The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy
Related Articles: The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy
- 3.1 Understanding the Gas Network: A Visual Representation
- 3.2 Key Components of the Gas Network
- 3.3 Benefits of a Robust Gas Network
- 3.4 Evolution of the Gas Network
- 3.5 The Future of the Gas Network
- 3.6 FAQs about the Gas Network in Ireland
- 3.7 Tips for Using the Gas Network Safely and Efficiently
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy

The Republic of Ireland’s gas network is a vital piece of infrastructure, facilitating the delivery of natural gas to homes, businesses, and industries across the country. This intricate network, spanning thousands of kilometers, plays a crucial role in powering Ireland’s economy, ensuring energy security, and contributing to environmental sustainability.
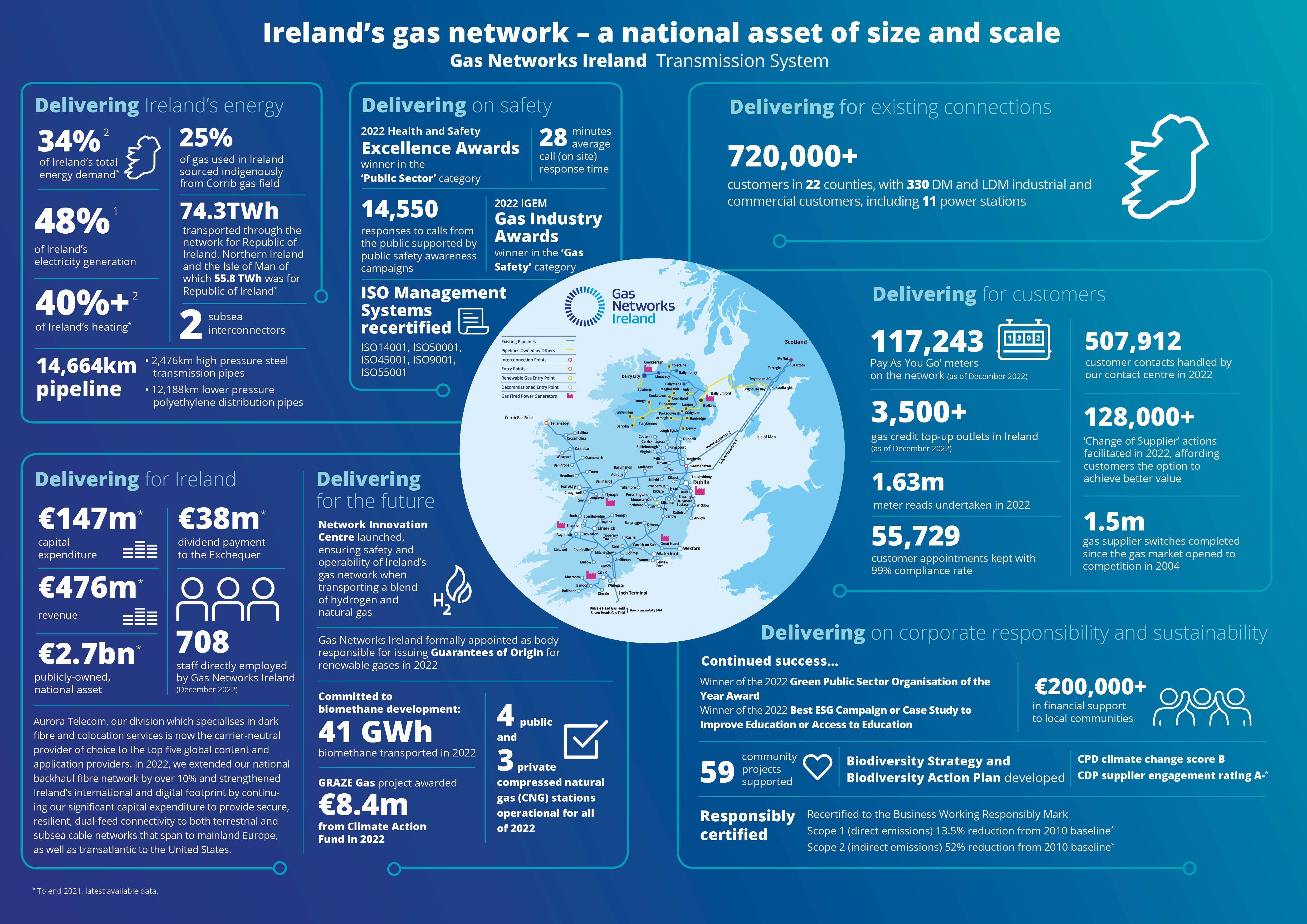
Understanding the Gas Network: A Visual Representation
The Gas Networks Ireland (GNI) map serves as a visual representation of this complex system. It illustrates the interconnected pipelines, compressor stations, and other critical components that enable the transportation of natural gas from its source to end users. The map provides a clear overview of the network’s geographical reach, highlighting major pipelines, regional distribution networks, and key connection points.
