Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping
- 3.1 The Power of Visualizing Data on Maps
- 3.2 Types of Maps Used for Data Visualization
- 3.3 Tools and Techniques for Creating Data Visualization Maps
- 3.4 Importance of Ethical Considerations in Data Visualization Maps
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Data Visualization Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping
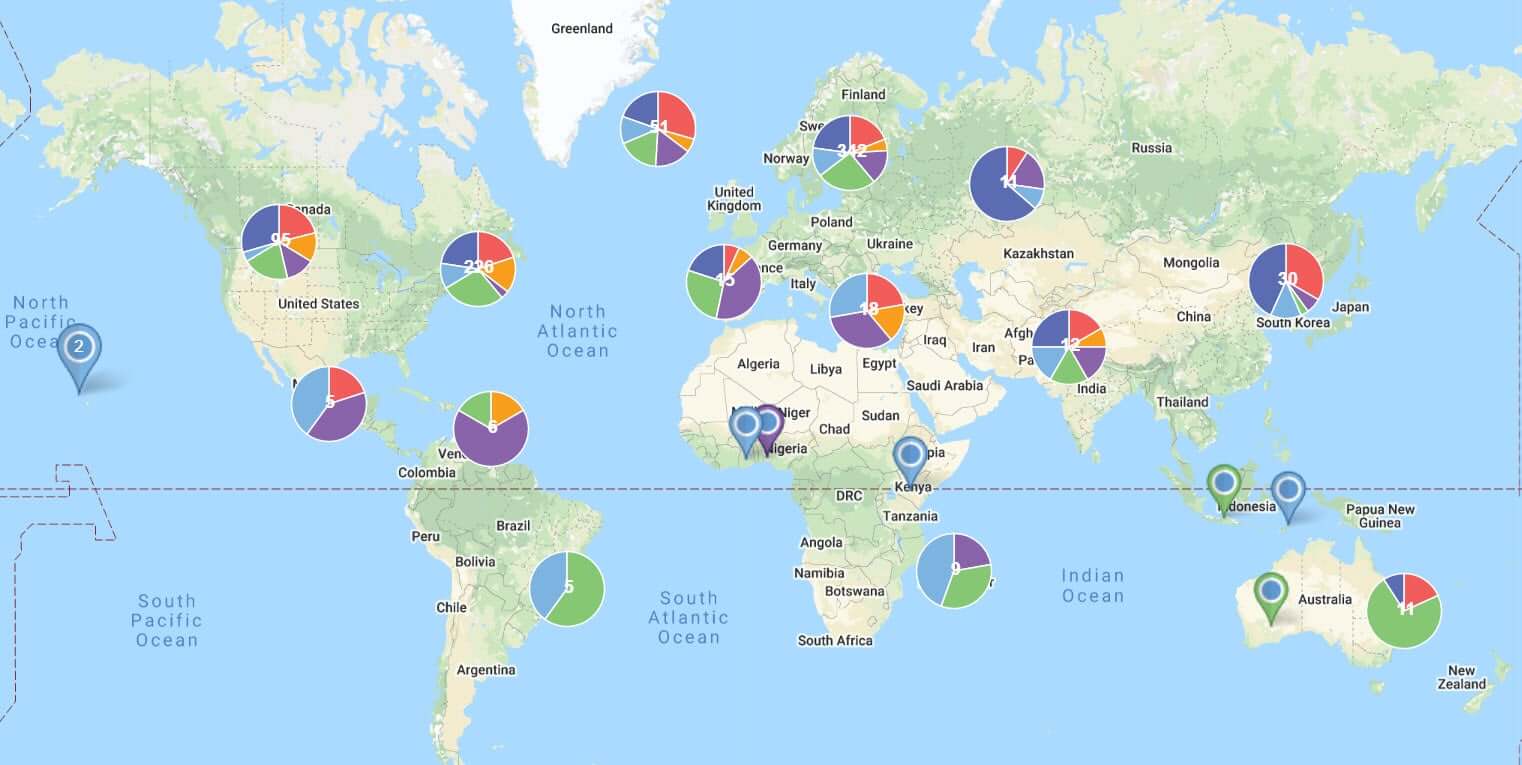
Data visualization is a powerful tool for understanding complex information. By transforming raw data into visual representations, we can identify patterns, trends, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden. Among the many techniques employed in data visualization, mapping stands out for its ability to reveal spatial relationships and geographical context.
