Mapping the World: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Data
Related Articles: Mapping the World: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the World: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the World: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Data

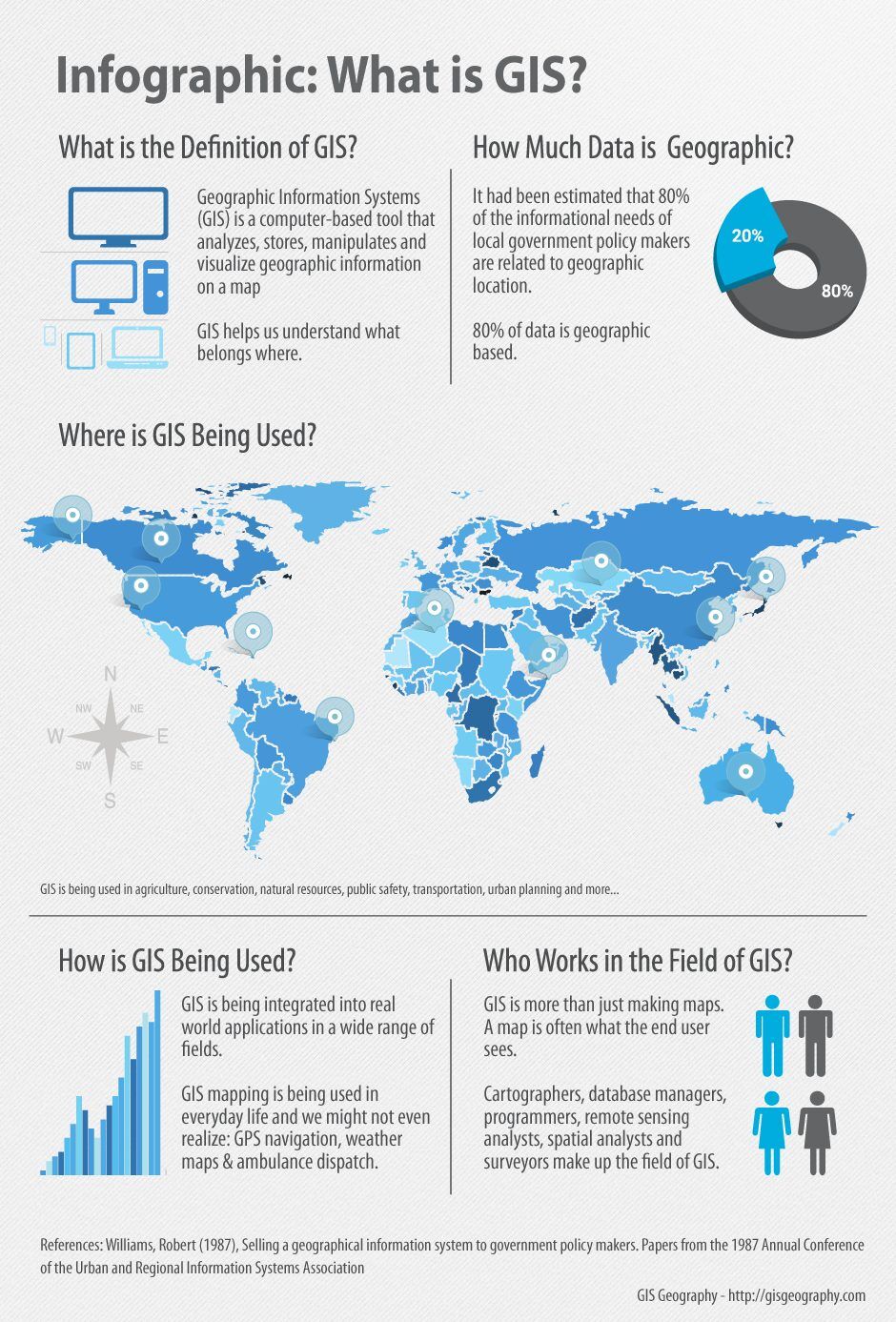
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) data has become an indispensable tool for understanding and managing our world. This data, which encompasses location-specific information, plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from urban planning and disaster management to environmental monitoring and resource management.
What is GIS Data?
