The Concept of "Map Flag Not Valid" in Geographic Data and its Implications
Related Articles: The Concept of "Map Flag Not Valid" in Geographic Data and its Implications
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Concept of "Map Flag Not Valid" in Geographic Data and its Implications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Concept of "Map Flag Not Valid" in Geographic Data and its Implications
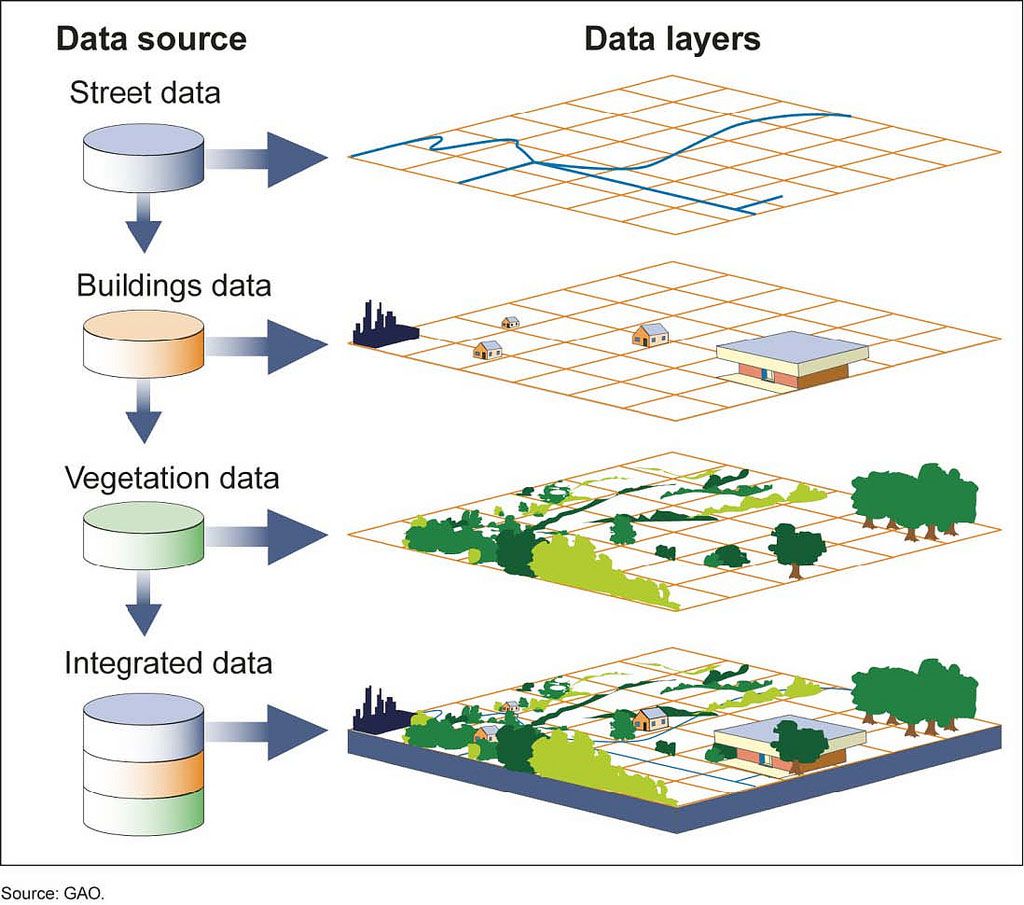
The phrase "map flag not valid" is not a standard term in the realm of geographic information systems (GIS) or cartography. However, it likely refers to situations where data associated with a specific location on a map is deemed inaccurate, unreliable, or incomplete. This could arise due to various factors, including:
1. Data Acquisition Errors:
- Inaccurate GPS readings: GPS devices can be affected by atmospheric conditions, signal interference, or even deliberate manipulation, resulting in inaccurate location data.
- Human error: Data entry mistakes, misinterpretation of field observations, or incorrect data processing can lead to errors in the map’s representation.
- Outdated data: Maps are often based on data collected at specific points in time. As environments evolve, infrastructure changes, or new information becomes available, the data on the map may become outdated and inaccurate.
