The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps
Related Articles: The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps
- 3.1 The Evolution of Byzantine Flags: A Tale of Imperial Identity
- 3.2 The Byzantine Empire on the Map: A Dynamic Tapestry of Territories
- 3.3 The Enduring Legacy: A Visual Representation of Byzantine Influence
- 3.4 FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Byzantine Empire’s Flag Map
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding the Byzantine Empire’s Flag Map
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Enduring Influence of a Visual Legacy
- 4 Closure
The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps
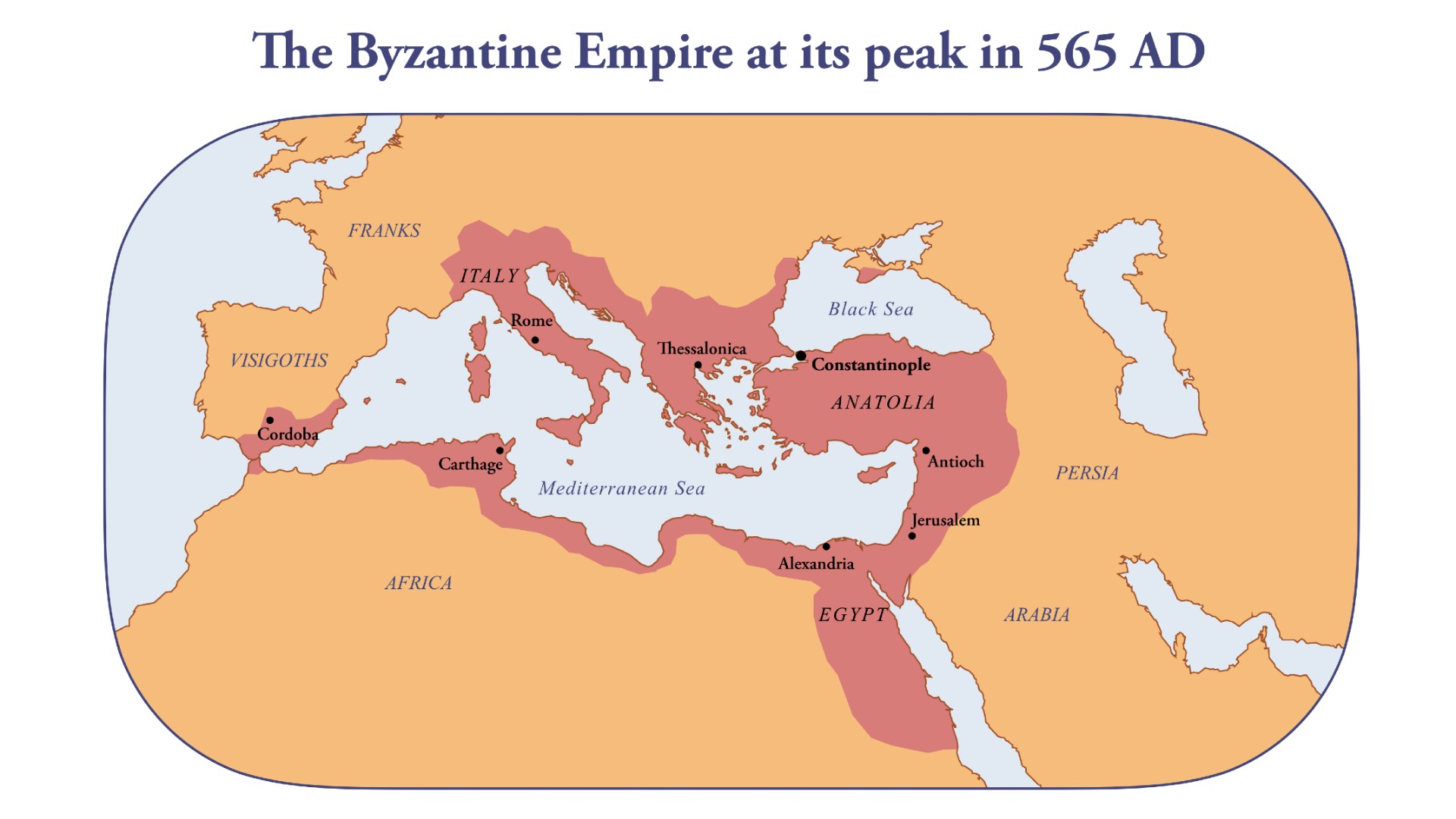
The Byzantine Empire, a powerful and influential civilization that spanned over a millennium, left behind a rich tapestry of history and culture. One of the most fascinating aspects of this legacy is the evolution of its flags and the intricate geographical landscape that defined its existence. Examining the Byzantine Empire’s flag map allows us to understand the shifting tides of power, the complex interplay of cultures, and the enduring symbols that defined this remarkable empire.
