Reconstructing the World Before Ice: A Journey Through Earth’s Pre-Glacial Past
Related Articles: Reconstructing the World Before Ice: A Journey Through Earth’s Pre-Glacial Past
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Reconstructing the World Before Ice: A Journey Through Earth’s Pre-Glacial Past. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Reconstructing the World Before Ice: A Journey Through Earth’s Pre-Glacial Past
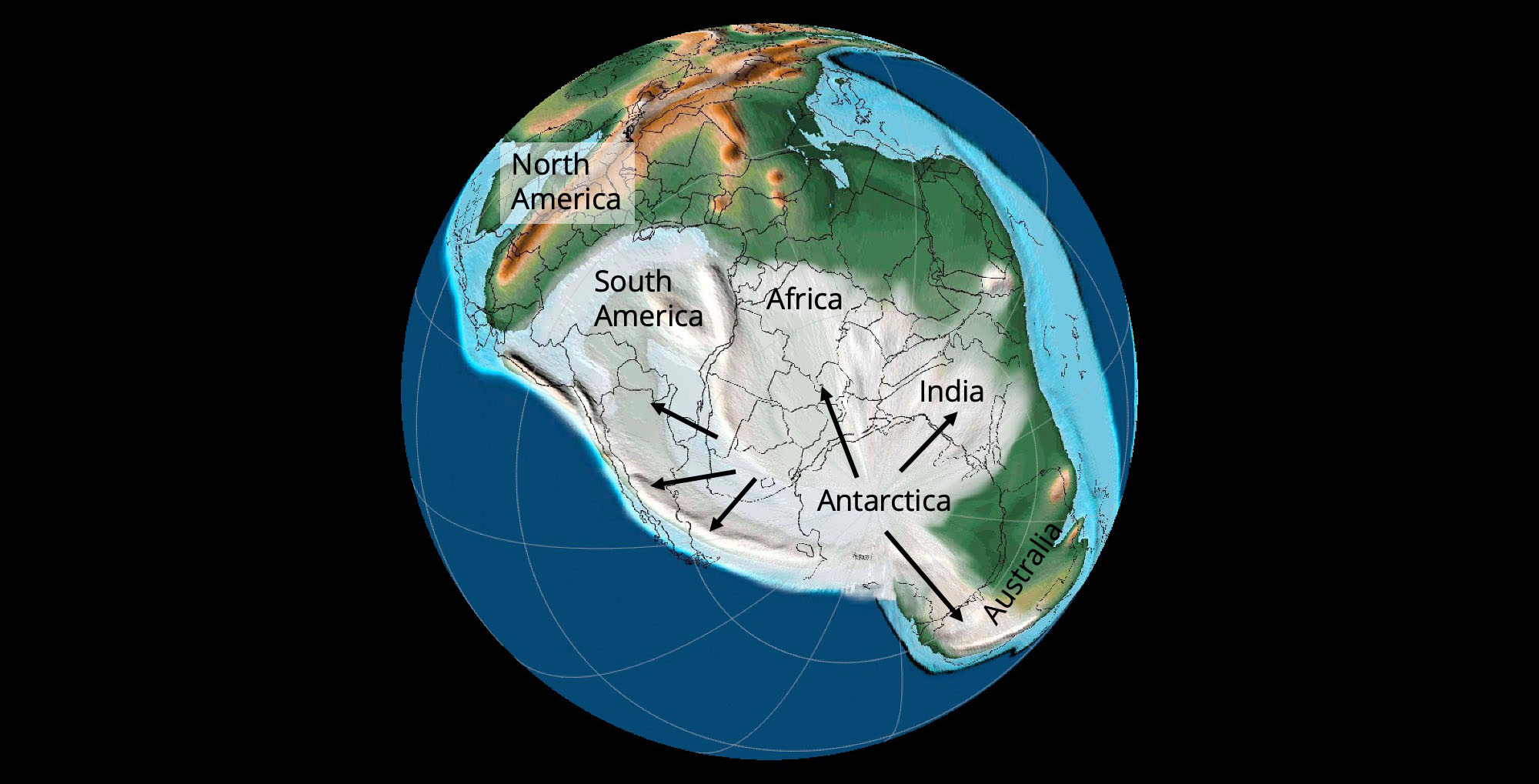
The Earth’s surface, as we know it today, is a product of countless geological transformations, with ice ages playing a pivotal role in shaping continents, coastlines, and ecosystems. However, before the onset of these dramatic glacial periods, the planet presented a vastly different landscape. Understanding this pre-glacial world is crucial for comprehending the evolution of our planet, the distribution of life, and the factors that influence modern climate patterns.
