Navigating the American Landscape: Understanding the East and West Coasts
Related Articles: Navigating the American Landscape: Understanding the East and West Coasts
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the American Landscape: Understanding the East and West Coasts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the American Landscape: Understanding the East and West Coasts

The United States, a vast and diverse nation, is often understood through the lens of its two iconic coastlines: the East Coast and the West Coast. These regions, while geographically distant, have played distinct and significant roles in shaping the nation’s history, culture, and identity. This exploration delves into the geographical, historical, and cultural nuances of the East and West Coasts, highlighting their unique characteristics and the enduring impact they have on the American narrative.
A Geographical Divide:
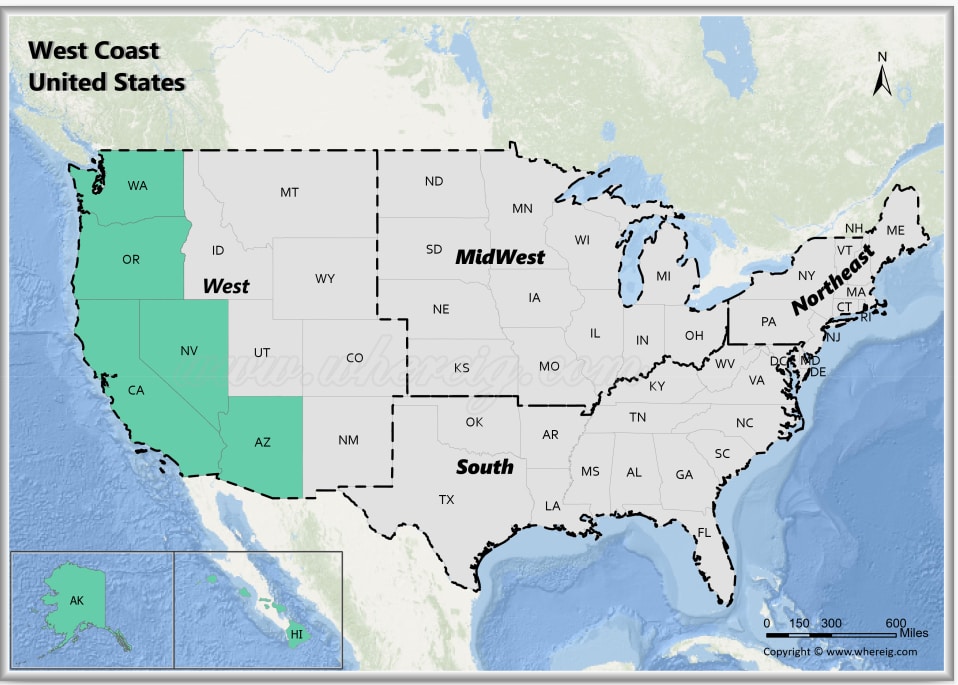
The East Coast, facing the Atlantic Ocean, encompasses a narrow strip of land stretching from Maine in the north to Florida in the south. This region is characterized by its diverse geography, including rolling hills, dense forests, and vast coastal plains. The Appalachian Mountains, a defining feature of the East Coast, run parallel to the Atlantic and offer breathtaking vistas. Major cities like New York, Boston, Philadelphia, and Washington D.C. dot the East Coast, serving as centers of commerce, culture, and political power.
In contrast, the West Coast, bordering the Pacific Ocean, stretches from Washington state in the north to California in the south. This region features a more dramatic and varied landscape, encompassing towering mountain ranges, vast deserts, and fertile valleys. The Sierra Nevada and Cascade Ranges, with their snow-capped peaks, dominate the West Coast’s geography. Major cities like Seattle, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and San Diego thrive along the Pacific coast, each offering a unique blend of urban life and natural beauty.
Historical Crossroads:
The East Coast played a pivotal role in the early development of the United States. Colonized by European powers, it served as the initial point of entry for immigrants and the cradle of American democracy. The Revolutionary War, fought primarily on the East Coast, established the United States as an independent nation. The region witnessed the rise of major industries, including shipping, manufacturing, and finance, laying the foundation for the nation’s economic growth.
The West Coast, initially explored by Spanish conquistadors, became a vital part of the United States during the Gold Rush of the 19th century. The influx of prospectors transformed the region, leading to the development of new towns and cities. The transcontinental railroad, completed in 1869, connected the East and West Coasts, further solidifying the West’s importance in the national narrative. The West Coast also played a significant role in the 20th century, becoming a hub for the burgeoning film industry and the technology revolution.
