Exploring the Geographic Context of Finland: A Comprehensive Look at Neighboring Regions
Related Articles: Exploring the Geographic Context of Finland: A Comprehensive Look at Neighboring Regions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Geographic Context of Finland: A Comprehensive Look at Neighboring Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Geographic Context of Finland: A Comprehensive Look at Neighboring Regions
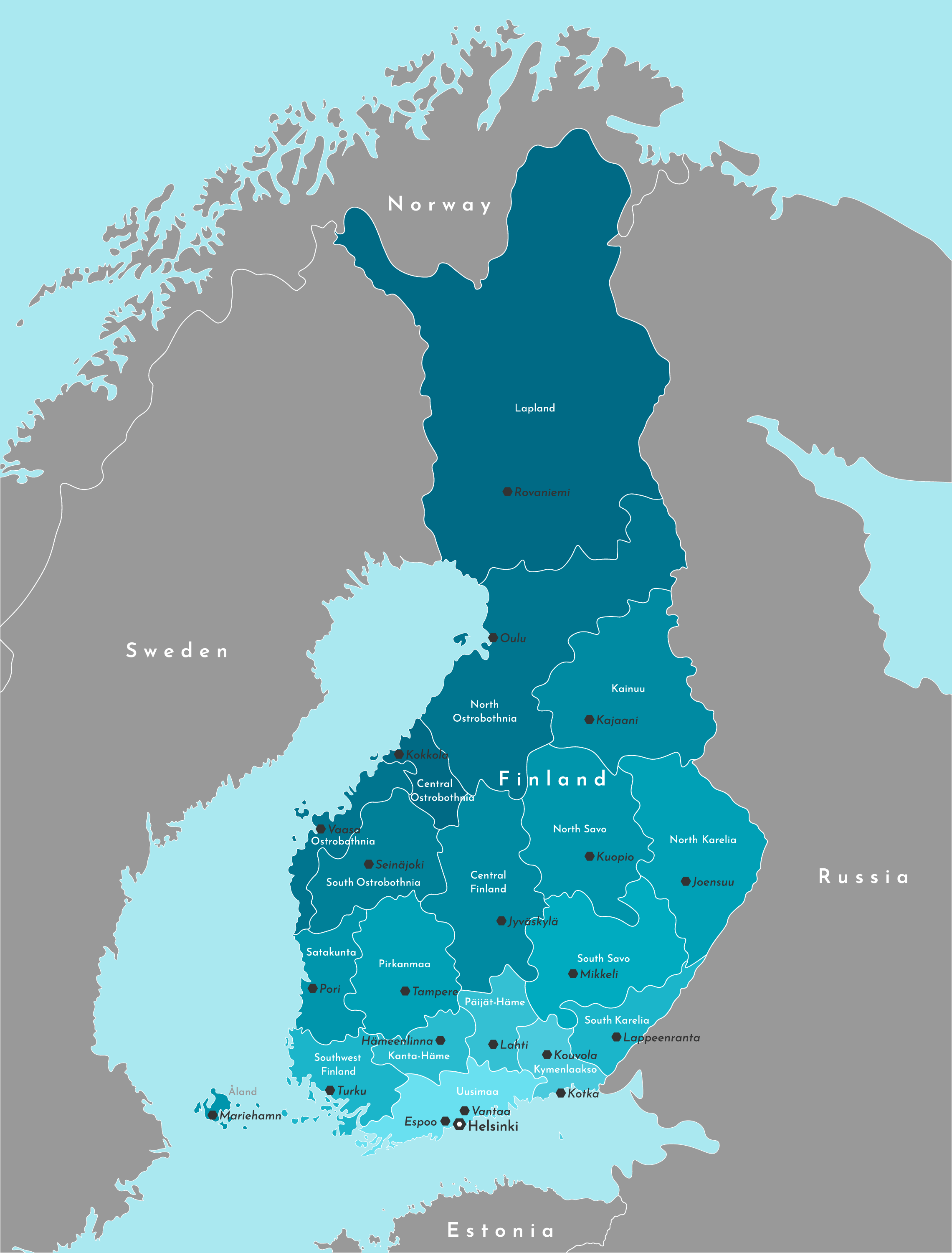
