Navigating the Netherlands: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Topography
Related Articles: Navigating the Netherlands: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Topography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Netherlands: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Netherlands: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Topography
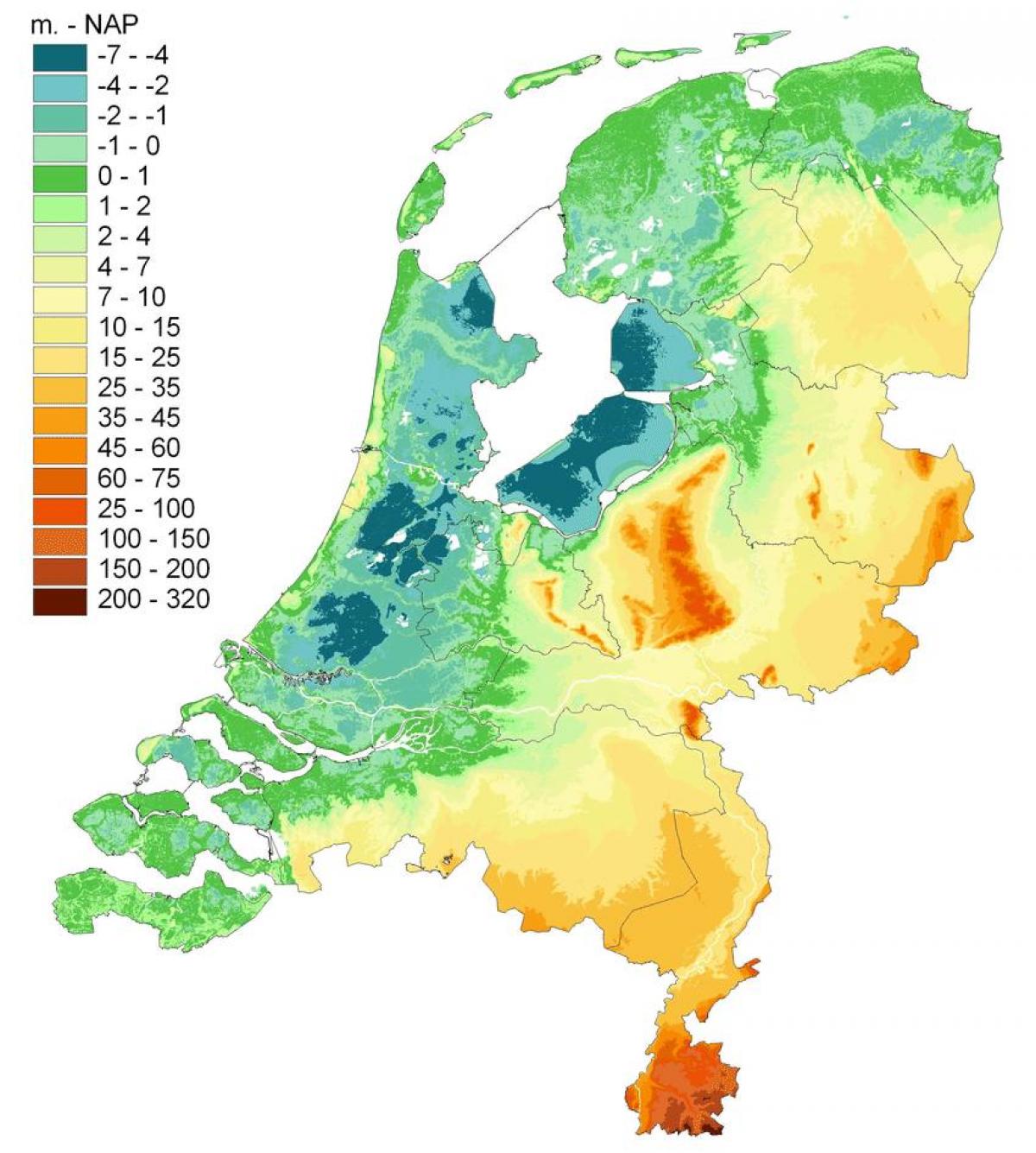