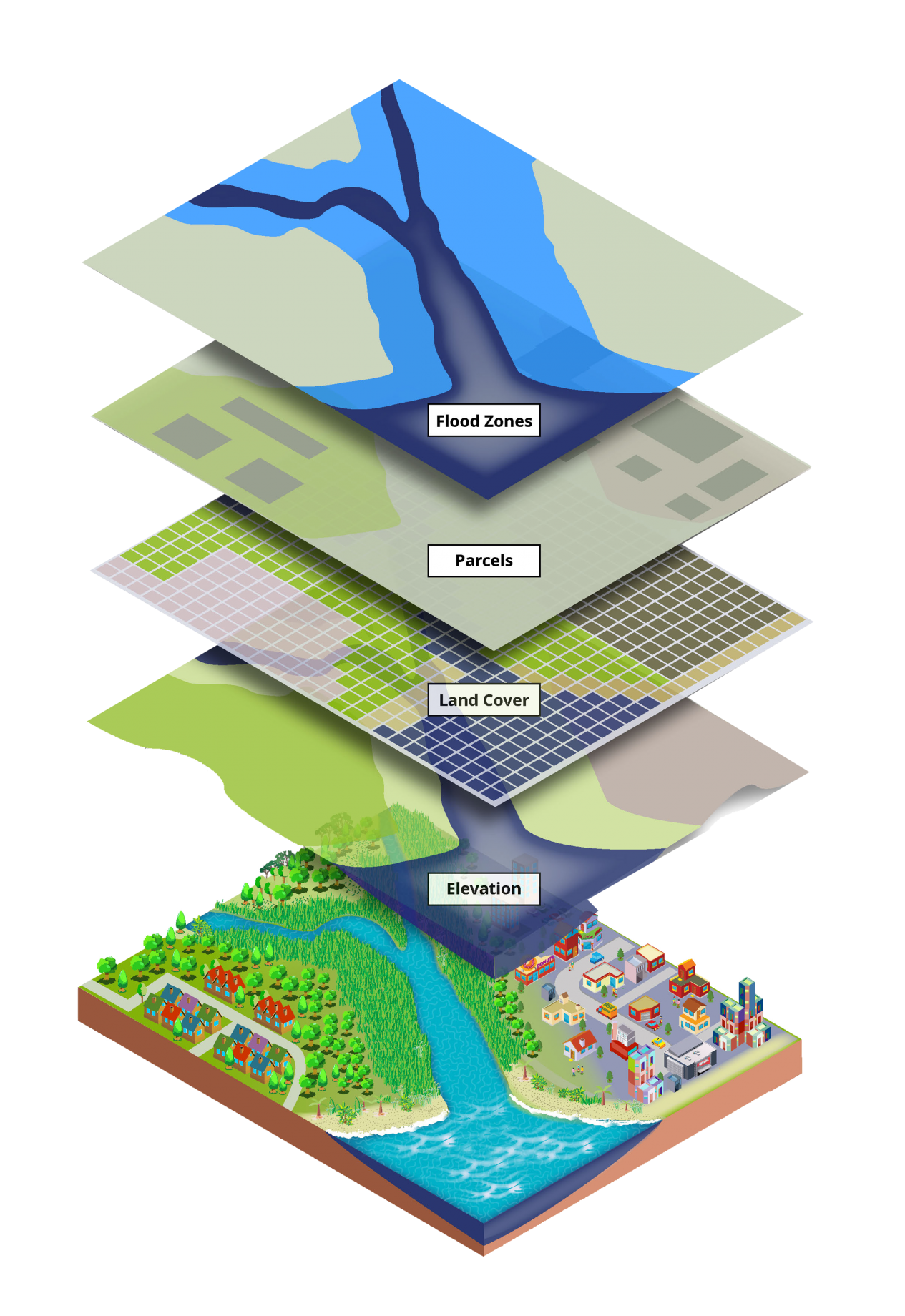
At its core, GIS data is a collection of information that is geographically referenced. This means that each piece of data is associated with a specific location on Earth. This location is usually represented by coordinates, such as latitude and longitude, but can also be defined by addresses, place names, or even postal codes.
GIS data can be categorized into two primary types:
-
Vector Data: This type of data represents geographic features as points, lines, or polygons.
- Points: Represent discrete locations, such as buildings, trees, or wells.
