The Earth’s Interconnected Systems: A Comprehensive View
Related Articles: The Earth’s Interconnected Systems: A Comprehensive View
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Earth’s Interconnected Systems: A Comprehensive View. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth’s Interconnected Systems: A Comprehensive View
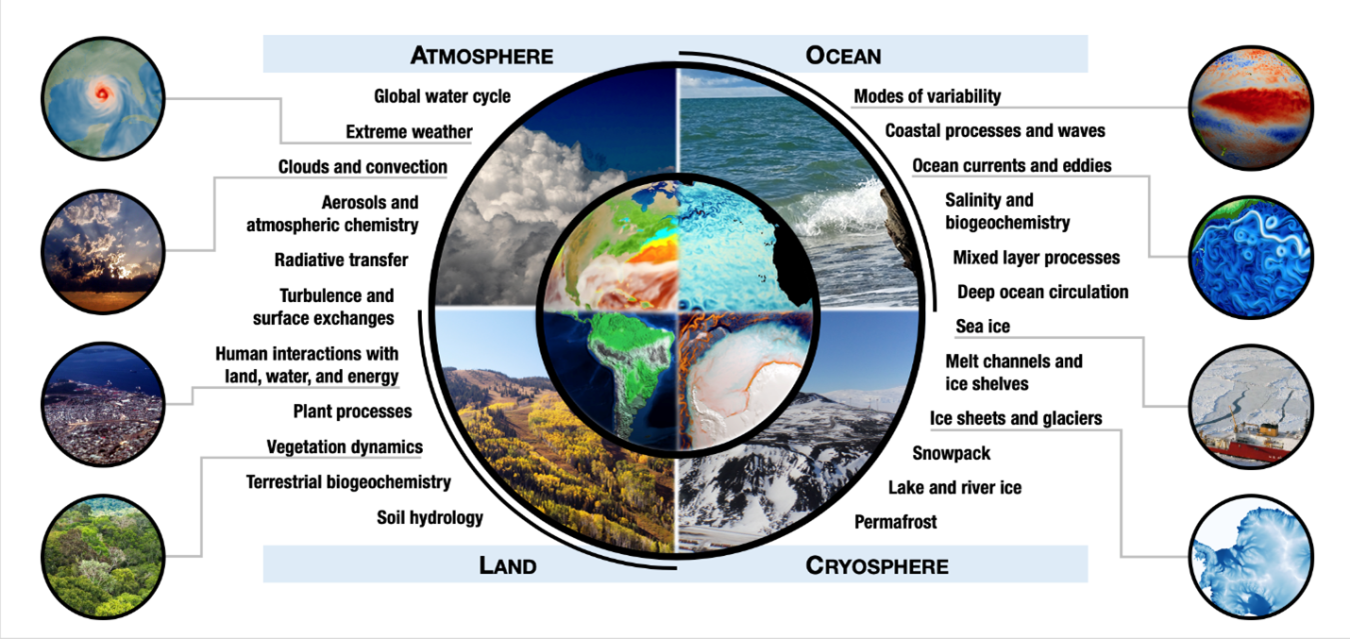
Our planet Earth is not a static entity but a dynamic, interconnected system composed of four major subsystems: the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere. These subsystems interact and influence each other in intricate ways, creating the complex and diverse environment we inhabit. Understanding these interactions is crucial for comprehending the Earth’s past, present, and future.
1. The Atmosphere: A Blanket of Gases
The atmosphere, the gaseous layer surrounding the Earth, plays a vital role in regulating temperature, weather patterns, and the distribution of life. Composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), it also contains trace amounts of other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ozone.
Key Features:
- Temperature Regulation: The atmosphere acts as a blanket, trapping heat from the sun and preventing drastic temperature fluctuations between day and night.
- Weather and Climate: Atmospheric circulation patterns, driven by solar energy and the Earth’s rotation, create weather systems like storms and influence long-term climate patterns.
- Protection from Harmful Radiation: The ozone layer within the stratosphere absorbs most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, protecting life on Earth.