A World Without Ice Sheets:
The most significant difference between the Earth before and after the ice ages lies in the absence of vast ice sheets that covered much of the northern hemisphere. This lack of glacial ice significantly altered global sea levels, leading to:
-
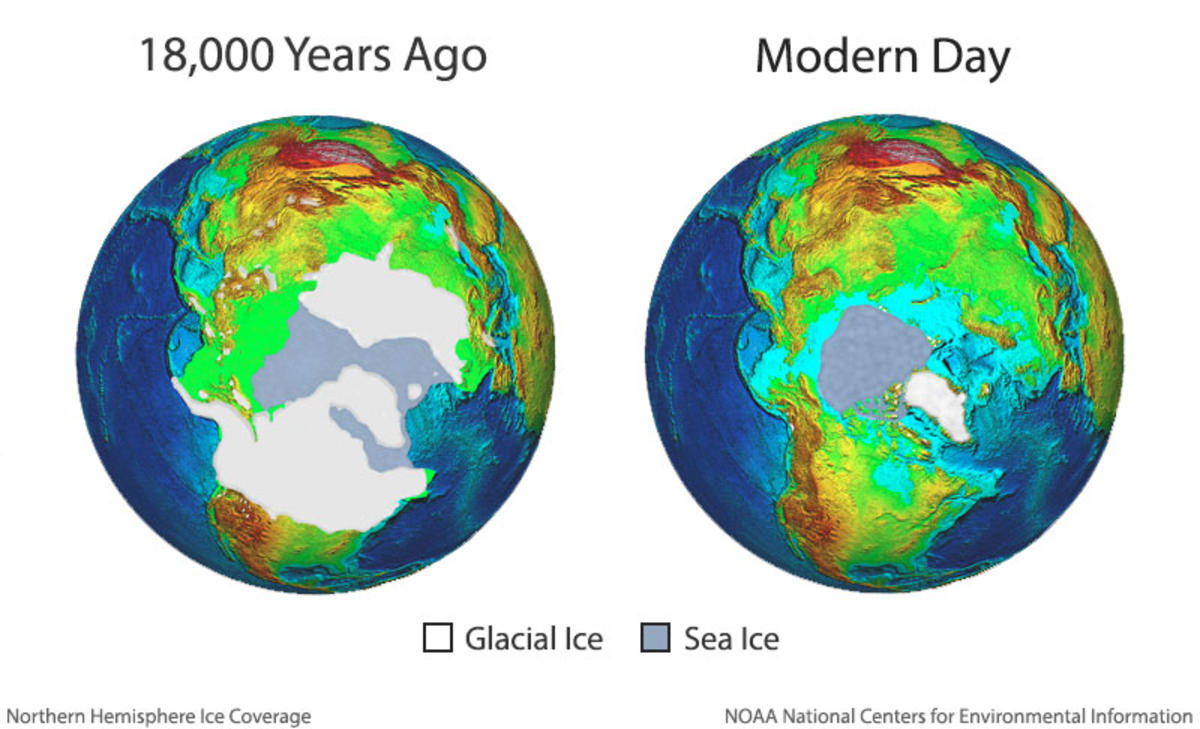
Lower Sea Levels: Without the immense volume of water locked up in ice sheets, global sea levels were significantly lower than they are today. This resulted in land bridges connecting continents that are now separated by vast oceans. For example, during the last interglacial period (between 125,000 and 11,700 years ago), sea levels were about 120 meters lower than present levels, exposing landmasses that now lie submerged beneath the ocean.
