The Earth’s Map: A Window to Our World
Related Articles: The Earth’s Map: A Window to Our World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Earth’s Map: A Window to Our World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth’s Map: A Window to Our World
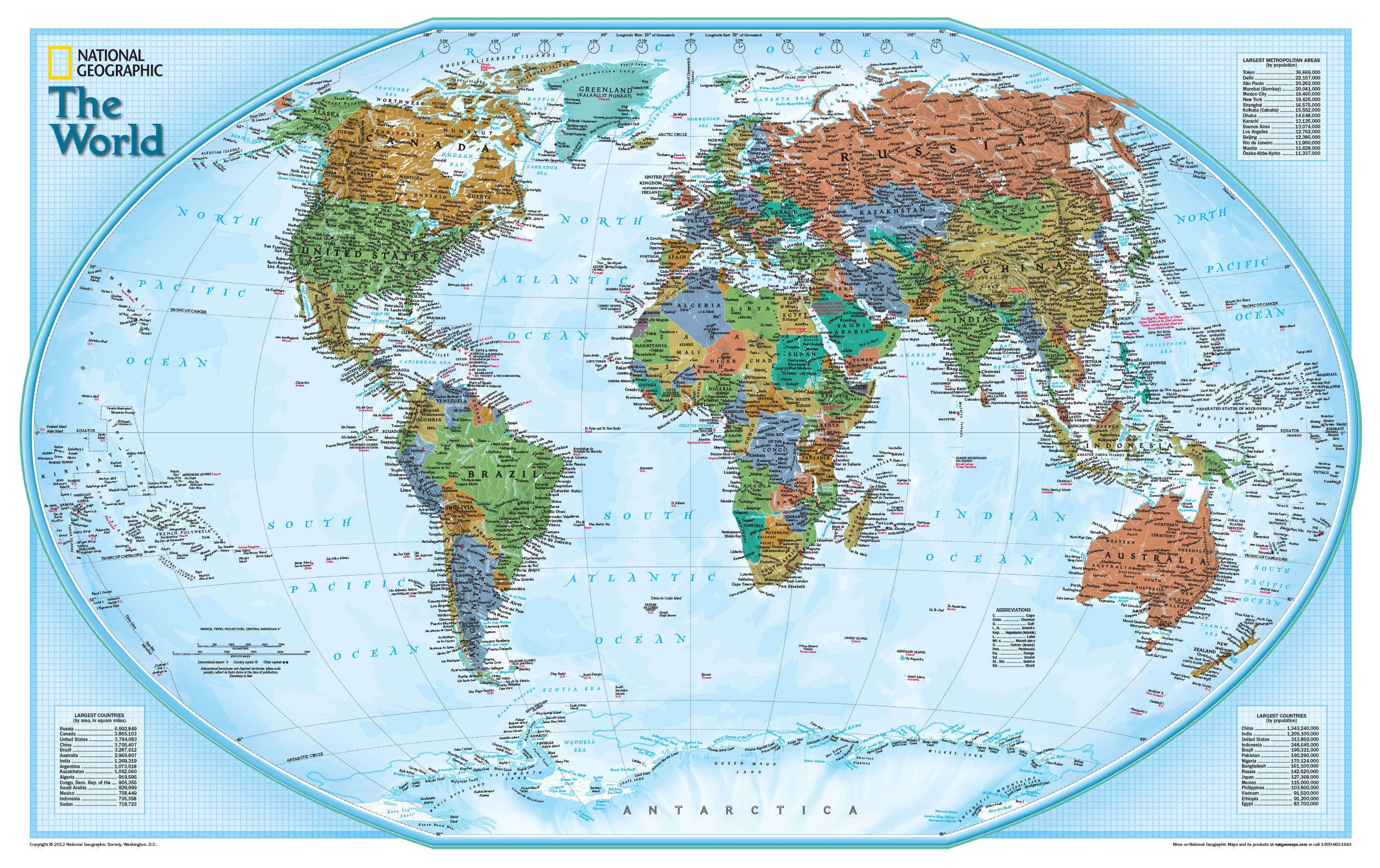