The Evolution of Byzantine Flags: A Tale of Imperial Identity
The Byzantine Empire, inheriting the legacy of the Roman Empire, embraced a rich tradition of heraldry. Its flags, often referred to as "labarums," were not merely decorative elements but powerful symbols of authority, faith, and imperial ambition.
Early Years: The Cross and the Emperor
The earliest Byzantine flags were simple yet profound. A prominent feature was the cross, a symbol of Christianity, reflecting the empire’s strong religious identity. The cross was often depicted on a field of purple, the imperial color, representing the emperor’s divine mandate. This early design emphasized the close relationship between the emperor and the Church, a defining characteristic of Byzantine society.
The Rise of the Double-Headed Eagle:
The iconic double-headed eagle, often associated with the Byzantine Empire, emerged later in its history. This symbol, representing power and dominion over both east and west, was first adopted in the 10th century. The eagle, with its wings spread wide, symbolized the empire’s ambition to restore the Roman Empire’s former glory. The double head symbolized the empire’s dual identity: a continuation of the Roman tradition while embracing a distinctly Eastern Christian character.
The "Christogram" and the "Tetramorph":
As the empire evolved, its flags became more elaborate. The "Christogram," a monogram combining the first two letters of the Greek word "Christos," was frequently incorporated, further emphasizing the importance of Christianity. Another significant symbol was the "Tetramorph," depicting the four evangelists as a lion, an ox, a man, and an eagle, representing the divine authority of the empire.
Regional Variations and Symbolic Significance:
While the double-headed eagle became the most prominent symbol, regional variations existed. Some Byzantine emperors adopted personal emblems, incorporating elements like lions, griffins, or specific colors, reflecting their individual ambitions and family lineage. These regional variations, while acknowledging the central authority of the emperor, also highlighted the diversity of the empire’s cultural and political landscape.
