Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of France
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of France
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of France
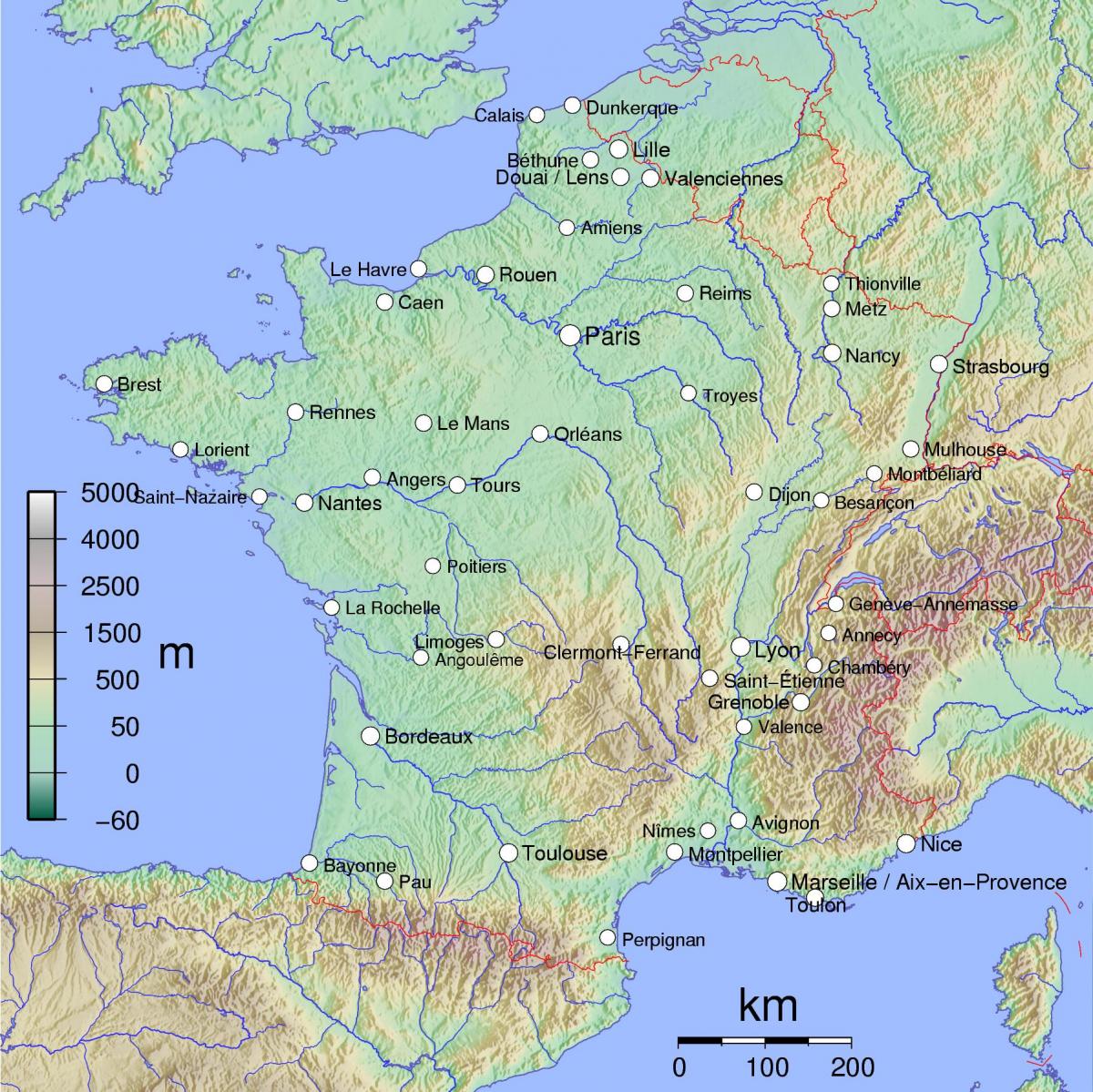
France, a land of diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture, is often perceived as a unified entity. However, a deeper dive reveals a tapestry woven from distinct regional identities, each with its own unique character, traditions, and charm. Understanding the regional divisions of France provides a valuable lens through which to appreciate the country’s multifaceted nature. This article offers a comprehensive exploration of the French regions, their geographical and cultural distinctiveness, and the significance of this regional tapestry.
