The Arteries of Queensland: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Gas Pipeline Network
Related Articles: The Arteries of Queensland: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Gas Pipeline Network
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Arteries of Queensland: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Gas Pipeline Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Arteries of Queensland: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Gas Pipeline Network

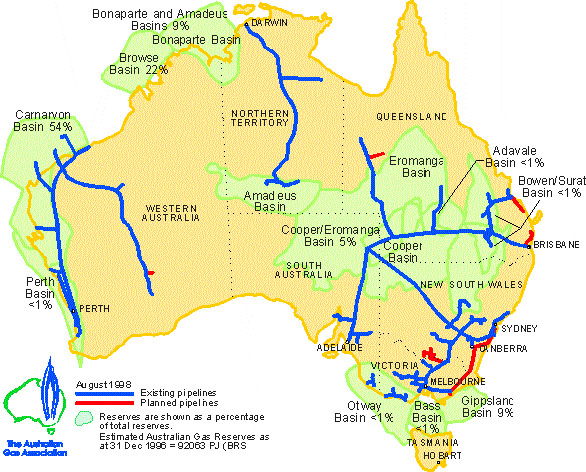
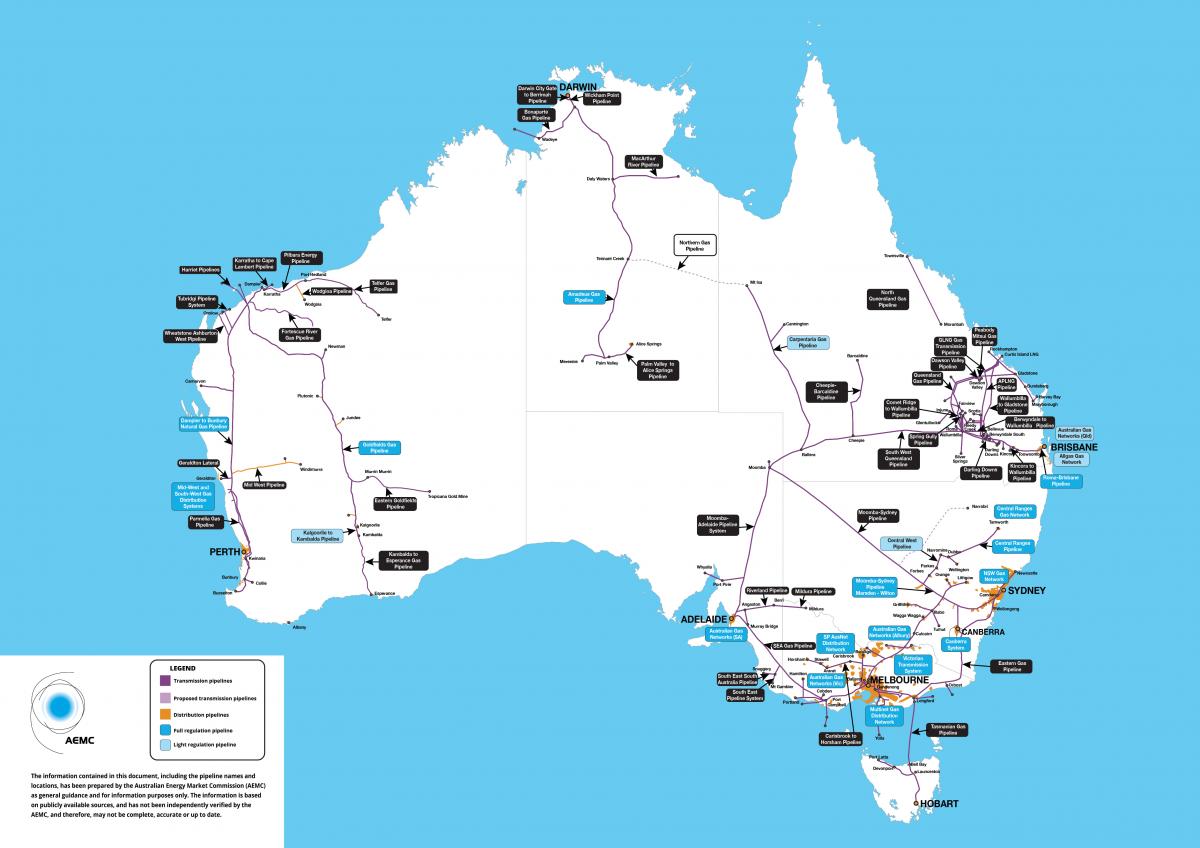
Queensland, a state renowned for its diverse natural resources, boasts a robust gas pipeline network that plays a crucial role in powering its economy and fulfilling its energy needs. This intricate web of pipelines, stretching across the state, facilitates the transportation of natural gas from production sites to various consumers, including homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. Understanding the Queensland gas pipeline map provides valuable insights into the state’s energy infrastructure, its economic dependence on natural gas, and the challenges and opportunities associated with this vital resource.
A Network of Vital Arteries
The Queensland gas pipeline map showcases a network of interconnected pipelines that transport natural gas from various sources across the state. These sources include offshore gas fields in the Bass Strait, onshore gas fields in the Surat Basin and Cooper Basin, and coal seam gas (CSG) fields in the Bowen Basin. The pipelines, varying in size and capacity, form a complex network that ensures the efficient delivery of natural gas to diverse consumers throughout Queensland.