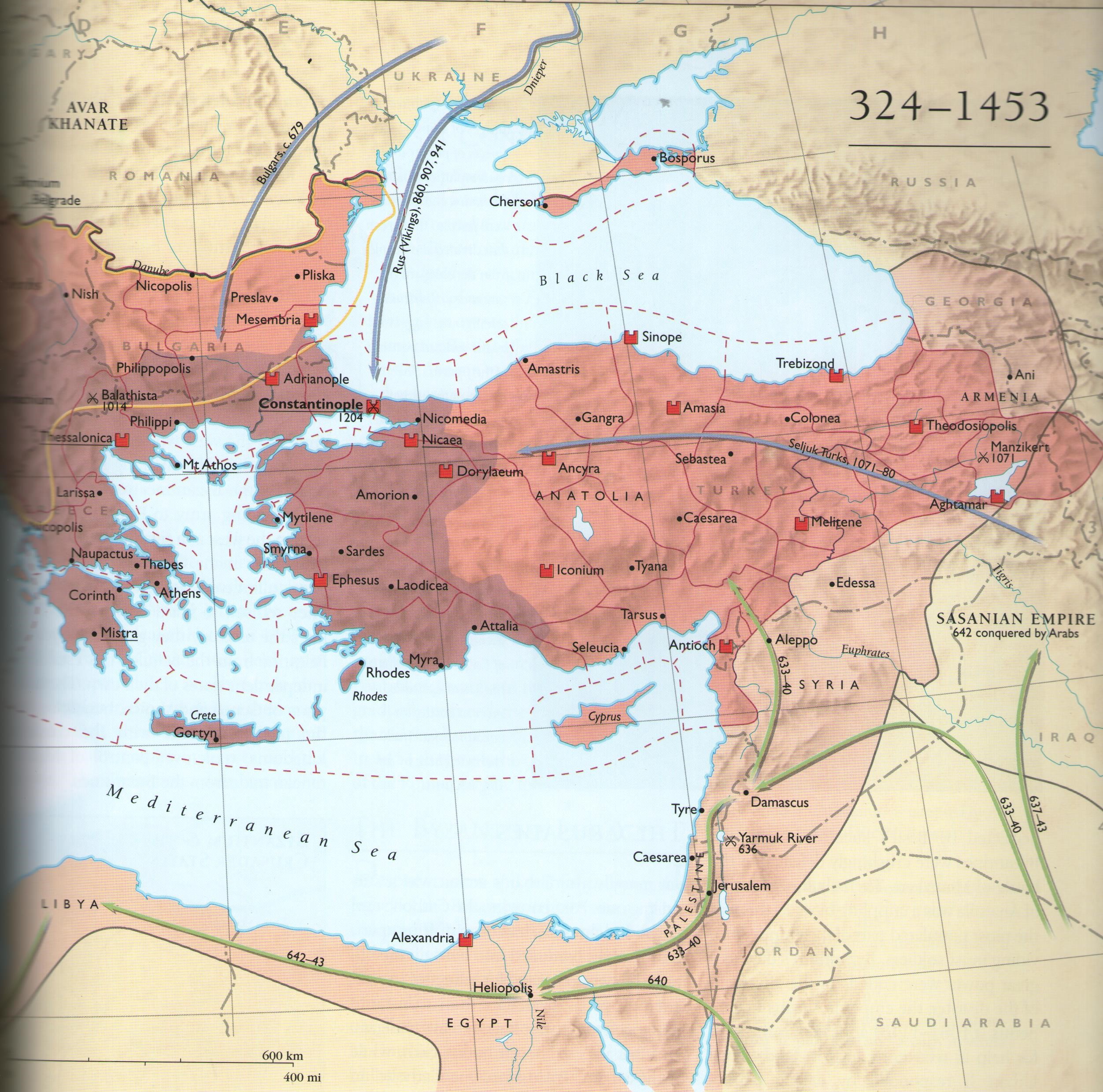
The Byzantine Empire on the Map: A Dynamic Tapestry of Territories
The map of the Byzantine Empire is a testament to its fluctuating fortunes and territorial changes over centuries. It’s not a static entity but a dynamic landscape that reflects the empire’s expansion, contraction, and resilience.
The Golden Age:
During the 6th and 7th centuries, the Byzantine Empire reached its zenith, stretching from the Balkans to North Africa and encompassing vast swathes of the Eastern Mediterranean. This period saw the empire’s cultural and economic flourishing, solidifying its position as a dominant force in the region.
The Loss of Territories:
The empire’s fortunes began to decline in the 7th and 8th centuries, facing challenges from the Arab conquests and internal strife. The loss of key territories, including Egypt, Syria, and North Africa, significantly reduced the empire’s geographical reach. However, it managed to retain control of the Balkans, Anatolia, and parts of the Mediterranean coast.
The Macedonian Renaissance:
The 9th and 10th centuries witnessed a resurgence of the empire under the Macedonian dynasty. A period of economic and military prosperity led to the reconquest of territories lost to the Arabs and the expansion into Bulgaria and the south of Italy. This period is marked by a renewed sense of imperial ambition and a return to the cultural and political heights of the earlier era.
The Last Centuries:
The 13th and 14th centuries saw the empire facing increasing pressure from the Seljuk Turks and the Latin Crusaders. The empire contracted further, losing most of its Asian territories and facing internal divisions. The final centuries were marked by a gradual decline, culminating in the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks in 1453.
The Enduring Legacy: A Visual Representation of Byzantine Influence
The Byzantine Empire’s flag map serves as a visual testament to its enduring legacy. Even after its fall, the empire’s symbols, its cultural influence, and its geographical footprint continued to resonate across Europe and the Middle East.