A Historical Perspective:
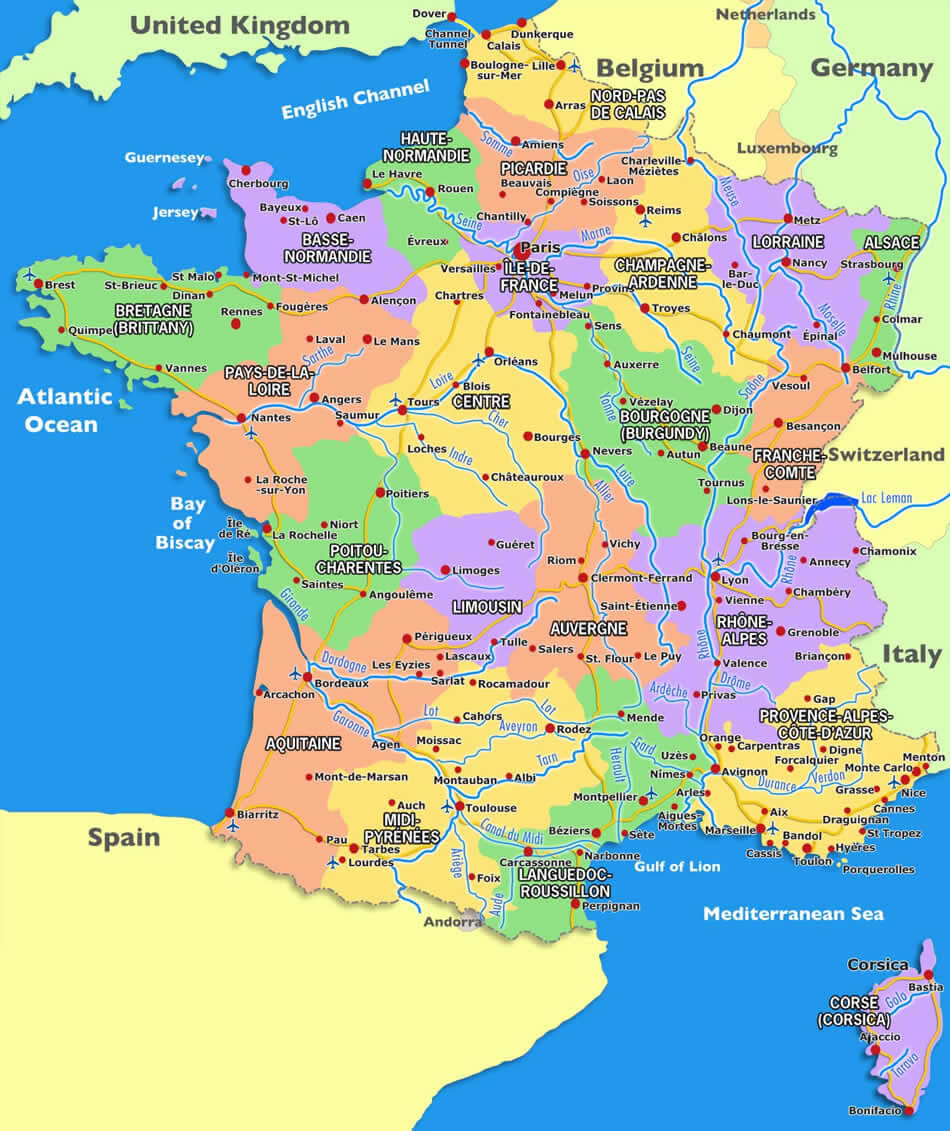
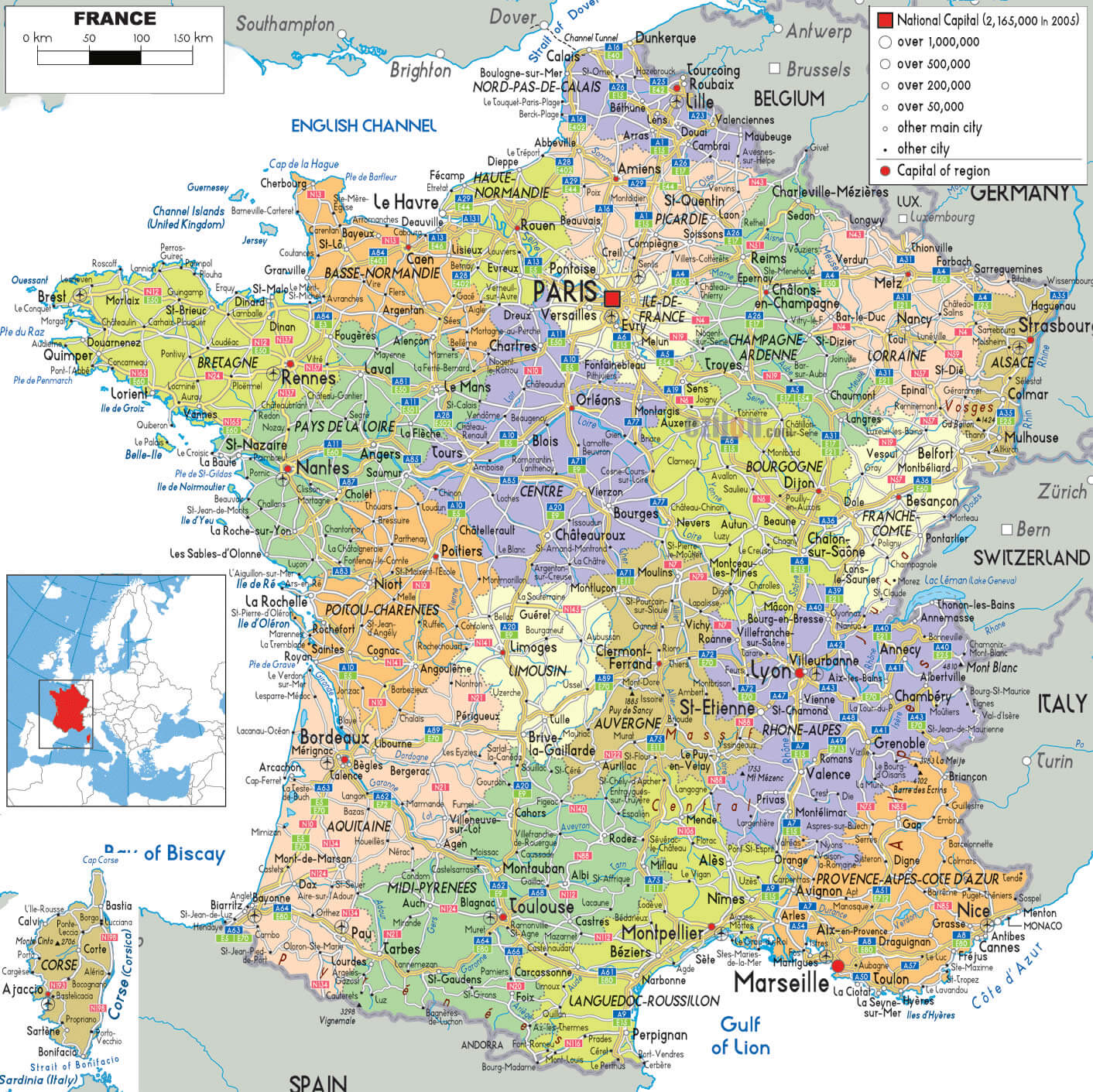
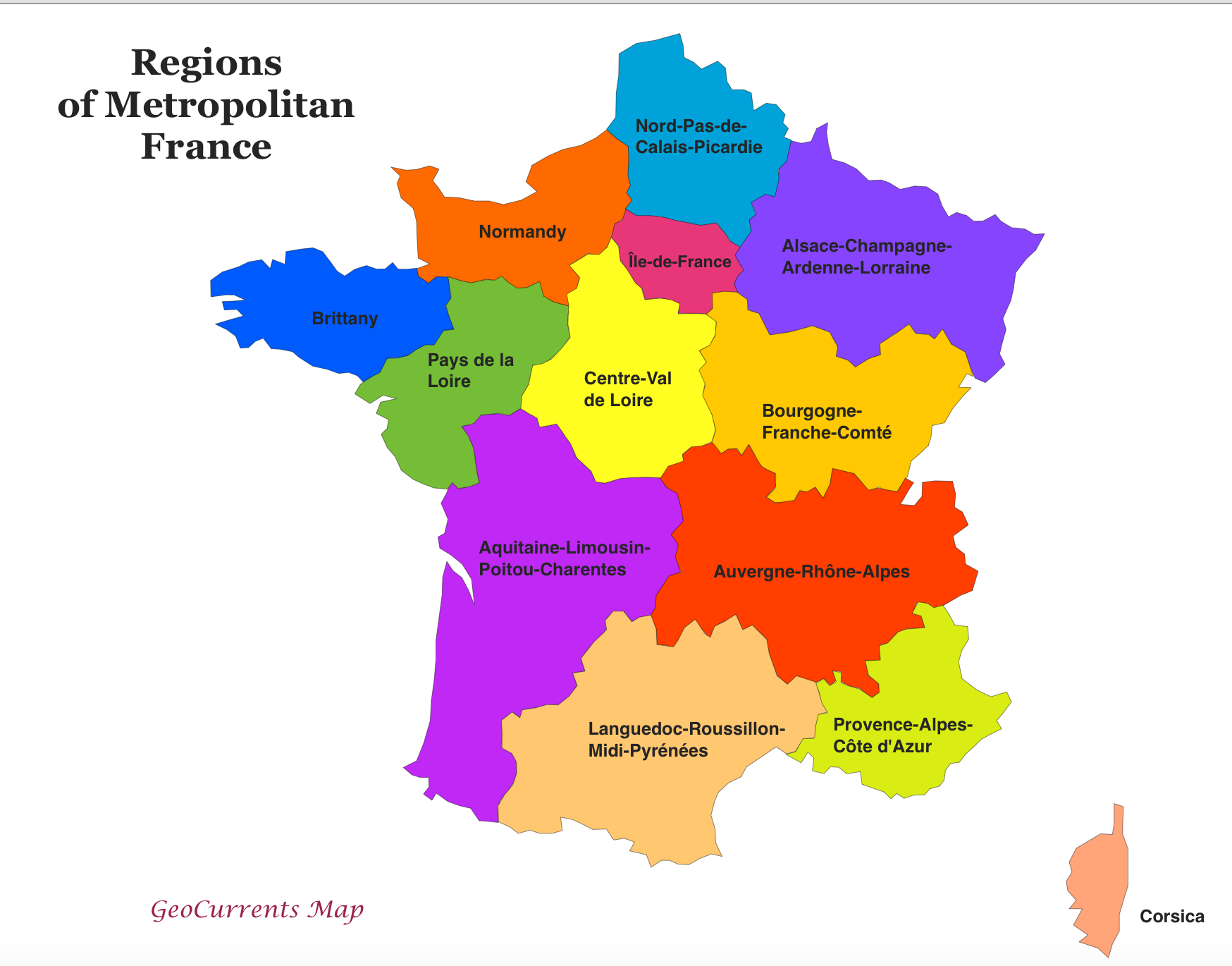
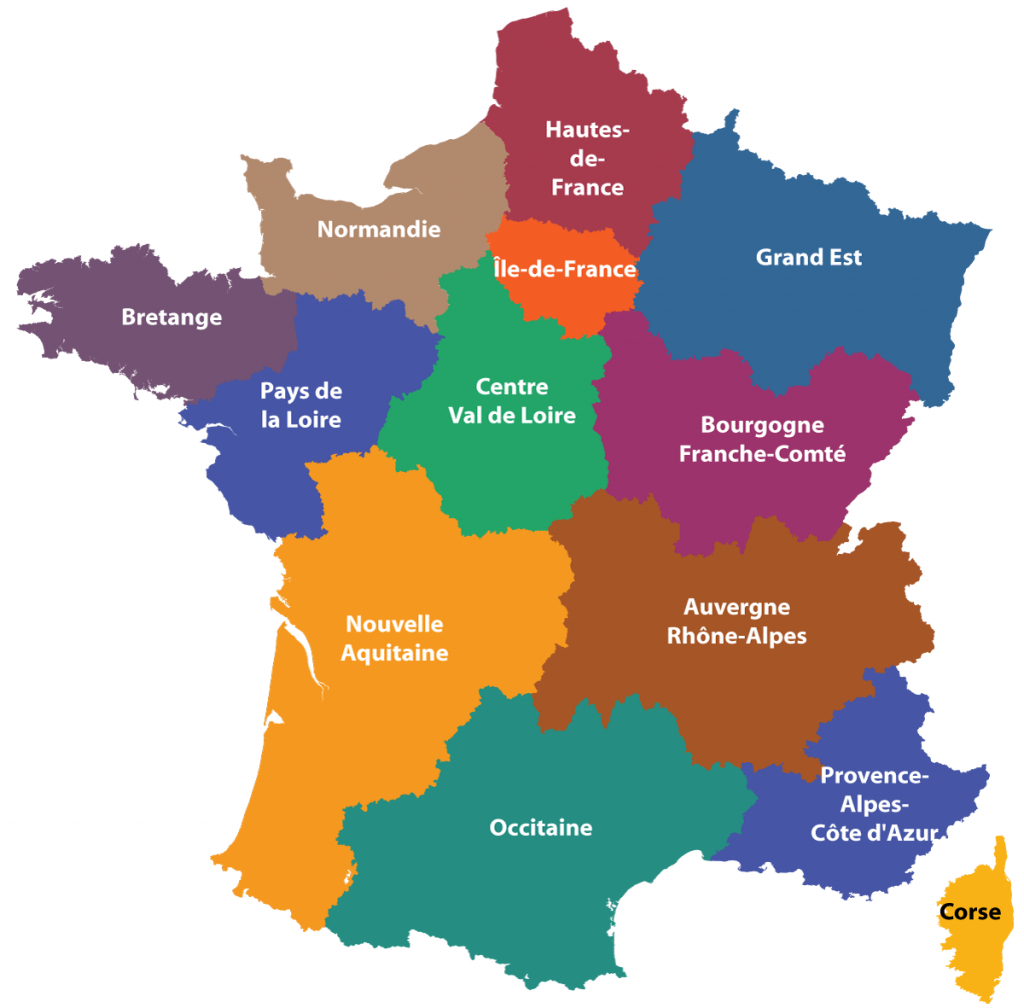
The current administrative division of France into regions is a relatively recent development. Prior to the 2016 administrative reform, France was divided into 22 regions, including overseas territories. This system, established in 1982, aimed to decentralize power and foster regional development. The 2016 reform, however, consolidated these regions into 13 mainland regions and 5 overseas regions.
This regional structure reflects a long history of political and cultural evolution. From the feudal era, when powerful