Mapping the Spread: A Comprehensive Look at Virus Maps in France
Related Articles: Mapping the Spread: A Comprehensive Look at Virus Maps in France
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Spread: A Comprehensive Look at Virus Maps in France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Spread: A Comprehensive Look at Virus Maps in France

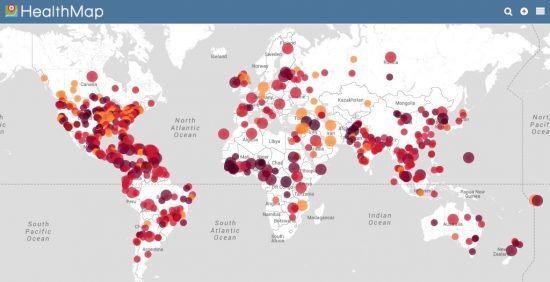
The visualization of disease spread has become an indispensable tool in public health, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of outbreaks and guiding effective response strategies. In France, the development and utilization of virus maps have proven particularly crucial, allowing for a nuanced understanding of disease transmission, identifying high-risk areas, and informing targeted interventions. This article delves into the significance of virus maps in France, exploring their historical context, current applications, and future potential.
Historical Context: Tracing the Path of Epidemics
The use of maps to track disease outbreaks dates back centuries, with early examples emerging from the 17th century during the bubonic plague. However, the development of modern virus maps in France can be traced to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, coinciding with the rise of bacteriology and the recognition of infectious disease transmission mechanisms.