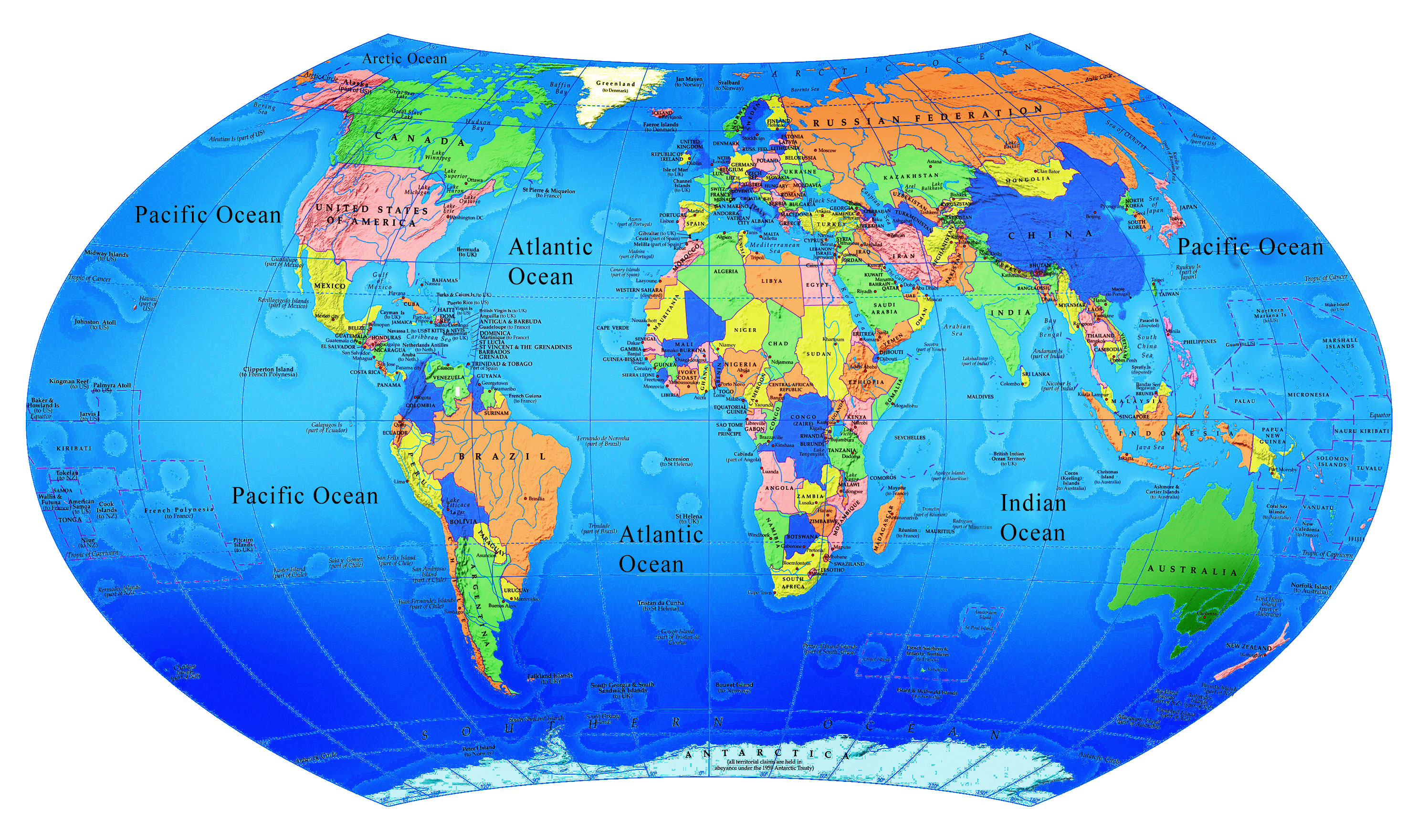
The Earth’s map, a seemingly simple representation of our planet, is in fact a powerful tool that unlocks a vast array of information and understanding. It serves as a visual key to the world, enabling us to navigate, explore, and comprehend the intricate relationships between its diverse elements.