- Compositional Variations: The atmosphere is stratified into distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and composition.
2. The Hydrosphere: The Global Water Cycle
The hydrosphere encompasses all the water on Earth, including oceans, lakes, rivers, groundwater, and ice. This dynamic system is constantly in motion, driven by the water cycle.
Key Features:
- Water Cycle: The continuous movement of water through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff regulates the distribution of water across the planet.
- Climate Regulation: Water has a high heat capacity, moderating temperatures and influencing climate patterns.
- Habitat for Life: The hydrosphere provides a vital habitat for a vast array of aquatic organisms.
- Resource for Life: Water is essential for all living organisms, playing a critical role in biological processes.
3. The Geosphere: The Solid Earth
The geosphere encompasses the Earth’s solid, rocky outer layer, including the crust, mantle, and core. It is a dynamic system characterized by geological processes like plate tectonics, volcanism, and erosion.
Key Features:
- Plate Tectonics: The Earth’s crust is divided into large plates that move and interact, causing earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation.
- Rock Cycle: Rocks are continuously transformed through processes like weathering, erosion, deposition, and metamorphism.
- Mineral Resources: The geosphere contains valuable mineral resources, including metals, fuels, and building materials.
- Landforms: Geological processes shape the Earth’s surface, creating diverse landforms like mountains, valleys, and plains.
4. The Biosphere: The Realm of Life
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on Earth, from microscopic bacteria to towering trees, along with their interactions with the environment. It is the most complex and diverse subsystem, driven by the flow of energy and nutrients.
Key Features:
- Ecosystems: Living organisms interact with their physical environment to form complex ecosystems, with intricate webs of food chains and nutrient cycles.
- Biodiversity: The biosphere exhibits incredible biodiversity, with millions of species inhabiting diverse environments.
- Evolution and Adaptation: Living organisms evolve and adapt to changing environmental conditions, driving the constant evolution of life on Earth.
- Essential Services: The biosphere provides essential services to humans, including food, clean air and water, and regulation of climate.
Interconnections and Feedback Loops
The four subsystems of Earth are not isolated but interconnected in complex ways. Changes in one subsystem can trigger responses in others, creating intricate feedback loops that influence the overall functioning of the Earth system.
Examples:
- Greenhouse Effect: Increased atmospheric carbon dioxide, released through human activities, traps more heat, leading to global warming.
- Ocean Acidification: Increased atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves into the ocean, making it more acidic, impacting marine ecosystems.
- Deforestation: Removing forests disrupts the carbon cycle, affects water cycles, and reduces biodiversity.
Understanding these interconnections is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and ensuring the sustainability of our planet.
FAQs by 4 Subsystems of the Earth Concept Map
Atmosphere:
-
Q: What are the main factors that influence atmospheric circulation patterns?
- A: Atmospheric circulation is driven by unequal heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun, the Earth’s rotation, and differences in air pressure.
-
Q: How does the atmosphere protect life from harmful radiation?
- A: The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing it from reaching the Earth’s surface.
-
Q: What are the main causes of air pollution?
- A: Air pollution can be caused by both natural sources like volcanic eruptions and human activities like burning fossil fuels and industrial emissions.
Hydrosphere:
-
Q: What is the role of the water cycle in regulating the Earth’s climate?
- A: The water cycle helps regulate climate by transporting heat and moisture around the globe, influencing temperature and precipitation patterns.
-
Q: What are the main threats to water resources?
- A: Water resources are threatened by pollution, overuse, and climate change, which can alter precipitation patterns and lead to droughts.
-
Q: How does ocean circulation influence global climate?
- A: Ocean currents transport heat and nutrients around the globe, influencing regional climates and supporting marine ecosystems.
Geosphere:
-
Q: What is the evidence for plate tectonics?
- A: Evidence for plate tectonics includes the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes, the fit of continents, and the presence of similar fossils on distant continents.
-
Q: How do geological processes influence the formation of landforms?
- A: Geological processes like plate tectonics, erosion, and deposition shape the Earth’s surface, creating diverse landforms like mountains, valleys, and plains.
