Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Geographical Exploration of Finland, Sweden, and Russia
Related Articles: Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Geographical Exploration of Finland, Sweden, and Russia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Geographical Exploration of Finland, Sweden, and Russia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Geographical Exploration of Finland, Sweden, and Russia
The Nordic region, a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes and rich histories, encompasses Finland, Sweden, and Russia, each contributing unique elements to the region’s character. Understanding the geography of this area is crucial for appreciating its cultural, economic, and political dynamics. This exploration delves into the geographical features of Finland, Sweden, and Russia, highlighting their interconnectedness and individual characteristics.
Finland: The Land of a Thousand Lakes
Finland, nestled between Sweden and Russia, is a land of stark beauty, characterized by its vast stretches of forests, countless lakes, and rugged coastline. The country’s geography is heavily influenced by the last glacial period, which sculpted its terrain into a mosaic of rolling hills, low-lying plains, and numerous lakes.
-
Lake-Rich Landscape: Finland boasts over 188,000 lakes, earning it the moniker "The Land of a Thousand Lakes." These lakes, ranging from small ponds to vast expanses, are interconnected by a network of rivers, creating a unique and picturesque landscape. The largest lake, Lake Saimaa, is the fourth largest in Europe and a haven for diverse flora and fauna.
-
Forest Dominance: Forests cover over 70% of Finland, primarily consisting of coniferous trees such as pine, spruce, and birch. This extensive forest cover plays a vital role in the country’s economy, providing timber and other resources.
-
Coastal Frontier: Finland’s coastline stretches for over 1,100 kilometers along the Baltic Sea, offering stunning archipelagos and numerous harbors. The Gulf of Finland, a shallow arm of the Baltic Sea, separates Finland from Estonia and Russia.
Sweden: The Kingdom of Mountains and Archipelagoes
Sweden, the largest country in Scandinavia, is renowned for its diverse landscapes, from the snow-capped peaks of the Scandinavian Mountains to the picturesque archipelagos of its western coast.
-
Scandinavian Mountains: The Scandinavian Mountains, a majestic range stretching across Norway and Sweden, dominate the country’s northern and western regions. These mountains, reaching elevations of over 2,000 meters, provide breathtaking scenery and opportunities for outdoor recreation.
-
Archipelago Coast: Sweden’s western coastline is characterized by a series of stunning archipelagos, formed by thousands of islands and skerries. The largest of these, the Stockholm archipelago, is a popular tourist destination with its charming islands and picturesque harbors.
-
Central Plains: A vast plain, known as the Central Swedish Plain, stretches across the southern and central parts of the country, providing fertile land for agriculture.
Russia: The Vast Eurasian Powerhouse
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, straddles both Europe and Asia, encompassing a vast range of geographical features, from the tundra of the Arctic to the fertile steppes of the south.
-
European Russia: The European portion of Russia, where Finland and Sweden share a border, is characterized by a diverse landscape, including the vast East European Plain, the Ural Mountains, and the Caucasus region. The Volga River, the longest river in Europe, flows through this region, providing essential transportation and agricultural resources.
-
Ural Mountains: The Ural Mountains, a range stretching over 2,500 kilometers, form a natural boundary between Europe and Asia. These mountains are rich in mineral resources, contributing significantly to Russia’s economy.
-
Siberian Landscape: Russia’s Asian territory, Siberia, is vast and diverse, encompassing the Siberian Plain, the Altai Mountains, and the vast Siberian forests. This region is home to unique flora and fauna, including the Siberian tiger and the Amur leopard.
Interconnectedness and Influence
The geography of Finland, Sweden, and Russia is not merely a collection of individual features; it is a complex web of interconnectedness that has shaped the region’s history, culture, and economy.
-
Historical Ties: The shared border between Finland and Russia has been a source of both conflict and cooperation throughout history. Similarly, Sweden’s historical influence on Finland, evident in shared cultural and linguistic elements, continues to shape the region’s identity.
-
Economic Interdependence: The countries’ economies are intertwined, with trade and investment flowing between them. Finland’s close economic ties with Russia, particularly in energy and forestry, are a defining characteristic of its relationship with its eastern neighbor.
-
Environmental Connectivity: The region’s ecosystems are interconnected, with shared environmental challenges such as climate change and pollution. Collaborative efforts are crucial to address these issues and ensure the sustainable management of the region’s natural resources.
Importance and Benefits
Understanding the geography of Finland, Sweden, and Russia is essential for comprehending the region’s past, present, and future. This knowledge provides insights into:
-
Cultural Heritage: The diverse landscapes and natural resources have shaped the cultural identities of the region’s inhabitants, influencing their traditions, art, and literature.
-
Economic Development: The region’s geographical features have played a significant role in its economic development, providing natural resources, transportation routes, and agricultural potential.
-
Political Dynamics: The shared borders and historical interactions have shaped the region’s political dynamics, influencing relationships between the countries and their involvement in international affairs.