The Double-Headed Eagle:
The double-headed eagle, adopted by the Byzantine Empire, became a prominent symbol of imperial power in Eastern Europe. It was adopted by the Russian Empire, the Holy Roman Empire, and various Balkan states, reflecting the lasting influence of the Byzantine tradition.
The Orthodox Church:
The Byzantine Empire’s legacy also extended to the realm of religion. The Orthodox Church, which emerged from the Byzantine tradition, became a dominant force in Eastern Europe and the Balkans. The empire’s cultural and religious influence is still evident in the architecture, art, and customs of these regions.
The Legacy of Constantinople:
The city of Constantinople, the empire’s capital, remained a significant cultural and trading center even after its conquest by the Ottomans. Its strategic location and its rich history continued to attract merchants, scholars, and travelers, making it a bridge between East and West.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Byzantine Empire’s Flag Map
1. What is the significance of the color purple in Byzantine flags?
Purple, a costly dye derived from shellfish, was associated with royalty and imperial power. It symbolized the emperor’s divine mandate and his connection to the divine.
2. Why did the double-headed eagle become such a prominent symbol in the Byzantine Empire?
The double-headed eagle symbolized the empire’s dual identity: a continuation of the Roman tradition while embracing a distinctly Eastern Christian character. It represented dominion over both east and west, reflecting the empire’s ambition to restore the Roman Empire’s former glory.
3. Did the Byzantine Empire have a national flag in the modern sense?
The Byzantine Empire did not have a single national flag in the modern sense. Instead, it used a variety of flags, each with its own symbolic significance, depending on the context, the emperor, or the specific event.
4. How did the Byzantine flag map change over time?
The Byzantine flag map changed significantly over time, reflecting the empire’s fluctuating fortunes and territorial changes. It expanded during periods of prosperity and contracted during times of decline. The loss of key territories and the emergence of new empires impacted the empire’s geographical boundaries.
5. What is the significance of the Byzantine flag map in understanding the empire’s history?
The Byzantine flag map offers a visual representation of the empire’s history, its territorial expansion and contraction, its cultural influence, and its enduring legacy. It helps us understand the empire’s complex political landscape, its religious identity, and its cultural impact on the wider world.
Tips for Understanding the Byzantine Empire’s Flag Map
1. Explore the evolution of Byzantine flags: Examining the different flags used by the Byzantine Empire over time provides insights into the empire’s evolving identity, religious beliefs, and political ambitions.
2. Connect the flag map with historical events: Understanding the historical context behind territorial changes and the rise and fall of dynasties helps to make sense of the dynamic nature of the Byzantine flag map.
3. Analyze the symbolism of the flags: The symbols used on Byzantine flags, such as the cross, the double-headed eagle, and the "Christogram," provide clues about the empire’s religious beliefs, political ideology, and cultural influences.
4. Compare the Byzantine flag map with other historical maps: Comparing the Byzantine flag map with maps of other empires and civilizations helps to understand the empire’s geographical context and its interactions with other powers.
5. Engage with primary sources: Studying primary sources, such as Byzantine chronicles, historical texts, and archaeological evidence, provides a deeper understanding of the empire’s flag map and its significance.
Conclusion: The Enduring Influence of a Visual Legacy
The Byzantine Empire’s flag map is not merely a historical artifact but a powerful symbol of a civilization’s enduring legacy. It reflects the empire’s rich history, its cultural achievements, and its enduring influence on the world. By understanding the symbolism of its flags and the dynamic nature of its geographical boundaries, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and richness of this remarkable civilization. The Byzantine Empire, through its flags and its map, continues to inspire and captivate, offering a glimpse into a world of faith, power, and enduring cultural influence.
