Navigating the Cityscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Urban Mapping in France
Related Articles: Navigating the Cityscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Urban Mapping in France
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Cityscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Urban Mapping in France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Cityscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Urban Mapping in France

Urban mapping, a crucial aspect of city planning and management, plays a vital role in understanding and optimizing urban environments. In France, a nation renowned for its rich history and diverse urban landscapes, mapping has evolved into a multifaceted discipline, encompassing various applications and methodologies. This article delves into the intricacies of urban mapping in France, exploring its significance, diverse uses, and the challenges it presents.
The Historical Context of Urban Mapping in France
France’s engagement with urban mapping can be traced back centuries, with early maps serving as essential tools for navigating bustling cities and managing urban development. The cadastral maps, introduced in the 18th century, provided detailed records of land ownership and property boundaries, laying the groundwork for modern land management systems.
The advent of modern cartography in the 19th century saw the creation of highly detailed urban plans, incorporating streets, buildings, and infrastructure. These maps served as crucial references for urban planning and infrastructure projects, facilitating the growth of major cities like Paris and Lyon.
The Evolution of Urban Mapping Technologies
The 20th century witnessed a revolution in urban mapping technologies, with the introduction of aerial photography and remote sensing. These advancements enabled the creation of large-scale maps, providing a comprehensive overview of urban environments. The development of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the latter half of the century further transformed the field, offering powerful tools for data analysis and visualization.
Contemporary Urban Mapping in France: Applications and Benefits
