The East Coast Transformed: A Visual Guide to an 80-Foot Sea Level Rise
Related Articles: The East Coast Transformed: A Visual Guide to an 80-Foot Sea Level Rise
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The East Coast Transformed: A Visual Guide to an 80-Foot Sea Level Rise. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The East Coast Transformed: A Visual Guide to an 80-Foot Sea Level Rise
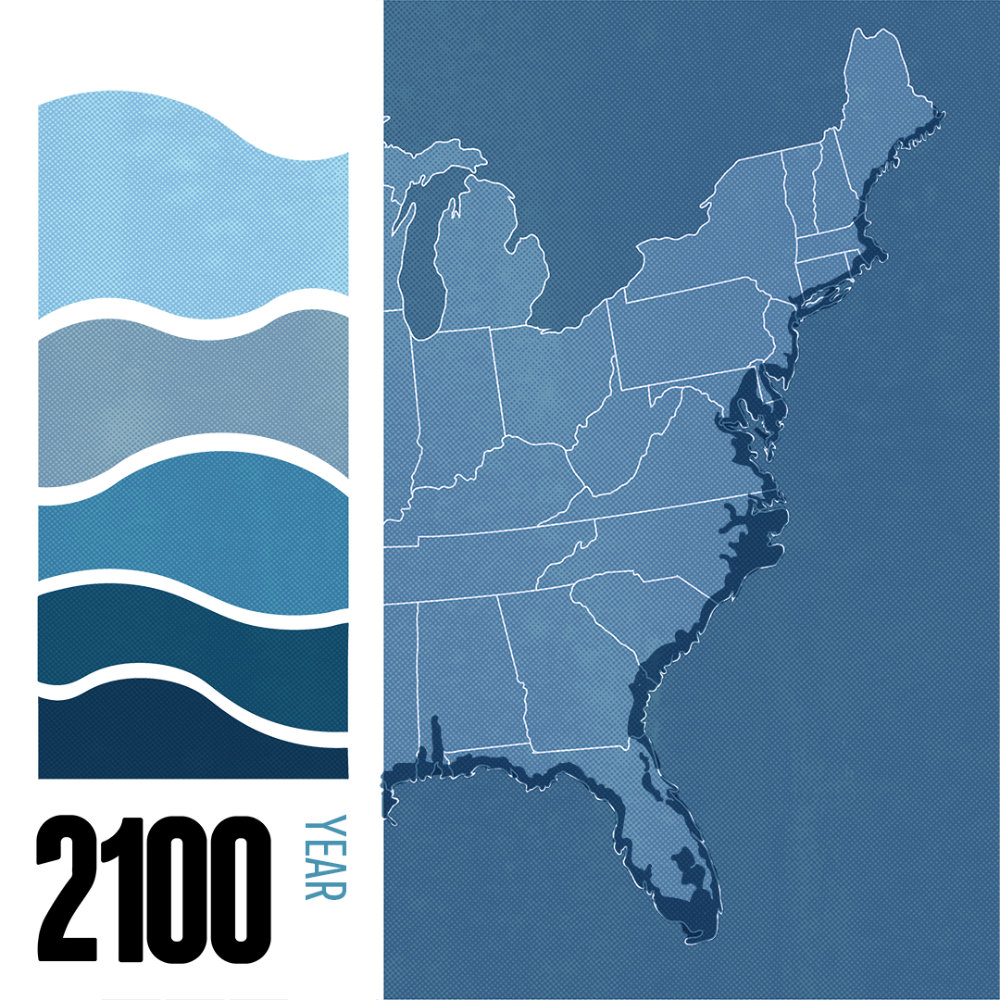

The prospect of an 80-foot sea level rise might seem like a distant, apocalyptic scenario. However, the reality is that such an event, though unlikely in the immediate future, is a plausible outcome of unchecked climate change. While the specific timeline remains uncertain, understanding the potential consequences of such a drastic shift in sea level is crucial for informed policy decisions and adaptation strategies.
This article uses a combination of text and visual representations to explore the profound impact an 80-foot sea level rise would have on the East Coast of the United States. We will examine the geographical transformations, the societal and economic implications, and the challenges posed by such a drastic environmental shift.
