Mapping New France in 1600: A Glimpse into a Nascent Empire
Related Articles: Mapping New France in 1600: A Glimpse into a Nascent Empire
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping New France in 1600: A Glimpse into a Nascent Empire. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping New France in 1600: A Glimpse into a Nascent Empire
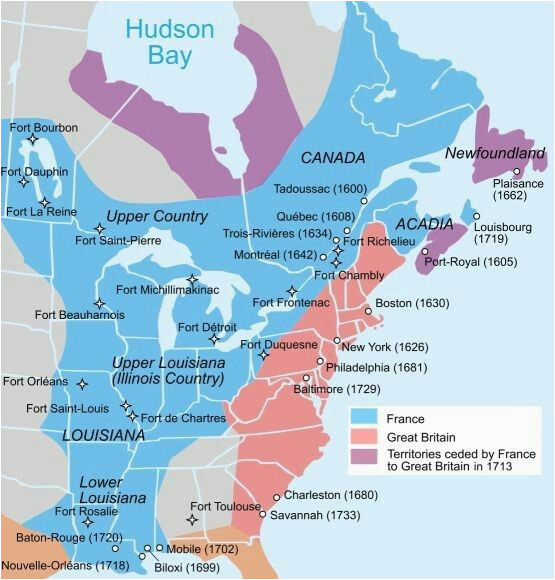
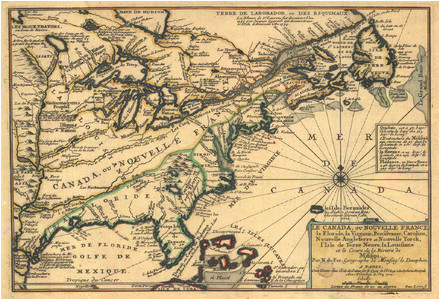
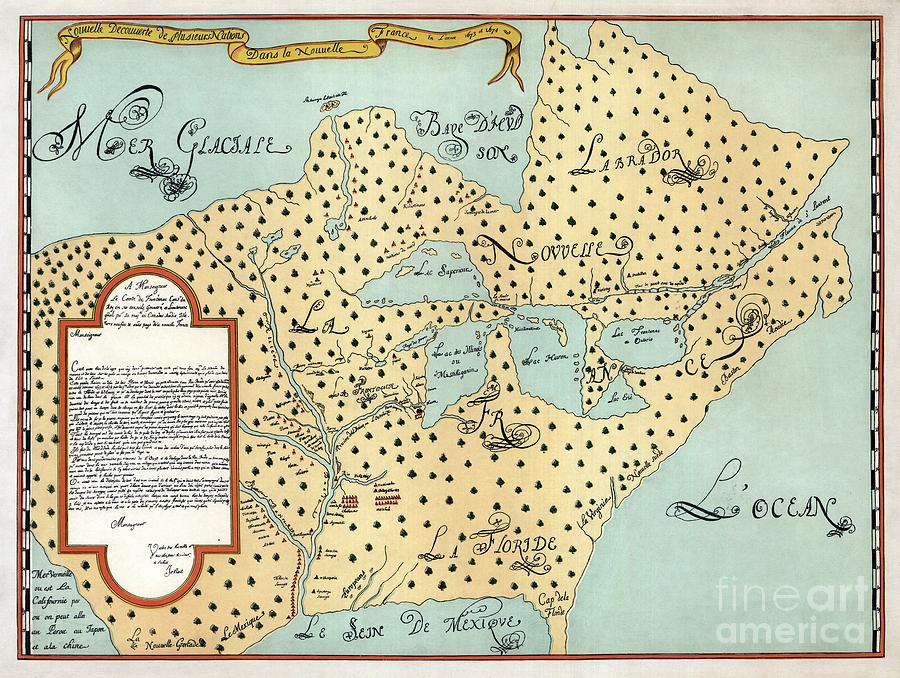
The year 1600 witnessed the nascent stages of French colonization in North America, a period marked by exploration, trade, and the establishment of early settlements. A map of New France in 1600 provides a fascinating snapshot of this burgeoning enterprise, revealing the ambition and challenges faced by the French in their bid to carve out a colonial empire in the New World.