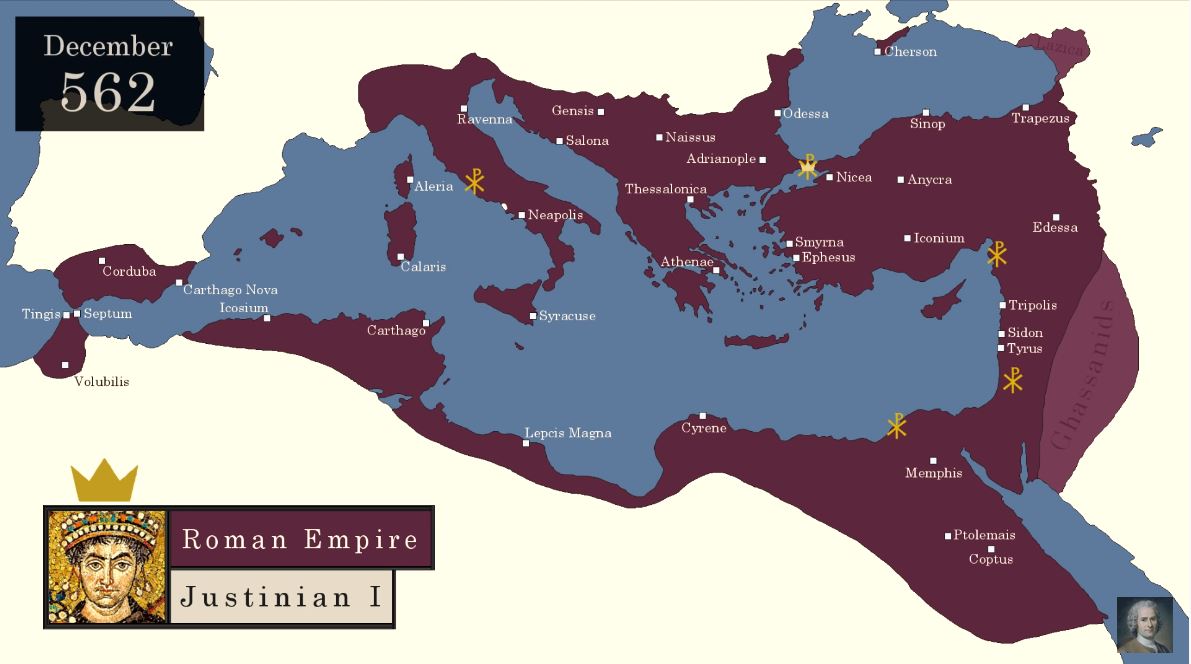
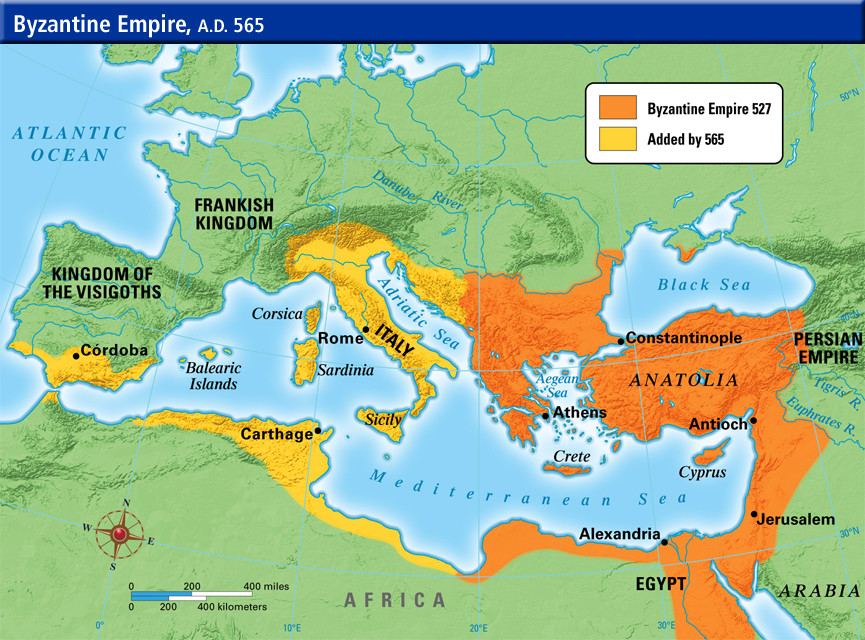
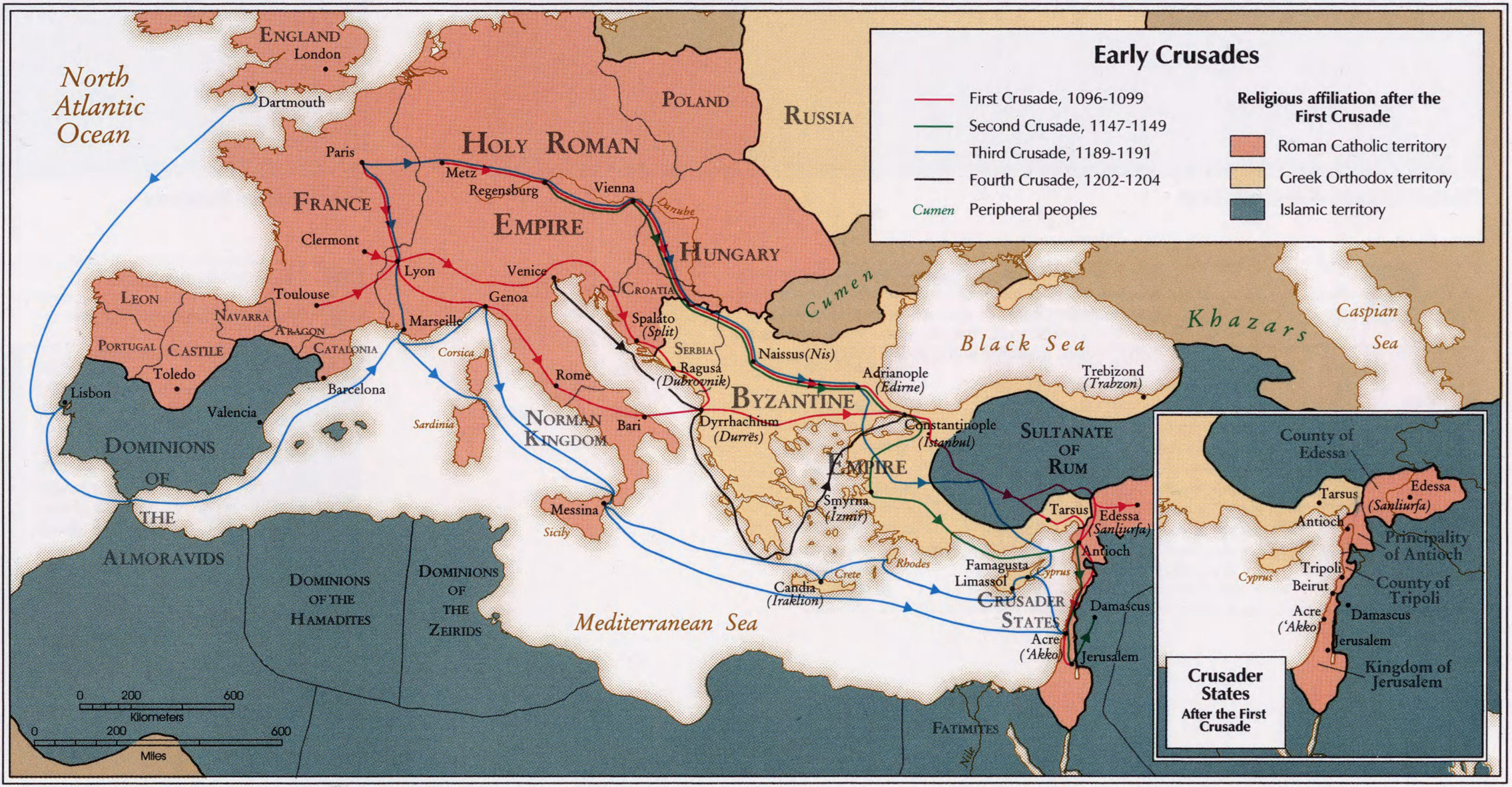




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Byzantine Empire: A Visual Journey Through Flags and Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!