The 1892 cholera epidemic in Paris, for instance, highlighted the need for sophisticated mapping techniques to understand the spread of the disease. This event led to the establishment of the "Service de la Carte Sanitaire" (Health Map Service), tasked with collecting and analyzing health data to create maps illustrating disease distribution.
During the 20th century, advancements in cartography and data analysis further propelled the development of virus maps in France. The 1918 influenza pandemic, known as the "Spanish Flu," further underscored the importance of mapping to track the rapid spread of infectious diseases.
Modern Applications: Unveiling the Invisible Threat
Today, virus maps in France play a pivotal role in public health surveillance and response. They are utilized for a wide range of purposes, including:
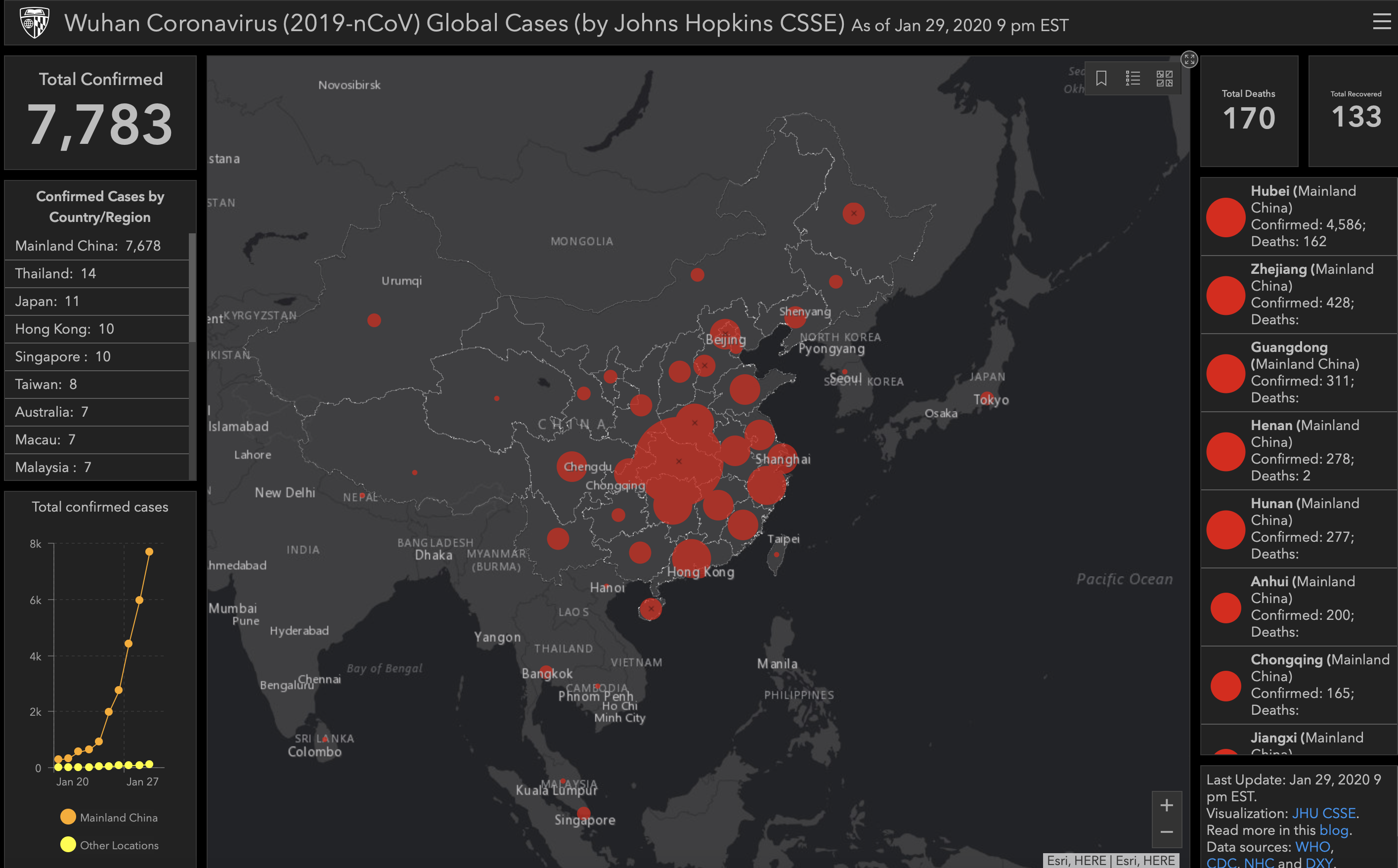
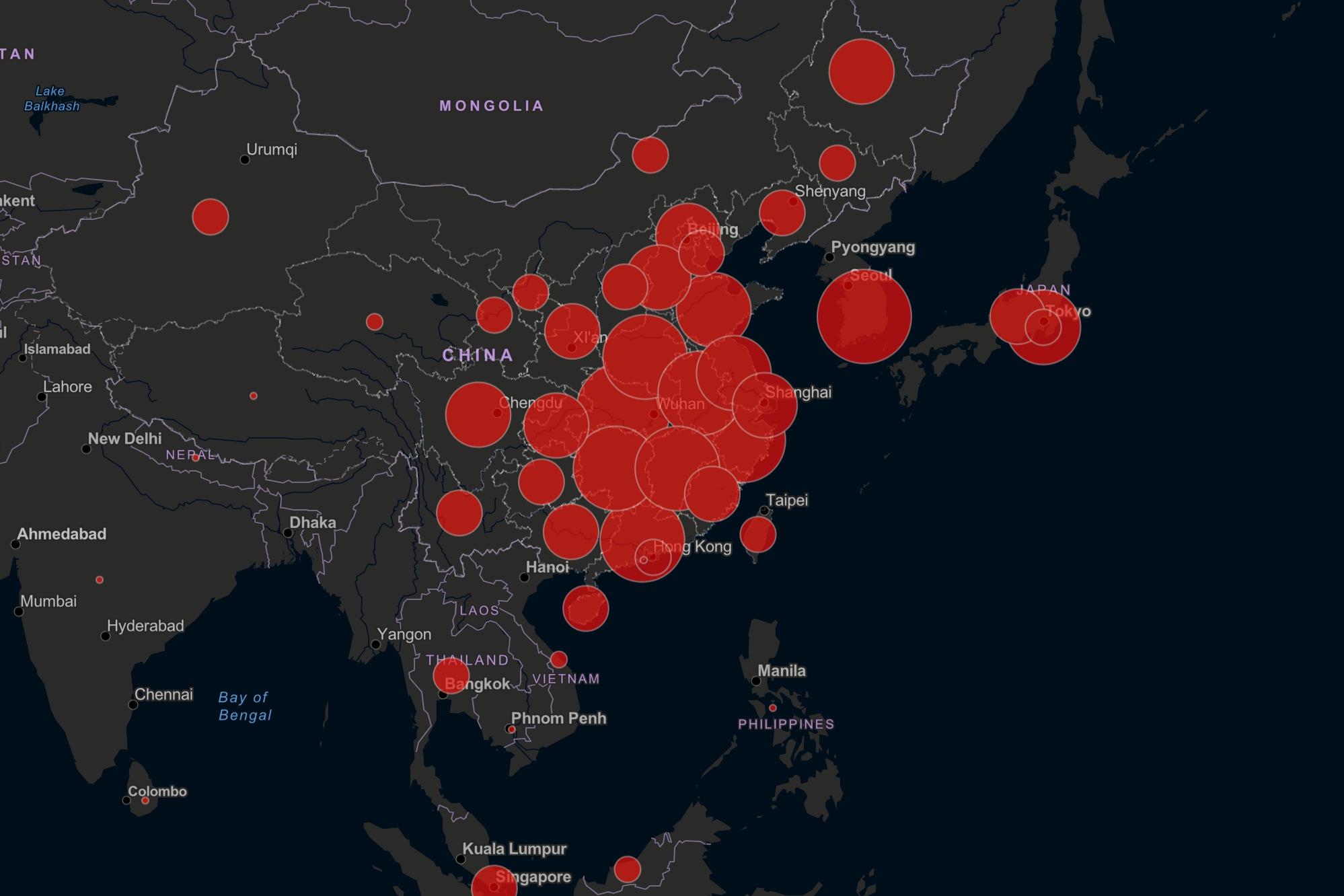
- Monitoring and Tracking Disease Outbreaks: Virus maps provide a real-time snapshot of disease prevalence, allowing public health officials to identify emerging outbreaks and assess their geographical distribution. This information is crucial for deploying resources and implementing targeted interventions.