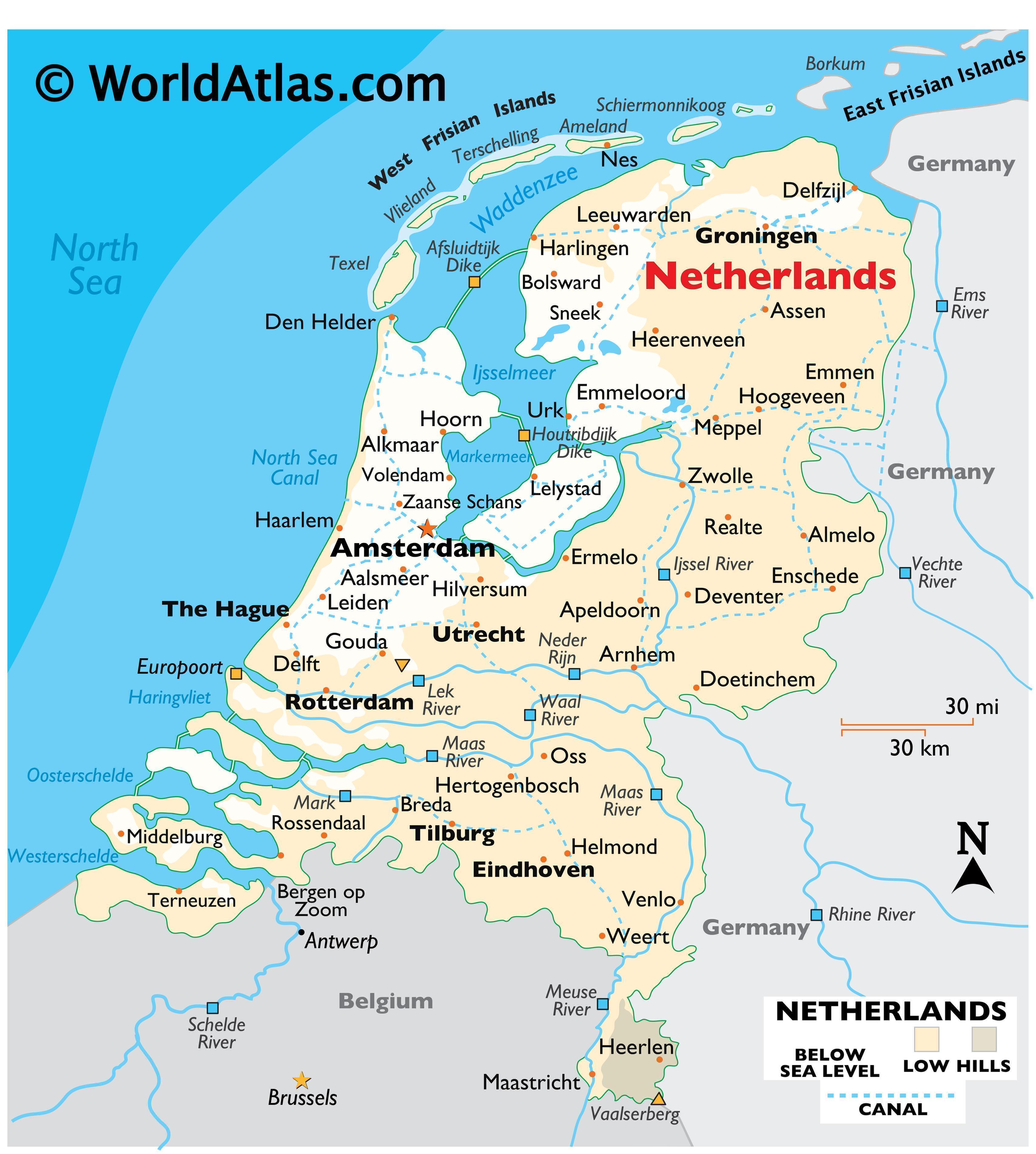
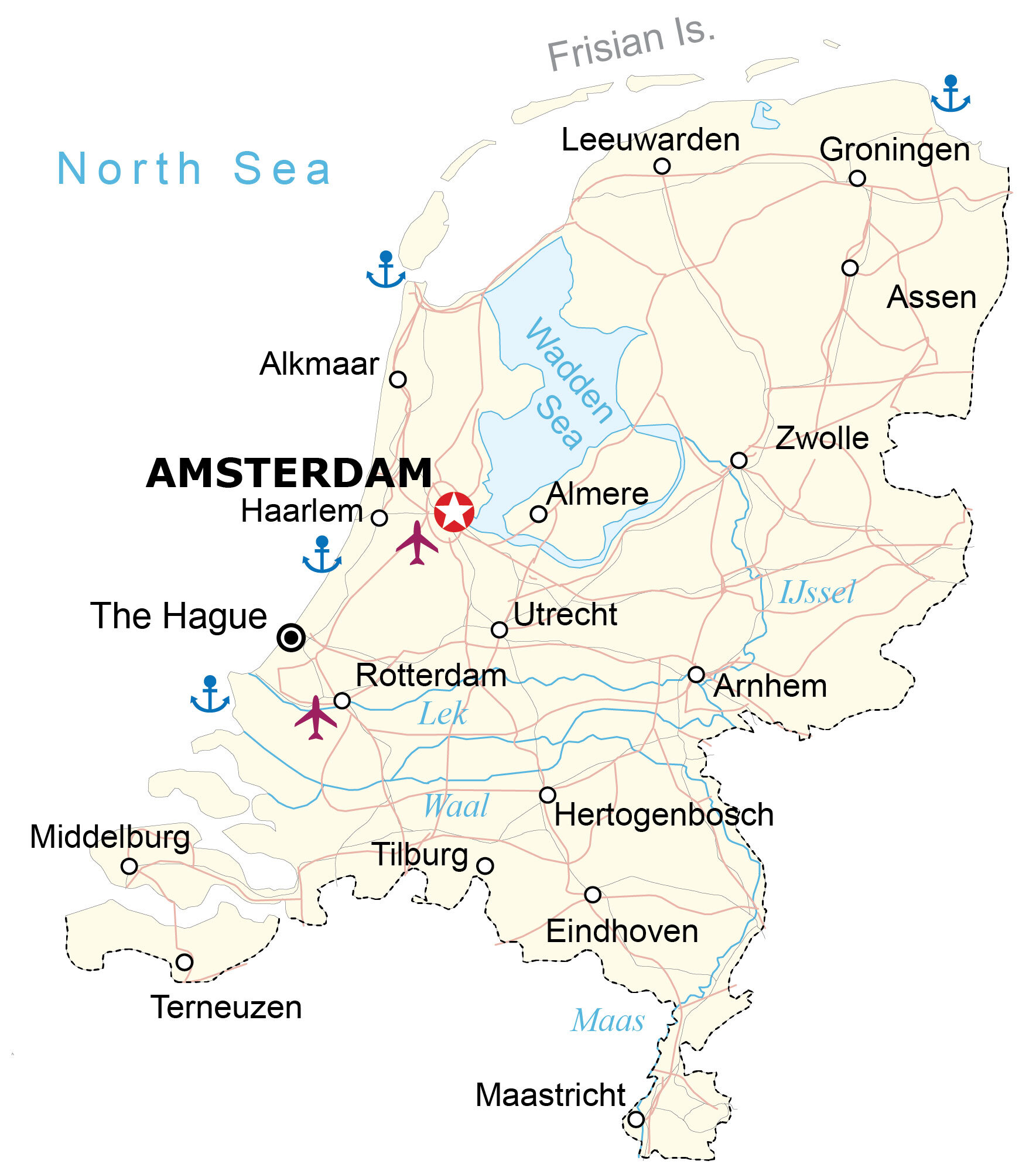
The Netherlands, often referred to as Holland, is a small but densely populated country in Western Europe. Its distinctive landscape, characterized by flat plains, intricate waterways, and man-made structures, is a testament to the country’s long history of interaction with the forces of nature. Understanding the geographical features of the Netherlands is essential for appreciating its unique cultural identity, economic prowess, and environmental challenges.
A Land Shaped by Water:
The Netherlands’ defining characteristic is its low-lying terrain. Approximately 26% of the country lies below sea level, a legacy of centuries of land reclamation and constant struggle against the encroaching sea. This unique geography has profoundly shaped the country’s history, culture, and infrastructure.