Today, urban mapping in France encompasses a wide range of applications, driven by the need to address complex urban challenges and promote sustainable development. Key areas where urban mapping plays a crucial role include:
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Land Use and Zoning: Mapping provides detailed insights into land use patterns, enabling planners to optimize zoning regulations, promote sustainable development, and manage urban sprawl.
- Infrastructure Planning: Detailed maps of existing infrastructure, including roads, utilities, and transportation networks, are essential for planning new infrastructure projects, ensuring efficient connectivity, and mitigating traffic congestion.
- Urban Renewal and Redevelopment: Mapping helps identify areas requiring revitalization, assess existing infrastructure, and plan for the effective allocation of resources for urban renewal projects.
2. Environmental Management:
- Air Quality Monitoring: Mapping air quality data allows for the identification of pollution hotspots, enabling targeted interventions to improve air quality and protect public health.
- Flood Risk Assessment: Detailed maps of flood-prone areas, incorporating topographic data and historical flood records, provide valuable information for mitigating flood risk and implementing effective disaster preparedness strategies.
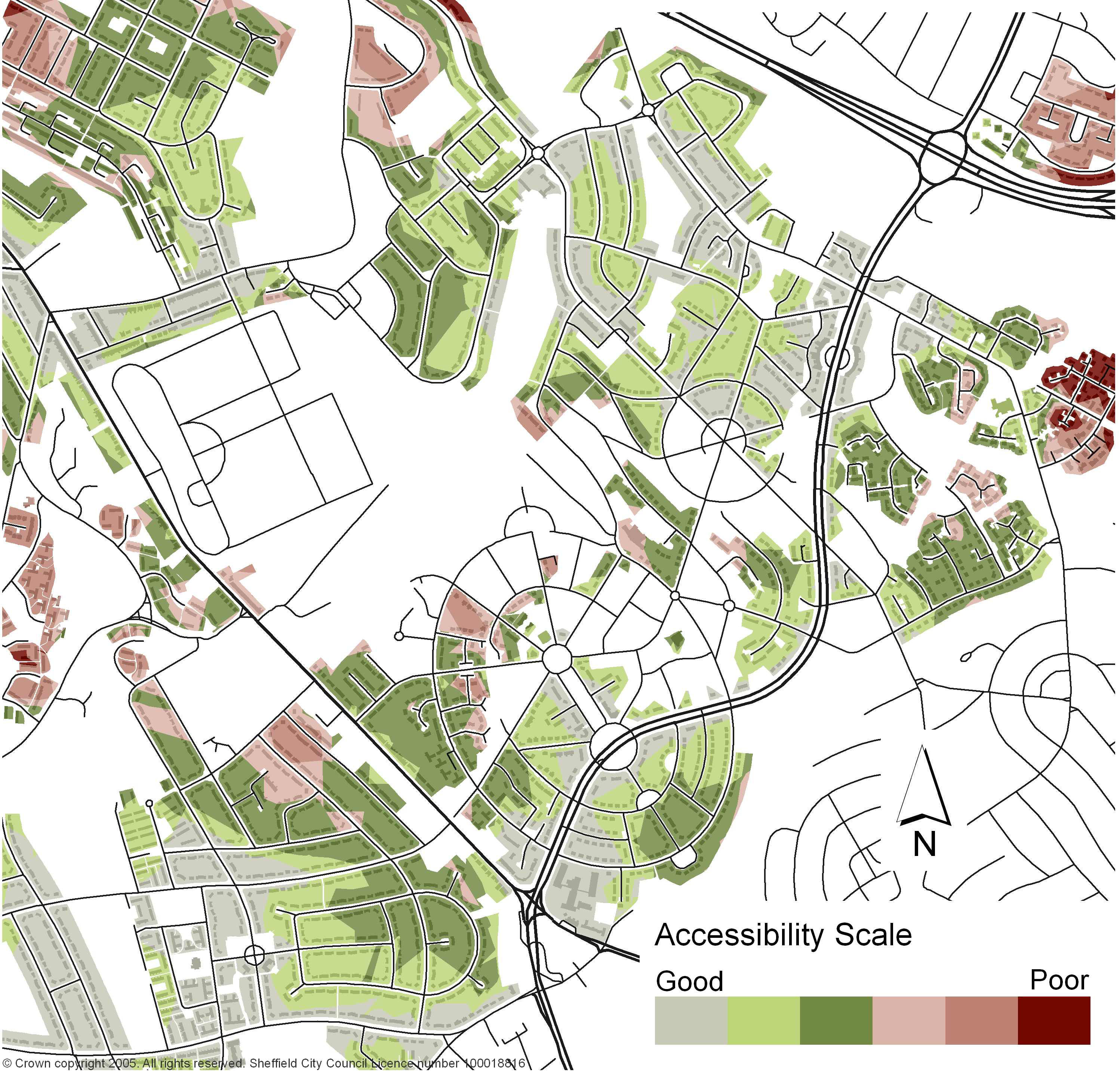
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Mapping urban heat islands helps identify areas experiencing extreme temperatures, facilitating the development of urban greening strategies to mitigate the heat island effect and enhance urban livability.
3. Transportation and Mobility:
- Traffic Management: Real-time traffic data, integrated into mapping systems, enables efficient traffic management, reducing congestion and improving travel times.
- Public Transportation Planning: Mapping public transport networks, including bus routes, metro lines, and bicycle infrastructure, helps optimize public transport services and promote sustainable modes of transportation.
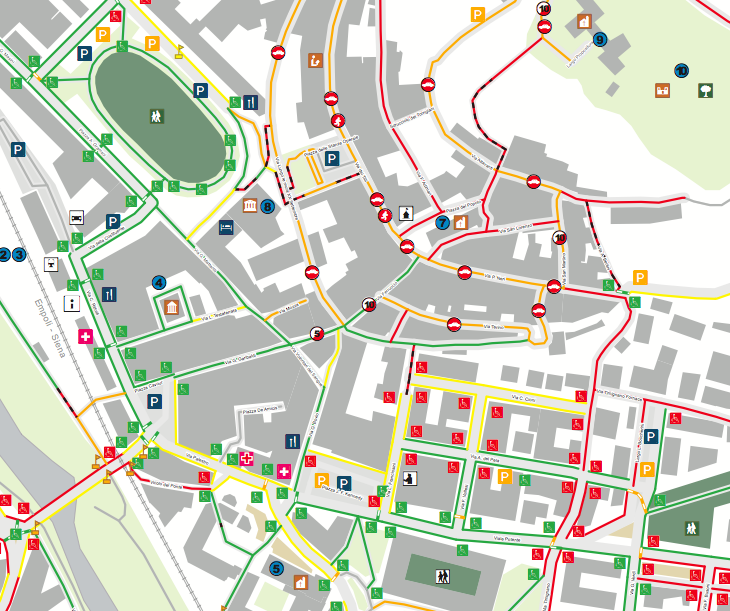
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety: Mapping pedestrian and cyclist routes, incorporating safety features and identifying potential hazards, helps create safer and more accessible urban environments for non-motorized transportation.
