Navigating the Finnish Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cities and Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the Finnish Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cities and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Finnish Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cities and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Finnish Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cities and Geography
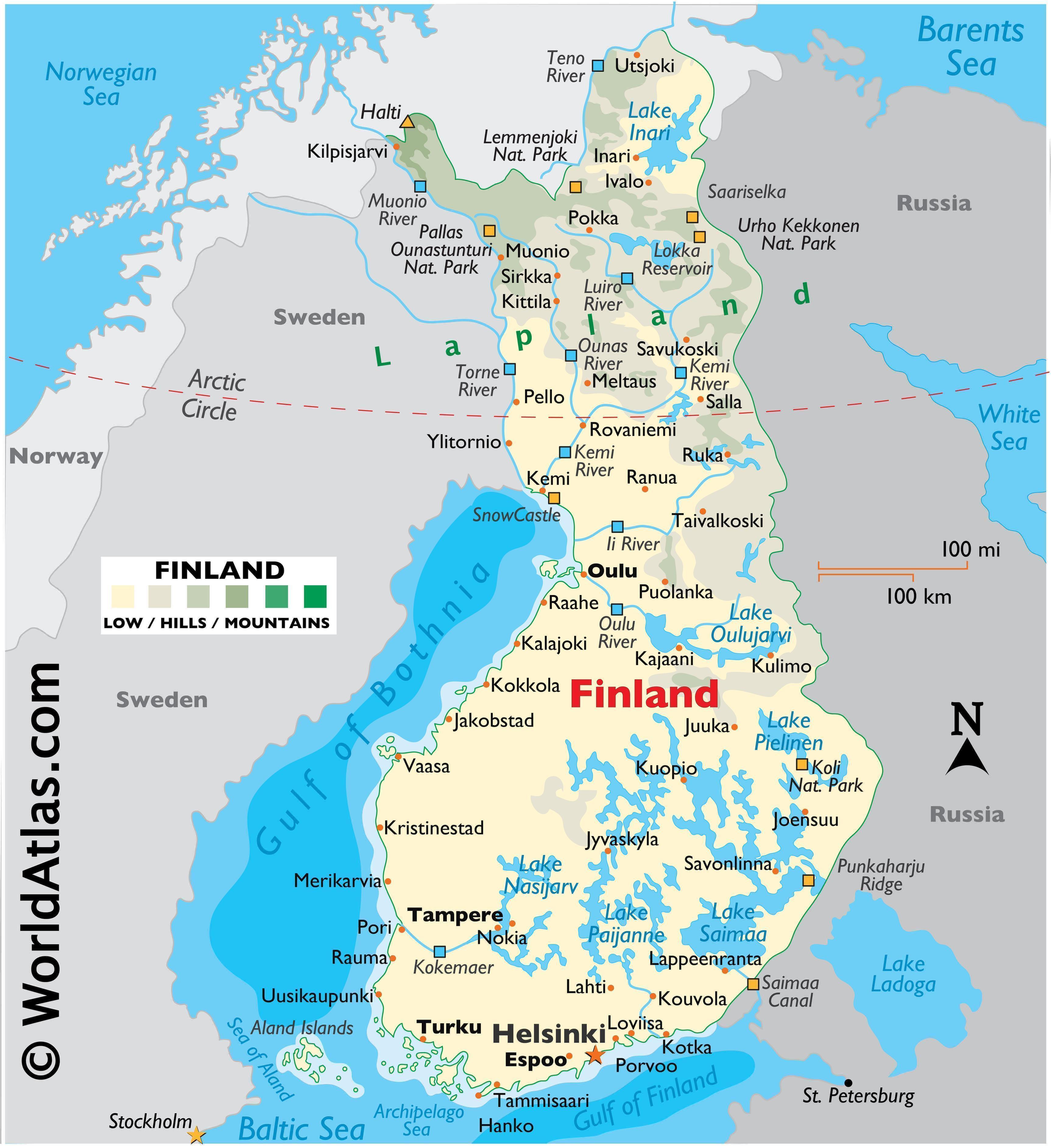
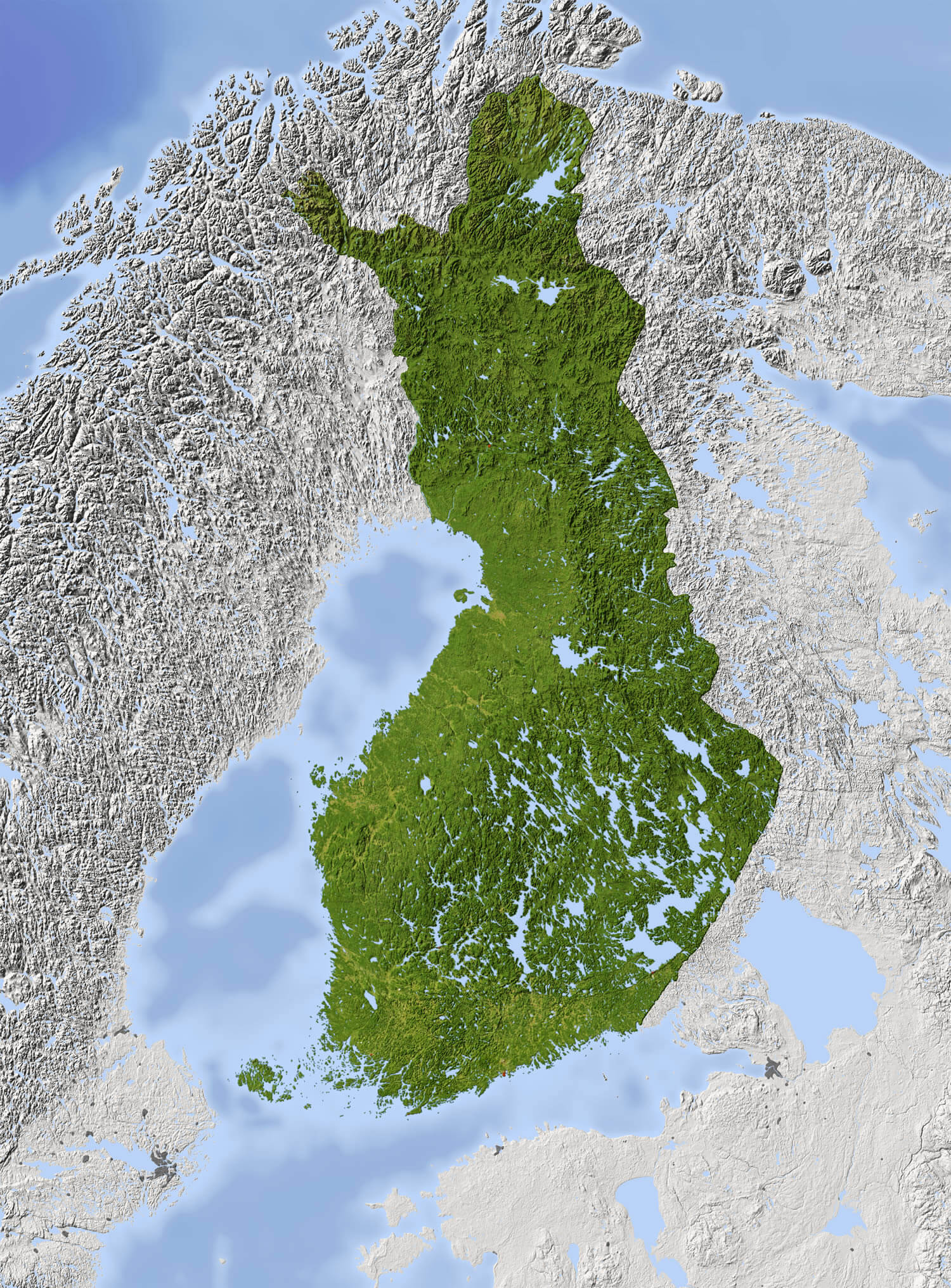
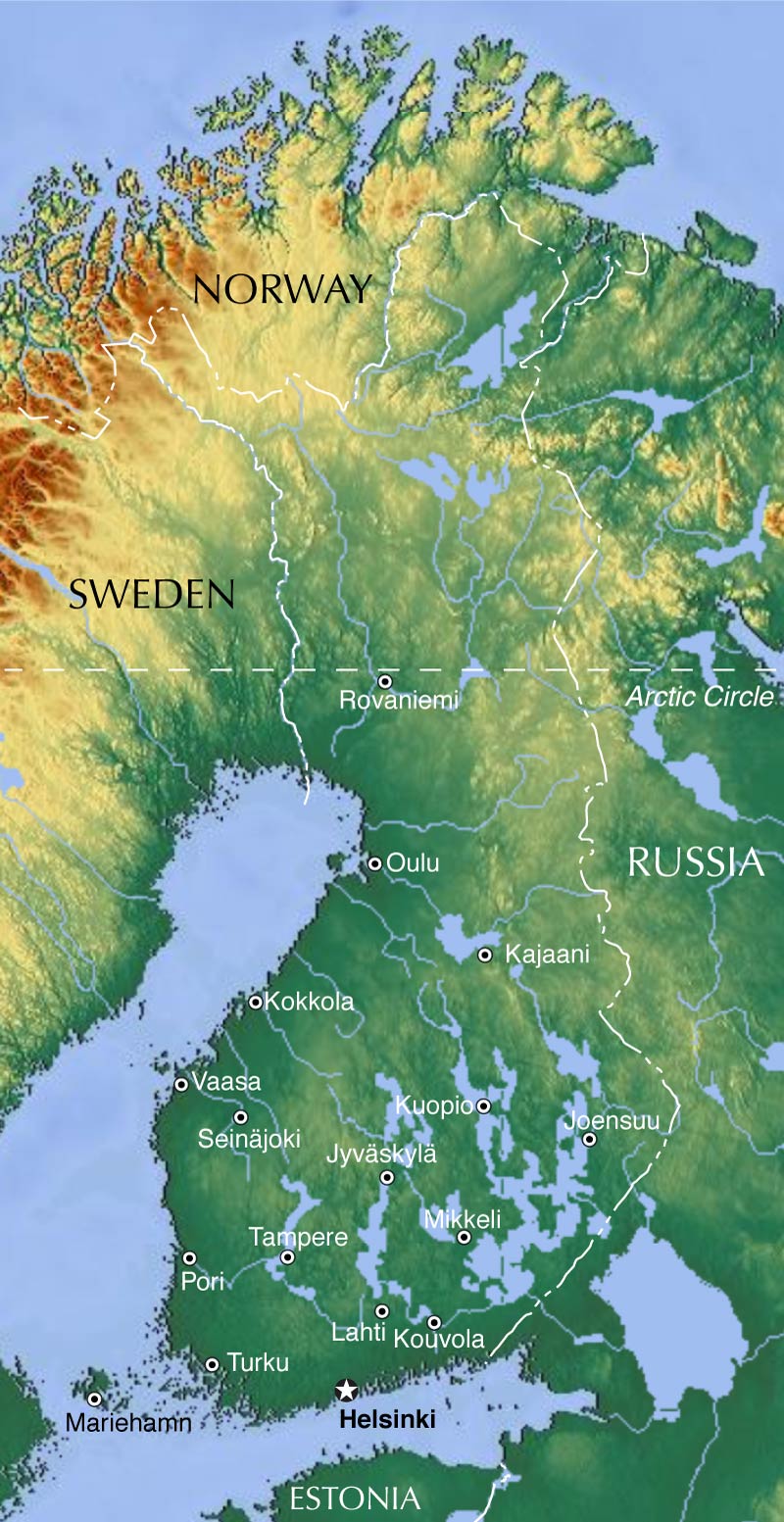
Finland, the land of a thousand lakes and vast forests, is a captivating nation with a unique and diverse geography. Its landscape, sculpted by the last Ice Age, features rolling hills, pristine lakes, and a rugged coastline, all contributing to its distinctive beauty and rich natural resources. Understanding the geographical layout of Finland, including its major cities, is essential for appreciating its cultural, economic, and historical significance.