2. Data Integrity Issues:
- Missing or incomplete data: A map might lack crucial information about a specific location, making it difficult to draw reliable conclusions. This could include missing attribute data, such as elevation, population density, or land use classification.
- Data inconsistencies: Inconsistencies between different data sources can lead to conflicting information and inaccurate representations. For example, a map might display a road as paved when it’s actually unpaved due to discrepancies between the road network dataset and the land cover data.
- Data corruption: Data files can become corrupted due to technical errors, software issues, or external factors, leading to inaccurate or missing information.
3. Data Quality Control:
- Lack of proper validation: Data should be rigorously checked for accuracy and consistency before being incorporated into maps. Without proper validation, errors can easily propagate through the entire system, leading to misleading representations.
- Insufficient data quality standards: The absence of clear and consistent data quality standards can result in varying levels of accuracy across different data sources, making it challenging to create reliable maps.
Understanding the Implications of "Map Flag Not Valid"
The consequences of using invalid or inaccurate map data can be significant, ranging from minor inconveniences to major financial losses and safety risks:
1. Navigation Errors:
- Misleading directions: Inaccurate maps can lead to drivers taking incorrect routes, potentially resulting in delays, increased fuel consumption, and even accidents.
- Difficulty in locating destinations: Users may struggle to find specific locations if the map data is incorrect or incomplete, leading to frustration and wasted time.
2. Planning and Development Errors:
- Infrastructure projects: Misleading data can lead to costly mistakes in infrastructure planning, such as building roads in areas with unsuitable terrain or constructing buildings on land with restricted access.
- Resource management: Inaccurate data can result in inefficient resource allocation, such as allocating water resources to areas with lower demand or building housing developments in areas with insufficient infrastructure.
3. Environmental and Safety Risks:
- Environmental hazards: Maps that misrepresent environmental features, such as flood zones or areas with high pollution levels, can put individuals and communities at risk.
- Public safety: Inaccurate maps can hinder emergency response efforts, making it difficult for first responders to locate victims or access emergency areas.
FAQs: Addressing the "Map Flag Not Valid" Concept
1. How can I identify "map flag not valid" situations?
- Examine the data sources and their reliability.
- Check for inconsistencies and conflicting information.
- Look for missing or incomplete data points.
- Evaluate the accuracy and precision of the data based on the intended use.
2. What are the best practices for avoiding "map flag not valid" situations?
- Utilize high-quality data sources with clear documentation and provenance.
- Implement rigorous data quality control procedures, including validation and verification steps.
- Establish clear data quality standards and ensure adherence to those standards.
- Regularly update and maintain the data to reflect changes in the real world.
3. What are the consequences of ignoring "map flag not valid" issues?
- Inaccurate decisions based on flawed data.
- Financial losses due to costly mistakes.
- Safety risks for individuals and communities.
- Damage to the reputation of organizations using the data.
4. How can I ensure the validity of map data?
- Use reputable data sources and data providers.
- Implement data validation tools and procedures.
- Employ experienced cartographers and GIS professionals to analyze and interpret data.
- Continuously monitor and update data to maintain its accuracy and relevance.
Tips for Mitigating "Map Flag Not Valid" Issues
- Data provenance: Track the origin and history of data to understand its reliability and potential biases.
- Data visualization: Use maps and charts to visually identify inconsistencies and patterns in data.
- Data aggregation: Combine data from multiple sources to create a more comprehensive and accurate representation.
- Data analysis: Employ statistical and spatial analysis techniques to identify outliers and potential errors.
- User feedback: Encourage users to report errors and inconsistencies in map data.
Conclusion
While the term "map flag not valid" is not a standard term, it highlights a crucial aspect of geographic data management: the importance of data quality and accuracy. Ensuring the validity of map data is essential for making informed decisions, minimizing risks, and maximizing the benefits of geographic information. By employing rigorous data quality control practices, utilizing reputable data sources, and continuously monitoring data for accuracy, we can mitigate the risks associated with "map flag not valid" situations and ensure the reliability of our maps.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Concept of "Map Flag Not Valid" in Geographic Data and its Implications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!