Key Components of the Gas Network
1. Pipelines: The backbone of the network, pipelines carry natural gas across the country. These pipelines are categorized by their size and function:
- Transmission Pipelines: Large-diameter pipelines, typically operating at high pressure, transport natural gas from import points or production facilities to regional distribution centers.
- Distribution Pipelines: Smaller pipelines, operating at lower pressure, distribute natural gas to individual consumers, including homes, businesses, and industries.
2. Compressor Stations: These stations are strategically located along the pipeline network to maintain gas pressure and ensure efficient transportation. They use powerful compressors to increase the pressure of the gas, allowing it to travel long distances.
3. Metering Stations: These facilities measure the volume of gas flowing through the network, enabling accurate billing and monitoring of gas consumption.
4. Interconnections: The Irish gas network is interconnected with networks in neighboring countries, such as the United Kingdom, providing access to alternative gas sources and enhancing energy security.
Benefits of a Robust Gas Network
The presence of a well-developed gas network brings numerous benefits to Ireland:
1. Energy Security: The network provides access to a reliable and diverse range of gas sources, reducing dependence on a single supplier and enhancing energy security.
2. Economic Growth: Natural gas is a cost-effective and reliable fuel source, supporting economic growth by powering homes, businesses, and industries.
3. Environmental Sustainability: Natural gas is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to coal or oil, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
4. Energy Efficiency: The network facilitates the efficient transportation of gas, minimizing energy losses and promoting energy efficiency.
5. Job Creation: The development and operation of the gas network generate employment opportunities in various sectors, including construction, engineering, and maintenance.
Evolution of the Gas Network
The Irish gas network has undergone significant development over the years, expanding its reach and capacity to meet the growing energy demands of the country. This expansion has been driven by factors such as:
- Increased Demand: The growing population and economic development have led to an increase in energy demand, prompting the expansion of the gas network to accommodate this demand.
- Government Policy: The government’s commitment to promoting renewable energy sources and reducing carbon emissions has encouraged the development of the gas network as a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels.
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in pipeline technology and construction techniques have facilitated the expansion of the network to remote areas.
The Future of the Gas Network
As Ireland transitions towards a low-carbon future, the role of the gas network is evolving. While natural gas remains a vital energy source, the network is increasingly being used to transport renewable gases, such as biomethane, which are produced from sustainable sources. This integration of renewable gases into the existing network is crucial for achieving Ireland’s climate change targets.
FAQs about the Gas Network in Ireland
1. What is the main source of natural gas for Ireland?
The majority of natural gas consumed in Ireland is imported from the United Kingdom through the Interconnector pipeline. However, Ireland also has a small domestic gas production capacity.
2. Who owns and operates the gas network in Ireland?
The gas network in Ireland is owned and operated by Gas Networks Ireland (GNI), a regulated company responsible for the safe and reliable transportation of natural gas.
3. How can I connect to the gas network?
If you wish to connect to the gas network, you need to contact your local gas supplier. They will assess your requirements and arrange for the necessary connections to be made.
4. What is the role of the Commission for Regulation of Utilities (CRU) in the gas network?
The CRU is an independent regulator responsible for ensuring that the gas network is operated efficiently and that consumers are protected.
5. What are the safety measures in place for the gas network?
The gas network is designed and operated with stringent safety measures in place. These include regular inspections, maintenance, and monitoring to ensure the safe transportation of natural gas.
Tips for Using the Gas Network Safely and Efficiently
1. Regular Maintenance: Ensure that your gas appliances are regularly inspected and maintained by a qualified technician to prevent potential hazards.
2. Gas Leak Detection: Be aware of the signs of a gas leak, such as a hissing sound, a rotten egg smell, or bubbles in water. If you suspect a leak, evacuate the area immediately and contact your gas supplier or emergency services.
3. Energy Efficiency: Install energy-efficient appliances and adopt energy-saving practices to reduce your gas consumption and lower your energy bills.
4. Gas Safety Awareness: Educate yourself and your family about gas safety practices, including proper ventilation, appliance usage, and emergency procedures.
5. Contact your Gas Supplier: If you have any questions or concerns about your gas supply or usage, contact your local gas supplier for assistance.
Conclusion
The gas network in Ireland is a vital piece of infrastructure, playing a crucial role in powering the country’s economy and contributing to its energy security and environmental sustainability. The network’s continued development, coupled with the integration of renewable gases, will ensure its continued importance in Ireland’s energy landscape for years to come. By understanding the network’s complexities and adopting responsible energy practices, individuals and businesses can contribute to the safe and efficient operation of this essential infrastructure.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Gas Network of Ireland: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Economy. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!