The Earth Transformed: A World Without Ice Caps
Related Articles: The Earth Transformed: A World Without Ice Caps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Earth Transformed: A World Without Ice Caps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth Transformed: A World Without Ice Caps

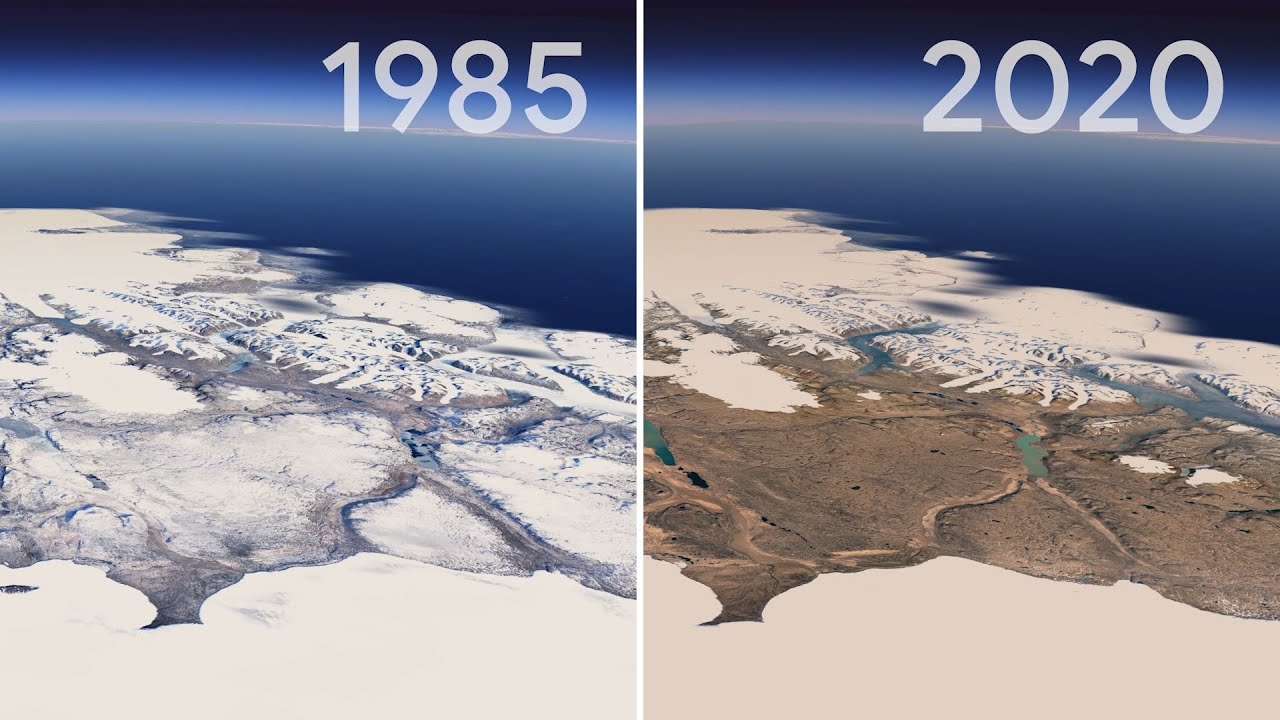
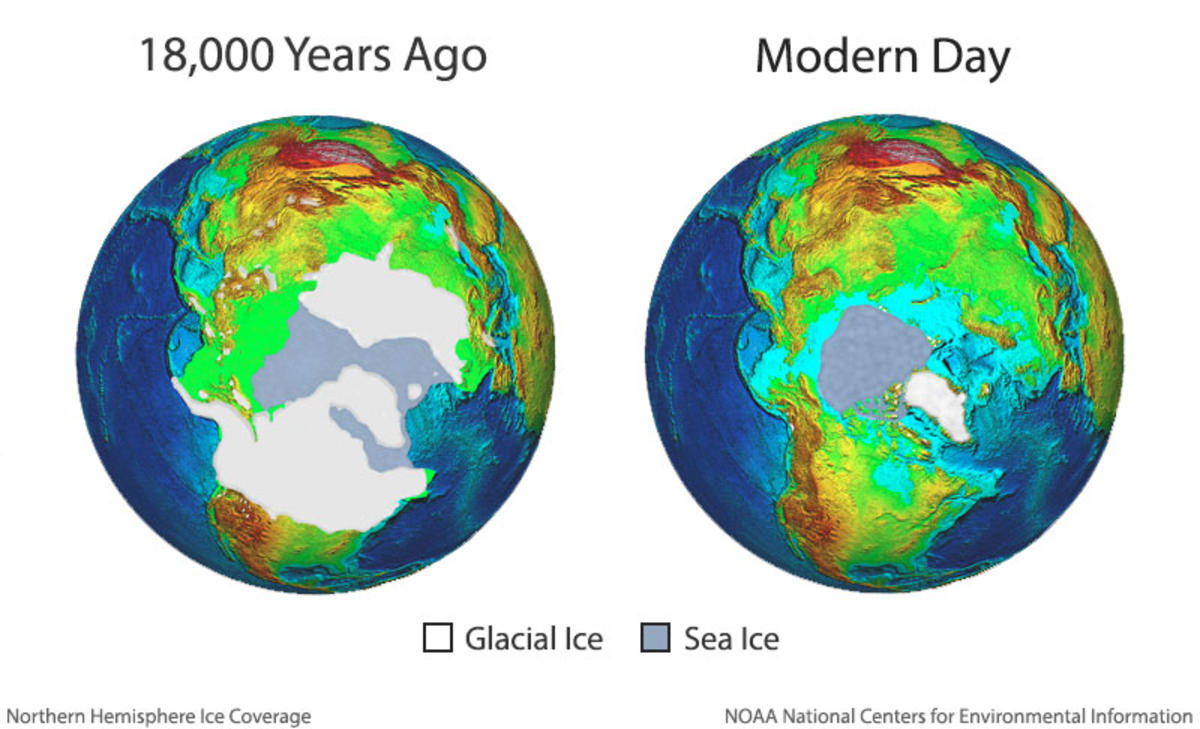
The Earth’s ice caps, vast reservoirs of frozen water covering Greenland, Antarctica, and high-altitude regions, play a crucial role in regulating global climate and shaping the planet’s geography. However, under the influence of climate change, these icy giants are shrinking at an alarming rate. While the complete melting of the ice caps is a distant prospect, its potential consequences are profound, radically altering coastlines, impacting ecosystems, and reshaping the world as we know it.