The Power of Visualizing Data on Maps
Maps are inherently intuitive. We are accustomed to using them to navigate our physical world, and this familiarity translates seamlessly to understanding data displayed on them. By representing data points, flows, or distributions on a map, we can instantly grasp their geographical significance and make connections that might not be apparent from tabular data alone.
The Benefits of Using Maps for Data Visualization:
- Spatial Context: Maps provide a visual representation of the geographical location of data, allowing users to understand the spatial relationships between different points and areas. This is crucial for analyzing phenomena that are influenced by geographical factors, such as population density, environmental conditions, or disease outbreaks.
- Pattern Recognition: Maps can reveal patterns and trends in data that might not be obvious from looking at raw numbers. For example, a map showing crime rates in a city can highlight areas with higher crime concentration, enabling law enforcement to focus their resources accordingly.
- Data Exploration and Storytelling: Maps can be used to explore data interactively, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas, filter data by different criteria, and uncover hidden relationships. This interactive nature makes maps particularly effective for storytelling and communicating insights to a wider audience.
- Improved Decision-Making: By visualizing data on maps, decision-makers can gain a deeper understanding of the spatial context of their problems and make more informed decisions. This is particularly relevant in fields such as urban planning, resource management, and public health.
Types of Maps Used for Data Visualization
The choice of map type depends on the specific data being visualized and the insights desired. Some common types of maps used for data visualization include:
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use color or shading to represent data values across different geographical regions. For example, a choropleth map could show population density by county or income levels by state.
- Dot Density Maps: These maps use dots to represent individual data points, with the density of dots reflecting the concentration of data in different areas. This type of map is useful for visualizing data with a large number of individual observations, such as population distribution or crime incidents.
- Flow Maps: These maps use lines or arrows to represent the movement of data, such as trade routes, migration patterns, or transportation flows. Flow maps can be particularly effective for visualizing dynamic processes and understanding how data moves across space.
- Isoline Maps: These maps use lines to connect points with equal values, creating contours that represent different levels of a particular variable. Isoline maps are commonly used to visualize elevation, temperature, or rainfall patterns.
- Cartograms: These maps distort the size of geographical regions to reflect the magnitude of a particular data value. For instance, a cartogram might enlarge countries based on their population size, providing a visually compelling representation of population distribution.
Tools and Techniques for Creating Data Visualization Maps
The creation of data visualization maps involves several key steps:
- Data Preparation: The first step is to prepare the data for mapping. This may involve cleaning, transforming, and aggregating the data to ensure it is suitable for visualization.
- Map Selection: Choosing the appropriate map type is crucial for effectively communicating the desired insights. Factors to consider include the type of data being visualized, the intended audience, and the specific questions being addressed.
- Data Visualization: Once the map type is selected, the data is visualized on the map using appropriate symbols, colors, and other visual elements. The goal is to create a map that is both visually appealing and informative.
- Map Customization: Maps can be further customized to enhance their clarity and effectiveness. This may involve adding labels, legends, and other annotations to provide context and facilitate understanding.
A wide range of software tools is available for creating data visualization maps. These tools offer varying levels of functionality and ease of use, catering to different skill levels and needs. Some popular options include:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software: GIS software, such as ArcGIS and QGIS, provides advanced capabilities for spatial analysis, data manipulation, and map creation.
- Data Visualization Platforms: Platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio offer intuitive interfaces for creating interactive maps and dashboards.
- Mapping Libraries: Libraries like Leaflet and Mapbox GL JS allow developers to integrate interactive maps into web applications.
Importance of Ethical Considerations in Data Visualization Maps
While maps are powerful tools for understanding and communicating data, it is crucial to use them responsibly and ethically. Misleading or biased maps can distort reality and lead to incorrect conclusions.
Key ethical considerations in data visualization maps include:
- Data Accuracy: Ensure the data used for mapping is accurate and reliable. This involves verifying data sources, checking for errors, and using appropriate data collection methods.
- Map Projections: Different map projections distort geographical shapes and sizes in different ways. Choose a projection that minimizes distortion for the specific region and data being visualized.
- Color Choice: Use colors effectively to represent data values. Avoid using colors that are visually distracting or misleading.