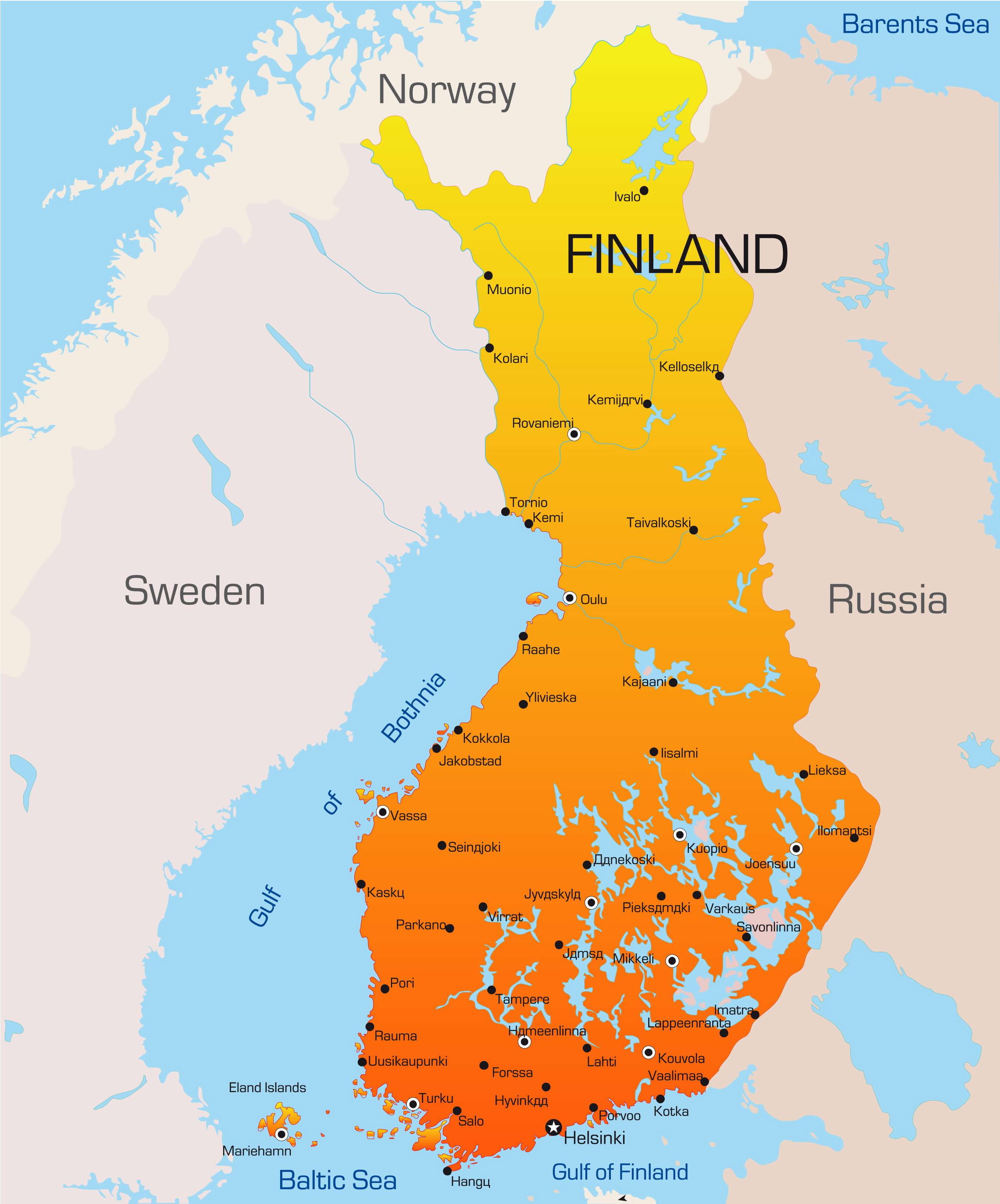
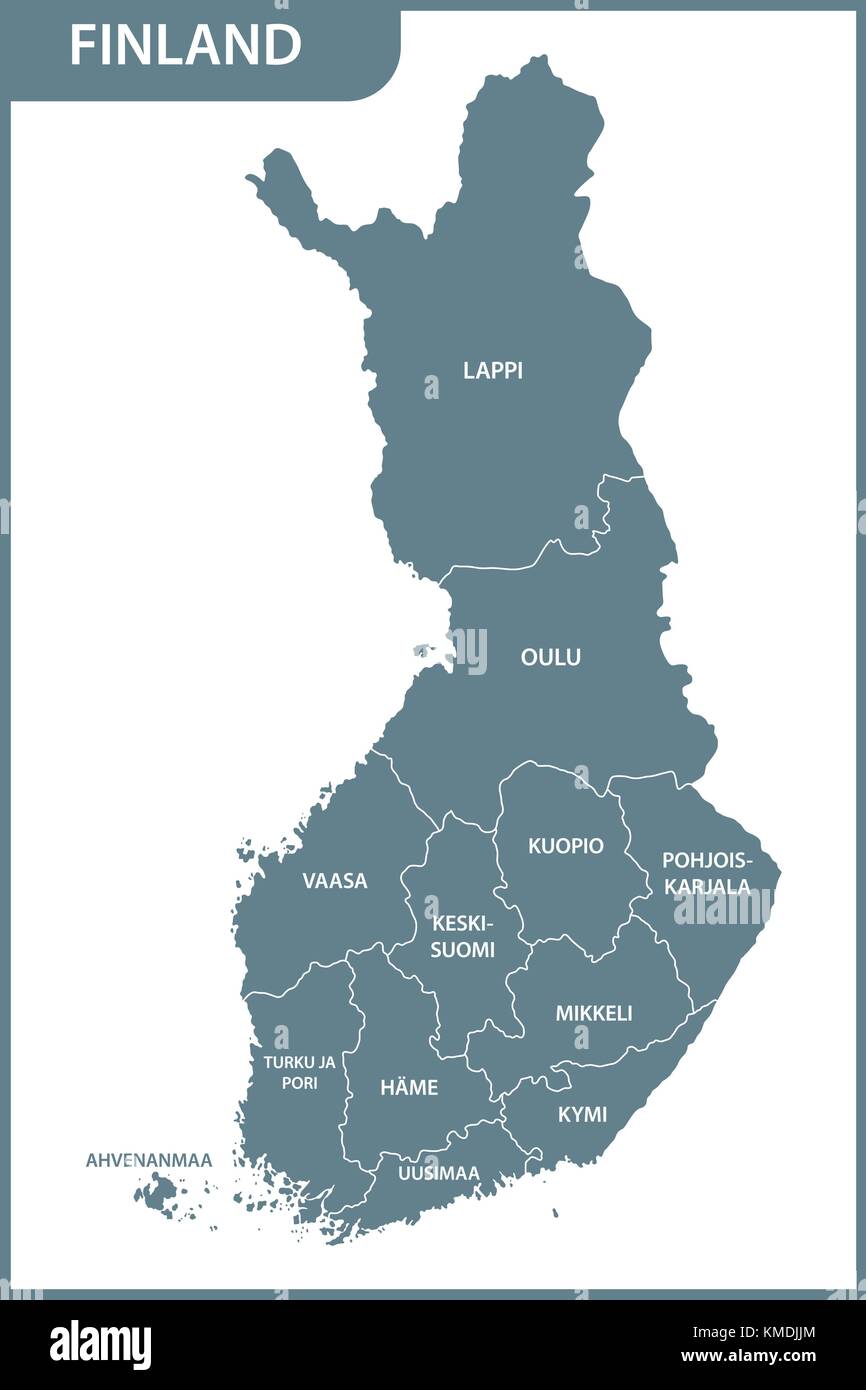
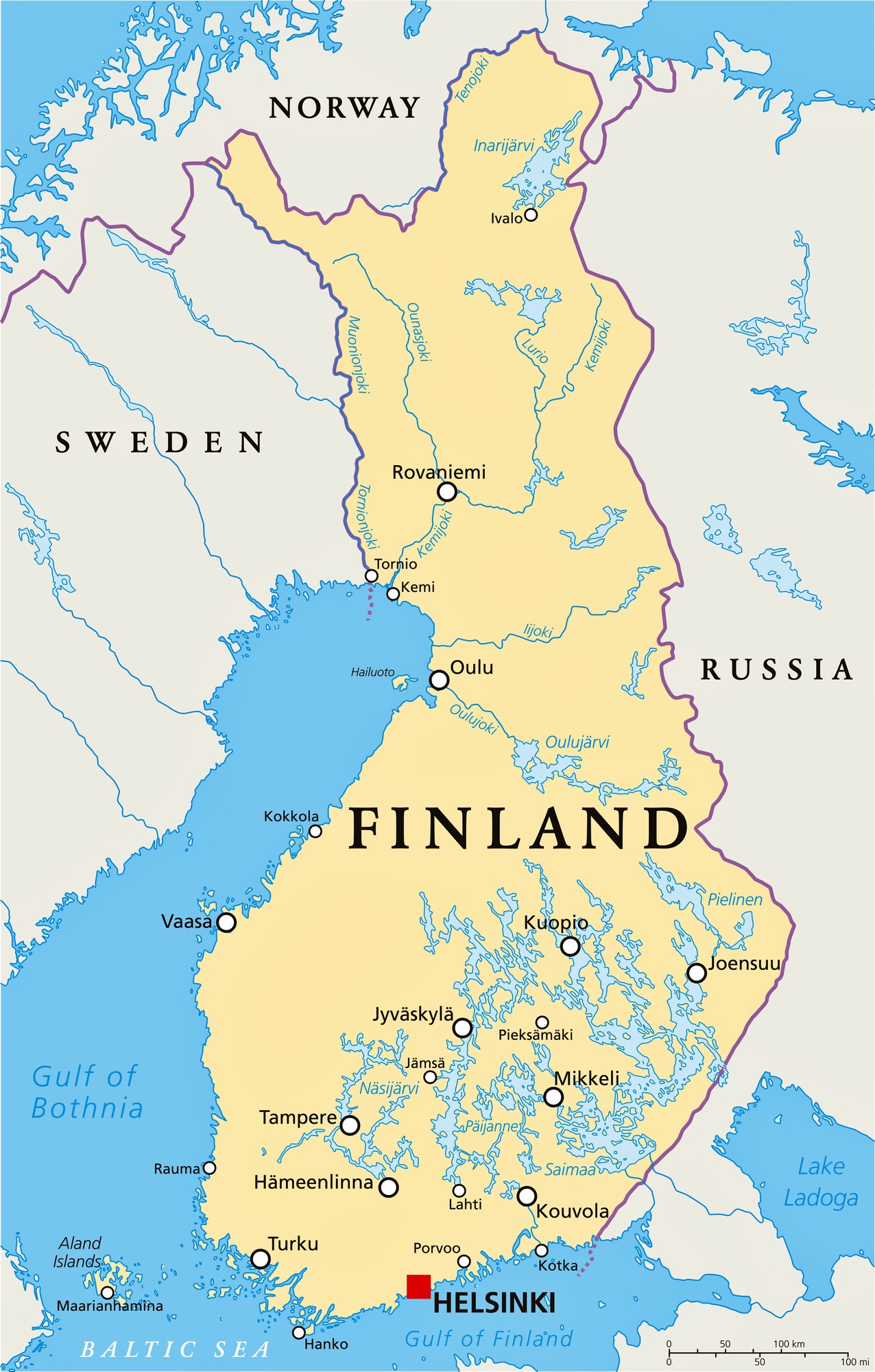
Finland, a Nordic nation renowned for its pristine landscapes, rich culture, and technological prowess, occupies a unique position within the European landscape. Understanding its geographic context, particularly the regions surrounding it, is crucial to comprehending the country’s history, culture, and contemporary challenges.
