The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications
Related Articles: The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications
- 3.1 Understanding the Mechanics of Gas Igniters
- 3.2 Types of Gas Igniters
- 3.3 Applications of Gas Igniters
- 3.4 Benefits of Gas Igniters
- 3.5 FAQs about Gas Igniters
- 3.6 Tips for Using and Maintaining Gas Igniters
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications

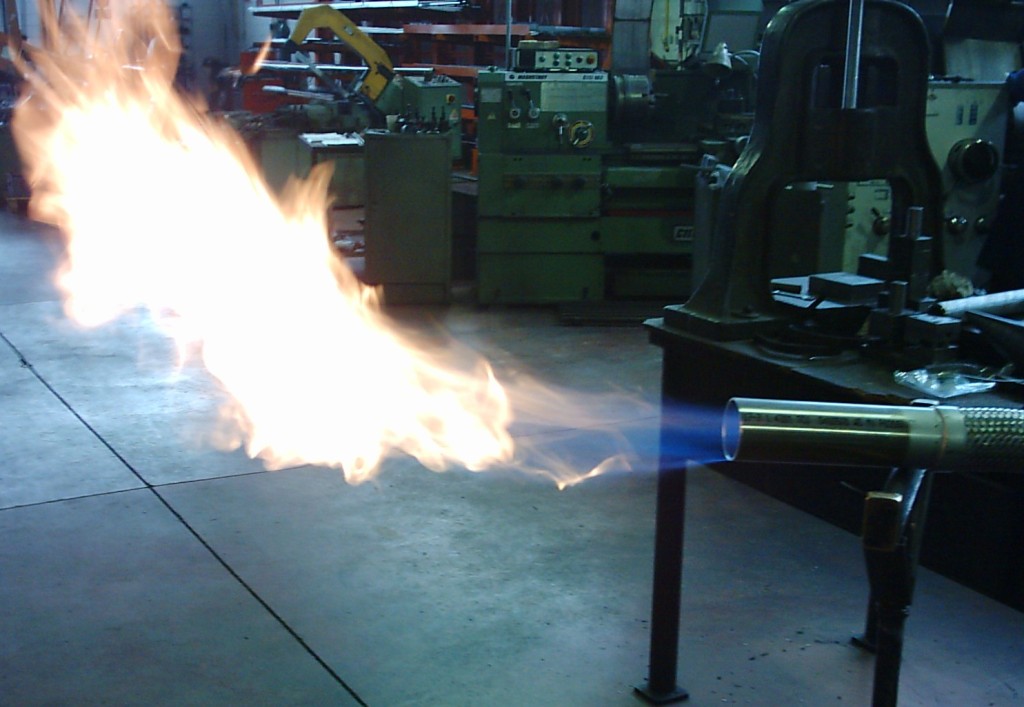
Gas igniters, also known as spark igniters, are crucial components in numerous industrial and domestic applications. Their primary function is to initiate combustion in a controlled manner by generating a spark or flame to ignite a combustible gas mixture. This seemingly simple action underpins a wide range of processes, from the operation of gas appliances in homes to the intricate workings of industrial furnaces and power generation systems.
Understanding the Mechanics of Gas Igniters
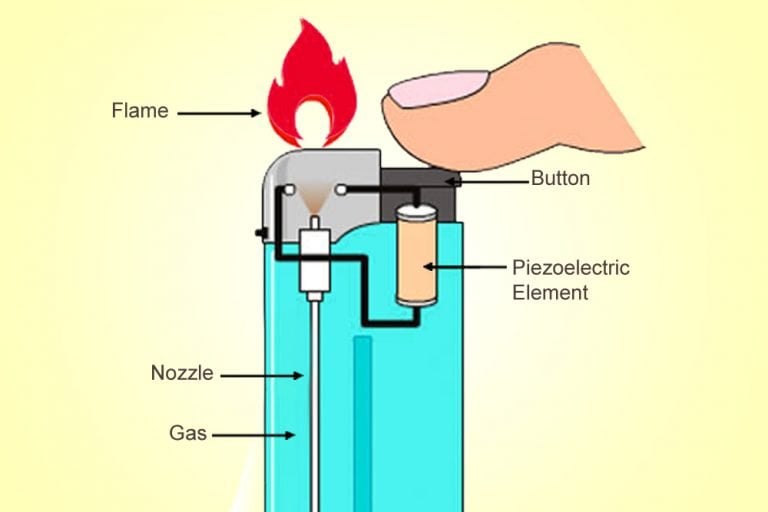
Gas igniters operate on the principle of generating a high-energy spark or flame to initiate combustion. This process typically involves the following steps:
1. Power Supply: The igniter receives power from an external source, usually an electrical circuit. This power is essential for generating the spark or flame.
2. Spark Generation: The most common type of igniter uses an electrical spark to initiate combustion. This spark is generated by passing a high voltage current across a gap between two electrodes. The gap is typically filled with a dielectric material, such as air, to prevent short circuiting.
3. Flame Ignition: The spark, upon reaching a sufficient temperature, ignites the surrounding combustible gas mixture. The resulting flame then sustains the combustion process.
4. Flame Sensing: Some igniters incorporate a flame sensor, which detects the presence of a stable flame. This sensor acts as a safety mechanism, ensuring that the gas supply is only turned on when a flame is present.
