The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Industrial Applications
Related Articles: The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Industrial Applications
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Industrial Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Industrial Applications
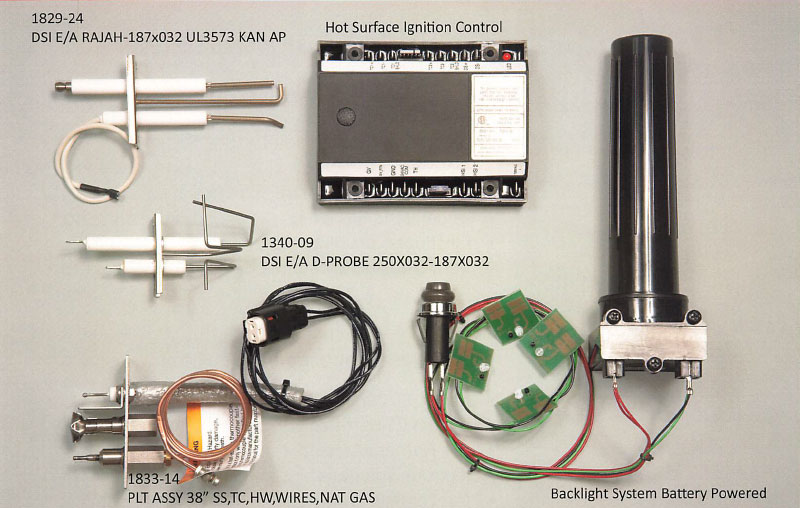
Gas igniters, often referred to as flame igniters, play a crucial role in a wide range of industrial applications where reliable and safe ignition of gas-fueled processes is paramount. These devices serve as the vital link between the gas supply and the combustion process, ensuring consistent and controlled flame initiation for various industrial operations.
Understanding the Mechanics of Gas Igniters
Gas igniters are typically composed of a few key components:
- Gas Inlet: This component allows the controlled flow of fuel gas into the igniter.
- Ignition Source: This element generates the initial spark or flame that ignites the gas. Common ignition sources include electrical sparks, hot surfaces, or pilot flames.
- Flame Detection System: This critical component monitors the flame’s presence and stability, ensuring safe operation and preventing uncontrolled gas flow.
- Control System: This element manages the gas flow and ignition sequence, ensuring a controlled and reliable ignition process.
Types of Gas Igniters and Their Applications
Gas igniters are categorized based on their ignition source and application:
1. Spark Ignition Systems: These systems utilize an electrical spark to initiate combustion. They are commonly employed in applications requiring rapid and precise ignition, such as gas-fired furnaces, boilers, and industrial ovens.
2. Hot Surface Ignition Systems: These systems rely on a heated surface to ignite the gas. They are often used in applications where continuous flame is required, such as gas-fired water heaters, industrial burners, and gas turbines.
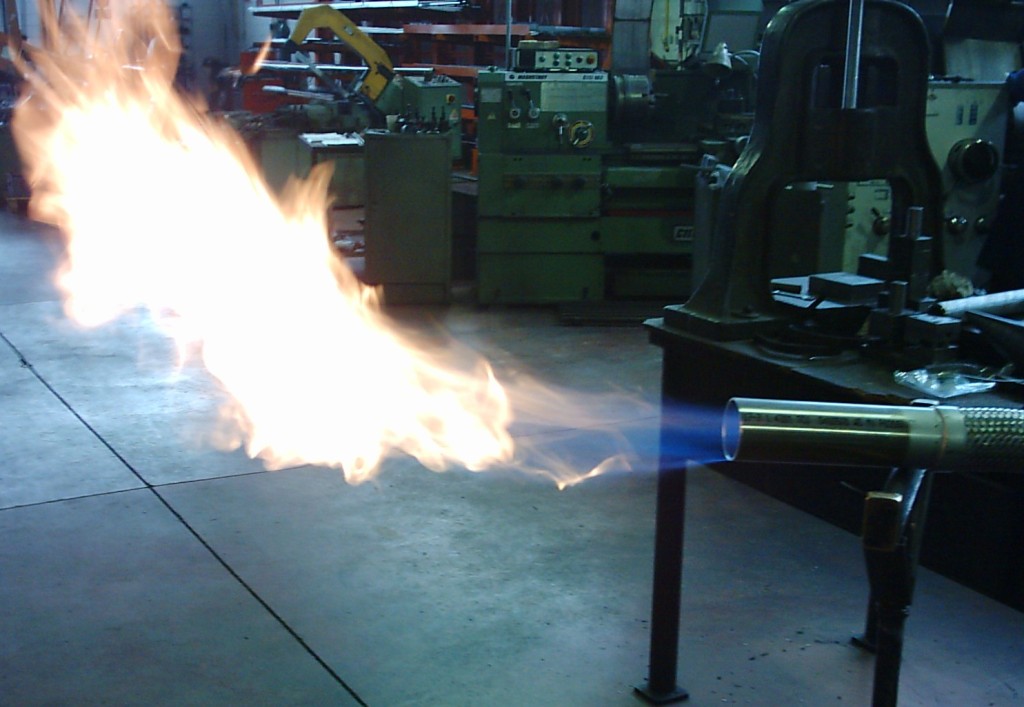
3. Pilot Flame Ignition Systems: These systems use a small, continuously burning pilot flame to ignite the main gas stream. They are typically found in applications where reliability and safety are paramount, such as gas stoves, fireplaces, and some industrial burners.
