The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization
Related Articles: The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization
- 3.1 A Deeper Look into the Function of Gas Pressure Regulators
- 3.2 Types of Gas Pressure Regulators
- 3.3 Importance of Gas Pressure Regulators
- 3.4 Installation and Maintenance of Gas Pressure Regulators
- 3.5 FAQs about Gas Pressure Regulators
- 3.6 Tips for Selecting and Using Gas Pressure Regulators
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization
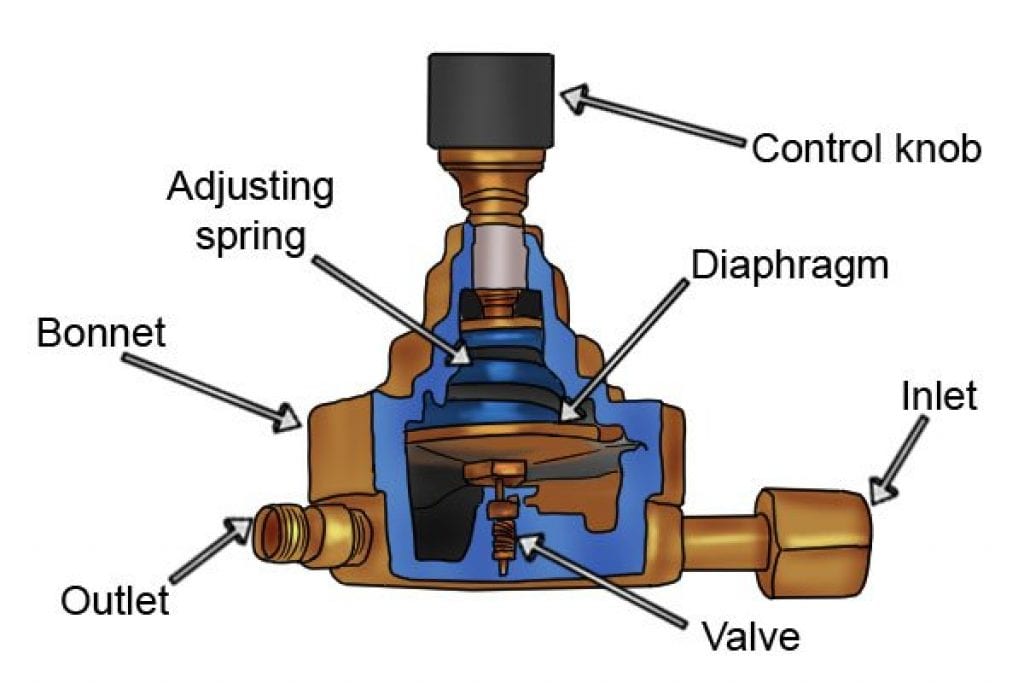
Gas pressure regulators are essential components in any system that utilizes compressed gases, playing a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient operation. These devices are responsible for reducing the high pressure of a gas source to a safe and usable level, thereby controlling the flow of gas and preventing potential hazards. Understanding the workings of gas pressure regulators is vital for anyone working with compressed gases, as it allows for informed decision-making regarding their selection, installation, and maintenance.
A Deeper Look into the Function of Gas Pressure Regulators
Gas pressure regulators are designed to maintain a constant downstream pressure regardless of fluctuations in the upstream pressure or demand. This is achieved through a combination of mechanical components that work in concert to control the gas flow. The key components include:
- Inlet Port: This is where the high-pressure gas enters the regulator.
- Diaphragm: A flexible membrane that separates the high-pressure side from the low-pressure side.
- Spring: Provides a counterforce to the diaphragm, setting the desired output pressure.
- Valve: Controls the flow of gas through the regulator.
- Outlet Port: This is where the regulated, low-pressure gas exits the regulator.
The operation of a gas pressure regulator is based on the principle of balanced forces. When the incoming gas pressure exceeds the desired output pressure, the diaphragm is pushed downwards, compressing the spring. This movement opens the valve, allowing gas to flow until the pressure on both sides of the diaphragm equalizes. Conversely, when the demand for gas decreases, the pressure on the downstream side drops, causing the diaphragm to move upwards and close the valve, reducing the flow of gas.
Types of Gas Pressure Regulators
Gas pressure regulators come in various types, each designed for specific applications and gas types. Some common types include:
- Single-Stage Regulators: These regulators reduce the incoming pressure to the desired output pressure in a single stage. They are typically used for applications with moderate pressure drops.
- Two-Stage Regulators: These regulators use two stages to reduce the incoming pressure, providing a more precise and stable output pressure. They are often used for applications requiring high precision or where the pressure drop is significant.
- High-Pressure Regulators: These regulators are designed to handle high incoming pressures, typically found in industrial applications.
- Low-Pressure Regulators: These regulators are designed for low incoming pressures, commonly used in residential and commercial settings.
- Overpressure Relief Valves: These valves are designed to automatically release excess pressure in the system, preventing potential damage or explosions.
The specific type of gas pressure regulator required for a particular application depends on factors such as:
- Incoming Pressure: The pressure of the gas source.