4. Social and Economic Development:
- Demographic Analysis: Mapping population density and distribution, combined with socioeconomic data, enables the identification of areas experiencing social and economic disparities, facilitating targeted interventions to address these challenges.
- Community Engagement: Mapping platforms can empower communities by providing access to relevant data and tools for collaborative planning, fostering community engagement and participation in urban decision-making.
- Business and Economic Development: Mapping commercial areas, identifying business clusters, and assessing market potential helps attract investment, promote business growth, and contribute to economic development.
Challenges and Future Directions in Urban Mapping in France
Despite its numerous benefits, urban mapping in France faces several challenges:
- Data Availability and Accessibility: Ensuring the availability of accurate and up-to-date data from diverse sources remains a critical challenge, requiring collaboration among government agencies, private companies, and research institutions.
- Data Privacy and Security: Balancing the need for data-driven urban planning with concerns regarding data privacy and security requires careful consideration and robust data protection measures.
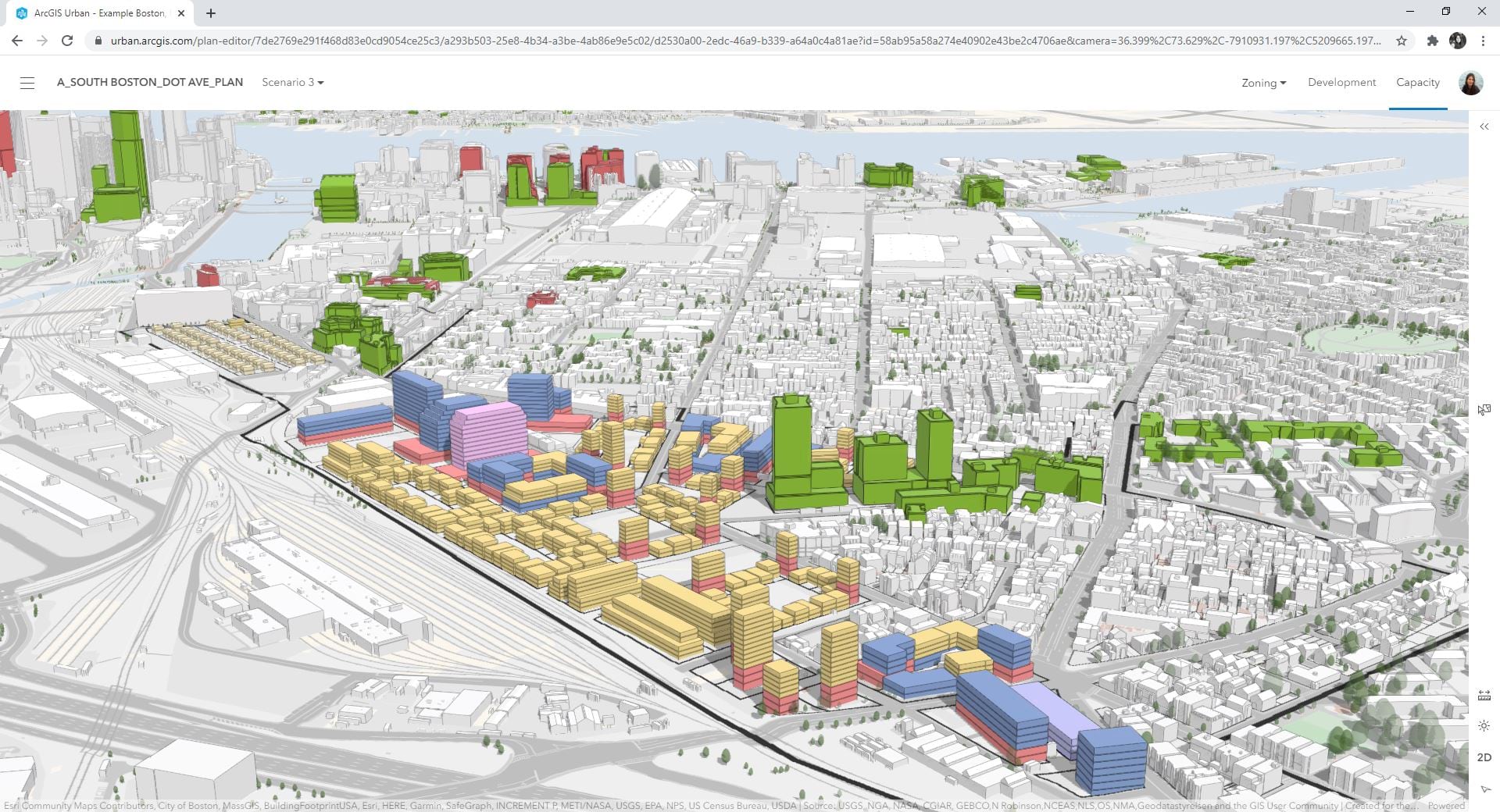
- Integration of Emerging Technologies: Incorporating emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and 3D modeling into urban mapping systems presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring ongoing research and development.