A World Reshaped by Rising Seas:
The most immediate and visible consequence of ice cap melting is the rise in global sea levels. As glacial ice melts, the water flows into the oceans, causing them to expand and encroach upon landmasses. This phenomenon, already underway, threatens coastal communities worldwide.
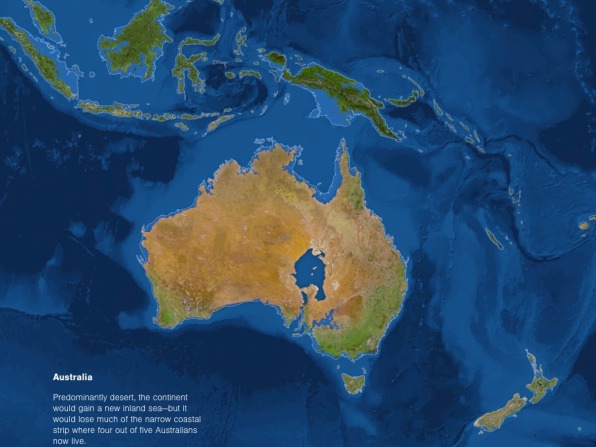
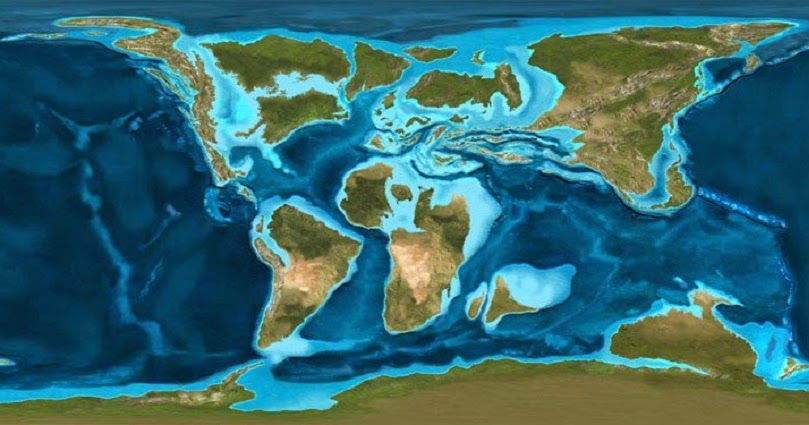
A map depicting the Earth after the complete melting of the ice caps would reveal a dramatically altered coastline. Low-lying islands and coastal regions would be submerged, displacing millions of people and causing significant economic and social disruption. Major cities like New York, London, Shanghai, and Tokyo would face substantial flooding, necessitating massive infrastructure adjustments and relocation efforts.
