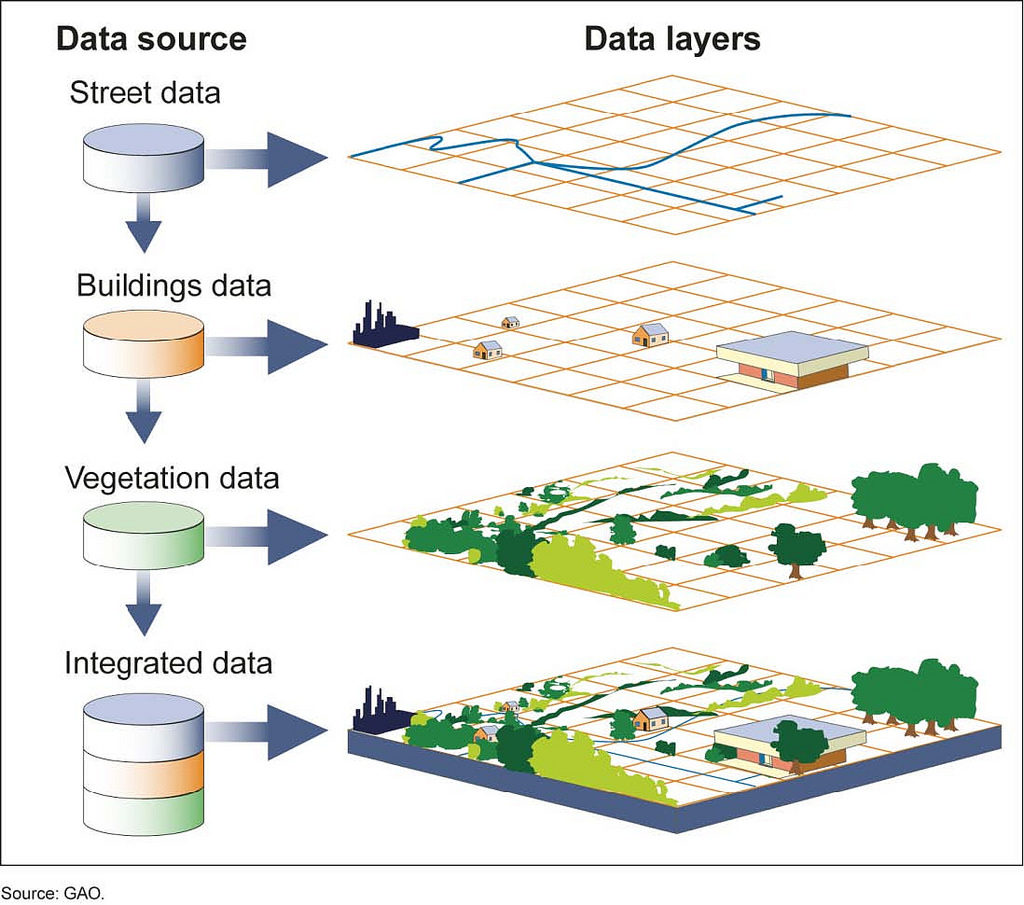
Data Integration and Interoperability: DMAP GIS excels in seamlessly integrating data from diverse sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, sensor networks, and traditional databases. This ability to unify disparate data sets is crucial for creating a holistic understanding of complex spatial phenomena.
-
Advanced Spatial Analysis: DMAP GIS provides a rich set of analytical tools, enabling users to perform sophisticated spatial queries, statistical analysis, and modeling. These capabilities allow for the identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within spatial data, leading to valuable insights.
-
Visualization and Communication: DMAP GIS facilitates the creation of compelling maps, charts, and reports, effectively communicating complex spatial information to diverse audiences. This visual representation empowers decision-makers with a clear and accessible understanding of data-driven insights.
-
Scalability and Customization: DMAP GIS is designed to handle large datasets and complex workflows, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes. The platform’s customizable nature allows users to tailor the software to meet their specific needs and applications.
-
Workflow Automation: DMAP GIS supports the automation of repetitive tasks, streamlining workflows and improving efficiency. This automation reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and frees up resources for more strategic initiatives.
Applications of DMAP GIS: A Spectrum of Possibilities
DMAP GIS finds applications across a wide range of disciplines, demonstrating its versatility and impact:
-
Environmental Management: DMAP GIS is used to monitor and analyze environmental changes, track deforestation, assess air and water quality, and manage natural resources.
-
Urban Planning: DMAP GIS assists in urban planning by visualizing population density, transportation patterns, infrastructure development, and land use changes. This information helps optimize urban development and address challenges like traffic congestion and resource allocation.
-
Disaster Management: DMAP GIS plays a crucial role in disaster response and recovery. It helps visualize flood zones, track wildfire spread, assess earthquake damage, and coordinate relief efforts.
-
Agriculture and Forestry: DMAP GIS assists in optimizing crop yields, managing forest resources, monitoring pest outbreaks, and analyzing soil conditions.
-
Healthcare: DMAP GIS is used to analyze disease outbreaks, identify health risks, and optimize healthcare resource allocation.
-
Transportation and Logistics: DMAP GIS helps optimize transportation routes, track vehicle movements, and analyze traffic patterns, improving efficiency and safety in logistics operations.
-
Security and Law Enforcement: DMAP GIS supports crime analysis, resource allocation, and emergency response, enhancing public safety and security.
Frequently Asked Questions about DMAP GIS
Q1: What are the key differences between DMAP GIS and traditional GIS software?
A1: DMAP GIS goes beyond traditional GIS by emphasizing data integration, advanced analysis, and workflow automation. It provides a more comprehensive platform for managing and interpreting spatial data, enabling users to perform more sophisticated tasks.
Q2: What are the technical requirements for using DMAP GIS?
A2: DMAP GIS typically requires a robust computer system with sufficient processing power, memory, and storage capacity. The software also requires a compatible operating system and may need specific software libraries or extensions.
Q3: How can I learn more about DMAP GIS and its capabilities?
A3: You can explore the DMAP GIS website, attend workshops and training programs, or consult with industry experts to gain a deeper understanding of the software’s functionalities and applications.
Q4: What are the potential challenges associated with implementing DMAP GIS?
A4: Challenges may include data quality issues, integration complexities, technical expertise requirements, and the need for specialized training.
Tips for Effective DMAP GIS Implementation
-
Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of your geospatial data before integrating it into DMAP GIS.
-
Training and Expertise: Invest in training programs to equip your team with the necessary skills to effectively utilize DMAP GIS.
-
Workflow Optimization: Identify and automate repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
-
Data Visualization and Communication: Leverage DMAP GIS’s visualization tools to create compelling and informative maps, charts, and reports.
-
Collaboration and Sharing: Foster collaboration among team members and stakeholders by implementing data sharing and communication protocols.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of Spatial Data
DMAP GIS empowers organizations to harness the power of spatial data, transforming it into actionable insights and driving informed decision-making. Its unique features, versatile applications, and comprehensive approach make it a valuable tool for tackling complex challenges across diverse industries. By understanding and effectively utilizing DMAP GIS, organizations can gain a competitive advantage, optimize operations, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Power of DMAP GIS: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!