- Lines: Represent linear features, such as roads, rivers, or power lines.
- Polygons: Represent areas, such as parks, lakes, or administrative boundaries.
- Raster Data: This type of data represents continuous phenomena, such as elevation, temperature, or rainfall, as a grid of cells, each with a specific value.
The Power of GIS Data
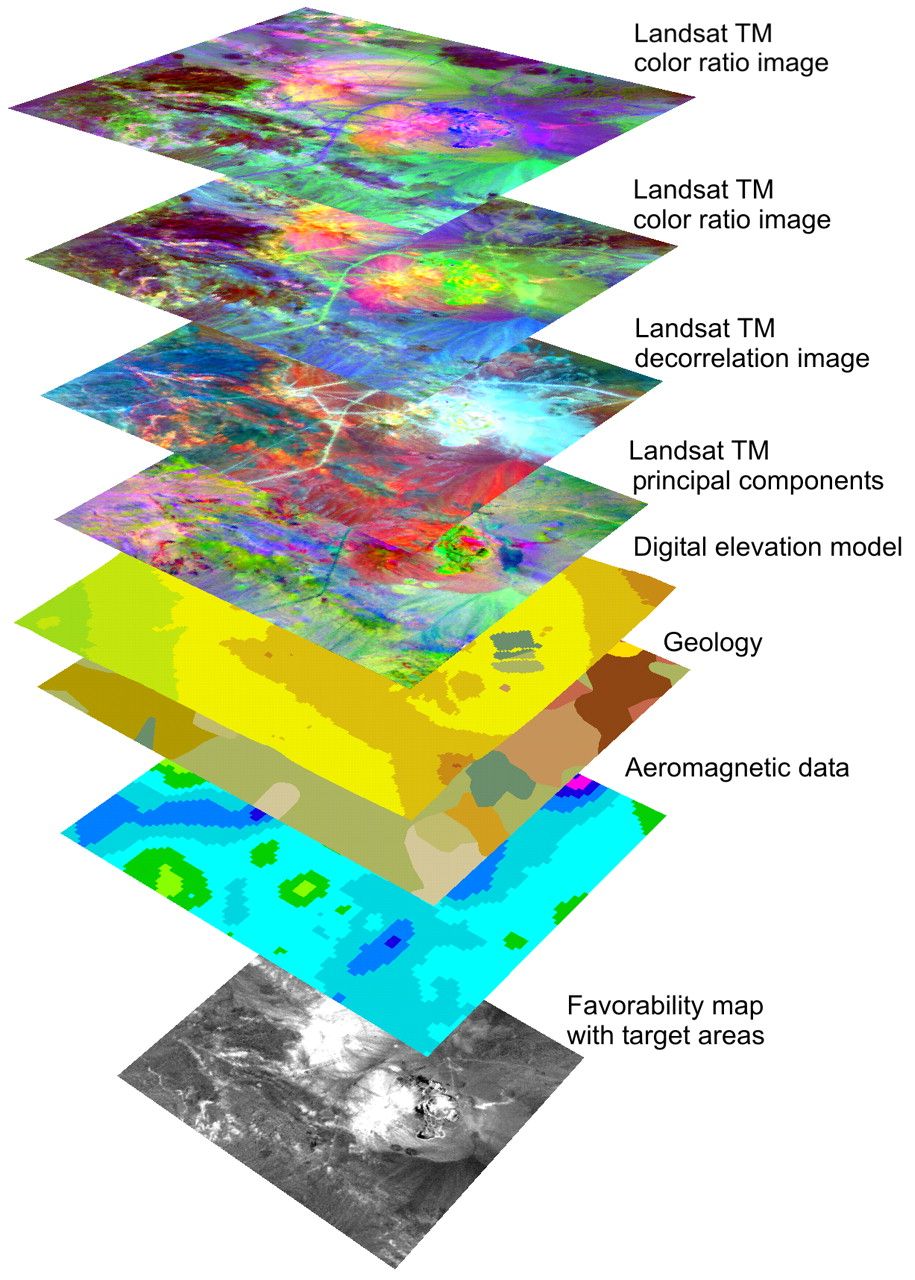
The strength of GIS data lies in its ability to combine and analyze information from various sources, providing a holistic understanding of the world. This capability is achieved through the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, which allows users to:
- Visualize spatial relationships: GIS software enables users to create maps and other visualizations that reveal patterns, trends, and relationships between different geographic features.