-
Wider Continental Shelves: The lower sea levels exposed vast continental shelves, creating larger land areas for terrestrial life to flourish. These shelves provided fertile ground for diverse flora and fauna, impacting the distribution of ecosystems and the evolution of species.
-
Different Coastlines: With lower sea levels, coastlines were significantly different from their current configurations. Coastal areas that are now submerged were once home to diverse ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and freshwater habitats. This shift in coastline impacted the distribution of plant and animal life, shaping the evolution of ecosystems.
Shifting Landscapes and Climate:
The absence of ice sheets also affected global climate patterns. The pre-glacial Earth experienced:
-
Warmer Temperatures: The absence of vast ice sheets, which reflect solar radiation back into space, led to warmer global temperatures. This warmer climate supported a greater diversity of flora and fauna, particularly in higher latitudes where ice sheets now dominate.
-
Different Precipitation Patterns: The lack of ice sheets altered global precipitation patterns. Without the large-scale ice sheets acting as a source of moisture, precipitation patterns were likely more localized and influenced by other factors like ocean currents and topography.
-
Greater Biodiversity: The warmer temperatures and diverse landscapes provided suitable conditions for a wide range of plant and animal species to thrive. This increased biodiversity contributed to the evolution of unique ecosystems and species that are no longer found in the modern world.
Reconstructing the Pre-Glacial World:
While the Earth’s pre-glacial past is a distant memory, scientists can reconstruct this lost world using various tools and techniques:
-
Geological Evidence: Geologists study rock formations, sediment layers, and glacial deposits to understand the Earth’s past climates and landscapes. These studies provide insights into the extent of past ice sheets, the locations of ancient coastlines, and the types of ecosystems that once thrived in different regions.
-
Fossil Records: Fossils of extinct plants and animals provide invaluable evidence about the distribution of life in the pre-glacial world. Analyzing these fossils helps scientists understand the evolution of species, the types of ecosystems that existed, and the climatic conditions that prevailed.
-
Paleoclimate Data: By analyzing ice cores, tree rings, and other natural archives, scientists can reconstruct past climate conditions. These data reveal fluctuations in temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric composition, providing insights into the pre-glacial climate and its impact on life.
-
Computer Modeling: Sophisticated computer models can simulate past climates and landscapes, allowing scientists to test hypotheses about the pre-glacial world. These models incorporate data from geological evidence, fossil records, and paleoclimate reconstructions to create a virtual representation of the Earth’s past.
The Importance of Understanding the Pre-Glacial World:
Reconstructing the Earth’s pre-glacial world is not just a historical exercise. Understanding this past provides crucial insights into:
-
Climate Change: By studying the pre-glacial climate and its response to natural fluctuations, we can gain valuable insights into the potential impacts of current and future climate change. This knowledge can guide strategies for mitigating climate change and adapting to its consequences.
-
Biodiversity Conservation: Understanding the distribution of life in the pre-glacial world helps us appreciate the long-term evolutionary processes that have shaped the Earth’s biodiversity. This knowledge is essential for developing effective strategies for conserving biodiversity in the face of ongoing environmental changes.
-
Resource Management: The pre-glacial world provides insights into the distribution of natural resources, such as water, minerals, and fossil fuels. This understanding can inform resource management strategies and ensure sustainable use for future generations.
FAQs about Earth Before the Ice Age:
Q: How long ago did the ice ages begin?
A: The Quaternary Ice Age, which is the most recent ice age, began approximately 2.6 million years ago and continues to this day, with interglacial periods interrupting the overall cooling trend.