A Glimpse into Finnish Geography:
Finland’s location in Northern Europe, bordering Sweden, Norway, and Russia, plays a crucial role in shaping its identity. Its northern latitude results in long, bright summers and equally long, dark winters, contributing to its unique cultural traditions. The country’s terrain is predominantly characterized by:
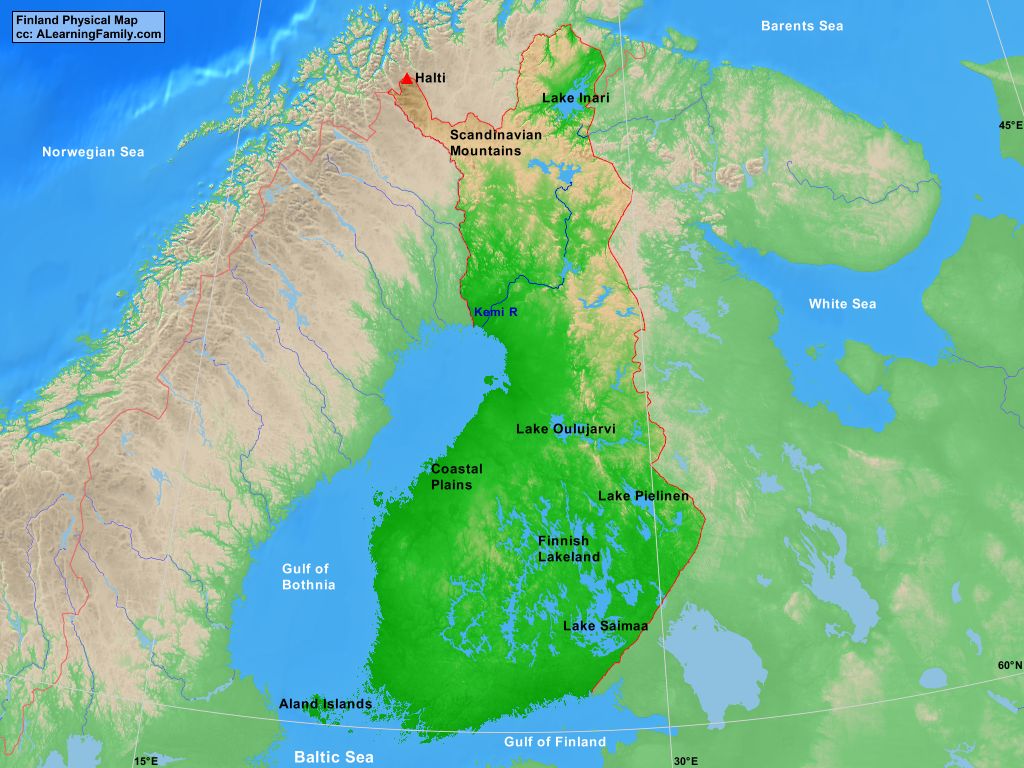
- The Fennoscandian Shield: This ancient geological formation, composed of granite and other hard rocks, forms the backbone of Finland, creating its characteristic rolling hills and numerous lakes.
- The Finnish Lakeland: This vast region, covering over 10% of the country, is home to thousands of lakes, interconnected by rivers and canals, creating a mesmerizing network of waterways.
- The Archipelago Sea: Located in the southwest, this region boasts over 40,000 islands, offering breathtaking coastal scenery and opportunities for maritime activities.
- The Åland Islands: This autonomous region, located in the Baltic Sea, enjoys a unique cultural identity and is known for its picturesque landscapes and thriving tourism industry.
