Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Flags
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Flags
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Flags. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Flags
.png/revision/20131215195645)
The concept of a "map flag" is not a singular entity but rather a broad term encompassing various visual markers and annotations used to enhance the comprehension and utility of maps. These markers, often in the form of flags, symbols, or icons, serve as visual cues to highlight specific locations, features, or data points on a map. Their primary purpose is to provide a clear and concise way to communicate information, making maps more informative and user-friendly.
The Evolution of Map Flags: From Simple Markers to Complex Data Visualizations
The use of map flags has evolved significantly over time, mirroring the advancements in cartography and technology. In the early days of mapmaking, simple flags or symbols were used to denote key locations like cities, towns, or landmarks. These early flags often served a purely navigational purpose, guiding travelers and explorers across unknown territories.
As cartography progressed, map flags became more sophisticated, incorporating diverse symbols and colors to represent different categories of information. These advancements allowed for the representation of complex data, such as population density, resource distribution, or geographical features. The use of different flag colors, sizes, and shapes enabled mapmakers to convey nuanced information and create visually engaging representations of the world.
Types of Map Flags and Their Applications:
Map flags can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose and catering to distinct audiences:
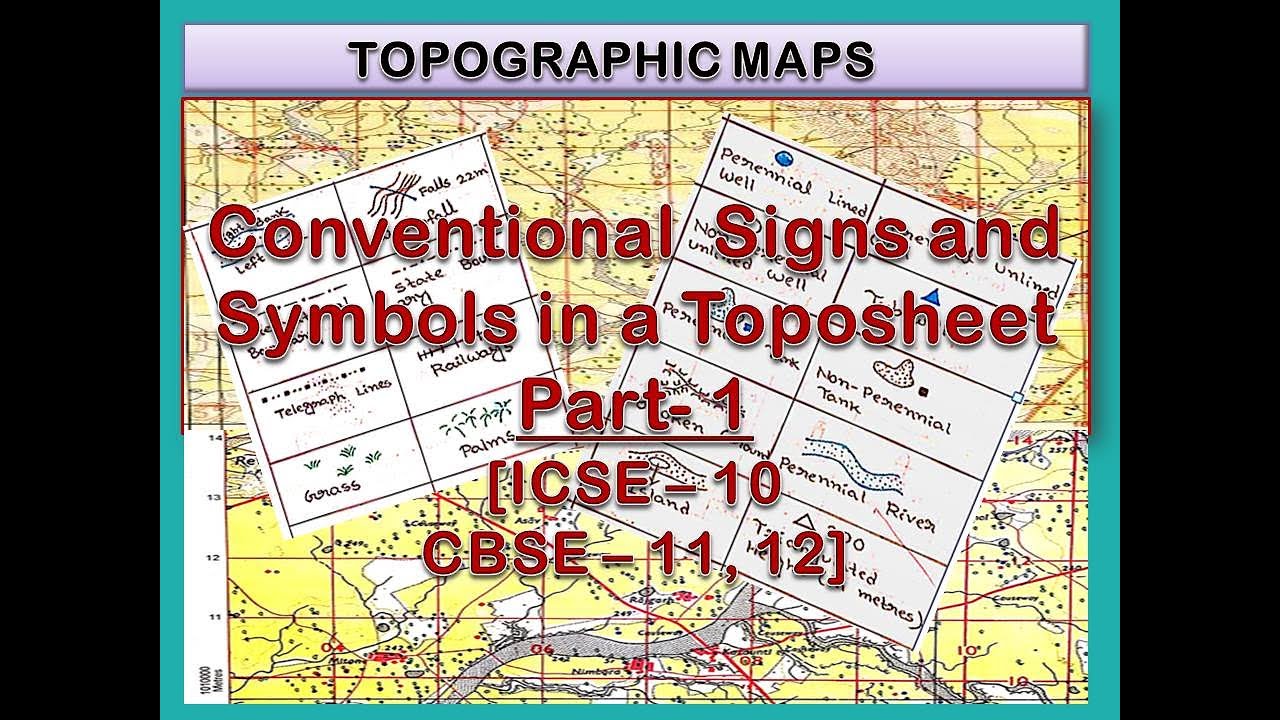
1. Location Markers:
These are the most basic type of map flag, used to pinpoint specific locations on a map. They can be used to highlight cities, towns, landmarks, or any other geographical point of interest. Location markers are often accompanied by labels or text annotations to provide additional information about the location.