dukes and counts held sway over vast territories, to the emergence of centralized power under the monarchy, France has witnessed a constant interplay between regional autonomy and national unity. The French Revolution, while aiming for a unified nation, also recognized the importance of regional identities and established departmental divisions, which remain a significant part of the administrative structure today.
Delving into the Regions:
1. Île-de-France: This region, encompassing Paris and its surrounding suburbs, is the heart of France, both politically and economically. Home to numerous historical landmarks, world-renowned institutions, and a diverse population, Île-de-France pulsates with a dynamic energy that draws visitors from around the globe.
2. Hauts-de-France: Situated in the north, this region is characterized by its vast plains, industrial heritage, and historic cities like Lille, Amiens, and Roubaix. Its proximity to Belgium and the UK has shaped its cultural landscape, making it a melting pot of influences.
3. Normandie: The scenic coastline of Normandy, with its iconic cliffs and picturesque villages, has long captivated artists and visitors alike. This region is steeped in history, from the D-Day landings to the rich tapestry of medieval architecture.
4. Centre-Val de Loire: The Loire Valley, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is the heart of this region, renowned for its magnificent châteaux, vineyards, and rich agricultural heritage. The region also boasts historic cities like Tours and Orléans, offering a glimpse into France’s past.
5. Bourgogne-Franche-Comté: This region, a blend of Burgundy and Franche-Comté, boasts a diverse landscape of rolling hills, vineyards, and forests. Its culinary heritage, particularly its renowned wines, and its historic cities like Dijon and Besançon make it a popular destination.
6. Pays de la Loire: This region, known for its charming coastline, lush countryside, and historic cities like Nantes and Angers, is a haven for nature enthusiasts and history buffs. Its vibrant cultural scene and thriving economy add to its appeal.
