Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning
Related Articles: Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning
- 3.1 Understanding Packet Fragmentation
- 3.2 The Mechanics of the -f Flag
- 3.3 Benefits of Using the -f Flag
- 3.4 Practical Applications of the -f Flag
- 3.5 Addressing Common Misconceptions
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of the -f Flag
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning

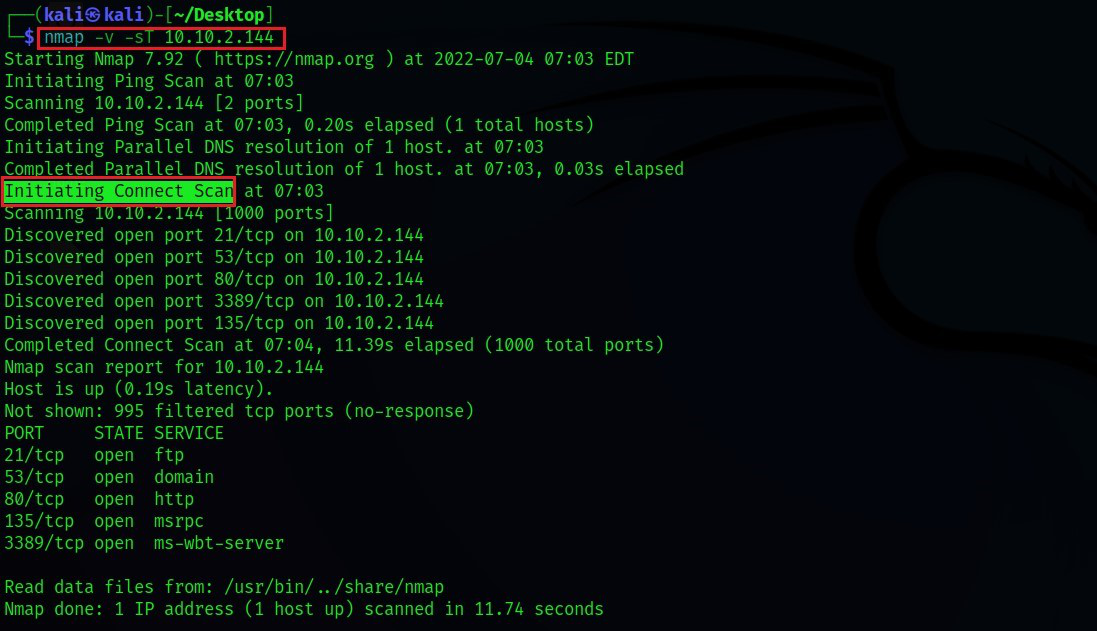
Nmap, the Network Mapper, is a powerful and versatile tool for network exploration and security auditing. Among its numerous features, the -f flag, also known as the "fragmentation" flag, stands out as a unique and valuable addition to the Nmap arsenal. This flag enables users to manipulate the way Nmap interacts with target systems by fragmenting its network packets.
This article delves into the intricacies of the -f flag, exploring its mechanism, benefits, and applications in detail. We will analyze its role in bypassing firewalls, evading intrusion detection systems (IDS), and enhancing scan stealthiness. The article will also address common misconceptions and provide practical tips for maximizing its effectiveness.
Understanding Packet Fragmentation
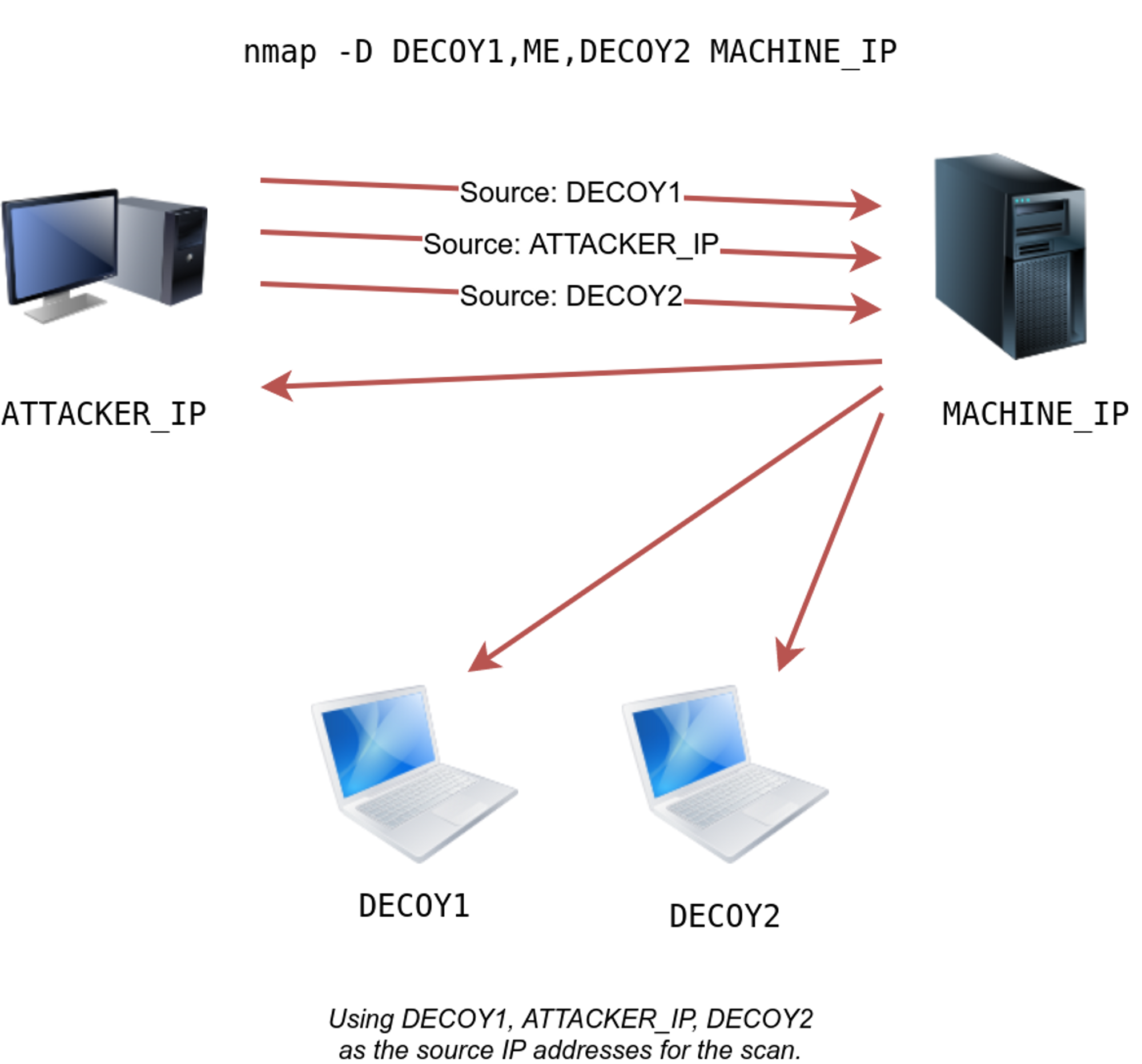
Before diving into the specifics of the -f flag, it is crucial to understand the concept of packet fragmentation in networking. When a network packet exceeds the maximum transmission unit (MTU) of a network interface, it is divided into smaller fragments. These fragments are then transmitted individually and reassembled at the destination.