-
Environmental Sustainability: Recognizing the interconnectedness of the region’s ecosystems is vital for promoting environmental sustainability and ensuring the long-term health of the Nordic landscape.
FAQs
Q: What are the main geographical features of Finland?
A: Finland is characterized by its numerous lakes, vast forests, and rugged coastline. The country’s terrain is sculpted by glacial activity, resulting in rolling hills, low-lying plains, and numerous lakes.
Q: What is the significance of the Scandinavian Mountains in Sweden?
A: The Scandinavian Mountains dominate Sweden’s northern and western regions, offering stunning scenery and opportunities for outdoor recreation. They also play a role in the country’s climate and water resources.
Q: How does Russia’s geography impact its economic development?
A: Russia’s vast size and diverse geography provide a wide range of natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and timber. These resources are crucial to the country’s economy, but also pose challenges for transportation and development.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the environment in the Nordic region?
A: The Nordic region faces environmental challenges such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution. Collaborative efforts are needed to address these issues and ensure the sustainable management of the region’s natural resources.
Tips
-
Utilize maps and atlases: Visualizing the geographical features of Finland, Sweden, and Russia through maps is essential for understanding their spatial relationships and relative locations.
-
Explore travel resources: Travel guides and websites offer valuable information about the region’s landscapes, attractions, and cultural experiences.
-
Engage with local communities: Interacting with people living in the region provides firsthand insights into their perspectives and experiences related to the environment, culture, and history.
Conclusion
The geography of Finland, Sweden, and Russia is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, interconnected ecosystems, and rich cultural histories. Understanding the region’s geographical features is crucial for appreciating its cultural, economic, and political dynamics. By recognizing the interconnectedness of the region’s landscapes and the challenges and opportunities they present, we can foster greater appreciation for the Nordic region’s unique character and its role in the global landscape.


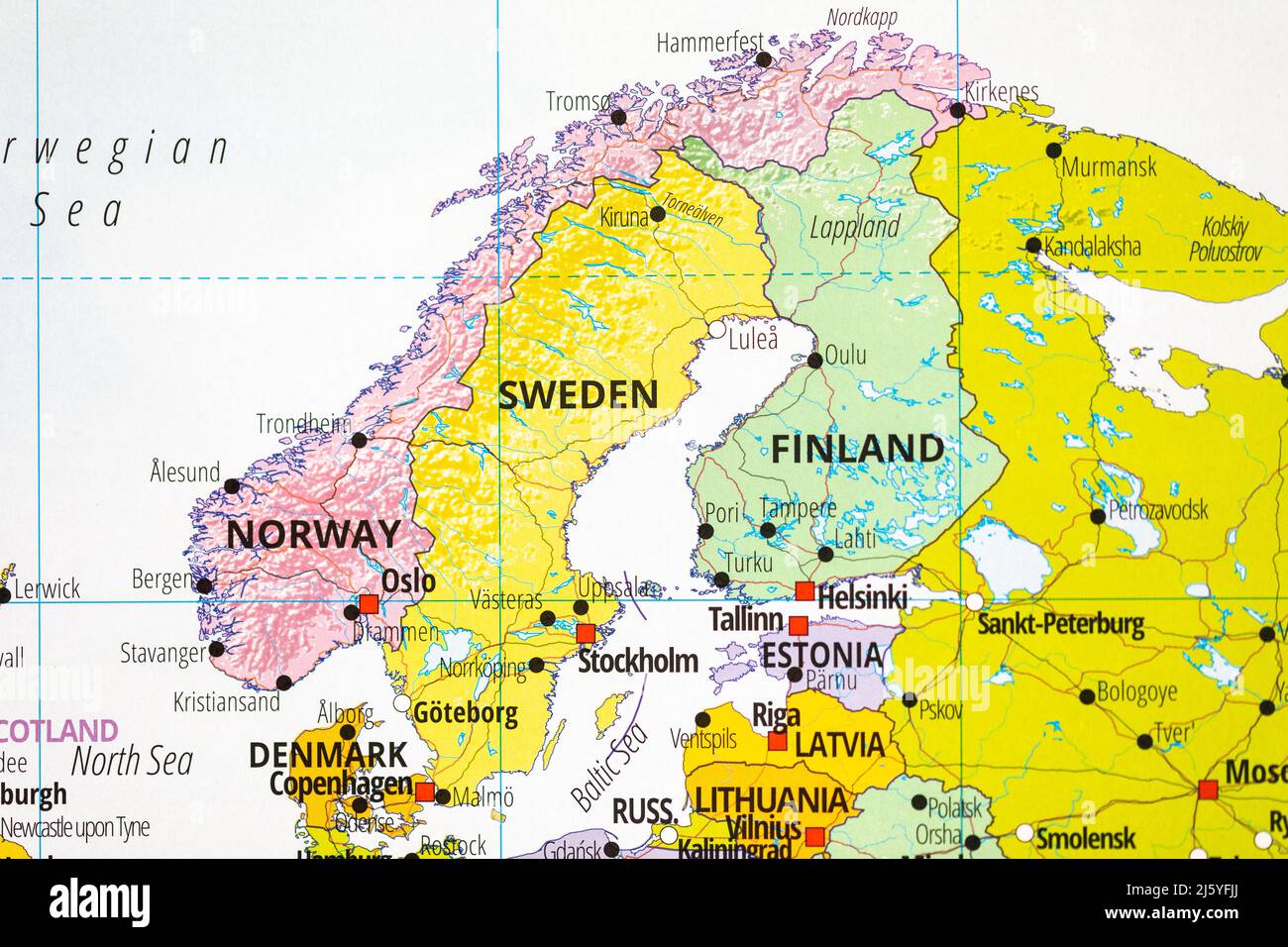

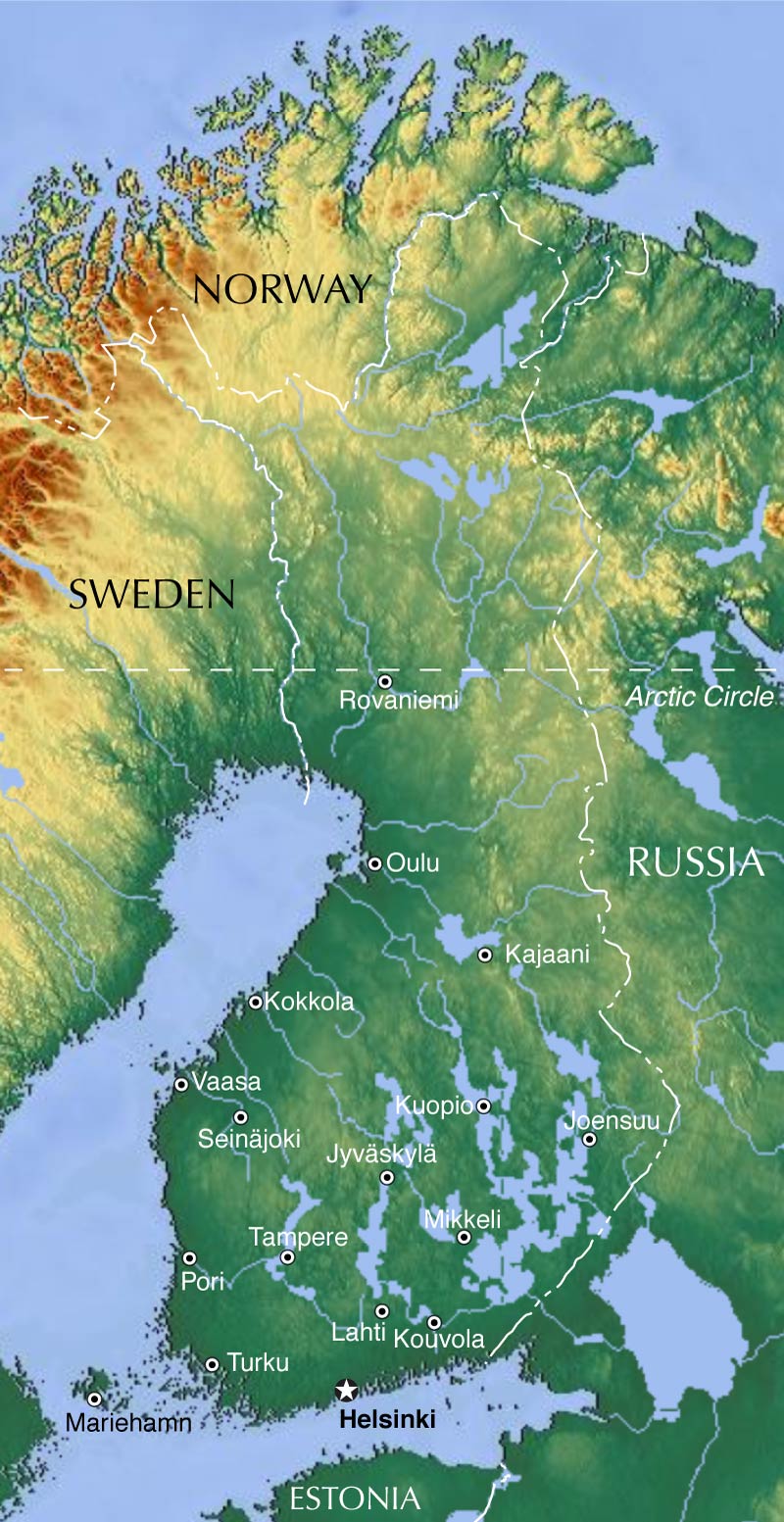



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Geographical Exploration of Finland, Sweden, and Russia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!