7. Bretagne: Brittany, with its rugged coastline, Celtic heritage, and unique language, offers a distinct cultural experience. Its picturesque towns, traditional festivals, and legendary myths continue to captivate visitors.
8. Nouvelle-Aquitaine: This vast region, encompassing the Aquitaine and Poitou-Charentes regions, boasts a diverse landscape of beaches, forests, vineyards, and mountains. Its rich cultural heritage, including the city of Bordeaux and its renowned wines, makes it a popular tourist destination.
9. Occitanie: This region, home to the Pyrenees mountains, the Mediterranean coastline, and the historic city of Toulouse, is a blend of vibrant culture, breathtaking landscapes, and rich history. Its unique traditions, including its Occitan language and festivals, make it a fascinating destination.
10. Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes: This region, encompassing the Auvergne and Rhône-Alpes regions, is a land of mountains, lakes, and vineyards. Its historic cities like Lyon and Clermont-Ferrand, its renowned gastronomy, and its active outdoor scene make it a popular destination.
11. Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur: This region, known for its sun-drenched Mediterranean coastline, lavender fields, and charming villages, is a haven for relaxation and indulgence. Its rich history, its vibrant culture, and its world-renowned cities like Nice, Marseille, and Aix-en-Provence make it a popular tourist destination.
12. Grand Est: This region, encompassing the Alsace, Champagne-Ardenne, and Lorraine regions, is a land of diverse landscapes, from the vineyards of Champagne to the Vosges mountains. Its rich cultural heritage, its historic cities like Strasbourg and Reims, and its unique traditions make it a fascinating destination.
13. Normandie: This region, encompassing the former Normandy and Upper Normandy regions, is a land of rolling hills, picturesque villages, and historic cities like Rouen and Caen. Its rich history, its stunning coastline, and its vibrant cultural scene make it a popular destination.
The Importance of Regional Diversity:
Understanding the regional divisions of France is crucial for appreciating the country’s multifaceted nature. Each region offers a distinct perspective on French culture, history, and identity. This diversity enriches the national tapestry, creating a vibrant and engaging experience for both residents and visitors.
FAQs by Map of France with Regions:
1. What is the significance of the 2016 administrative reform?
The 2016 reform aimed to streamline the administrative structure, reduce bureaucracy, and promote greater regional cooperation. It consolidated the 22 regions into 13 mainland regions, aiming to create larger and more powerful regional entities capable of driving economic development and tackling shared challenges.
2. How do regional boundaries influence cultural identities?
Regional boundaries often coincide with historical, linguistic, and cultural distinctions. For example, Brittany retains a strong Celtic identity, while Alsace boasts a unique Germanic influence. These regional identities contribute to the rich tapestry of French culture.
3. How do regional differences impact tourism in France?
Each region offers a unique tourist experience. Whether it’s the historical grandeur of the Loire Valley, the rugged beauty of Brittany, or the sun-drenched coast of Provence, each region caters to specific interests and preferences.
4. What are the economic implications of regional diversity?
Regional diversity fosters economic development by creating specialized industries and economies. For example, the Loire Valley is renowned for its wine production, while the Rhône-Alpes region is a hub for manufacturing and technology.
5. How do regional differences impact political landscape?
Regional identities can influence political discourse and voting patterns. For example, regions with strong historical traditions may have different perspectives on national policies and governance.
Tips by Map of France with Regions:
1. Explore the regional cuisines: Each region boasts a unique culinary tradition, offering a diverse range of flavors and ingredients. Sample local specialties and immerse yourself in the culinary heritage of each region.
2. Visit regional festivals and events: Engage with local culture by attending regional festivals and events, celebrating traditions, music, and art.
3. Learn about local history and heritage: Delve into the rich history and heritage of each region by visiting museums, historical sites, and local landmarks.