Visualizing the Transformation
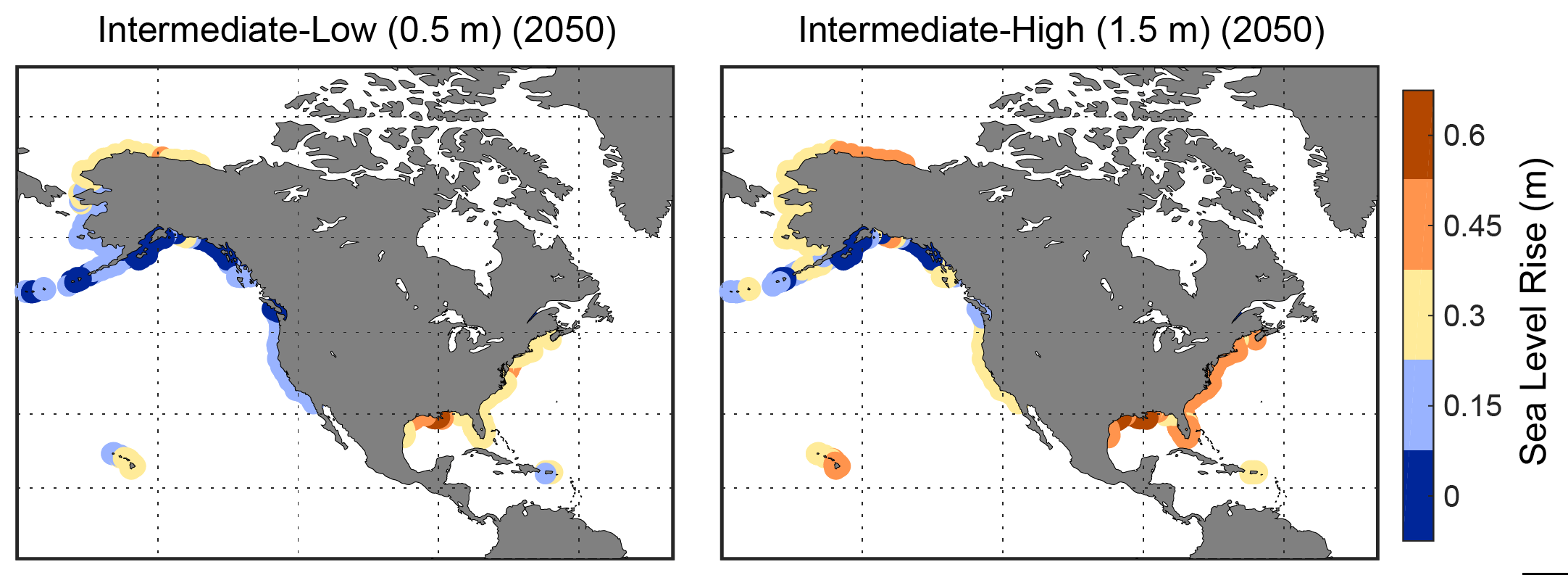
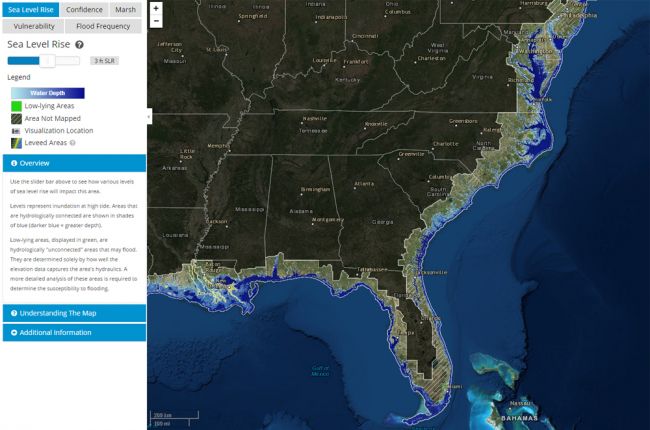
To grasp the scale of this potential disaster, it is essential to visualize the East Coast under an 80-foot sea level rise. Imagine the Atlantic Ocean engulfing vast swathes of land, transforming familiar landscapes into submerged territories.