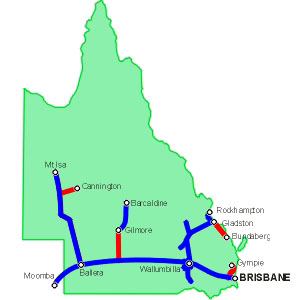
Key Pipelines and Their Significance
Several key pipelines contribute significantly to the state’s gas infrastructure:
- The Queensland Gas Pipeline (QGP): This major pipeline, running from the Surat Basin to Brisbane and the Gold Coast, plays a vital role in supplying natural gas to the state’s largest population centers.
- The Darling Downs Pipeline: This pipeline transports natural gas from the Surat Basin to the Darling Downs region, providing energy for agricultural and industrial activities.
- The Roma to Brisbane Pipeline: This pipeline connects the Roma gas field in the Surat Basin to Brisbane, delivering natural gas to residential and commercial customers in the capital city.
- The South East Queensland Gas Pipeline: This pipeline connects various gas fields in the Surat Basin to the South East Queensland region, providing gas for power generation and industrial use.
- The Gladstone LNG Pipeline: This pipeline transports natural gas from the Surat Basin to the Gladstone LNG plant, where it is processed and exported as liquefied natural gas (LNG).
Benefits of the Queensland Gas Pipeline Network
The Queensland gas pipeline network offers numerous benefits to the state’s economy and society:
- Reliable Energy Supply: The network ensures a reliable and consistent supply of natural gas to homes, businesses, and industries, providing a stable energy source for various activities.
- Economic Growth: Natural gas production and transportation contribute significantly to the Queensland economy, generating employment opportunities, supporting local businesses, and boosting economic activity.
- Environmental Sustainability: Natural gas is a relatively clean-burning fossil fuel, emitting fewer greenhouse gases than other fossil fuels like coal. The pipeline network contributes to reducing reliance on coal-fired power generation, promoting environmental sustainability.
- Industrial Development: The availability of natural gas fuels industrial development, attracting investments in sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and energy-intensive industries.
- Affordable Energy: Natural gas is often a more affordable energy source compared to other options, making it accessible to a wider range of consumers and supporting economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its numerous benefits, the Queensland gas pipeline network faces certain challenges and opportunities:
- Environmental Concerns: Gas extraction and pipeline construction can raise environmental concerns, particularly regarding water usage, land disturbance, and potential impacts on ecosystems.
- Infrastructure Investment: Maintaining and expanding the pipeline network requires significant investment to ensure its long-term reliability and capacity to meet growing energy demands.
- Competition from Renewable Energy: The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, presents competition for natural gas, posing challenges to the long-term sustainability of the gas industry.
- Gas Pricing Volatility: Global gas prices can fluctuate significantly, impacting the affordability of natural gas and the economic viability of gas-related industries.
- Community Engagement: Building and operating gas pipelines require strong community engagement to address concerns, mitigate potential impacts, and ensure the project’s social license to operate.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the role of the Queensland gas pipeline network in the state’s energy mix?
A: The network plays a crucial role in supplying natural gas to various sectors, including power generation, industrial use, and residential consumption. It contributes significantly to Queensland’s energy mix, providing a reliable and affordable energy source.
Q: How does the pipeline network contribute to Queensland’s economic growth?
A: The network supports gas production, transportation, and distribution, generating employment opportunities, boosting local businesses, and attracting investments in gas-related industries.
Q: What are the environmental implications of the Queensland gas pipeline network?
A: Gas extraction and pipeline construction can have environmental impacts, including water usage, land disturbance, and potential emissions. However, natural gas is a cleaner-burning fuel than coal, contributing to a more sustainable energy mix.
Q: What are the future prospects for the Queensland gas pipeline network?
A: The network’s future will depend on factors like gas demand, technological advancements, and the adoption of renewable energy sources. Continued investment in infrastructure, responsible environmental practices, and community engagement will be crucial for its long-term sustainability.
Tips for Understanding the Queensland Gas Pipeline Map
- Focus on key pipelines: Identify the major pipelines and their connections to gas production sites and consumption centers.
- Understand pipeline capacity: Recognize the volume of gas transported by each pipeline, indicating its importance in the network.
- Consider geographic distribution: Analyze the network’s coverage across the state, highlighting its role in supplying different regions.
- Research gas production sources: Identify the various gas fields supplying the network, including their location and production capacity.
- Explore potential future expansions: Consider how the network might evolve to meet growing energy demands and changing energy landscapes.
Conclusion: A Vital Infrastructure for Queensland’s Future
The Queensland gas pipeline network is a vital infrastructure asset, playing a crucial role in powering the state’s economy and fulfilling its energy needs. While facing challenges related to environmental concerns, competition from renewable energy, and gas price volatility, the network offers numerous benefits, including a reliable energy supply, economic growth, and environmental sustainability. Continued investment in infrastructure, responsible environmental practices, and robust community engagement will be essential to ensure the long-term viability and sustainability of this vital resource for Queensland’s future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Arteries of Queensland: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Gas Pipeline Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!