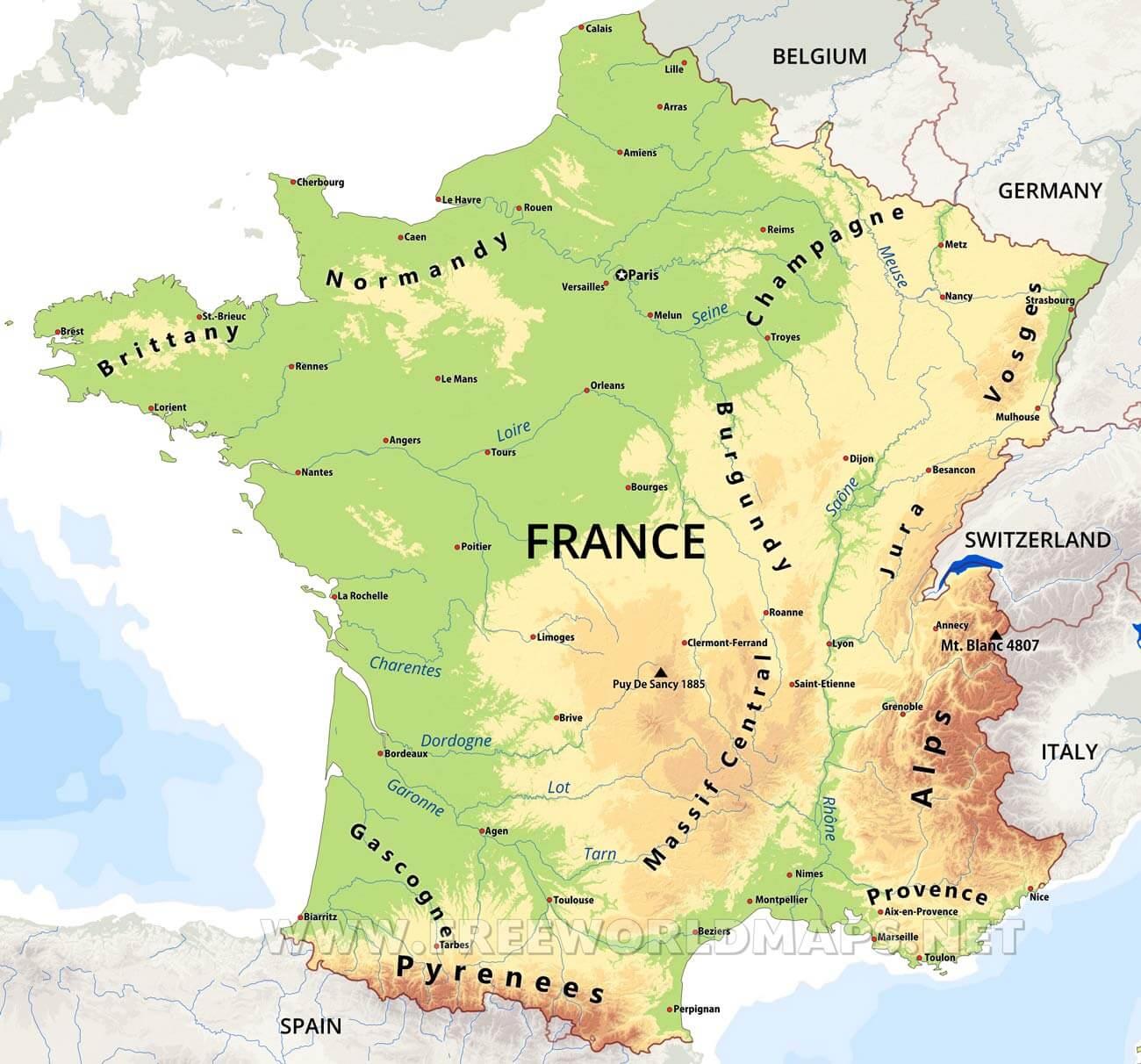
4. Explore regional landscapes: Discover the diverse landscapes of France, from the rugged mountains of the Pyrenees to the rolling hills of Normandy.
5. Engage with local communities: Interact with local residents and learn about their lives, traditions, and perspectives.
Conclusion by Map of France with Regions:
The map of France with its regions is more than just a geographical division; it’s a window into the country’s rich cultural tapestry. Each region, with its unique character and identity, contributes to the vibrant mosaic of French life. Understanding these regional differences enhances our appreciation for the country’s multifaceted nature, its historical evolution, and its enduring cultural legacy. As you explore the diverse landscapes and vibrant communities of France, remember that each region holds a unique story waiting to be discovered.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions of France. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!