- Analyze spatial data: GIS tools provide a range of analytical functions, allowing users to perform operations such as proximity analysis, overlay analysis, and spatial statistics.
- Model and simulate scenarios: GIS can be used to create models and simulations that help predict the impact of different decisions or events on the environment, infrastructure, or population.
- Share and collaborate: GIS data can be easily shared and collaborated on, fostering communication and decision-making among stakeholders.
Applications of GIS Data
The applications of GIS data are vast and diverse, impacting virtually every aspect of our lives. Some key examples include:
- Urban Planning: GIS data helps city planners assess population density, transportation infrastructure, land use patterns, and environmental factors to develop sustainable urban development strategies.
- Disaster Management: GIS data plays a crucial role in disaster response and recovery efforts, providing real-time information on affected areas, infrastructure damage, and population displacement.
- Environmental Monitoring: GIS data is used to monitor environmental conditions such as air and water quality, deforestation rates, and climate change impacts, enabling informed decision-making for environmental protection.
- Resource Management: GIS data helps in managing natural resources such as water, forests, and minerals, optimizing extraction, allocation, and conservation efforts.
- Agriculture: GIS data allows farmers to monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and analyze soil conditions, leading to increased productivity and resource efficiency.
- Public Health: GIS data is used to track disease outbreaks, identify high-risk areas, and develop targeted public health interventions.
- Transportation: GIS data helps in planning and managing transportation networks, optimizing traffic flow, and improving public transit services.
- Education: GIS data is used in educational settings to teach students about geography, spatial thinking, and data analysis.
FAQs about GIS Data
1. What are the different formats for GIS data?
GIS data can be stored in various formats, including:
- Shapefiles: A common format for vector data, storing points, lines, and polygons.
- GeoJSON: A lightweight format for representing geographic features, often used in web applications.
- GeoTIFF: A format for storing raster data, such as satellite imagery or elevation maps.
- KML: A format for representing geographic features and data in Google Earth.
2. How can I access GIS data?
There are numerous sources for accessing GIS data:
- Government agencies: Many government agencies, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), provide open-source GIS data.
- Commercial data providers: Companies such as Esri, HERE Technologies, and Mapbox offer commercial GIS data and services.
- OpenStreetMap: A collaborative project for creating and maintaining a free and open-source map of the world.
- Research institutions: Universities and research institutions often publish GIS data related to their research projects.
3. What software is used for working with GIS data?
There are several popular GIS software programs available, including:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive suite of GIS tools from Esri, widely used in various industries.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software, popular for its flexibility and ease of use.
- Google Earth Pro: A powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing geographic data, including 3D models and satellite imagery.
- Mapbox Studio: A web-based platform for creating and publishing interactive maps.
4. What are the challenges associated with GIS data?
While GIS data offers immense potential, it also presents challenges:
- Data accuracy and completeness: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of GIS data is crucial for reliable analysis and decision-making.
- Data accessibility and sharing: Accessing and sharing GIS data can be challenging due to data ownership, security, and format compatibility issues.
- Data interpretation and analysis: Understanding the complexities of GIS data and applying appropriate analysis techniques requires specialized skills and knowledge.
- Data maintenance and updates: GIS data needs to be regularly updated and maintained to reflect changes in the real world.
Tips for Working with GIS Data
- Understand the data source and its limitations: Before using any GIS data, it is crucial to understand its origin, accuracy, and potential biases.
- Use appropriate data visualization techniques: Choosing the right visualization techniques can effectively convey spatial patterns and relationships.
- Perform thorough data analysis and validation: Applying appropriate analysis methods and validating results are essential for ensuring data reliability.
- Collaborate with experts and stakeholders: Involving experts and stakeholders can enhance data quality, ensure its relevance, and facilitate effective decision-making.
Conclusion
GIS data is transforming the way we understand and manage our world. Its ability to combine and analyze location-specific information provides a powerful tool for addressing complex challenges in various fields. By leveraging the power of GIS data, we can make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and create a more sustainable and equitable future. As technology continues to advance, GIS data will continue to evolve and play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the World: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Data. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!