Navigating the Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Guide to its Regions
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Guide to its Regions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Guide to its Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Guide to its Regions
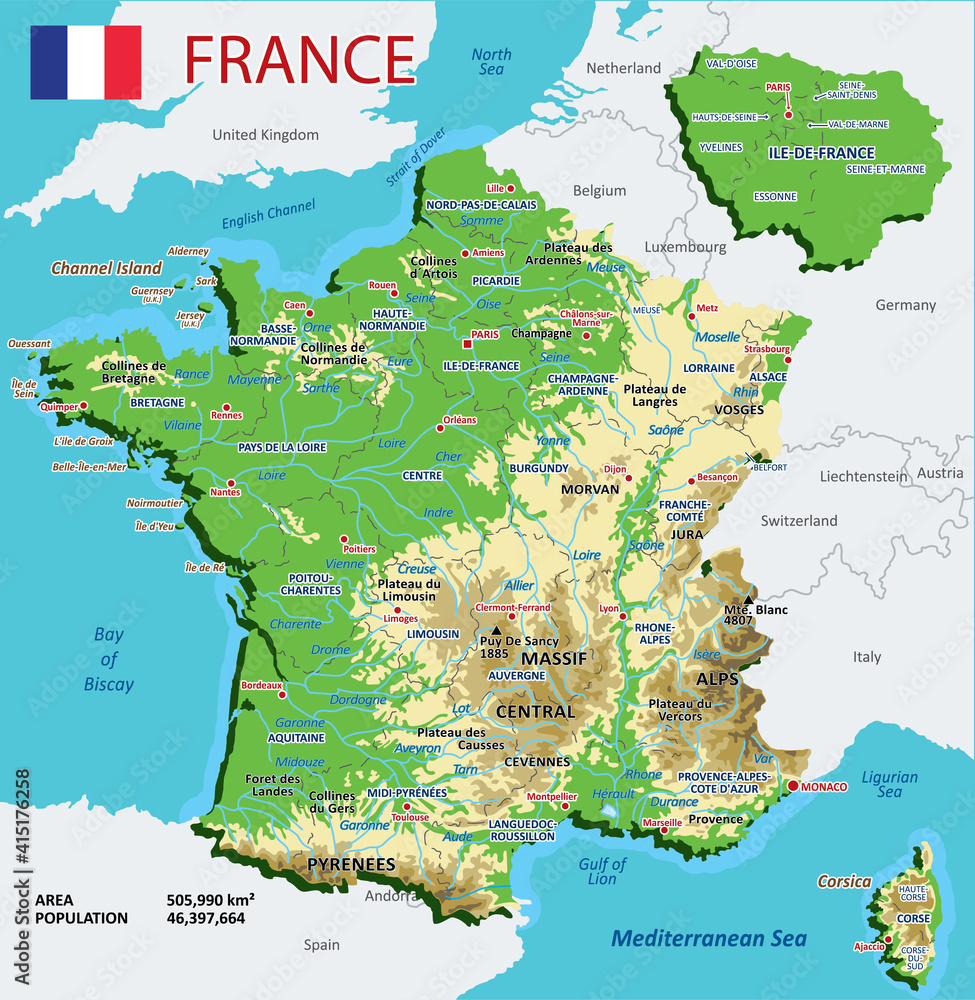
France, a nation renowned for its rich history, diverse landscapes, and vibrant culture, is also a country with a fascinating administrative structure. Understanding its regional divisions is essential for anyone seeking to appreciate the nuances of French identity, delve into its regional specificities, or simply plan a trip. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of France’s regional map, exploring its evolution, significance, and the unique characteristics of each region.
A History of Division: From Provinces to Regions
France’s administrative division has evolved over centuries, reflecting shifting political and social landscapes. The initial framework was based on "provinces," historical entities with distinct identities and traditions. These provinces, numbering over 30, were largely abolished during the French Revolution (1789-1799) as part of a drive for centralisation and national unity.
The 19th century saw the emergence of "departments," smaller administrative units, which remain the primary level of local government in France today. However, the desire for regional recognition persisted, leading to the creation of "regions" in 1956. These initial regions were primarily designed for economic and administrative purposes, with little emphasis on cultural or historical distinctiveness.
The 2016 Restructuring: A New Map of France
The year 2016 marked a significant shift in the French regional landscape. The number of regions was reduced from 22 to 13, merging some existing regions to create larger, more cohesive entities. This restructuring aimed to streamline administrative processes, enhance regional competitiveness, and encourage a greater sense of unity.