The New Coastline:
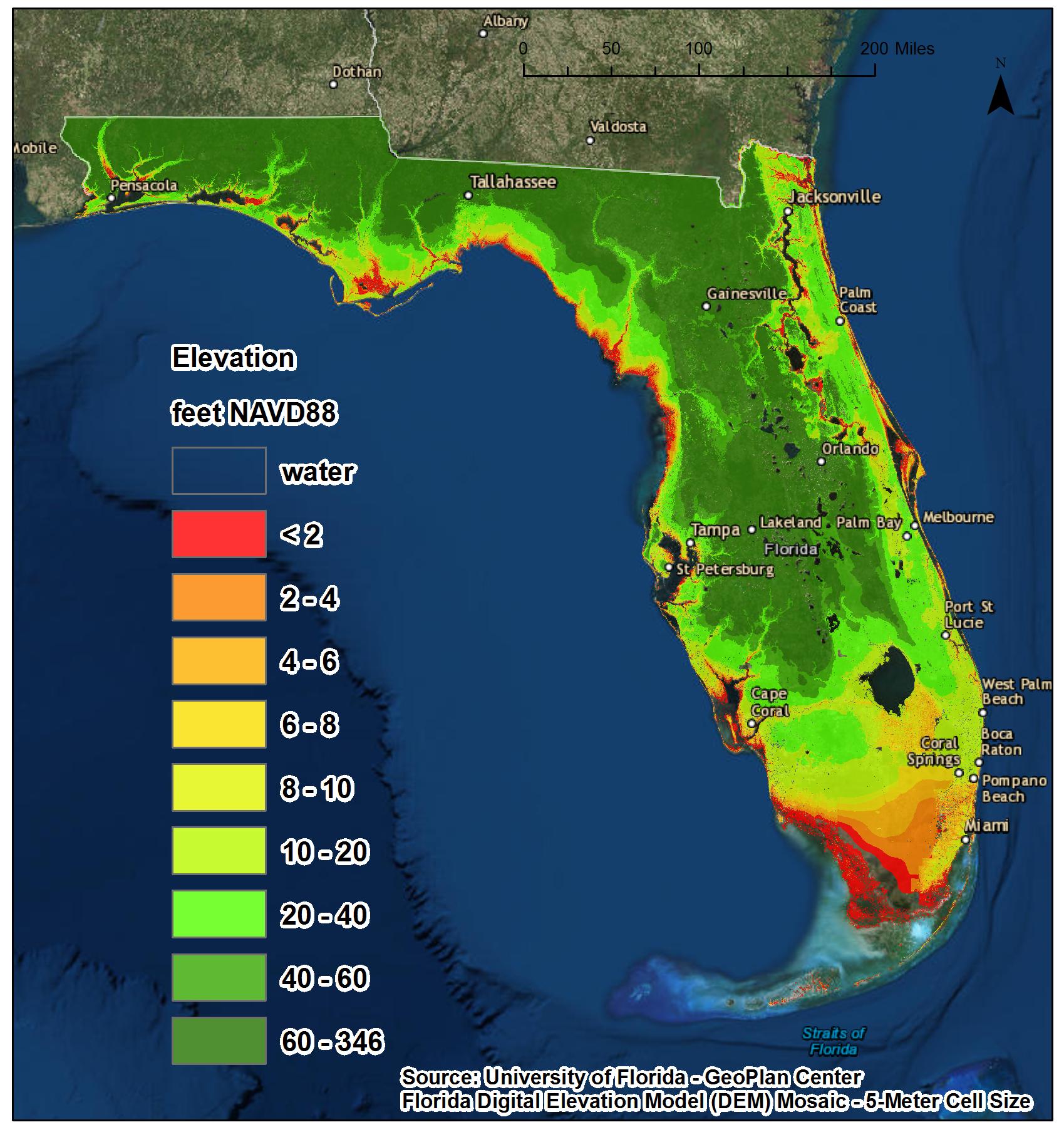
- Florida: The Sunshine State, known for its beaches and coastal cities, would be drastically reshaped. Much of the peninsula, including Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and Orlando, would disappear beneath the waves. The iconic Florida Keys would become a distant memory.
- The Carolinas: Charleston, South Carolina, a historic port city, would be submerged. The Outer Banks, a popular tourist destination, would be entirely underwater. Coastal areas of North Carolina would face significant inundation.
- Virginia and Maryland: The Chesapeake Bay, a vital ecosystem and economic hub, would be significantly expanded. Cities like Norfolk, Virginia, and Annapolis, Maryland, would face severe flooding and potential submergence.
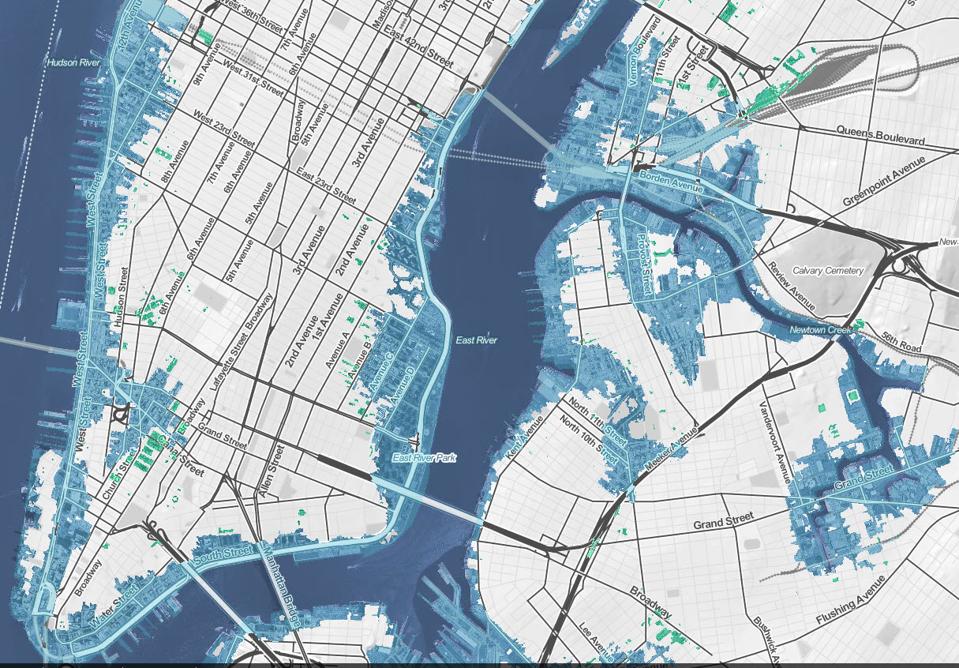
- New York and New Jersey: The densely populated metropolitan areas of New York City and New Jersey would experience extensive flooding. Iconic landmarks like the Statue of Liberty and the World Trade Center would be partially or fully submerged.