Cultural Tapestry:
The East Coast is known for its rich history, traditional values, and intellectual pursuits. The region boasts renowned universities, museums, and cultural institutions, attracting artists, writers, and scholars from around the world. Its urban centers, with their diverse populations and vibrant street life, offer a cosmopolitan atmosphere. The East Coast’s cultural landscape is shaped by its colonial heritage, reflected in its architecture, cuisine, and social customs.
The West Coast, on the other hand, embodies a spirit of innovation, creativity, and a laid-back lifestyle. It is a region where individualism and a "can-do" attitude prevail. The West Coast is home to a thriving technology sector, attracting entrepreneurs and innovators from across the globe. Its diverse population, influenced by Asian and Latin American cultures, contributes to a vibrant and eclectic cultural scene.
Navigating the Differences:
While the East and West Coasts share a common American identity, their distinct geographical, historical, and cultural characteristics create a fascinating contrast. The East Coast, steeped in tradition and history, embodies a sense of sophistication and formality. The West Coast, with its youthful energy and embrace of innovation, exudes a more casual and entrepreneurial spirit.
These differences are reflected in the regions’ lifestyles, values, and political leanings. The East Coast, with its established institutions and traditional power structures, often leans towards a more conservative approach. The West Coast, with its embrace of change and a focus on individual expression, tends to embrace a more liberal outlook.
Beyond the Coastlines:
It is important to remember that the East and West Coasts are not monolithic entities. Within each region, diverse communities and subcultures exist, each with its own unique characteristics and perspectives. The American South, with its distinct history and culture, stands as a powerful example of a region that defies easy categorization.
Furthermore, the United States is a nation constantly evolving, and the lines between the East and West Coasts are becoming increasingly blurred. As transportation and communication technologies advance, the nation’s regions are becoming more interconnected, fostering cultural exchange and blurring regional distinctions.
Conclusion:
The East and West Coasts, with their contrasting landscapes, histories, and cultures, offer a compelling glimpse into the diverse tapestry of the United States. Understanding these regions, with their unique strengths and perspectives, provides a deeper appreciation for the nation’s complexity and its ongoing evolution. While the East and West Coasts continue to shape the American narrative, it is essential to recognize the diversity and dynamism that exist within each region and across the nation as a whole.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main geographical differences between the East and West Coasts?
A: The East Coast features rolling hills, dense forests, and coastal plains, while the West Coast is characterized by towering mountain ranges, vast deserts, and fertile valleys.
Q: How did the East and West Coasts contribute to the development of the United States?
A: The East Coast played a crucial role in the nation’s founding, serving as the initial point of colonization and the site of the Revolutionary War. The West Coast’s importance grew during the Gold Rush and the transcontinental railroad’s construction.
Q: What are the key cultural differences between the East and West Coasts?
A: The East Coast is known for its traditional values, intellectual pursuits, and sophisticated urban centers. The West Coast embodies a spirit of innovation, creativity, and a laid-back lifestyle.
Q: Are the East and West Coasts monolithic entities?
A: No, both regions contain diverse communities and subcultures, each with its own unique characteristics and perspectives.
Q: How are the East and West Coasts changing in the 21st century?
A: Increased connectivity and cultural exchange are blurring regional distinctions, fostering a more integrated and dynamic American landscape.
Tips:
- Travel and experience: Visit both coasts to gain firsthand understanding of their unique landscapes, cultures, and lifestyles.
- Engage with local communities: Connect with people from different regions to gain diverse perspectives and broaden your understanding of the American experience.
- Explore historical sites: Visit museums, historical landmarks, and cultural institutions to learn about the significant events and figures that shaped the East and West Coasts.
- Read literature and watch films: Immerse yourself in stories and films set in different regions to gain insights into their unique cultures and perspectives.
- Embrace the differences: Appreciate the contrasting characteristics of the East and West Coasts, recognizing that diversity enriches the American narrative.
Conclusion:
The East and West Coasts, while geographically distinct, continue to shape the American experience, offering a captivating window into the nation’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing evolution. By understanding their unique characteristics, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and dynamism of the United States.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the American Landscape: Understanding the East and West Coasts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!