Nmap’s -f flag leverages this principle by intentionally fragmenting its scan packets. This allows it to bypass firewalls or IDS that might be configured to block large packets or specific packet types.
The Mechanics of the -f Flag
The -f flag in Nmap offers flexibility in manipulating packet fragmentation. It accepts a variety of arguments, each influencing how the packets are fragmented:
- -f: This basic usage results in Nmap fragmenting packets into the smallest possible units, minimizing their size and increasing the number of fragments.
-
-f
: This form specifies the desired fragment size in bytes. For example,-f 1024will fragment packets into 1024-byte chunks. -
-f
: This allows for defining a range of fragment sizes. For instance,-f 1024-2048will create fragments ranging from 1024 to 2048 bytes in size. -
-f
- :
-f 512,1024,2048will fragment packets into sizes of 512, 1024, and 2048 bytes.
By adjusting the fragment size, users can fine-tune Nmap’s scan behavior to bypass specific security measures or exploit network vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Using the -f Flag
The -f flag provides several key benefits for network scanning, including:
- Firewall Evasion: Firewalls often block large packets, assuming they are malicious. By fragmenting packets, Nmap can bypass these restrictions and reach target systems undetected.
- IDS Evasion: Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) often rely on signature-based detection methods, analyzing packet content and size. Fragmentation can disrupt these patterns, making it harder for IDS to identify Nmap’s scan activity.
- Increased Stealth: Fragmentation can make Nmap scans less noticeable. By breaking down packets into smaller units, the scan traffic appears less suspicious and harder to detect.
-
Enhanced Scan Flexibility: The
-fflag allows for precise control over packet fragmentation, enabling users to tailor their scans to specific network environments and security configurations.
Practical Applications of the -f Flag
The -f flag can be employed in various network scanning scenarios, including:
-
Penetration Testing: During penetration testing, the
-fflag can help bypass firewalls and IDS, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment of a target network’s security posture. - Network Discovery: When performing network discovery, fragmentation can aid in identifying hidden devices or services that might be obscured by security measures.
- Vulnerability Scanning: By fragmenting scan packets, Nmap can reach vulnerable systems that might otherwise be inaccessible due to firewall restrictions.
-
Research and Development: Network researchers and security professionals can leverage the
-fflag to study the behavior of firewalls, IDS, and other network security mechanisms.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
While the -f flag offers significant benefits, it is essential to address some common misconceptions:
-
Guaranteed Firewall Bypass: The
-fflag does not guarantee firewall bypass. Many firewalls employ advanced filtering mechanisms that can detect fragmented packets and block them. - Complete IDS Evasion: Fragmentation does not always guarantee complete IDS evasion. Some IDS systems can identify fragmented traffic patterns and flag them as suspicious.
-
Universal Solution: The
-fflag is not a universal solution for every network scanning scenario. Its effectiveness depends on the specific configuration of the target network and the security measures in place.
Tips for Effective Use of the -f Flag
To maximize the effectiveness of the -f flag, consider these tips:
- Experiment with Fragmentation Sizes: Try different fragment sizes and combinations to find the optimal settings for your target network.
-
Combine with Other Nmap Flags: The
-fflag can be combined with other Nmap flags for enhanced functionality. For example, using-fwith-sS(stealth scan) can increase scan stealthiness. -
Monitor Network Traffic: Monitor network traffic carefully while using the
-fflag to ensure that your scans are not causing unintended disruption. -
Respect Network Security: Use the
-fflag responsibly and ethically, respecting the security of target networks.
Conclusion
Nmap’s -f flag is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance network scanning capabilities. By fragmenting scan packets, it allows users to bypass firewalls, evade IDS, and increase scan stealthiness. While it is not a universal solution, the -f flag offers valuable flexibility and control over Nmap’s scanning behavior. Understanding its mechanics, benefits, and limitations is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness in various network scanning scenarios. Always remember to use the -f flag responsibly and ethically, respecting the security of target networks.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Nmap’s -f Flag: A Powerful Tool for Flexible Port Scanning. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!