Q: How did the Earth’s continents shift before the ice ages?
A: The Earth’s continents have been shifting for millions of years due to plate tectonics. Before the ice ages, the continents were in different positions, with some landmasses closer together and others further apart. These shifts influenced the distribution of life and the flow of ocean currents.
Q: What were the major differences in flora and fauna between the pre-glacial and post-glacial periods?
A: The pre-glacial world supported a greater diversity of flora and fauna, particularly in higher latitudes. The warmer temperatures and diverse landscapes allowed for a wider range of species to thrive. After the ice ages, many species went extinct, and the distribution of life shifted significantly.
Q: Did the Earth’s magnetic field change during the pre-glacial period?
A: The Earth’s magnetic field has flipped numerous times throughout its history, including during the pre-glacial period. These flips can affect climate and the distribution of life, although the exact mechanisms are still under investigation.
Tips for Exploring the Pre-Glacial World:
- Visit Natural History Museums: Museums house collections of fossils, geological specimens, and other artifacts that provide a glimpse into the Earth’s past.
- Explore Geological Sites: Visit locations with exposed rock formations, sediment layers, and glacial deposits to observe firsthand the geological processes that shaped the Earth.
- Read Books and Articles: Numerous books and articles explore the pre-glacial world, providing insights into the Earth’s history, climate, and life.
- Use Online Resources: Websites and online databases offer access to geological data, fossil records, and paleoclimate reconstructions, allowing you to explore the pre-glacial world virtually.
Conclusion:
The Earth before the ice ages was a world vastly different from the one we inhabit today. By reconstructing this lost world, scientists gain crucial insights into the Earth’s evolution, the distribution of life, and the factors that influence modern climate patterns. This understanding is essential for addressing current and future challenges related to climate change, biodiversity conservation, and resource management. As we continue to explore the pre-glacial world, we unlock valuable knowledge that informs our understanding of the planet and our place within it.


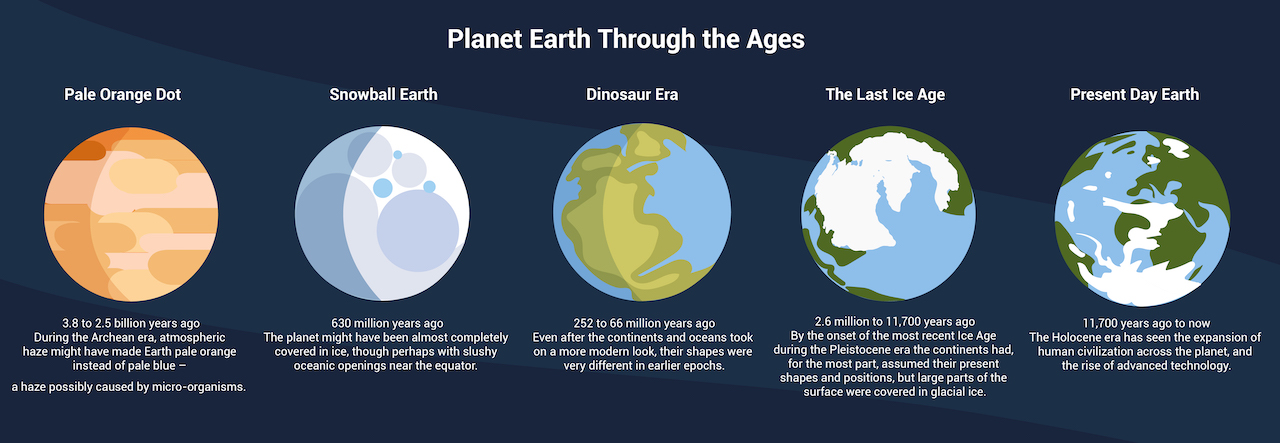




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Reconstructing the World Before Ice: A Journey Through Earth’s Pre-Glacial Past. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!