2. Data Markers:
Data markers are used to represent quantitative or qualitative data on a map. They can be used to depict population density, crime rates, economic activity, or any other data that can be spatially represented. Different colors, sizes, or shapes can be used to represent different data values or categories.
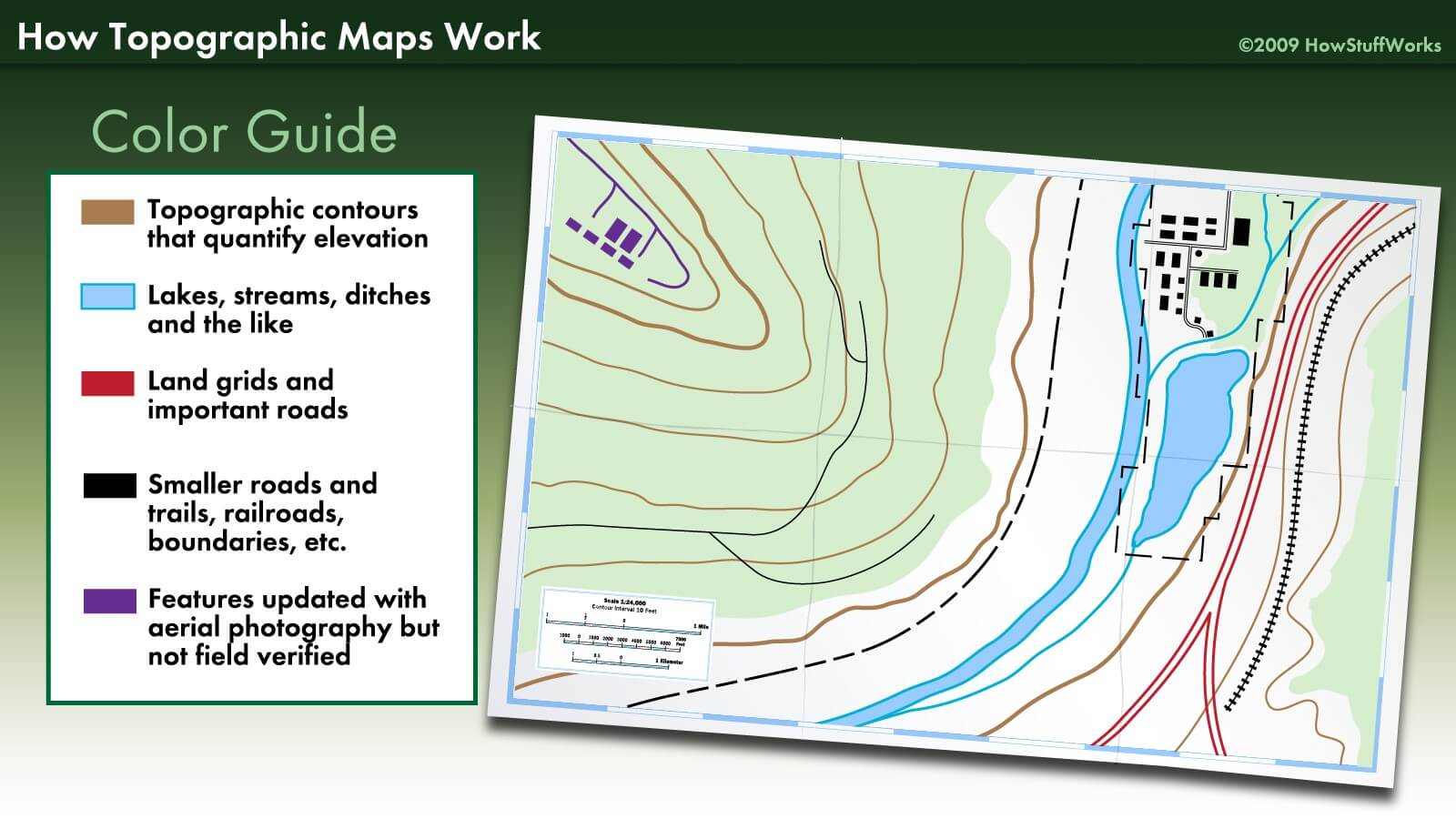
3. Feature Markers:
Feature markers are used to highlight specific geographical features on a map, such as rivers, mountains, forests, or bodies of water. They are often used in conjunction with location markers to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
4. Route Markers:
Route markers are used to indicate specific routes or paths on a map. They can be used to depict highways, roads, trails, or any other route of travel. Route markers are often used in conjunction with location markers and feature markers to provide a complete picture of the journey.