The Dutch Delta:
The southwestern portion of the Netherlands, known as the Dutch Delta, is a complex network of rivers, estuaries, and reclaimed land. The Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt rivers converge here, creating a fertile delta region that has been a focal point of human activity for millennia. The delta’s complex ecosystem is a delicate balance between land and water, requiring constant attention to manage water levels and prevent flooding.
Polders: A Triumph of Engineering:
The Netherlands is renowned for its polders, areas of land reclaimed from the sea or lakes. These engineered landscapes are a testament to Dutch ingenuity and their ability to adapt to their environment. Polders are typically enclosed by dykes and managed by sophisticated drainage systems, showcasing the country’s commitment to sustainable land use.
The Wadden Sea: A Natural Wonder:
The Wadden Sea, located along the North Sea coast, is a unique ecosystem of tidal flats, mudflats, and sandbanks. This UNESCO World Heritage Site is home to a rich biodiversity, supporting a vast array of bird species, seals, and other marine life. The Wadden Sea is a testament to the Netherlands’ commitment to protecting its natural heritage and promoting sustainable tourism.
The Influence of Topography:
The Netherlands’ flat terrain has facilitated the development of a dense network of canals and waterways, making it a nation of interconnected cities and towns. This intricate network has historically served as a vital transportation route, fostering trade and economic growth. The flat landscape also influenced the development of unique architectural styles, with houses often featuring narrow facades and steep gables.
Challenges of a Low-Lying Nation:
The Netherlands’ low-lying terrain poses significant challenges, particularly in the face of rising sea levels and climate change. The country’s extensive system of dykes and drainage infrastructure requires constant maintenance and adaptation. The Netherlands is a global leader in water management and climate change mitigation, constantly striving to find innovative solutions to address the challenges of its unique geography.
Beyond the Flatlands:
While the Netherlands is primarily known for its flatlands, it also boasts rolling hills and wooded areas. The Veluwe, a large national park located in the eastern part of the country, is a testament to this diversity. The park offers a sanctuary for wildlife and offers a stark contrast to the heavily populated and industrialized regions of the Netherlands.
A Nation Shaped by its Landscape:
The Netherlands’ geography has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and identity. From the ingenuity of its water management systems to the unique architecture of its cities, the country’s landscape is a testament to its resilience and innovative spirit. Understanding the Netherlands’ topography is crucial for appreciating its rich cultural heritage, its economic success, and its ongoing commitment to sustainable development.
FAQs:
1. What is the highest point in the Netherlands?
The highest point in the Netherlands is the Vaalserberg, which rises to a modest 322.4 meters (1,058 feet) above sea level.
2. What percentage of the Netherlands is below sea level?
Approximately 26% of the Netherlands lies below sea level, a significant portion of the country’s total landmass.
3. What is a polder?
A polder is an area of land reclaimed from the sea or lakes, typically enclosed by dykes and managed by drainage systems.
4. What is the Wadden Sea?
The Wadden Sea is a unique ecosystem of tidal flats, mudflats, and sandbanks located along the North Sea coast of the Netherlands.
5. What are the main rivers in the Netherlands?
The main rivers in the Netherlands are the Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt. These rivers converge in the southwestern portion of the country, creating the Dutch Delta.
Tips:
1. Visit the Delta Works:
The Delta Works is a series of innovative engineering structures designed to protect the Netherlands from flooding. Visiting these impressive structures provides a fascinating insight into the country’s history of water management.
2. Explore the Wadden Sea:
The Wadden Sea is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a must-visit destination for nature enthusiasts. Take a boat trip or go birdwatching to appreciate the unique ecosystem of this natural wonder.
3. Cycle through the Dutch countryside:
The Netherlands is a cyclist’s paradise, with dedicated bike paths crisscrossing the country. Explore the picturesque villages, windmills, and canals at your own pace.
4. Learn about the history of polders:
Visit a polder museum or take a guided tour to learn about the history of land reclamation and the challenges of managing these engineered landscapes.