- Map Scale: The scale of the map can significantly impact the perception of data. Choose a scale that is appropriate for the data and the intended audience.
- Context and Transparency: Provide context and transparency in map creation. Clearly label data sources, explain the methodology used, and acknowledge any potential biases or limitations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the different types of maps used for data visualization?
A: Several map types are commonly used for data visualization, including choropleth maps, dot density maps, flow maps, isoline maps, and cartograms. The choice of map type depends on the specific data being visualized and the desired insights.
Q: What are the benefits of using maps for data visualization?
A: Maps provide a visual representation of the geographical location of data, enabling users to understand spatial relationships, recognize patterns, explore data interactively, and make informed decisions.
Q: What are some popular tools for creating data visualization maps?
A: Popular tools include GIS software like ArcGIS and QGIS, data visualization platforms like Tableau and Power BI, and mapping libraries like Leaflet and Mapbox GL JS.
Q: How can I ensure ethical considerations in data visualization maps?
A: Ensure data accuracy, use appropriate map projections, choose colors effectively, select the correct map scale, and provide context and transparency in map creation.
Tips for Effective Data Visualization Maps
- Keep it Simple: Aim for clarity and simplicity in map design. Avoid overwhelming the user with too much information.
- Use Visual Hierarchy: Highlight important data points and trends using different visual elements, such as color, size, or shape.
- Include Context: Provide context for the data by including labels, legends, and annotations.
- Consider Accessibility: Ensure maps are accessible to all users, including those with visual impairments.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously test and refine maps based on user feedback to ensure they are effective in conveying the desired insights.
Conclusion
Data visualization maps are powerful tools for understanding and communicating complex information. By leveraging the intuitive nature of maps, we can gain valuable insights from data and make more informed decisions. However, it is crucial to use maps responsibly and ethically, ensuring data accuracy, appropriate map projections, effective color choices, and clear communication of context and limitations. By adhering to these principles, we can harness the power of data visualization maps to unlock the full potential of data and drive meaningful change.
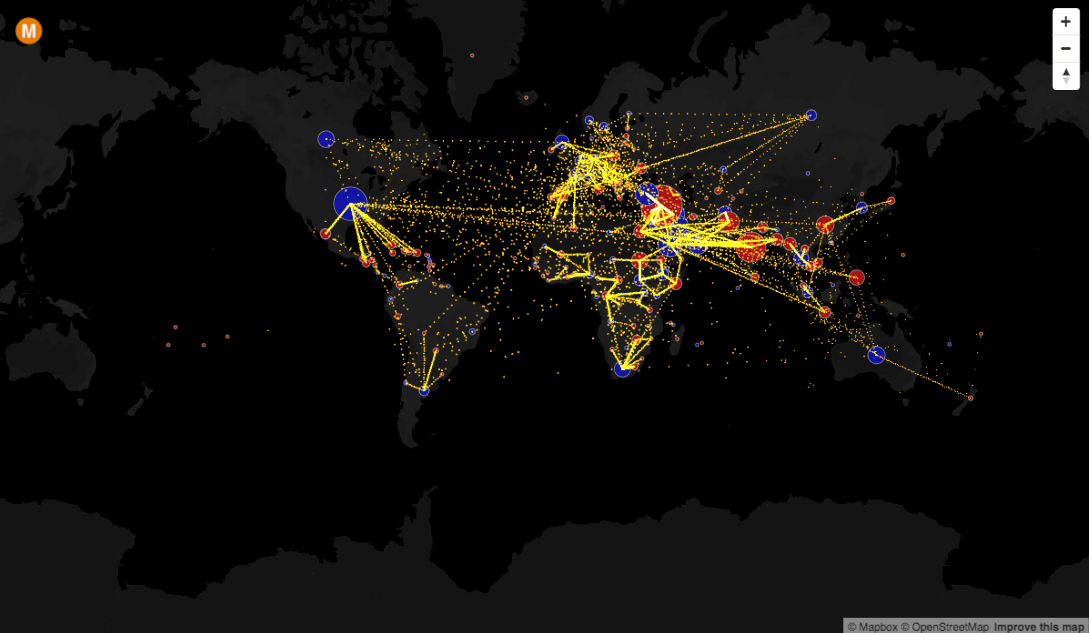



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Look at Data Visualization through Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!