-
Q: What are the potential risks associated with volcanic eruptions?
- A: Volcanic eruptions can pose risks to human life and property through ash fall, lava flows, and gas emissions.
Biosphere:
-
Q: What are the main threats to biodiversity?
- A: Biodiversity is threatened by habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
-
Q: How do ecosystems provide essential services to humans?
- A: Ecosystems provide essential services like food production, clean air and water, regulation of climate, and pollination.
-
Q: What is the role of evolution in the biosphere?
- A: Evolution drives the constant adaptation of living organisms to changing environmental conditions, shaping the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Tips by 4 Subsystems of the Earth Concept Map
Atmosphere:
- Reduce your carbon footprint: Choose sustainable transportation, conserve energy, and support policies that promote clean energy sources.
- Be mindful of air quality: Stay informed about air quality alerts and take precautions during periods of high pollution.
- Support research on climate change: Encourage investment in research and innovation to address the challenges of climate change.
Hydrosphere:
- Conserve water: Take shorter showers, fix leaks promptly, and use water-efficient appliances.
- Reduce pollution: Properly dispose of chemicals and avoid using excessive fertilizers and pesticides.
- Support sustainable water management practices: Encourage the development of water conservation and management strategies.
Geosphere:
- Support responsible mining practices: Advocate for sustainable mining practices that minimize environmental damage.