The Importance of Gas Igniters in Industrial Processes
Gas igniters are essential for numerous reasons:
- Safety: They ensure safe and controlled ignition, preventing uncontrolled gas flow and potential explosions.
- Reliability: They provide consistent and reliable ignition, ensuring uninterrupted operation of gas-fueled equipment.
- Efficiency: They optimize combustion efficiency by ensuring complete and rapid ignition, maximizing energy utilization.
- Automation: They enable automated ignition systems, reducing manual intervention and potential errors.
- Environmental Impact: They contribute to cleaner combustion by ensuring complete burning of fuel, minimizing emissions.
Benefits of Utilizing Gas Igniters in Industrial Settings
- Increased Productivity: Reliable ignition minimizes downtime and ensures continuous operation, boosting productivity.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Consistent ignition reduces wear and tear on equipment, leading to lower maintenance expenses.
- Enhanced Safety: Controlled ignition minimizes hazards associated with gas leaks and explosions, ensuring a safer working environment.
- Improved Efficiency: Complete combustion maximizes energy utilization, reducing energy consumption and costs.
- Environmental Responsibility: Optimized combustion reduces emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
FAQs Regarding Gas Igniters
1. What are the safety considerations when using gas igniters?
- Ensure the igniter is properly installed and maintained according to manufacturer guidelines.
- Regularly inspect the igniter for signs of damage or malfunction.
- Always use the correct gas type and pressure for the specific igniter model.
- Ensure adequate ventilation in the area where the igniter is used.
- Train personnel on safe operation and troubleshooting procedures.
2. How do I choose the right gas igniter for my application?
- Consider the type of gas being used (natural gas, propane, etc.).
- Determine the required ignition energy and flame size.
- Assess the operating environment (temperature, pressure, etc.).
- Factor in safety considerations and regulatory requirements.
- Consult with a qualified gas appliance specialist for guidance.
3. How do I troubleshoot a malfunctioning gas igniter?
- First, ensure the gas supply is turned on and the pilot flame is lit (if applicable).
- Check for any visible damage or obstructions in the igniter.
- Inspect the electrical wiring and connections (if applicable).
- Verify the flame detection system is functioning correctly.
- Consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for specific instructions.
Tips for Optimizing Gas Igniter Performance
- Regularly clean the igniter and its surrounding area to prevent buildup of dirt or debris.
- Inspect the igniter for signs of wear and tear and replace any damaged components promptly.
- Ensure the gas supply pressure is within the specified range for the igniter.
- Maintain proper ventilation around the igniter to prevent the accumulation of combustion byproducts.
- Train operators on proper igniter operation and troubleshooting procedures.
Conclusion
Gas igniters are indispensable components in various industrial processes, playing a critical role in ensuring safe, reliable, and efficient operation of gas-fueled equipment. By understanding the principles of gas ignition, choosing the right igniter for specific applications, and implementing proper maintenance and safety practices, industries can optimize their processes, enhance productivity, and minimize environmental impact. As technology continues to advance, gas igniters are expected to become even more sophisticated and integrated with other industrial systems, further streamlining operations and improving overall efficiency.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Industrial Applications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!