- Output Pressure: The desired pressure for the application.
- Gas Type: Different gases have different properties that need to be considered.
- Flow Rate: The amount of gas required by the application.
Importance of Gas Pressure Regulators
The use of gas pressure regulators is crucial for various reasons:
- Safety: Regulators prevent over-pressurization in downstream equipment and pipelines, minimizing the risk of explosions or fires.
- Efficiency: By maintaining a constant output pressure, regulators ensure consistent gas flow and efficient operation of gas-consuming equipment.
- Reliability: Regulators protect equipment from damage caused by pressure fluctuations, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
- Control: Regulators allow for precise control of gas flow, enabling optimal utilization and reducing waste.
Installation and Maintenance of Gas Pressure Regulators
Proper installation and maintenance of gas pressure regulators are essential for their safe and effective operation.
Installation:
- Correct Regulator Selection: Choosing the right regulator for the specific application is crucial. Factors like incoming pressure, output pressure, gas type, and flow rate must be carefully considered.
- Proper Location: The regulator should be installed in a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and inspection. It should also be protected from extreme temperatures and weather conditions.
- Secure Mounting: The regulator should be securely mounted to prevent accidental disconnection or damage.
- Leak Testing: After installation, the regulator should be thoroughly tested for leaks.
Maintenance:
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the regulator for signs of damage, wear, or leaks.
- Cleaning: Clean the regulator periodically to remove dirt and debris that can affect its performance.
- Calibration: Calibration ensures the regulator maintains the desired output pressure.
- Replacement: Replace the regulator if it shows signs of wear, damage, or if it fails to meet performance specifications.
FAQs about Gas Pressure Regulators
Q: What is the difference between a single-stage and a two-stage regulator?
A: A single-stage regulator reduces the incoming pressure to the desired output pressure in one step, while a two-stage regulator uses two stages to achieve the same result. Two-stage regulators offer greater precision and stability, especially for applications with high pressure drops or where precise pressure control is critical.
Q: How do I know what size regulator I need?
A: The size of the regulator is determined by the flow rate required by the application. The regulator should be sized to handle the maximum flow rate without exceeding its capacity.
Q: How often should I inspect my gas pressure regulator?
A: The frequency of inspection depends on the application and the environment in which the regulator is operating. However, a general guideline is to inspect the regulator at least annually or more frequently if it is subject to high usage or harsh conditions.
Q: How do I know if my gas pressure regulator needs to be replaced?
A: Signs that a gas pressure regulator needs to be replaced include:
- Leaks: Any leaks from the regulator should be addressed immediately.
- Damage: Physical damage to the regulator, such as dents, cracks, or corrosion, can compromise its safety and performance.
- Inaccurate Output Pressure: If the regulator is not maintaining the desired output pressure, it may need to be replaced.
Q: What are some safety precautions to take when working with gas pressure regulators?
A: When working with gas pressure regulators, it is important to:
- Wear appropriate safety gear: This includes safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions: Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for installation, operation, and maintenance.
- Never tamper with the regulator: Tampering with the regulator can lead to dangerous situations.
- Ensure proper ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid the buildup of flammable gases.
- Use a leak detector: Use a leak detector to check for leaks before and after working on the regulator.
Tips for Selecting and Using Gas Pressure Regulators
- Consult with a Gas Professional: Consult with a qualified gas professional for guidance on selecting the appropriate regulator for your specific application.
- Check Manufacturer’s Specifications: Ensure that the regulator you select meets the requirements of your application in terms of pressure, flow rate, and gas type.
- Consider Environmental Conditions: Take into account the environmental conditions in which the regulator will be operating, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances.
- Regularly Inspect and Maintain: Regularly inspect and maintain the regulator to ensure its safe and efficient operation.
- Follow Safety Procedures: Always follow safety procedures when working with gas pressure regulators.
Conclusion
Gas pressure regulators are vital components in any system that utilizes compressed gases. They play a crucial role in ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable operation by reducing high-pressure gas to a safe and usable level. By understanding the workings, types, and importance of gas pressure regulators, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their selection, installation, and maintenance. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are essential for the safe and effective operation of these devices, ensuring the protection of personnel and equipment.