Looking ahead, the future of urban mapping in France holds significant promise. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will further enhance data analysis capabilities, enabling more sophisticated predictions and informed decision-making. The development of 3D city models will provide a more immersive and realistic representation of urban environments, facilitating better understanding and planning.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Urban Mapping in France
1. What are the key agencies involved in urban mapping in France?
Several agencies play crucial roles in urban mapping, including:
- Institut National de l’Information Géographique et Forestière (IGN): The national mapping agency responsible for producing and maintaining topographic maps, aerial photographs, and geospatial data.
- Ministère de la Transition Écologique et Solidaire: The ministry responsible for environmental policy, including urban planning and sustainable development, utilizes mapping data for various initiatives.
- Ministère de la Cohésion des Territoires: The ministry responsible for territorial planning and regional development, relies on mapping data for infrastructure planning, economic development, and urban regeneration projects.
- Local Authorities: Municipalities and regional councils also play a significant role in urban mapping, utilizing data for local planning, infrastructure management, and citizen services.
2. How can I access urban mapping data in France?
Access to urban mapping data in France is generally available through:
- IGN’s website: The IGN provides access to a wide range of geospatial data, including topographic maps, aerial photographs, and cadastral data.
- Open Data Portals: Several government agencies and local authorities maintain open data portals, offering free access to urban mapping data.
- Commercial Data Providers: Private companies specialize in providing geospatial data and mapping services, offering tailored solutions for specific needs.
3. What are the ethical considerations associated with urban mapping?
Ethical considerations associated with urban mapping include:
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the responsible use of personal data collected through mapping systems, complying with data protection regulations, and protecting individual privacy.
- Data Equity: Ensuring that mapping data accurately reflects the diverse realities of urban communities and avoids perpetuating existing inequalities.
- Transparency and Accountability: Maintaining transparency in data collection, analysis, and dissemination, ensuring accountability for the use of mapping data for public benefit.
4. How can urban mapping contribute to a more sustainable future?
Urban mapping plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable urban development by:
- Facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy: Mapping infrastructure, transportation networks, and energy consumption patterns enables the development of sustainable urban planning strategies.
- Promoting green spaces and urban biodiversity: Mapping green spaces and natural habitats helps preserve biodiversity and create resilient urban ecosystems.
- Enhancing urban resilience: Mapping flood-prone areas, identifying vulnerable populations, and planning for emergency response helps improve urban resilience to climate change and other hazards.
Tips for Effective Urban Mapping
- Engage stakeholders: Involve communities, businesses, and other stakeholders in the mapping process to ensure the data reflects local needs and perspectives.
- Prioritize data accuracy: Ensure the collection and validation of accurate and up-to-date data to support informed decision-making.
- Utilize open data standards: Adhere to open data standards to facilitate data sharing and interoperability among different mapping platforms.
- Invest in training and capacity building: Provide training programs to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to effectively utilize and interpret urban mapping data.
- Promote data visualization: Utilize clear and engaging visualizations to communicate complex urban mapping data to a wide audience.
Conclusion: The Future of Urban Mapping in France
Urban mapping in France continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and the growing need for data-driven solutions to address complex urban challenges. As cities face increasing pressures from population growth, climate change, and social inequalities, the role of urban mapping will become even more critical. By leveraging the power of data, technology, and collaboration, France can harness the potential of urban mapping to create more sustainable, resilient, and equitable cities for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Cityscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Urban Mapping in France. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!