- New England: Coastal cities like Boston, Massachusetts, and Providence, Rhode Island, would face significant flooding and potential loss of land.
Beyond the Coastline:
- Inland Inundation: The impact of an 80-foot sea level rise extends far beyond the immediate coastline. Rivers and waterways would overflow, flooding vast inland areas.
- Saltwater Intrusion: The encroachment of saltwater into freshwater aquifers would contaminate drinking water sources, posing a significant threat to agriculture and human health.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Coastal ecosystems, including marshes, estuaries, and beaches, would be severely disrupted or destroyed. This would have cascading effects on biodiversity and wildlife populations.
The Human Cost:
- Displacement and Migration: Millions of people would be displaced from their homes, leading to large-scale migration and potential social unrest.
- Economic Disruption: Coastal industries, including tourism, fishing, and shipping, would be severely impacted, leading to job losses and economic decline.
- Infrastructure Damage: Roads, bridges, airports, and other vital infrastructure would be damaged or destroyed, disrupting transportation and communication networks.
- Public Health Concerns: Increased flooding would lead to a higher risk of waterborne diseases, while the disruption of healthcare infrastructure could exacerbate health problems.
Addressing the Challenge:
The potential consequences of an 80-foot sea level rise underscore the urgency of addressing climate change.
- Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable land use practices is crucial to limit the severity of future sea level rise.
- Adaptation: Developing strategies to adapt to the inevitable impacts of sea level rise is essential. This includes constructing seawalls and other coastal defenses, relocating communities, and investing in resilient infrastructure.
- International Cooperation: Addressing climate change and its consequences requires global cooperation. International agreements and joint efforts are essential to mitigate emissions and support adaptation strategies worldwide.
FAQs
Q: Is an 80-foot sea level rise a realistic scenario?
A: While an 80-foot sea level rise is a significant and potentially devastating event, it is not considered a near-term threat. However, it is a plausible outcome of unchecked climate change over the long term. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) projects that sea levels could rise by several feet by the end of the century, with higher levels possible if emissions continue unabated.
Q: What are the major factors contributing to sea level rise?
A: The primary drivers of sea level rise are:
- Thermal Expansion: As the ocean absorbs heat, it expands in volume, leading to rising sea levels.
- Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets: The melting of glaciers and ice sheets, primarily in Greenland and Antarctica, adds more water to the oceans.
Q: Can we prevent sea level rise entirely?
A: While we cannot completely prevent sea level rise, we can significantly reduce its rate and magnitude by taking decisive action to mitigate climate change. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions will limit the rate of warming and slow down the melting of glaciers and ice sheets.
Q: What are some specific actions individuals can take to address climate change?
A: Individuals can make a difference by:
- Reducing their carbon footprint: This includes using public transportation, walking, biking, and driving fuel-efficient vehicles.
- Conserving energy: Turning off lights when not in use, using energy-efficient appliances, and reducing water consumption are all effective ways to conserve energy.
- Supporting sustainable practices: Choosing products made from recycled materials, supporting businesses with environmentally responsible practices, and advocating for climate action are all important steps.
Tips
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest scientific research and policy developments related to climate change and sea level rise.
- Engage in discussions: Talk to family, friends, and community members about the issue and encourage them to take action.
- Support organizations working to address climate change: Donate to or volunteer for organizations dedicated to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting climate adaptation.
Conclusion
The potential consequences of an 80-foot sea level rise are profound and far-reaching. While this scenario may seem distant, it serves as a stark reminder of the urgency of addressing climate change. By taking decisive action to mitigate emissions, adapt to the changing climate, and promote international cooperation, we can work to avoid the worst-case scenarios and build a more sustainable future for generations to come.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__mnn__images__2016__02__sea-level-rise-map-nasa-4d8c65206cc94b4e80c507c7d0ebf757.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The East Coast Transformed: A Visual Guide to an 80-Foot Sea Level Rise. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!