5. Interactive Markers:
Interactive markers are a relatively new development in mapmaking, enabled by the rise of digital mapping platforms. These markers can be used to display additional information or activate specific functions when clicked or hovered over. Interactive markers can be used to provide more detailed information about a location, display multimedia content, or launch other applications.
The Importance of Map Flags:
Map flags play a crucial role in enhancing the clarity, efficiency, and effectiveness of maps. Their significance lies in their ability to:
- Simplify Complex Information: Map flags act as visual shortcuts, allowing viewers to quickly grasp key information without needing to read lengthy text descriptions.
- Improve Visual Communication: By utilizing different colors, shapes, and sizes, map flags create a visually engaging and intuitive representation of data.
- Facilitate Data Analysis: Map flags can be used to highlight trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, facilitating deeper analysis and understanding.
- Enhance Navigation: Map flags can guide users through complex environments by clearly marking routes, landmarks, and points of interest.
- Promote Accessibility: Map flags can make maps accessible to a wider audience, including those who may have difficulty reading or understanding complex text descriptions.
FAQs about Map Flags:
1. What are the different types of map flags?
Map flags can be categorized into location markers, data markers, feature markers, route markers, and interactive markers. Each type serves a specific purpose and caters to distinct audiences.
2. How are map flags used in different fields?
Map flags find applications in various fields, including cartography, geography, urban planning, environmental science, transportation, and marketing. They are essential tools for visualizing data, communicating information, and guiding decision-making.
3. What are some common examples of map flags?
Common examples of map flags include:
- Pin icons: Used to mark locations on maps, often with a specific color or shape to denote a category.
- Star symbols: Used to highlight important cities or landmarks.
- Line symbols: Used to depict routes or boundaries.
- Area symbols: Used to represent geographical features or data regions.
4. What are the benefits of using map flags?
Map flags simplify complex information, improve visual communication, facilitate data analysis, enhance navigation, and promote accessibility.
5. How have map flags evolved over time?
Map flags have evolved from simple markers to complex data visualizations, reflecting advancements in cartography and technology.
Tips for Using Map Flags Effectively:
- Choose appropriate colors and shapes: Select colors and shapes that are visually distinct and easily distinguishable.
- Use consistent symbols: Maintain consistency in the use of symbols across different maps to ensure clarity and ease of understanding.
- Provide clear labels: Include labels or text annotations to provide additional information about the location, feature, or data represented.
- Consider the target audience: Design map flags with the target audience in mind, using symbols and colors that are familiar and meaningful.
- Use interactive markers effectively: When using interactive markers, ensure that the additional information provided is relevant and engaging.
Conclusion:
Map flags are an integral part of mapmaking, serving as visual cues that enhance the comprehension and utility of maps. Their evolution from simple markers to complex data visualizations reflects the advancements in cartography and technology. By effectively utilizing map flags, we can create informative, engaging, and accessible maps that facilitate understanding, guide decision-making, and empower individuals to navigate the world around them.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Significance of Map Flags. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!