A History of Representation
The earliest attempts at depicting the Earth date back to ancient civilizations, with rudimentary maps etched onto clay tablets, papyrus scrolls, and cave walls. These early maps, often based on observations and speculation, served as rudimentary guides for navigation and exploration.
As scientific knowledge advanced, so too did the accuracy and detail of maps. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized mapmaking, allowing for mass production and dissemination. This spurred a surge in exploration and cartographic innovation, culminating in the development of more precise and comprehensive maps.
Types of Maps: A Visual Language
Maps are not merely static representations but rather dynamic tools that communicate information in various ways. The type of map used depends on the specific information being conveyed.
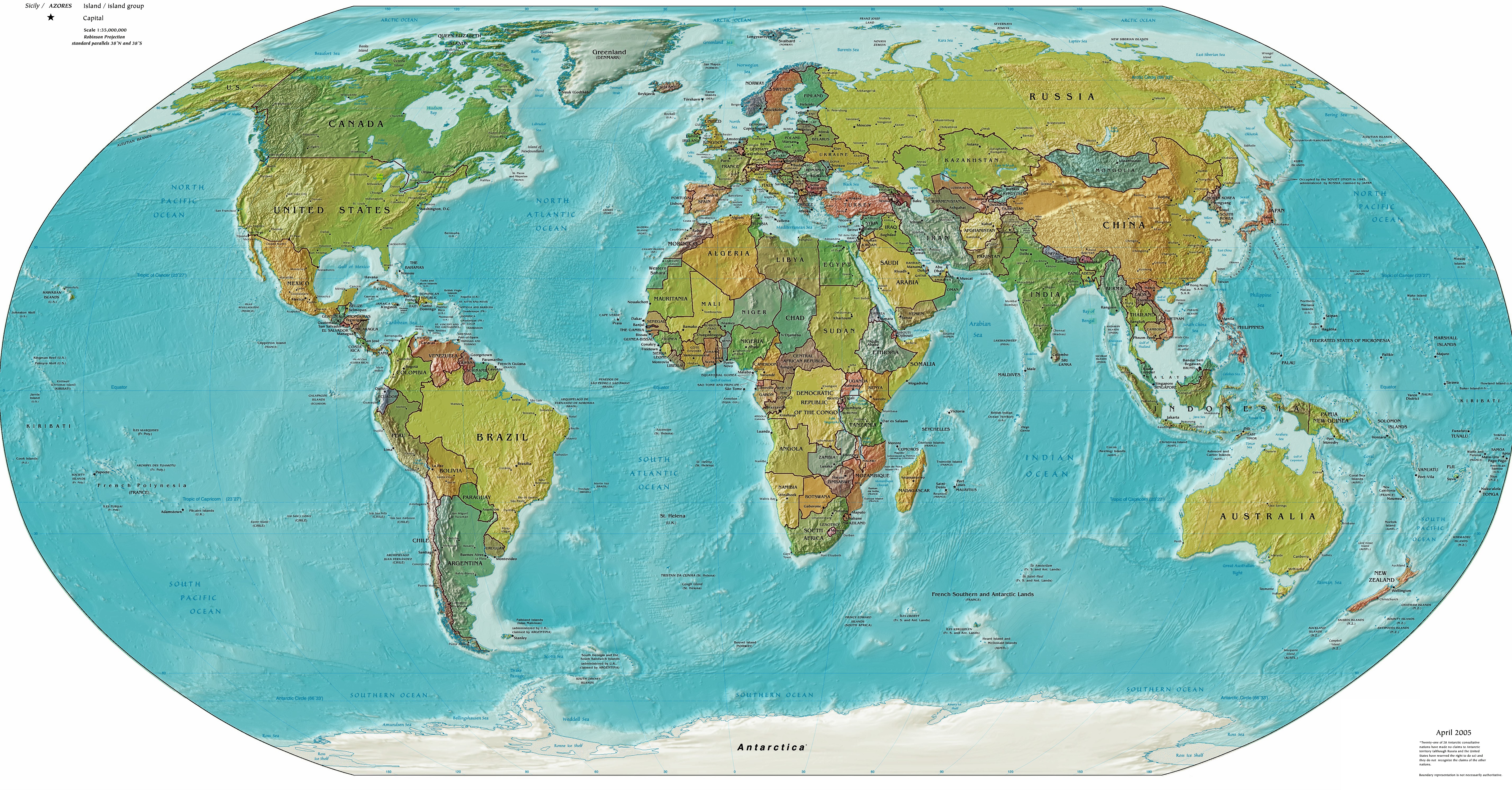
- Political Maps: These maps emphasize political boundaries, showing countries, states, and other administrative divisions. They are essential for understanding geopolitical relationships and global power dynamics.