The Landscape of New France in 1600
The map of New France in 1600 showcases a territory still largely unknown and unexplored. The St. Lawrence River, a vital waterway, dominates the landscape, serving as the primary artery for French exploration and trade. The map highlights key settlements along the river, including:
- Quebec City: Founded in 1608 by Samuel de Champlain, Quebec City served as the administrative and commercial hub of New France. Its strategic location on a high bluff provided a natural defensive advantage, making it a vital outpost for the French.
- Montreal: Established in 1642, Montreal emerged as a critical trading post, connecting the French with indigenous communities further inland. Its strategic location at the confluence of the St. Lawrence and Ottawa rivers facilitated access to the interior of North America.
- Three Rivers: Located midway between Quebec City and Montreal, Three Rivers served as a trading center and a point of departure for westward exploration.
Beyond these settlements, the map reveals the vast expanse of unexplored territory stretching westward. The Great Lakes region, the Mississippi River Valley, and the vast prairies remained largely unknown to the French.
French Exploration and Trade
The map of New France in 1600 underscores the crucial role played by exploration and trade in the early stages of colonization. French explorers, driven by the pursuit of wealth, furs, and new trade routes, ventured into the interior, establishing contact with indigenous communities and mapping vast swaths of territory.
- Samuel de Champlain: A key figure in the early exploration of New France, Champlain charted the St. Lawrence River, established trading posts, and forged alliances with indigenous tribes. His explorations extended southward along the Atlantic coast, laying the groundwork for future French settlements.
- The Fur Trade: The fur trade proved to be a lucrative enterprise, driving French expansion into the interior. French traders established trading posts throughout the Great Lakes region, exchanging European goods like tools, weapons, and textiles for furs, primarily beaver pelts.
The Impact of Indigenous Peoples
The map of New France in 1600 highlights the crucial role played by indigenous peoples in the development of the colony. French explorers and traders relied heavily on their knowledge of the land, their expertise in navigating waterways, and their relationships with other indigenous tribes.
- Alliances and Conflicts: The French sought to establish alliances with indigenous tribes, forming partnerships for trade and mutual protection. However, these relationships were not always harmonious, leading to conflicts over territory, resources, and cultural differences.
- Disease and Displacement: The arrival of the French brought with it devastating diseases like smallpox, which decimated indigenous populations. The encroachment of French settlements and the fur trade also led to displacement and disruption of traditional indigenous ways of life.
The Significance of the 1600 Map
The map of New France in 1600 holds significant historical value, offering a glimpse into the early stages of a colonial empire that would eventually span vast territories. It reveals the ambition, resourcefulness, and challenges faced by the French in their bid to establish a presence in North America.
- A Foundation for Expansion: The map serves as a reminder of the groundwork laid by early explorers and traders, paving the way for future French expansion and the establishment of a vast colonial empire.
- A Record of Indigenous Presence: The map acknowledges the presence and influence of indigenous peoples, highlighting their crucial role in the development of New France.
- A Window into Early Colonial Practices: The map provides insights into the early colonial practices of the French, their reliance on trade, their relationships with indigenous peoples, and the challenges they faced in establishing a foothold in a new land.
FAQs
Q: What was the primary motivation for French colonization of New France in 1600?
A: The primary motivations for French colonization of New France in 1600 were the pursuit of wealth, furs, and new trade routes. The fur trade, particularly the demand for beaver pelts, proved to be a lucrative enterprise, driving French expansion into the interior.
Q: How did the French interact with indigenous peoples in New France during this period?
A: The French sought to establish alliances with indigenous tribes, forming partnerships for trade and mutual protection. However, these relationships were not always harmonious, leading to conflicts over territory, resources, and cultural differences. The arrival of the French also brought with it devastating diseases like smallpox, which decimated indigenous populations.
Q: What were the key challenges faced by the French in establishing New France?
A: The French faced numerous challenges in establishing New France, including:
- The vastness of the territory: The sheer size and remoteness of the land presented logistical and navigational difficulties.
- The harsh climate: Winters in New France were long and harsh, posing challenges to survival and agriculture.
- Conflict with indigenous peoples: The French encountered resistance from some indigenous tribes, leading to skirmishes and warfare.
- Competition with other European powers: The French faced competition from other European powers, particularly the British, who were also seeking to establish colonies in North America.
Tips
- Utilize historical maps: Studying historical maps of New France in 1600 provides valuable insights into the geography, settlements, and trade routes of the period.
- Explore primary sources: Letters, journals, and official documents from the period offer firsthand accounts of the challenges and experiences of the French in New France.