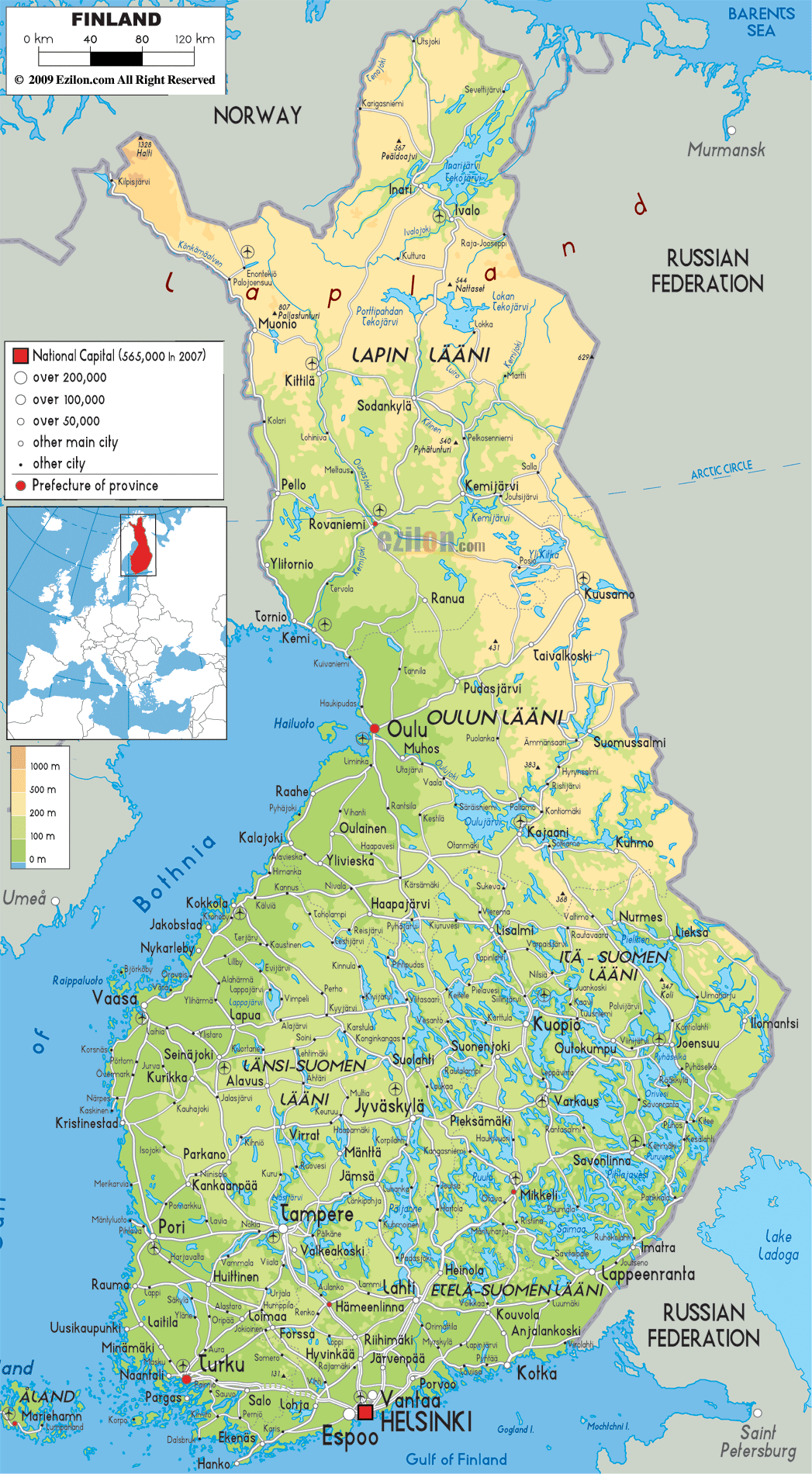
Major Cities: Hubs of Culture and Commerce:
Finland’s urban landscape is a blend of modern architecture, historical charm, and vibrant cultural life. Some of the most prominent cities include:
- Helsinki: As the capital and largest city, Helsinki embodies the spirit of modern Finland. Its iconic architecture, including the Finlandia Hall and the Helsinki Cathedral, reflects the country’s blend of Scandinavian design and historical influences. Helsinki serves as a major center for commerce, culture, and education, boasting a thriving arts scene, renowned universities, and a bustling port.