- Physical Maps: Focusing on the Earth’s physical features, these maps depict mountains, rivers, lakes, and other landforms. They are invaluable for understanding geographical patterns and natural processes.
- Thematic Maps: Designed to illustrate specific data or themes, thematic maps utilize various visual techniques like color, size, and symbols to represent information. Examples include population density maps, climate maps, and resource distribution maps.
- Road Maps: These maps are designed for navigation, providing detailed information on roads, highways, and other transportation infrastructure. They are essential for travelers and commuters alike.
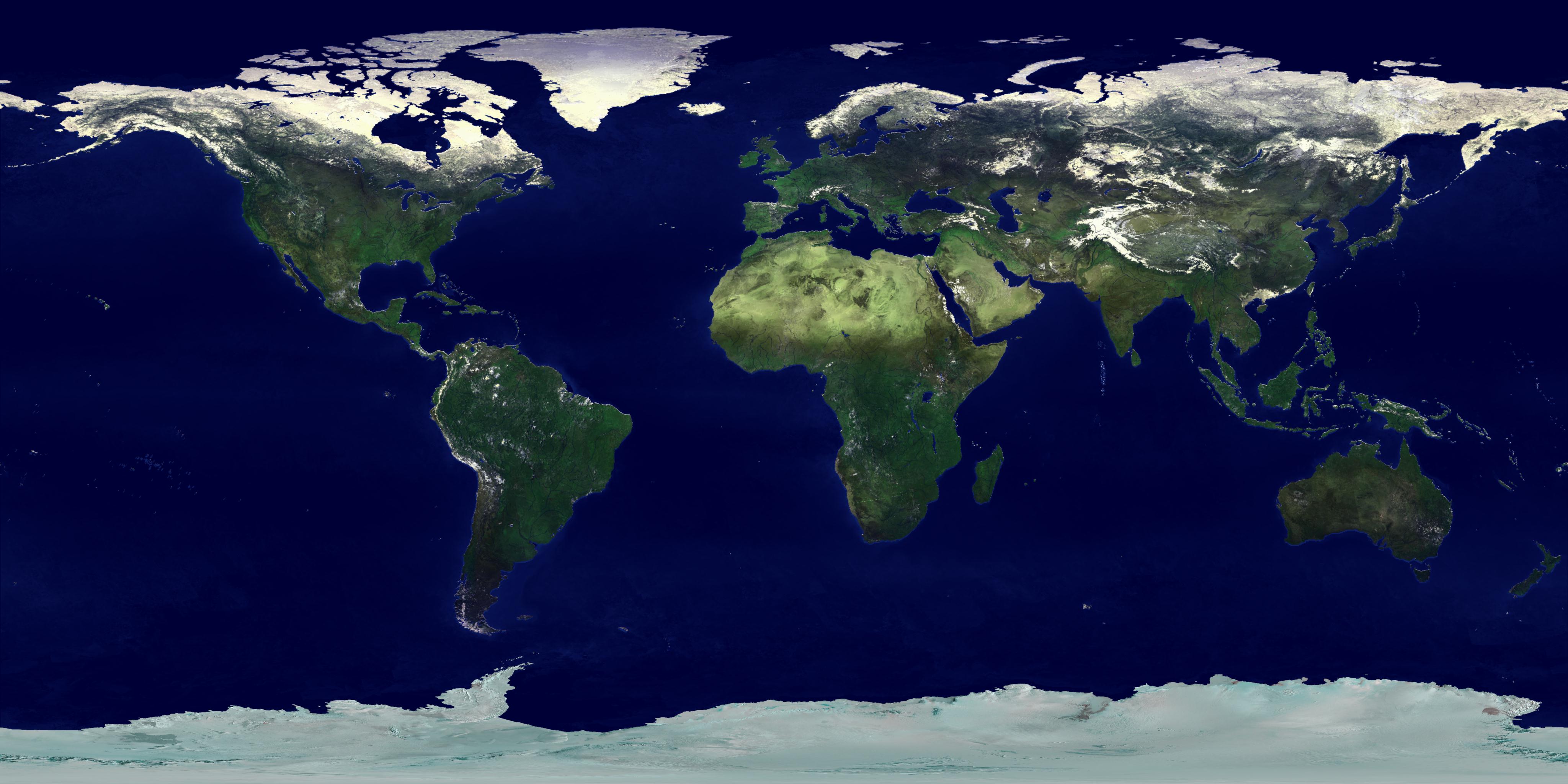
- Satellite Images: Captured from space, satellite images provide a bird’s-eye view of the Earth, offering valuable insights into land use, urban development, and environmental changes.
The Importance of Maps in Modern Life
Maps are deeply integrated into our daily lives, serving numerous purposes across various sectors.
- Navigation and Transportation: Maps are fundamental for navigation, guiding drivers, pilots, and sailors across land, air, and sea. From personal navigation apps to sophisticated GPS systems, maps facilitate efficient movement and transportation.
- Resource Management: Maps play a crucial role in resource management, enabling the mapping and monitoring of natural resources, such as water, minerals, and forests. This information is vital for sustainable development and environmental protection.
- Urban Planning and Development: Maps are essential for urban planning, providing insights into population density, infrastructure needs, and potential development areas. They help planners design sustainable and efficient urban environments.
- Emergency Response: During natural disasters or emergencies, maps are vital for coordinating rescue efforts, providing information on affected areas, and facilitating aid distribution.
- Scientific Research: Maps are essential tools for scientific research, enabling the analysis of environmental trends, climate patterns, and ecological changes.
FAQs about Maps
Q: What is the difference between a map and a globe?