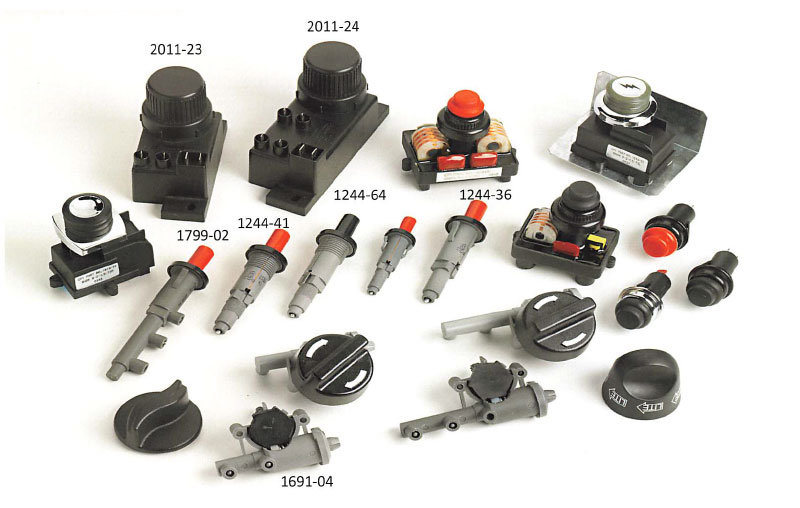
Types of Gas Igniters
Gas igniters come in various types, each tailored for specific applications. The most common types include:
-
Spark Igniters: These igniters are commonly found in gas appliances, such as stoves, ovens, and water heaters. They utilize a high-voltage spark to ignite the gas flow.
-
Hot Surface Igniters: These igniters use a heated surface to ignite the gas. They are often found in industrial applications, such as furnaces and boilers.
-
Pilot Flame Igniters: These igniters use a small, continuously burning flame to ignite the main gas flow. They are commonly used in older gas appliances.
-
Electronic Igniters: These igniters use electronic circuits to control the spark generation and flame sensing. They are becoming increasingly popular due to their reliability and efficiency.
Applications of Gas Igniters
Gas igniters are indispensable components in a wide range of applications, including:
-
Domestic Appliances: Gas stoves, ovens, water heaters, and fireplaces all rely on gas igniters to initiate combustion.
-
Industrial Furnaces and Boilers: Gas igniters play a crucial role in the operation of industrial furnaces, boilers, and other high-temperature processes.
-
Power Generation Systems: Gas-fired power plants utilize gas igniters to initiate combustion in their turbines, generating electricity.
-
Gas Chromatography: Gas igniters are used in gas chromatography systems to detect and analyze different gases.
-
Gas Welding and Cutting: Gas igniters are used in gas welding and cutting torches to ignite the fuel and oxygen mixture.
Benefits of Gas Igniters
The use of gas igniters offers several advantages in various applications:
-
Reliable Ignition: Gas igniters provide a reliable and consistent method of initiating combustion.
-
Safety: Flame sensing mechanisms in many igniters enhance safety by preventing gas leaks and uncontrolled combustion.
-
Efficiency: Gas igniters contribute to the efficient use of fuel by ensuring complete combustion.
-
Versatility: Gas igniters can be adapted to different types of gas fuels and applications.
-
Durability: Gas igniters are typically robust and durable, capable of withstanding harsh environments and frequent use.
FAQs about Gas Igniters
Q: How do gas igniters work?
A: Gas igniters work by generating a spark or flame to ignite a combustible gas mixture. The spark is typically generated by passing a high voltage current across a gap between two electrodes. The flame then sustains the combustion process.
Q: What are the different types of gas igniters?
A: The most common types of gas igniters include spark igniters, hot surface igniters, pilot flame igniters, and electronic igniters. Each type has specific characteristics and applications.
Q: What are the benefits of using gas igniters?
A: Gas igniters offer several benefits, including reliable ignition, safety, efficiency, versatility, and durability.
Q: What are some common applications of gas igniters?
A: Gas igniters are used in a wide range of applications, including domestic appliances, industrial furnaces and boilers, power generation systems, gas chromatography, and gas welding and cutting.
Q: How do I choose the right gas igniter for my application?
A: The choice of gas igniter depends on several factors, including the type of gas fuel, the required ignition energy, the operating environment, and the desired safety features.
Q: How do I maintain a gas igniter?
A: Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of a gas igniter. This includes cleaning the electrodes, checking the flame sensor, and inspecting the wiring.
Tips for Using and Maintaining Gas Igniters
-
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions: Always consult the user manual for specific instructions on how to use and maintain the gas igniter.
-
Regularly inspect the igniter: Check for any signs of damage, corrosion, or buildup.
-
Clean the electrodes: Regularly clean the electrodes to ensure proper spark generation.
-
Test the flame sensor: Ensure the flame sensor is functioning correctly by checking for a stable flame.
-
Replace worn-out parts: Replace any worn-out or damaged components promptly.
-
Keep the igniter area clean: Avoid dust, dirt, and debris accumulation around the igniter.
-
Do not tamper with the igniter: Avoid making any modifications or adjustments to the igniter without proper expertise.
Conclusion
Gas igniters are essential components in numerous applications, playing a crucial role in initiating combustion in a controlled and efficient manner. Their reliability, safety, and versatility have made them indispensable in various industries, from domestic appliances to industrial processes. Understanding the workings, types, and applications of gas igniters is crucial for ensuring their safe and effective operation. Regular maintenance and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for maximizing their lifespan and performance.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Role of Gas Igniters in Modern Applications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!