A Closer Look at the Map:
Finland shares borders with four countries:
-
Sweden: Located to the west, Sweden shares a long and complex history with Finland. Both nations have been intertwined through shared cultural influences, linguistic similarities, and historical ties dating back centuries. The border between the two countries runs along the Gulf of Bothnia, a significant waterway that has historically facilitated trade and cultural exchange.
-
Norway: Sharing a relatively short border with Finland in the north, Norway presents a distinct geographical contrast. The rugged terrain of Norway’s mountainous regions contrasts with Finland’s predominantly flat landscape. Despite their differences, the two nations share a common history of Viking settlements and a strong connection to the natural world.
-
Russia: The longest and most consequential border Finland shares is with Russia. This border, stretching over 1,300 kilometers, reflects a complex relationship marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. The historical influence of Russia on Finland is undeniable, impacting its language, culture, and political development.
-
Estonia: Located across the Gulf of Finland, Estonia is a Baltic nation with close cultural and linguistic ties to Finland. The two countries share a common history, with both having been part of the Swedish and Russian empires. The Gulf of Finland serves as a crucial waterway for trade and communication between the two nations.
Beyond Borders: The Wider Geographic Context
Beyond its immediate neighbors, Finland’s geographic location also places it within a broader context:
-
The Baltic Sea Region: Finland is an integral part of the Baltic Sea Region, a dynamic geopolitical area encompassing the Baltic Sea and its surrounding countries. This region is characterized by interconnected economies, shared environmental challenges, and a growing sense of regional identity.
-
The Nordic Region: As a member of the Nordic Council, Finland shares strong cultural, political, and economic ties with the other Nordic countries: Denmark, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden. This collective identity fosters cooperation in areas like environmental protection, social welfare, and research.
-
The European Union: As a member of the European Union, Finland participates in a vast network of political, economic, and cultural collaborations. The EU framework provides a platform for Finland to engage with other European nations on a range of issues, from trade and immigration to climate change and security.
The Significance of Geographic Context
Understanding the geographic context of Finland is crucial for several reasons:
-
Historical Understanding: The geographic location of Finland has shaped its history, from its Viking origins to its period under Swedish and Russian rule. Neighboring countries have influenced its language, culture, and political development.
-
Economic Development: Finland’s location within the Baltic Sea region and its proximity to major European markets has been instrumental in its economic growth. Trade and collaboration with neighboring countries have been vital for its development.
-
Environmental Challenges: Finland shares environmental challenges with its neighbors, particularly in relation to the Baltic Sea and its ecosystem. Collaborative efforts are crucial to address issues like pollution, overfishing, and climate change.
-
Security Considerations: Finland’s location near Russia has significant implications for its security policy. The country’s neutrality during the Cold War and its recent decision to join NATO reflect its strategic considerations in the face of geopolitical shifts.
FAQs Regarding Finland’s Geographic Context:
1. What are the main languages spoken in Finland’s neighboring countries?
- Sweden: Swedish
- Norway: Norwegian
- Russia: Russian
- Estonia: Estonian
2. What are some of the key historical events that have shaped Finland’s relationship with its neighbors?
- The Swedish Empire: Finland was part of the Swedish Empire for centuries, leaving a lasting imprint on its language, culture, and legal system.
- The Russian Empire: Finland was annexed by Russia in 1809, leading to a period of cultural and linguistic assimilation.
- The Finnish Civil War (1918): The conflict between pro-independence and pro-Russian forces highlighted the complex relationship between Finland and Russia.
- The Winter War (1939-1940) and the Continuation War (1941-1944): These wars against the Soviet Union further shaped Finland’s relationship with Russia.