- Turku: Located on the southwestern coast, Turku is Finland’s oldest city, steeped in history and cultural significance. It was once the capital of the country and played a vital role in trade and maritime activity. Today, Turku is known for its charming old town, its vibrant university, and its annual medieval festival.
- Tampere: Situated in the heart of the Finnish Lakeland, Tampere is a bustling industrial city, renowned for its manufacturing heritage and its picturesque setting. The city is home to numerous lakes, parks, and cultural attractions, including the Tampere Hall and the Tampere Art Museum.
- Oulu: Located in northern Finland, Oulu is a dynamic city with a strong focus on technology and innovation. It is home to the University of Oulu, a leading center for research and development, and plays a crucial role in the development of the country’s digital economy.
- Jyväskylä: This central Finnish city is renowned for its elegant architecture, designed by the renowned architect Alvar Aalto. Jyväskylä is a university town with a vibrant cultural scene and a focus on sustainable development.
- Lahti: Situated in southern Finland, Lahti is a city known for its natural beauty and its thriving winter sports industry. It is home to the Lahti Ski Jumping Hill, a popular venue for international competitions, and boasts numerous scenic hiking trails and lakes.
Navigating the Map: Understanding Geographic Significance:
The distribution of cities across Finland’s diverse landscape is a testament to the country’s history, economy, and cultural development. Cities located along the coast, such as Helsinki and Turku, have historically played a vital role in trade and maritime activity. Inland cities, such as Tampere and Jyväskylä, have developed as centers of industry and manufacturing, drawing on the country’s rich natural resources. Northern cities, like Oulu, are emerging as hubs of innovation and technological advancement, reflecting Finland’s commitment to a sustainable future.
FAQs: Unveiling the Insights:
Q: What is the significance of Finland’s numerous lakes?
A: Finland’s lakes play a crucial role in the country’s ecosystem, economy, and cultural identity. They provide vital water resources, support diverse wildlife, and offer recreational opportunities for fishing, swimming, and boating. The lakes also serve as important transportation routes, connecting different parts of the country.
Q: How does Finland’s geography influence its climate?
A: Finland’s location in Northern Europe results in a predominantly temperate climate with distinct seasons. Its northern latitude experiences long, bright summers and equally long, dark winters, characterized by snow and freezing temperatures. The country’s vast forests and lakes contribute to a relatively humid climate.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by Finland’s cities due to its geography?
A: Finland’s geographical features, while beautiful, also pose certain challenges. The country’s long coastline and numerous islands make transportation and infrastructure development more complex. The long winters and harsh weather conditions can impact transportation, construction, and outdoor activities.
Tips for Exploring Finnish Cities:
- Embrace the outdoors: Finland’s natural beauty is a major draw. Explore its lakes, forests, and national parks, enjoying hiking, kayaking, and other outdoor activities.
- Experience the cultural scene: Finland boasts a rich cultural heritage. Visit museums, art galleries, and theaters to delve into its history, art, and music.
- Sample local cuisine: Finnish cuisine is known for its simplicity and fresh ingredients. Try traditional dishes like reindeer stew, salmon soup, and rye bread.
- Learn a few Finnish phrases: While English is widely spoken, learning a few basic Finnish phrases will enhance your interactions with locals and deepen your appreciation of the culture.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Geography and Culture
Finland’s map, with its interconnected cities and diverse landscape, tells a captivating story of a nation shaped by its geography, history, and cultural spirit. From the bustling capital of Helsinki to the charming old town of Turku, each city offers a unique glimpse into the Finnish way of life. Understanding the geographical layout of Finland allows us to appreciate the country’s rich natural resources, its vibrant culture, and its unwavering commitment to innovation and sustainability. As you navigate the map of Finland, be prepared to be captivated by its beauty, inspired by its resilience, and enchanted by its unique charm.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Finnish Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cities and Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!