- Engage with indigenous perspectives: Understanding the perspectives of indigenous peoples who inhabited the land is essential to gaining a comprehensive understanding of the history of New France.
Conclusion
The map of New France in 1600 provides a powerful and evocative testament to the early stages of French colonization in North America. It reveals the ambition, challenges, and complexities of this nascent empire, highlighting the vital role played by exploration, trade, and the interactions with indigenous peoples. This map serves as a reminder of the intricate and interconnected history of this region, a history that continues to shape the landscape and identity of North America today.

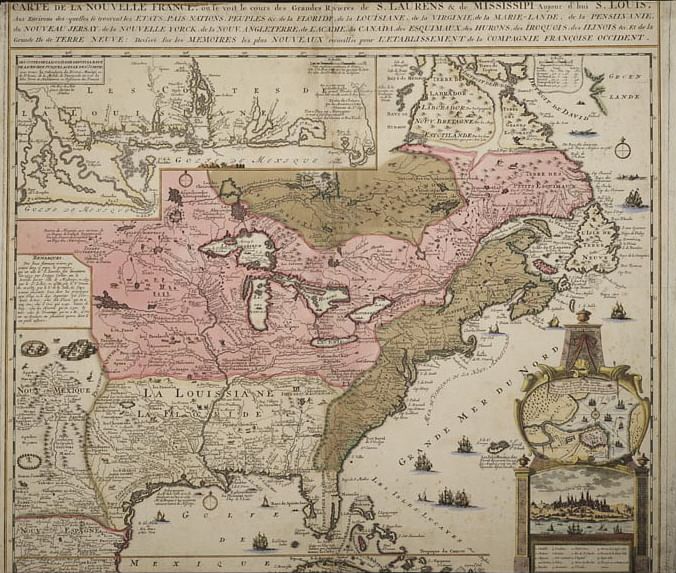
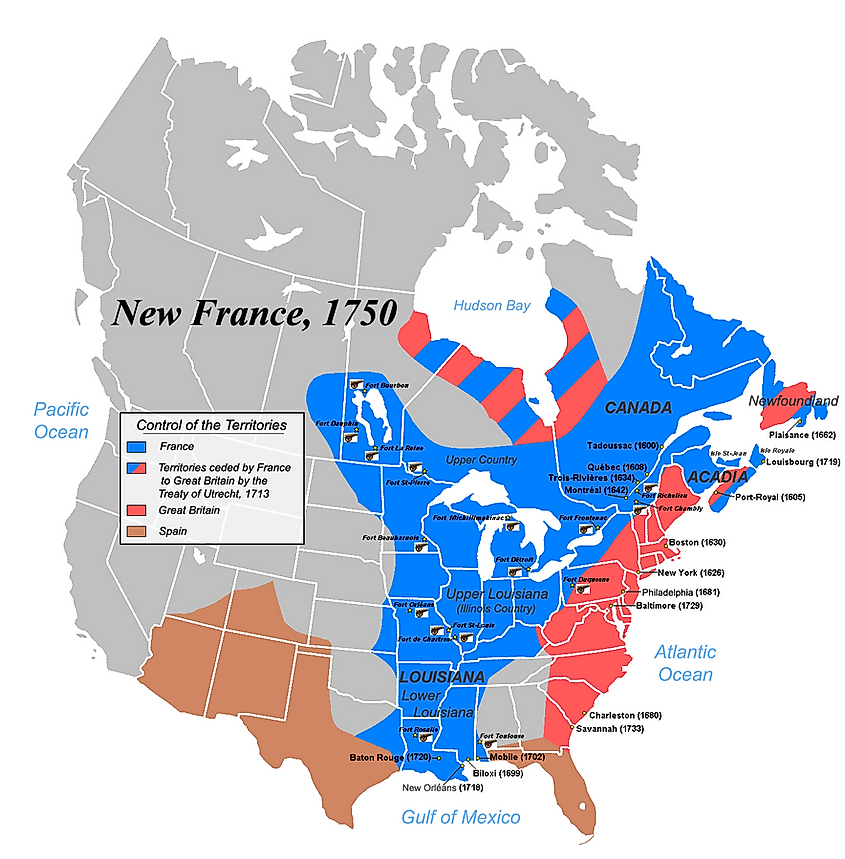


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping New France in 1600: A Glimpse into a Nascent Empire. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!