3. What are some of the major economic sectors in Finland’s neighboring countries?
- Sweden: Automotive industry, telecommunications, forestry, mining
- Norway: Oil and gas, shipping, fishing, tourism
- Russia: Energy sector, mining, manufacturing, agriculture
- Estonia: Information technology, telecommunications, tourism, manufacturing
4. What are some of the environmental challenges shared by Finland and its neighbors?
- Baltic Sea pollution: Runoff from agriculture and industrial activities has led to eutrophication, impacting the Baltic Sea ecosystem.
- Climate change: Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns pose challenges to the environment and economies of the region.
- Biodiversity loss: Habitat destruction and pollution threaten the biodiversity of the Baltic Sea region.
Tips for Understanding Finland’s Geographic Context:
- Explore Maps: Use online maps and atlases to visualize the geographic location of Finland and its neighbors.
- Read Historical Accounts: Explore historical texts and accounts to understand the historical interactions between Finland and its neighbors.
- Study the Political Landscape: Follow news and analysis about the political developments in Finland and its neighboring countries.
- Engage with Cultural Resources: Explore art, literature, and music from Finland and its neighboring countries to gain insights into their shared cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
Finland’s geographic context is a multifaceted and dynamic element that has shaped its history, culture, and contemporary challenges. Understanding the complex relationships with its neighboring countries, the broader regional dynamics, and the global implications of its location is crucial for comprehending the country’s present and future. By examining these relationships, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay of geography, history, and culture that defines Finland’s place in the world.
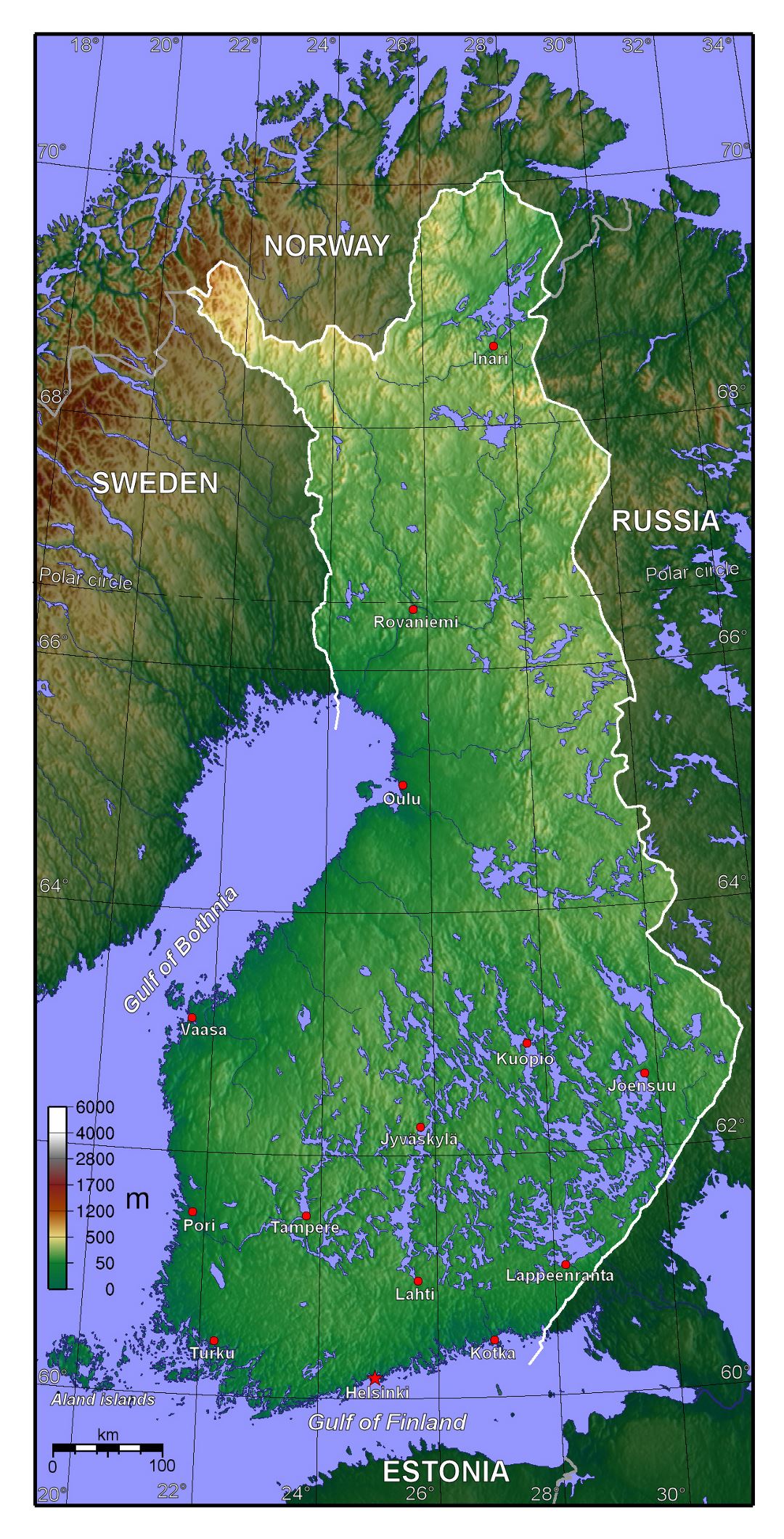
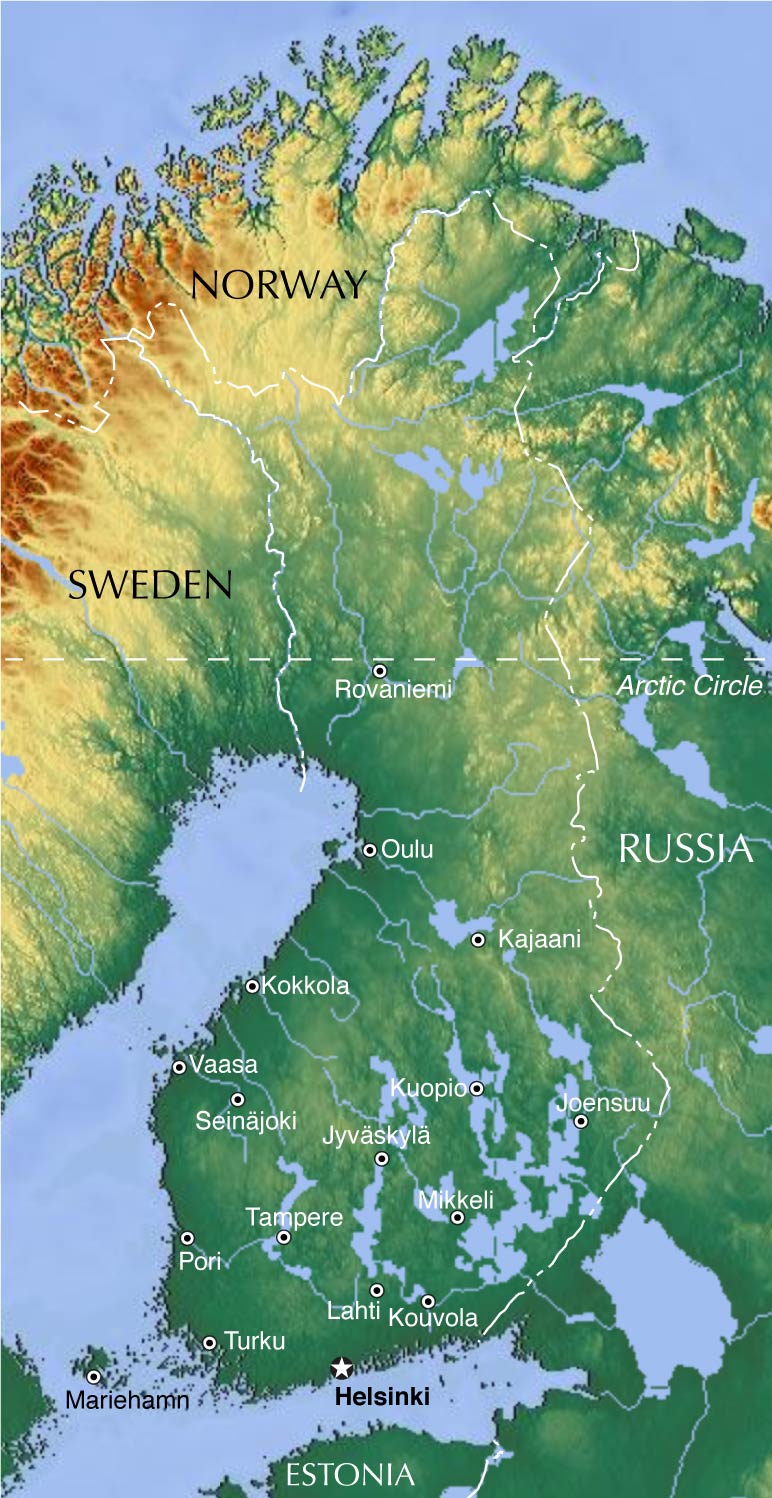

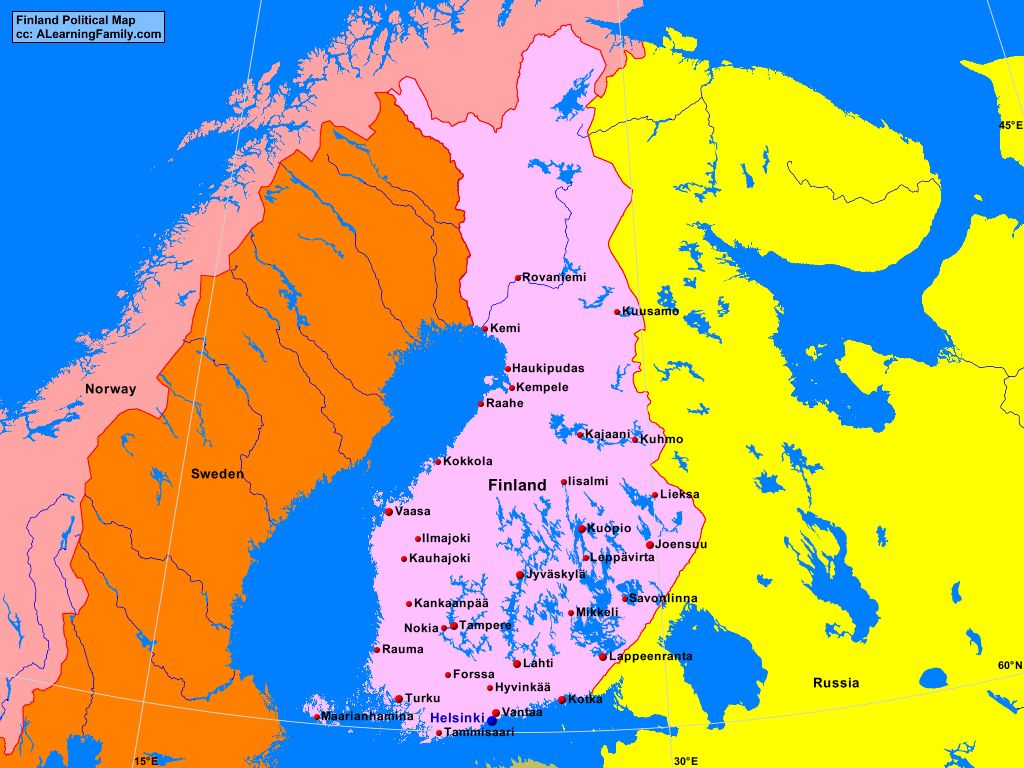

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Geographic Context of Finland: A Comprehensive Look at Neighboring Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!