5. Attend a water management conference:
The Netherlands is a global leader in water management, hosting numerous conferences and events on this topic. Attend a conference to gain insights into the latest innovations and challenges in water management.
Conclusion:
The Netherlands, with its distinctive geography and unique challenges, is a fascinating study in human ingenuity and adaptation. Its flat landscape, intricate waterways, and engineered landscapes are a testament to the country’s resilience and commitment to sustainable development. By understanding the Netherlands’ topography, we gain a deeper appreciation for its rich cultural heritage, its economic success, and its ongoing efforts to address the challenges of climate change and rising sea levels. The Netherlands is a nation that continues to innovate and adapt, showcasing the power of human ingenuity in the face of environmental challenges.
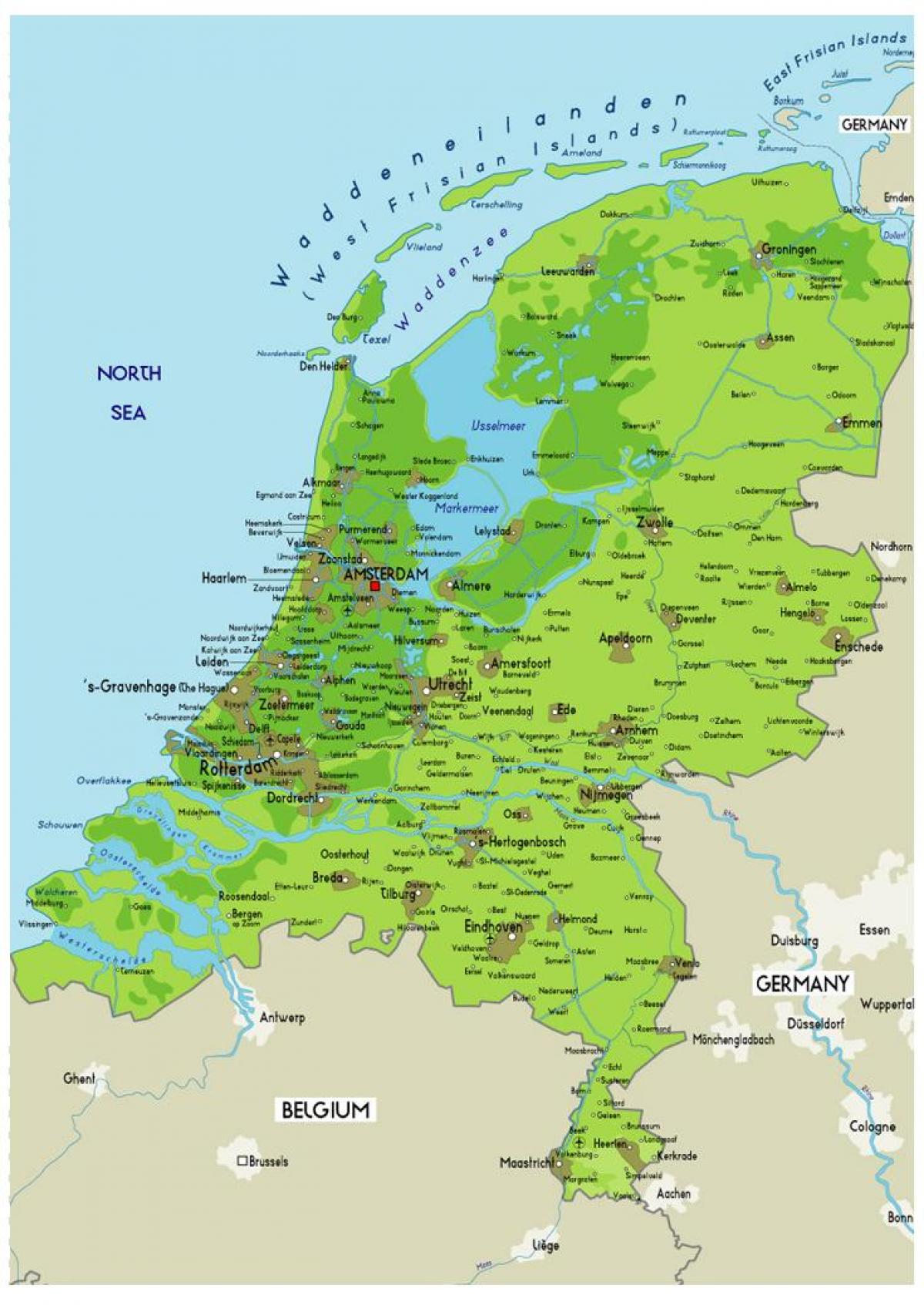

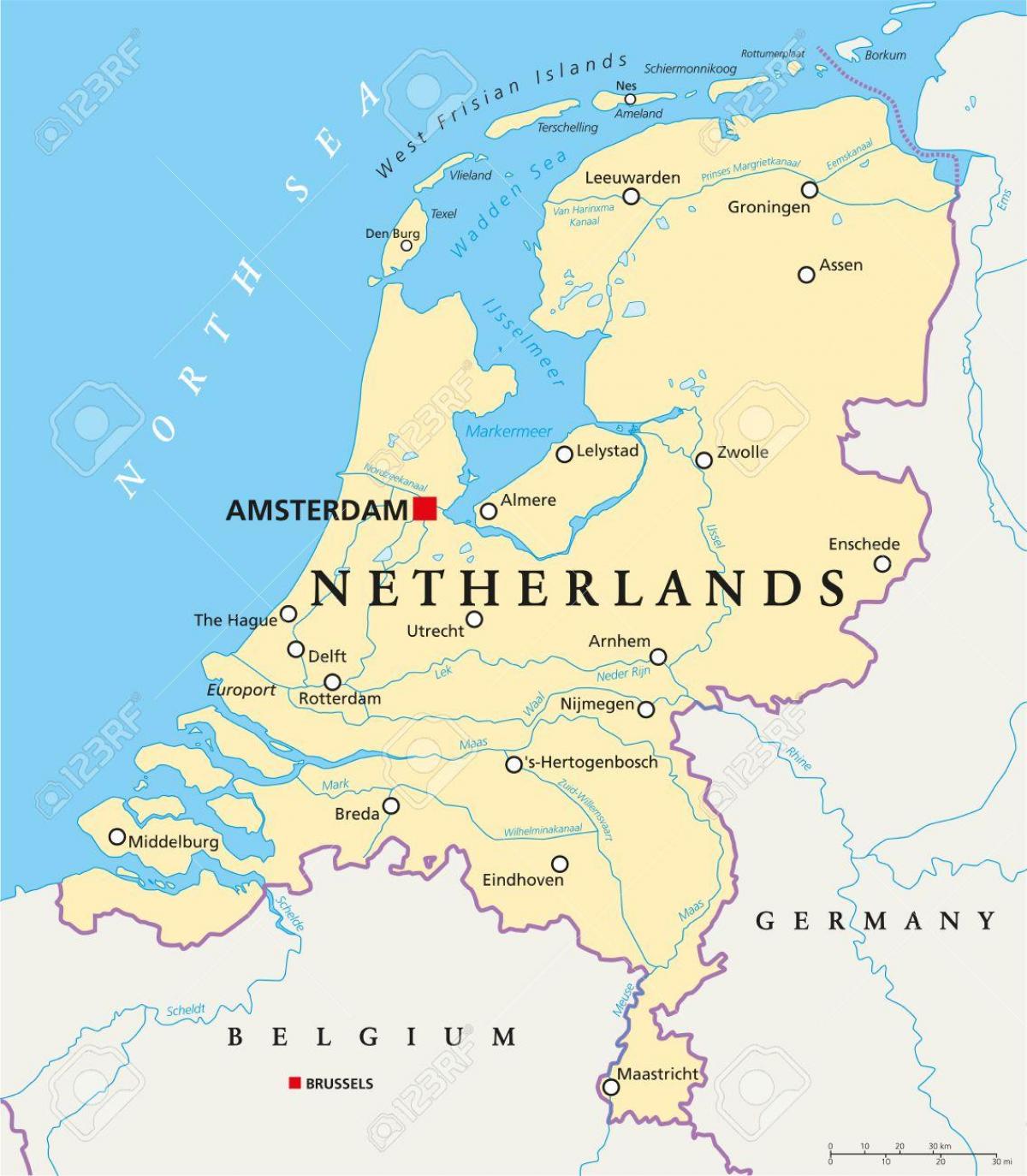
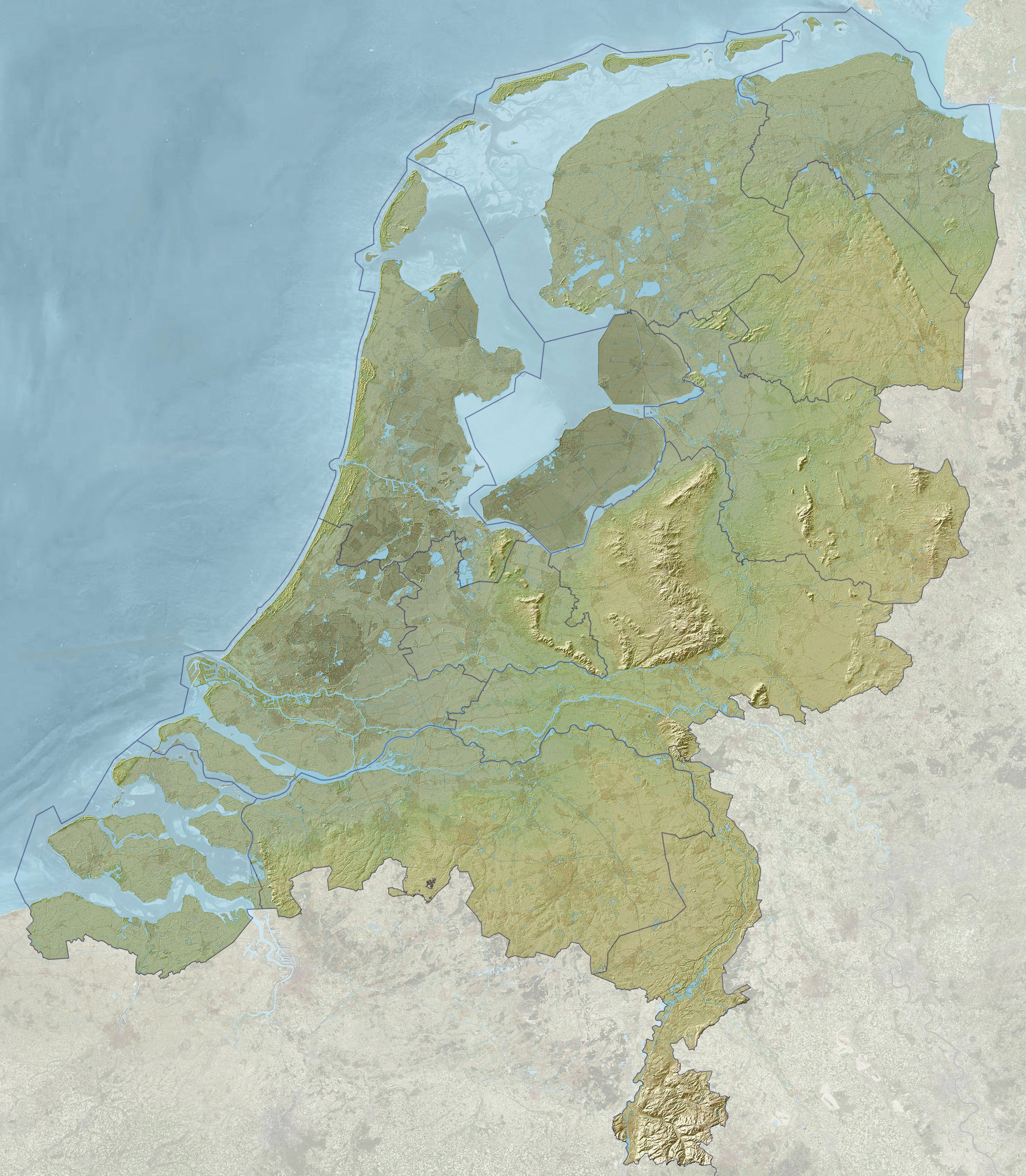

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Netherlands: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Topography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!