Understanding the 13 Regions of France
The current regional map of France presents a diverse tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and economies. Each region boasts unique characteristics, shaped by its history, geography, and local traditions. Below is a brief exploration of each region, highlighting its key features:
-
Île-de-France: The heart of France, encompassing Paris and its surrounding suburbs. It is a hub of finance, culture, and education, attracting millions of residents and tourists each year.
-
Grand Est: A vast region in northeastern France, combining the former regions of Alsace, Champagne-Ardenne, and Lorraine. It is known for its vineyards, historic cities, and industrial heritage.
-
Hauts-de-France: Located in northern France, this region comprises the former regions of Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy. It is characterized by its industrial landscape, agricultural plains, and historic cities like Lille and Amiens.
-
Normandie: Situated on the northern coast of France, Normandy is renowned for its rolling hills, picturesque beaches, and historic sites like Mont Saint-Michel. It is also a significant agricultural region.
-
Centre-Val de Loire: A region in central France, known for its castles, vineyards, and historic cities like Tours and Orléans. It is a popular destination for history buffs and wine enthusiasts.
-
Pays de la Loire: Situated on the Atlantic coast, this region boasts stunning beaches, historic cities like Nantes and Angers, and a thriving agricultural sector.
-
Bretagne: A region in northwestern France, known for its Celtic heritage, rugged coastline, and charming fishing villages. It is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts and those seeking a taste of traditional French culture.
-
Nouvelle-Aquitaine: A vast region in southwestern France, combining the former regions of Aquitaine, Limousin, and Poitou-Charentes. It is characterized by its diverse landscapes, including the Pyrenees mountains, the Atlantic coast, and the Bordeaux wine region.
-
Occitanie: Located in southern France, this region encompasses the former regions of Languedoc-Roussillon, Midi-Pyrénées, and part of the former region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur. It is known for its Mediterranean climate, vibrant culture, and historic cities like Toulouse and Montpellier.
-
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes: A mountainous region in southeastern France, combining the former regions of Auvergne and Rhône-Alpes. It is home to the Alps, the Massif Central, and the Rhône Valley, famous for its vineyards and gastronomy.
-
Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur: A region in southeastern France, known for its stunning coastline, lavender fields, and historic cities like Nice, Marseille, and Aix-en-Provence. It is a popular destination for sun-seekers and culture enthusiasts.
-
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté: A region in eastern France, combining the former regions of Burgundy and Franche-Comté. It is renowned for its vineyards, historic cities like Dijon and Besançon, and its rich culinary tradition.
-
Corse: An island region in the Mediterranean Sea, known for its rugged mountains, pristine beaches, and unique culture. It offers a blend of French and Italian influences, making it a truly unique destination.
The Importance of Understanding France’s Regions
Understanding the regional map of France offers numerous benefits:
-
Cultural Appreciation: Each region possesses distinct cultural traditions, languages, and dialects, contributing to the richness and diversity of French identity. Exploring these regional differences provides a deeper understanding of France’s cultural tapestry.
-
Travel Planning: Knowing the different regions allows travelers to tailor their itineraries to specific interests, whether it’s exploring historical sites, indulging in regional cuisine, or enjoying outdoor activities.
-
Economic Insights: Understanding regional economies provides valuable information about France’s economic strengths and challenges, highlighting key industries and regional development initiatives.
-
Political Context: Regional divisions play a role in French politics, as regions have their own elected assemblies and hold varying levels of autonomy. Understanding this framework helps to grasp the political landscape and regional dynamics.
FAQs about France’s Regions
-
What is the purpose of regional divisions in France?
- Regional divisions serve various purposes, including administrative efficiency, economic development, cultural preservation, and political representation.
-
Why was the regional map restructured in 2016?
- The restructuring aimed to streamline administrative processes, enhance regional competitiveness, and encourage a greater sense of unity.
-
What are the key differences between the regions?
- Each region boasts unique characteristics, shaped by its history, geography, and local traditions, including cultural practices, languages, cuisine, and economic activities.
-
How do regional divisions impact the daily lives of French citizens?
- Regional divisions influence access to public services, cultural events, and economic opportunities, shaping the daily experiences of French citizens.
-
Is it possible to travel between regions easily?
- France boasts a well-developed transportation network, making it easy to travel between regions by train, car, or plane.
Tips for Exploring France’s Regions
- Research specific regional attractions: Identify landmarks, historical sites, cultural events, and local specialties that interest you.
- Consider regional cuisine: Sample local delicacies and wines, immersing yourself in the culinary traditions of each region.
- Engage with local communities: Interact with locals to gain insights into their customs, traditions, and perspectives.