- Identifying High-Risk Areas: By visualizing disease clusters and hotspots, virus maps help pinpoint areas with elevated transmission rates. This enables authorities to focus public health campaigns and resource allocation on vulnerable populations and geographic locations.
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Interventions: Virus maps can be used to evaluate the impact of public health measures, such as vaccination campaigns or social distancing policies, by monitoring changes in disease prevalence over time.
- Predicting Future Disease Spread: Utilizing advanced statistical modeling and predictive analytics, virus maps can help forecast the potential spread of diseases based on various factors, including population density, travel patterns, and environmental conditions. This information is essential for proactive planning and resource allocation.
Data Sources and Visualization Tools
The creation of virus maps relies on a robust data infrastructure, incorporating information from various sources:
- National Surveillance Systems: The French Ministry of Health operates a comprehensive surveillance system, collecting data on reportable diseases from healthcare providers and laboratories across the country.
- Hospital Admissions and Mortality Data: Data on hospital admissions and deaths related to specific diseases provide valuable insights into disease severity and impact.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology allows for the integration of spatial data, such as population density, socioeconomic factors, and environmental variables, with disease information, providing a more comprehensive understanding of disease spread.
Examples of Virus Maps in France
- The "Carte de la grippe" (Flu Map): This map, maintained by the Institut de Veille Sanitaire (Health Surveillance Institute), tracks influenza activity nationwide, providing weekly updates on influenza cases and hospitalizations.
- The "Carte de la dengue" (Dengue Map): This map, developed by the Institut Pasteur, monitors the incidence of dengue fever in France and its overseas territories, highlighting areas with high transmission risk.
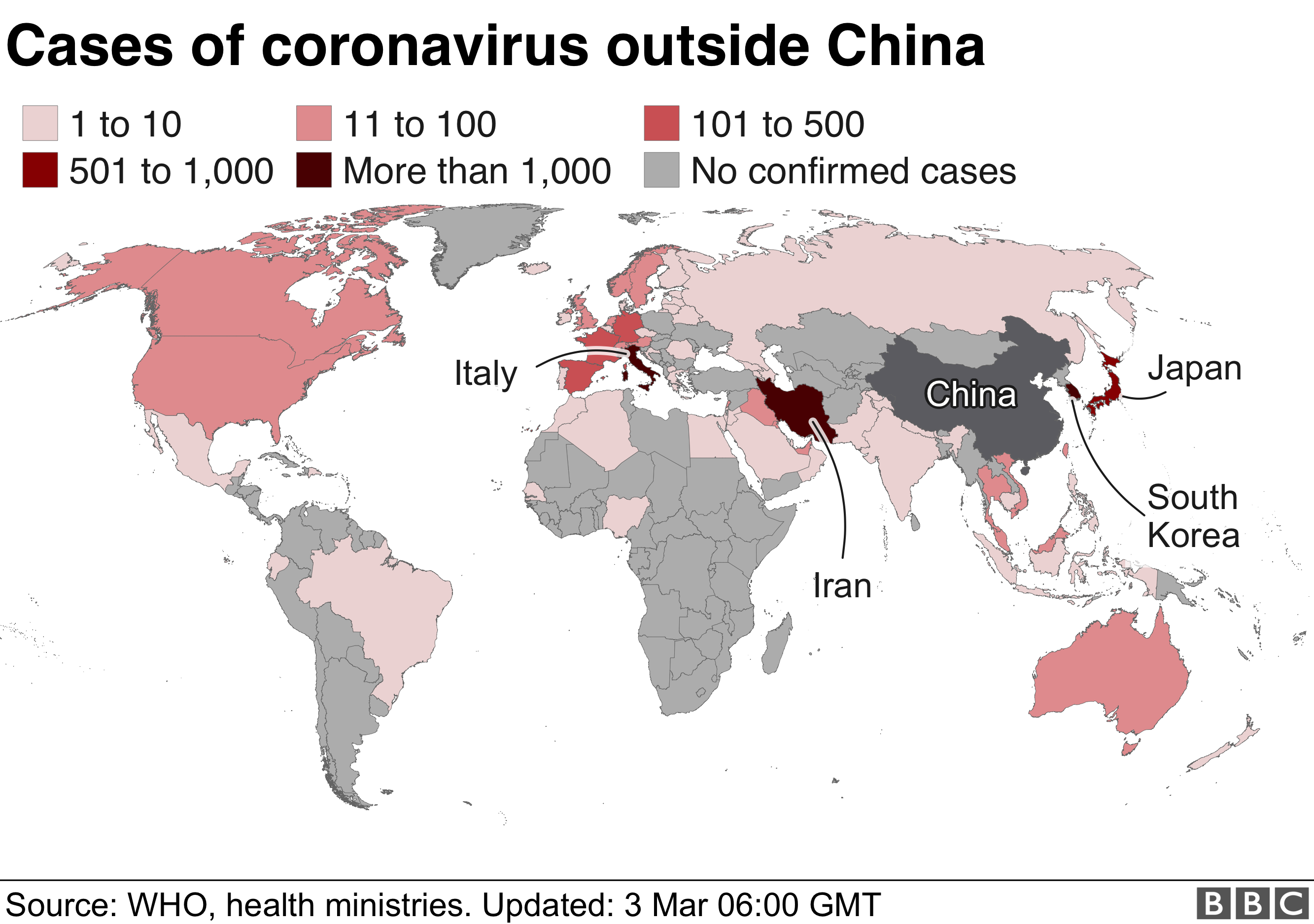
- The "Carte de la COVID-19" (COVID-19 Map): This map, developed by the French Ministry of Health, provides real-time data on COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths across France, allowing for a detailed understanding of the pandemic’s evolution.
Benefits and Importance
The use of virus maps in France offers significant benefits, contributing to:
- Improved Disease Surveillance: Virus maps provide a comprehensive and timely overview of disease activity, enabling early detection and response to outbreaks.
- Targeted Interventions: By identifying high-risk areas and vulnerable populations, virus maps facilitate the allocation of resources and the implementation of tailored interventions.
- Public Health Education: Virus maps can be used to raise awareness about disease risks and promote preventive measures, empowering individuals to protect themselves and their communities.
- Research and Development: Virus maps serve as valuable resources for researchers, providing data for epidemiological studies and informing the development of new prevention and treatment strategies.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their undeniable value, virus maps face certain challenges and limitations:
- Data Availability and Accuracy: The accuracy and completeness of data are crucial for effective mapping. Data gaps, reporting delays, and inaccuracies can affect the reliability of virus maps.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of personal health data raises privacy concerns, necessitating robust data protection measures to ensure confidentiality and ethical use.
- Public Perception: Some individuals may be hesitant to share their health information or may misinterpret the information presented on virus maps, leading to public anxiety or distrust.
Future Directions
The field of virus mapping continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and data analysis:
- Integration of Big Data: The use of big data, including social media data, mobility patterns, and environmental data, can enhance the predictive power of virus maps.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI algorithms can be used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict disease spread with greater accuracy.
- Interactive and User-Friendly Maps: The development of interactive and user-friendly maps can improve public engagement and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
FAQs about Virus Maps in France
1. Are virus maps publicly accessible?
Yes, many virus maps in France are publicly accessible, with information provided by government agencies and research institutions.
2. What data is used to create virus maps?
Virus maps utilize data from national surveillance systems, hospital admissions, mortality records, and geographic information systems.
3. How often are virus maps updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific map and the type of data being collected. Some maps are updated daily, while others are updated weekly or monthly.
4. How can I use virus maps to protect myself and my family?
Virus maps can help you understand the risk of disease transmission in your area, allowing you to take appropriate precautions, such as vaccination, social distancing, and hand hygiene.
5. What is the role of the government in virus mapping?
The French government plays a crucial role in coordinating data collection, funding research, and promoting the use of virus maps for public health purposes.
Tips for Using Virus Maps Effectively
- Understand the data sources and limitations: Be aware of the data sources used to create the map and any potential biases or inaccuracies.
- Consider the context: Interpret the information presented on the map in relation to broader factors, such as population density, travel patterns, and environmental conditions.
- Use the information to make informed decisions: Use the information provided by virus maps to make informed decisions about your health and safety, such as seeking medical advice or taking preventive measures.
- Engage with public health officials: Consult with public health officials for further clarification and guidance on interpreting and using virus map data.
Conclusion
Virus maps have become an indispensable tool in public health, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of disease outbreaks in France. Their ability to monitor disease spread, identify high-risk areas, and inform targeted interventions has significantly contributed to disease control and prevention. As technology and data analysis continue to advance, the use of virus maps is poised to play an even more prominent role in safeguarding public health in France and beyond. By embracing the power of visualization and data-driven decision-making, we can continue to navigate the challenges posed by infectious diseases and build a healthier future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Spread: A Comprehensive Look at Virus Maps in France. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!