A: A map is a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, while a globe is a three-dimensional model. Globes accurately depict the Earth’s curvature and relative sizes of continents and oceans, while maps, due to their flatness, necessarily distort these features.
Q: What are the different map projections?
A: Map projections are methods used to represent the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map. Each projection introduces distortions, but they vary in the type and extent of distortion. Common projections include Mercator, Robinson, and Winkel Tripel.
Q: How are maps created?
A: Map creation involves a complex process involving data collection, analysis, and visualization. Data is gathered from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground surveys. This data is then processed and transformed into a map using specialized software and cartographic techniques.
Q: What is the future of mapmaking?
A: The future of mapmaking is likely to be driven by advancements in technology, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, big data, and virtual reality. These innovations will enable the creation of more dynamic, interactive, and personalized maps, enhancing our understanding and interaction with the world.
Tips for Using Maps Effectively
- Understand the map’s scale: The scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground.
- Pay attention to the map’s projection: Different projections distort the Earth’s surface in different ways, so it’s important to be aware of these distortions when interpreting a map.
- Use multiple maps: Combining different types of maps can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular area.
- Consider the context: The purpose and intended audience of a map should be considered when interpreting its information.
Conclusion
Maps are powerful tools that offer a window into our world, enabling us to navigate, explore, and understand the complex relationships between its diverse elements. From ancient civilizations to the digital age, maps have evolved alongside our knowledge and technological advancements. As we continue to explore and interact with our planet, maps will remain essential tools for understanding, navigating, and shaping our world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth’s Map: A Window to Our World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!