- Explore regional languages and dialects: Learn a few phrases in the local language or dialect to enhance your cultural immersion.
- Plan your itinerary around regional events: Attend festivals, concerts, and cultural events to experience the vibrant spirit of each region.
Conclusion
The regional map of France is a testament to the country’s rich history, diverse landscapes, and vibrant cultural mosaic. Understanding these regional divisions provides a deeper appreciation for the nuances of French identity, offering a richer and more rewarding experience for travelers, researchers, and anyone seeking to explore the complexities of this fascinating nation. From the bustling metropolis of Paris to the picturesque landscapes of the countryside, each region offers a unique glimpse into the heart of France, inviting exploration and discovery.


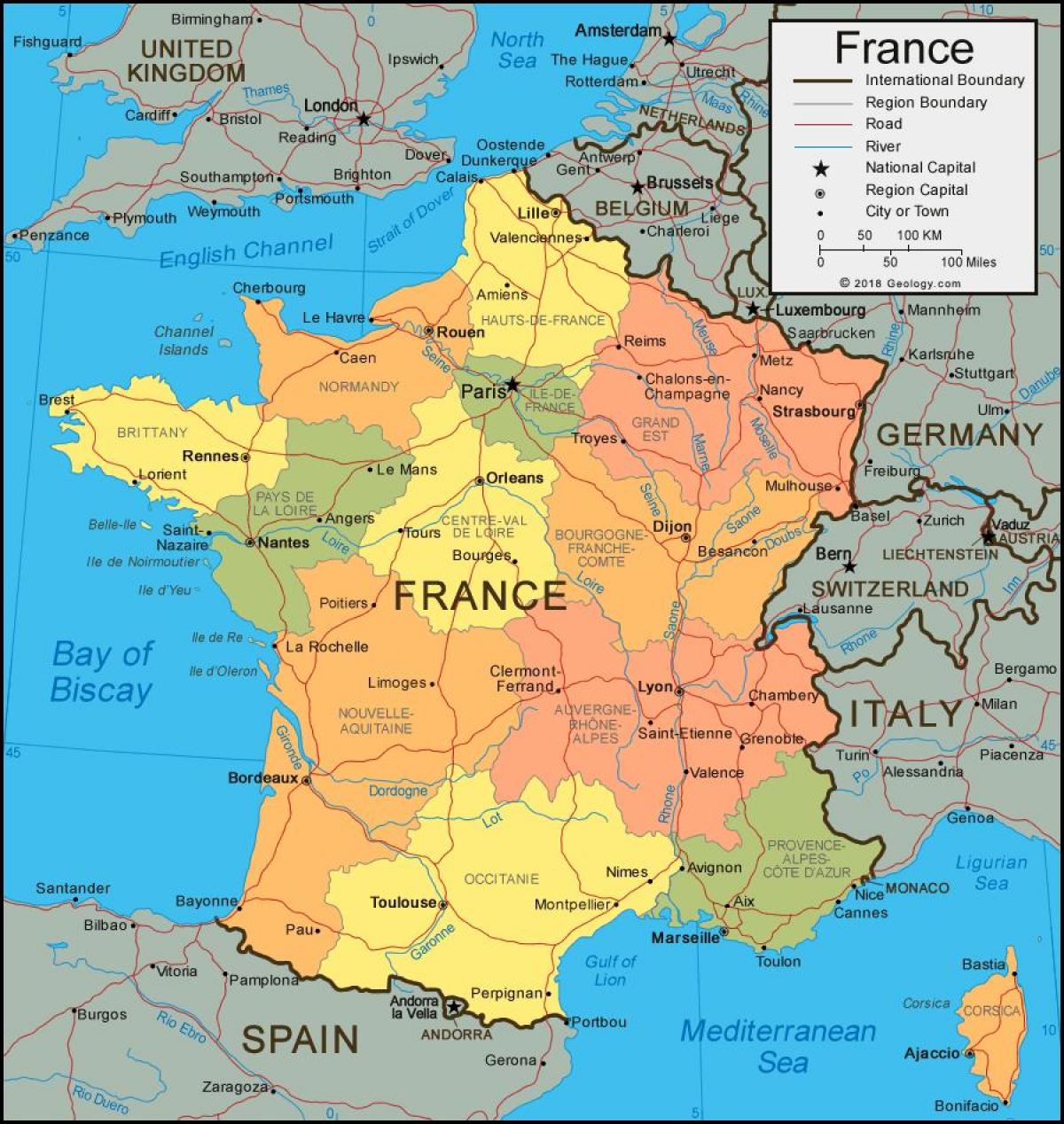


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Guide to its Regions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!