Finland’s Pre-War Borders: A Look at the Map Before World War II
Related Articles: Finland’s Pre-War Borders: A Look at the Map Before World War II
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Finland’s Pre-War Borders: A Look at the Map Before World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Finland’s Pre-War Borders: A Look at the Map Before World War II
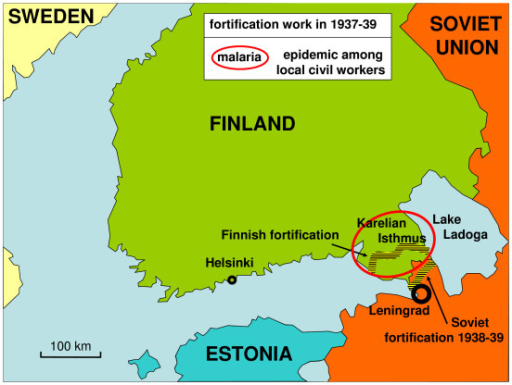
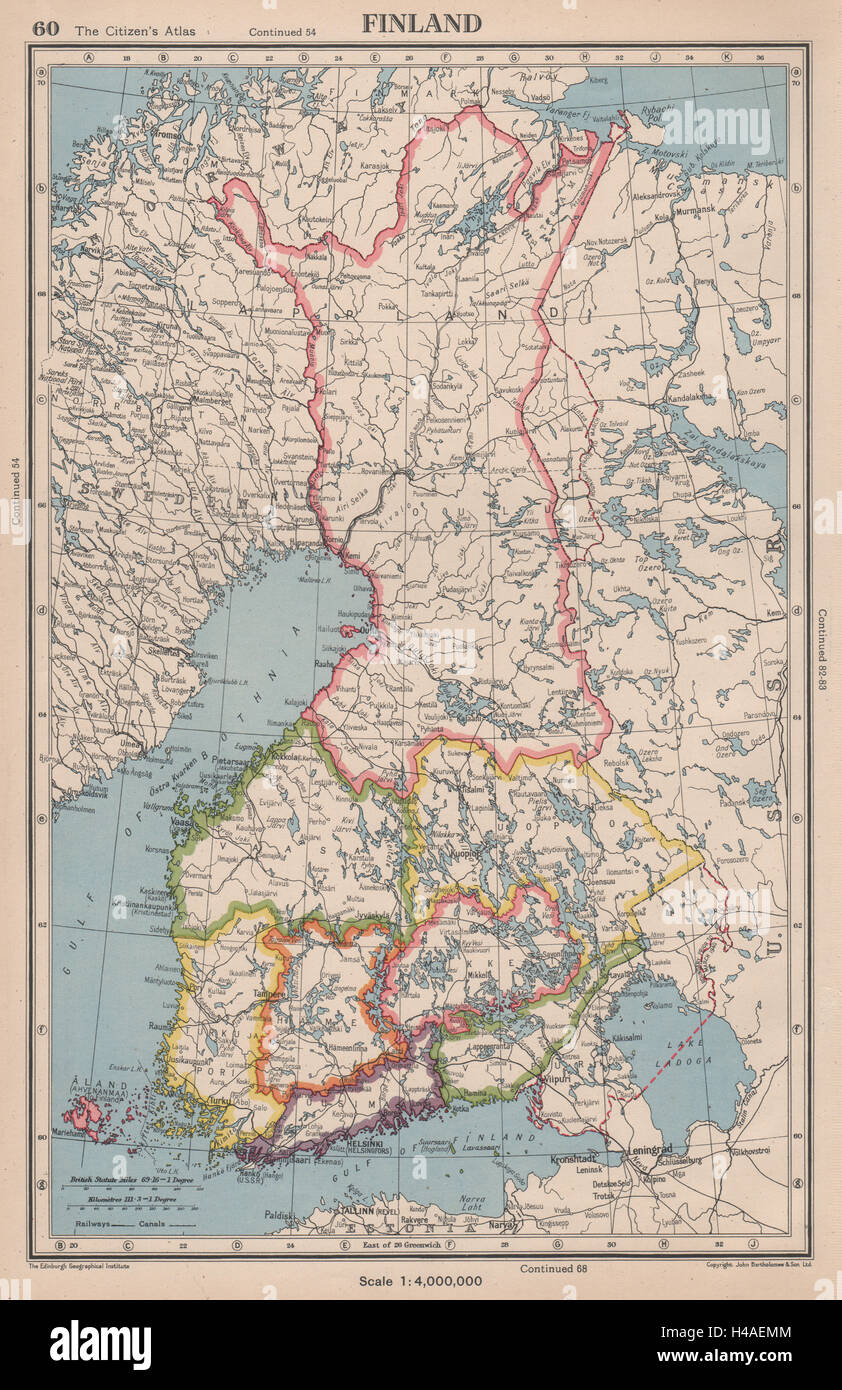
The map of Finland before World War II presents a stark contrast to the country’s current borders. It reveals a history of territorial shifts, political alliances, and ultimately, the enduring impact of conflict on the Finnish landscape. Understanding this pre-war map is crucial for grasping the historical context of Finland’s development, its complex relationship with its neighbors, and the enduring legacy of the Second World War on the nation’s identity.