Beyond the Coastlines:
The impact of ice cap melting extends far beyond coastal areas. As the ice sheets shrink, they expose vast tracts of land previously covered by ice. This newly revealed terrain presents both opportunities and challenges.
- Resource Exploration: The melting ice could unlock access to previously inaccessible mineral resources, including oil, gas, and valuable minerals. However, the potential environmental impact of resource extraction in these sensitive regions must be carefully considered.
- New Navigation Routes: The melting of Arctic ice opens up new shipping routes, potentially reducing travel times and costs. However, this development also raises concerns about environmental damage, increased shipping traffic, and geopolitical tensions.
- Ecosystem Changes: The melting of glaciers and ice sheets disrupts delicate ecosystems, affecting freshwater availability, altering habitats, and impacting biodiversity. The loss of glacial meltwater, a crucial source of water for many regions, could lead to water scarcity and conflict.
A Complex and Uncertain Future:
The melting of ice caps is a complex process with far-reaching consequences. While the complete melting of the ice caps is unlikely to occur in the near future, the ongoing melting poses significant risks and challenges.
- Climate Feedback Loops: The melting of ice caps accelerates climate change by reducing the Earth’s albedo (reflectivity), causing more sunlight to be absorbed by the planet. This creates a feedback loop where warmer temperatures lead to more melting, further accelerating the process.
- Global Climate Instability: The disruption of ocean currents caused by melting ice caps can lead to unpredictable weather patterns, extreme events, and changes in regional climates.
- Social and Economic Disruptions: The displacement of populations, loss of infrastructure, and disruption of economic activities due to rising sea levels could trigger social unrest, political instability, and global migration.
Addressing the Challenge:
The melting of ice caps is a global challenge requiring international cooperation and decisive action.
- Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices is crucial to mitigating climate change and slowing the rate of ice cap melting.
- Adaptation: Developing strategies for adapting to the impacts of rising sea levels, including sea walls, flood control systems, and sustainable land use planning, is essential for protecting coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring of ice cap dynamics, climate change impacts, and potential solutions are vital for understanding the scale of the problem and developing effective responses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How long will it take for the ice caps to melt completely?
A: The complete melting of the ice caps is a long-term process that could take centuries or even millennia to complete. The rate of melting is influenced by various factors, including global temperatures, greenhouse gas emissions, and natural fluctuations in climate.
Q: What are the potential benefits of ice cap melting?
A: While the potential benefits of ice cap melting are limited, they include access to new resources, potential for new shipping routes, and the possibility of expanding agricultural land in some regions. However, these potential benefits must be weighed against the significant environmental and societal risks associated with melting ice caps.
Q: What can individuals do to address the issue of ice cap melting?
A: Individuals can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by adopting sustainable practices, such as reducing energy consumption, using public transport, and supporting renewable energy sources. Engaging in advocacy and raising awareness about climate change and its impacts can also contribute to driving policy changes and promoting sustainable solutions.
Tips for Understanding and Addressing the Issue of Ice Cap Melting:
- Stay informed: Stay updated on the latest scientific research and data regarding ice cap melting, climate change, and its consequences.
- Support sustainable practices: Adopt eco-friendly habits in your daily life, such as reducing energy consumption, using public transport, and consuming less meat.
- Engage in advocacy: Support organizations and initiatives working to address climate change and promote sustainable solutions.
- Educate others: Share information and raise awareness about the importance of protecting the environment and mitigating climate change.
Conclusion:
The melting of ice caps is a stark reminder of the urgent need to address climate change. The consequences of this phenomenon are profound, impacting coastlines, ecosystems, and societies worldwide. While the complete melting of ice caps is a distant prospect, the ongoing melting poses significant risks and challenges. By understanding the complex dynamics of ice cap melting, taking decisive action to mitigate climate change, and adapting to its impacts, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.

![Earth without ice caps, 60m sea rise [16200x8100] : r/MapPorn](https://preview.redd.it/2jrgg01sg4kz.jpg?width=1080u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=77e78680efb90cc607525ad2a9dc51cb9623d620)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth Transformed: A World Without Ice Caps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!