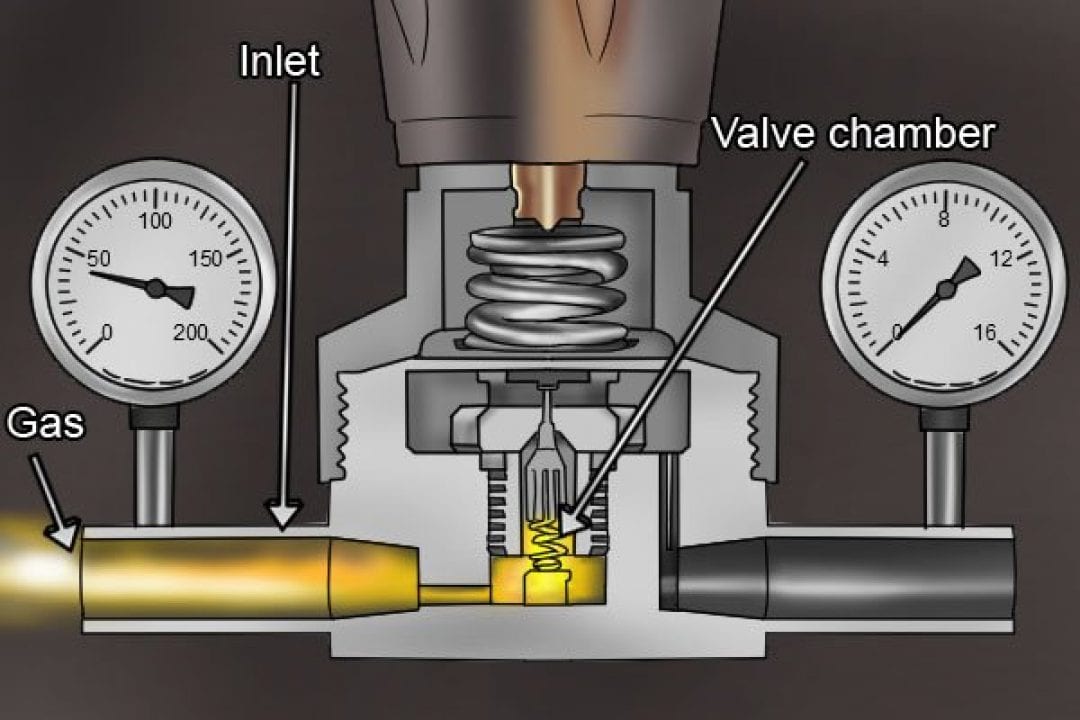

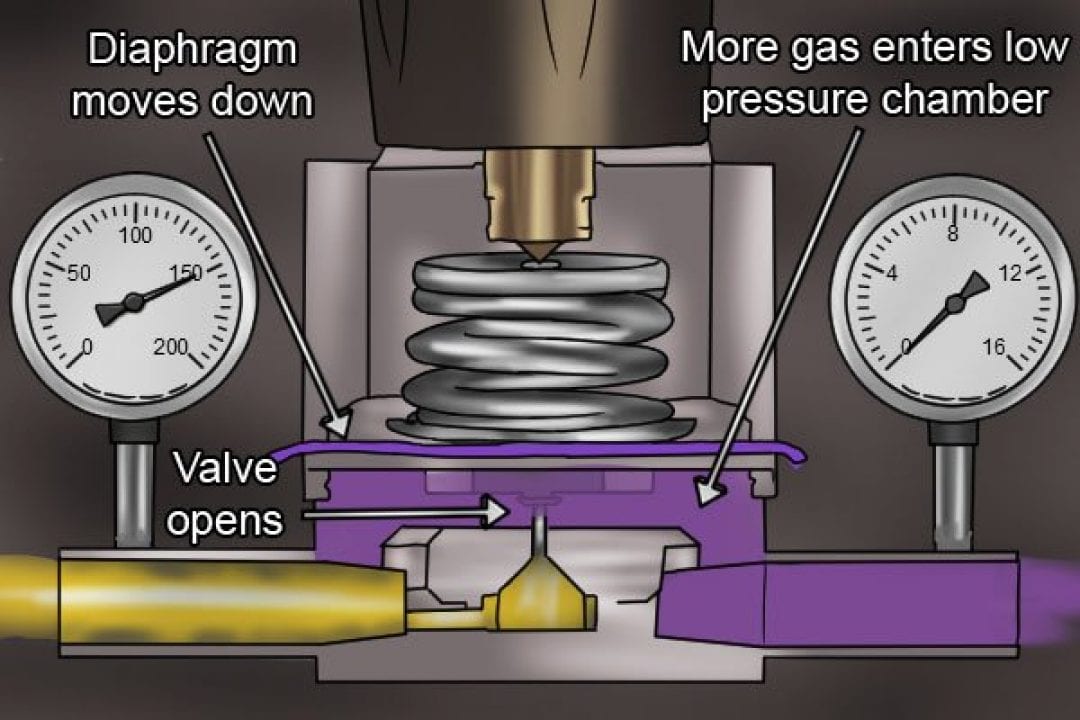


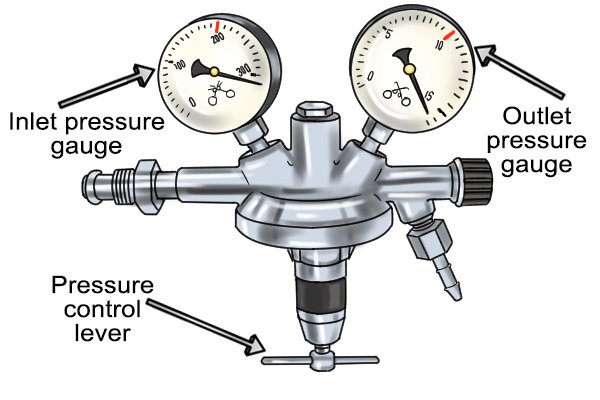


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Role of Gas Pressure Regulators in Safe and Efficient Gas Utilization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!