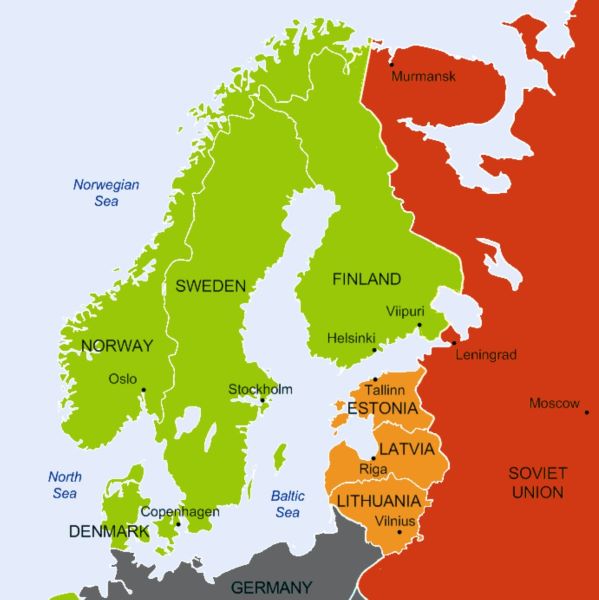
A Divided Nation: The Finnish-Swedish Border
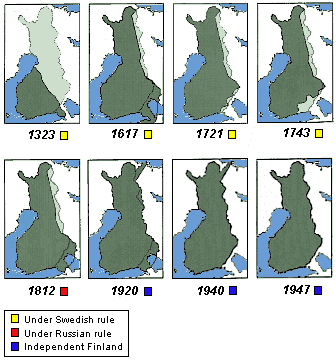
Prior to World War II, Finland’s eastern border with Russia was a relatively recent creation, established after the Finnish War of Independence (1917-1918). However, the western border with Sweden was a long-standing division, dating back centuries. This border, marked by a chain of lakes and forests, had been a defining feature of Finnish identity, shaping cultural and linguistic ties.
The Karelian Isthmus: A Contested Territory
The Karelian Isthmus, a narrow strip of land connecting Finland to the Soviet Union, was a point of contention throughout the 20th century. This strategically vital region, home to the city of Vyborg (Viipuri in Finnish), had been a constant source of tension between Finland and Russia. It was annexed by Russia in 1944, a loss that continues to resonate in Finnish national memory.
The Åland Islands: A Separate Entity
The Åland Islands, located in the Baltic Sea, were a unique case. While geographically part of Finland, they held a distinct cultural and linguistic identity, with Swedish as the dominant language. The islands enjoyed a semi-autonomous status, with a degree of self-governance, a testament to their unique position within Finland.
The Significance of the Pre-War Map
The pre-war map of Finland reveals a nation grappling with its identity, navigating complex geopolitical relationships, and striving for stability in a volatile region. It underscores the importance of territorial integrity and the enduring impact of conflict on national consciousness. The map also serves as a reminder of the historical forces that shaped Finland’s political landscape, its economic development, and its cultural identity.
The Impact of World War II
The Second World War dramatically altered Finland’s borders. The Winter War (1939-1940) and the Continuation War (1941-1944) resulted in significant territorial losses, including the Karelian Isthmus, parts of Lapland, and the strategically important Salla region. These territorial losses had a profound impact on Finland’s economy, demography, and cultural landscape.
Beyond the Borders: The Legacy of the Map
The pre-war map of Finland, while a historical artifact, continues to hold relevance today. It serves as a reminder of the sacrifices made by generations of Finns in the pursuit of national independence and territorial integrity. It also underlines the enduring impact of geopolitical shifts and the importance of peaceful resolution of disputes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What were the main differences between Finland’s pre-war and post-war borders?
A: Finland lost significant territory in the Karelian Isthmus, parts of Lapland, and the Salla region during World War II. The Åland Islands, however, retained their semi-autonomous status.
Q: Why was the Karelian Isthmus so important?
A: The Karelian Isthmus was strategically important due to its proximity to Leningrad (now St. Petersburg) and its connection to Finland’s mainland. It was also a source of economic activity, with significant industries and resources.
Q: How did the loss of territory impact Finland?
A: The territorial losses had a significant impact on Finland’s economy, demography, and cultural landscape. It resulted in the displacement of thousands of people, the loss of valuable resources, and a shift in the country’s economic focus.
Q: What is the significance of the Åland Islands?
A: The Åland Islands represent a unique case of a semi-autonomous region within Finland. They enjoy a degree of self-governance, reflecting their distinct cultural and linguistic identity.
Tips for Understanding the Pre-War Map
- Study the historical context: Understanding the events leading up to World War II, particularly the Finnish War of Independence and the rise of Soviet power, is crucial for interpreting the map.
- Focus on key regions: Pay attention to the Karelian Isthmus, the Åland Islands, and the Finnish-Swedish border, as these areas were particularly significant in shaping Finland’s pre-war landscape.
- Consider the impact of the war: Analyze the territorial changes that occurred as a result of World War II and their long-term consequences for Finland.
- Explore the cultural and linguistic aspects: Understand the diverse cultural and linguistic identities that existed within Finland’s pre-war borders, particularly in the Åland Islands.
Conclusion
The pre-war map of Finland is a powerful reminder of the complex historical forces that shaped the nation’s identity, its borders, and its relationship with its neighbors. It underscores the importance of territorial integrity, the enduring impact of conflict, and the dynamic nature of geopolitical landscapes. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of Finland’s past, its present, and its ongoing journey towards a secure and prosperous future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Finland’s Pre-War Borders: A Look at the Map Before World War II. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!