- Be aware of seismic hazards: Learn about the risks of earthquakes and tsunamis in your region and take appropriate precautions.
- Promote sustainable land use: Encourage responsible land management practices that conserve natural resources and minimize erosion.
Biosphere:
- Support conservation efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect biodiversity and restore ecosystems.
- Reduce your consumption: Make conscious choices about the products you buy and the impact they have on the environment.
- Educate yourself and others: Spread awareness about the importance of biodiversity and the threats it faces.
Conclusion by 4 Subsystems of the Earth Concept Map
The four subsystems of the Earth are interconnected and constantly interacting, creating a dynamic and complex system. Understanding these interactions is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and ensuring the sustainability of our planet. By recognizing the interconnectedness of the Earth’s systems and promoting sustainable practices, we can contribute to a healthier and more resilient planet for generations to come.

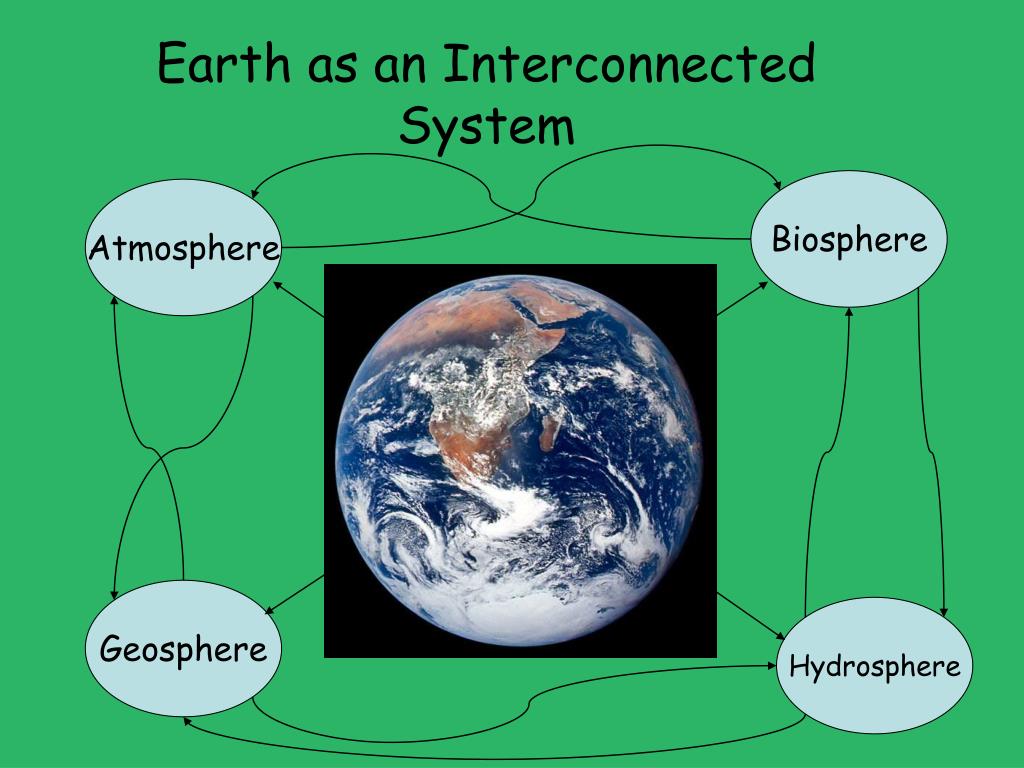

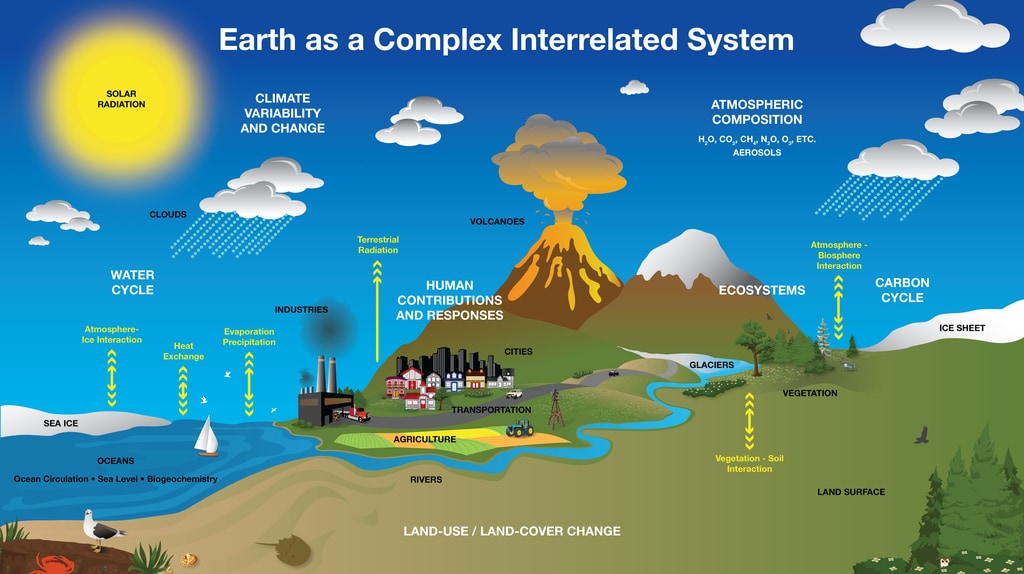

![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Earth Systems - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TieYKwde-3o/maxresdefault.jpg)
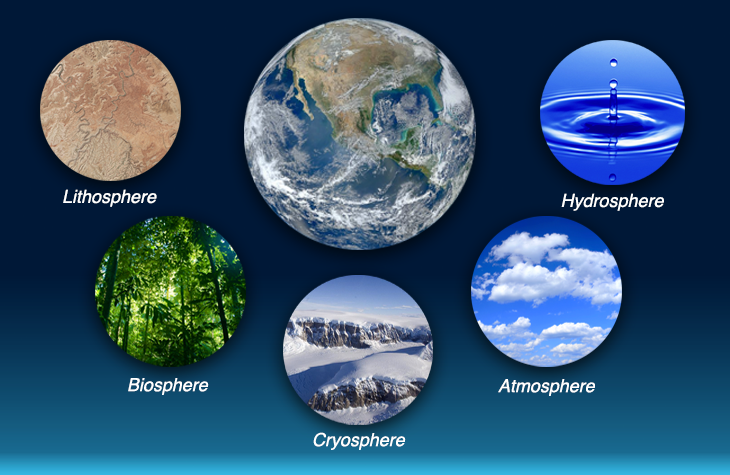


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth’s Interconnected Systems: A Comprehensive View. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!